When classifying various diseases, doctors are accustomed to using a specially created reference book, ICD 10. This abbreviation means the International Classification of Diseases, revised 10 times.
According to this publication, ovarian cysts belong to the class of non-inflammatory lesions of the ovary, fallopian tube and broad ligament of the uterus, code N83, and the class of benign ovarian neoplasms, code D27.
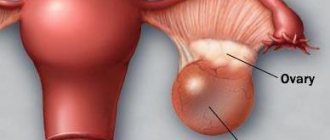
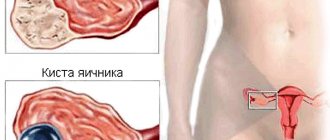
In general, these neoplasms are cavities filled with liquid secretion. Sometimes they contain blood, pus, and even inclusions atypical for the ovary, such as hair, nails, etc. In most cases, cysts do not manifest themselves until they reach a certain size. Characteristic signs of the formation of cystic cavities in the ovaries are:
- discomfort in the lower abdomen;
- intermenstrual bleeding of varying intensity;
- distortion of the menstrual cycle;
- change in the nature of menstruation.
Therefore, depending on the causes of occurrence, type and localization of the neoplasm, types of ovarian cysts are distinguished, and each of them received its own code in ICD 10.
Can an ovarian cyst burst?
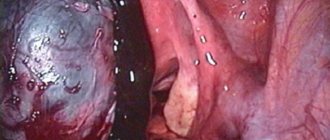
Ovarian cyst rupture occurs in patients of reproductive age. This phenomenon is due to the fact that apoplexy is associated with ovulation and follicle growth. If the release of eggs from Graaf's vesicle is impaired, the risk of the formation of pathological growths of ovarian tissue increases.
In gynecological practice, functional and other types of tumors are distinguished. Such a gradation is necessary to determine the treatment tactics for a woman. When functional formations are identified, there is a high risk of self-healing - resorption, possibly supplementing therapy with medications and folk methods. However, such tumors require monthly monitoring of the dynamics of the process: there is a risk of rupture of the pathological focus.
If other types of neoplasms are detected, surgical intervention is recommended. In such cases, the risk of complications is higher.
Attention! Rupture is more often provoked by certain factors. When determining appendage growths and deciding to monitor the formation, it is necessary to discuss with your doctor what not to do.
Treatment of pathology during pregnancy
Surgical intervention is used only as a last resort. If the disease does not manifest itself in any way and the cyst does not grow, gynecologists do not advise taking any therapeutic measures.
Doctors do not recommend removing a cyst, the presence of which does not provoke complications and poor health, since anesthesia is not advisable for pregnant women.
But if the tumor gradually increases, which leads to an inflammatory process, this is a reason to resort to therapy.
The only treatment method in this case is surgery to remove the cystic formation. It is performed under general anesthesia. You will not be able to get rid of this disease on your own.
Most often, laparoscopic surgery is performed.
Its main advantages are the minimal degree of tissue trauma and short recovery time. 3 or 4 punctures are made in the patient’s cavity (depending on the size of the tumor), an endoscope equipped with a microcamera is inserted into 1 of them. This manipulation allows you to broadcast the image on the monitor screen in the operating room.
If a woman in labor is admitted to the gynecological department with a diagnosis of a paraovarian cyst, her delivery is handled very carefully. In this case, the obstetrician will regularly change the position of her body, avoiding sudden movements.
Rupture of ovarian cyst: ICD code 10
According to the generally accepted medical classification, non-inflammatory lesions of the uterine appendages are coded N83. This category includes all types of cysts and complications of the disease. Follicular tumors are designated N83.0, ruptured cysts of the corpus luteum of the ovary are designated N83.1. Code N83.2 includes other and unspecified types of adnexal vesicles.
Important! This gradation is used exclusively for medical workers and documentation, including sick leave.
Non-inflammatory lesions of the ovaries (N83)
An unconventional technique with a stunning effect!
Representatives of this group of diseases are:
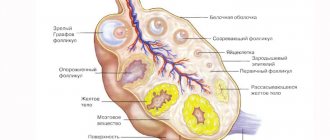
Follicular cysts
Neoplasms of this type usually have thin, smooth walls and lack chambers and partitions. The size of follicular cysts ranges from 2 to 7 cm, although larger cavities are sometimes found. Most often they affect one of the ovaries, but regardless of whether a cyst is detected on the right or left ovary, it will still have an ICD 10 code of N83.0, since it is formed from an unopened follicle.
But sometimes, due to a lack of appropriate hormones, the follicle remains intact. In such situations, it remains in the ovary and begins to grow due to the accumulation of liquid secretion, thereby transforming into a cyst.
Thus, the reasons for the formation of a follicular ovarian cyst may lie in the presence of pathologies of the endocrine system or inflammatory diseases of a gynecological nature. Therefore, absolutely any woman of childbearing age can encounter this problem.
Corpus luteum cysts
The corpus luteum is a temporary gland formed at the site of a destroyed follicle. It produces progesterone, a hormone necessary for the onset and normal course of pregnancy.
Such neoplasms are usually single-chamber, and their size does not exceed 8 cm. As a rule, corpus luteum cysts resolve on their own within 2–3 menstrual cycles or after pregnancy, although in certain cases hormonal therapy or surgical removal of the tumor is required.
As in the case of a follicular cyst, hemorrhage may also occur in the tissue of the corpus luteum. The result of this will be the formation of a hemorrhagic cyst, requiring immediate treatment.
Retention cysts
Retention cysts are rounded neoplasms with a colorless or somewhat bluish membrane that arise in the glands or their ducts. They can be congenital or acquired.
- In the first case, the cause of the formation of a cyst is the fusion of the gland ducts during the girl’s intrauterine development.
- In the second, they are a consequence of blockage of the excretory duct by a clot of secretion, a scar or some foreign body.
Be that as it may, the steady accumulation of fluid leads to stretching of the walls of the gland and the formation of a cyst. That is, this category of neoplasms includes:
- follicular;
- paraovarian cysts;
- Corpus luteum cysts.
Thus, a doctor can make a diagnosis of ovarian retention cyst and assign a code according to ICD 10 N83.2 if a cavitary neoplasm is detected in the tissues of an organ, the nature of which cannot be accurately determined for one reason or another.
Dermoid cysts
All dermoid cysts are congenital, since the prerequisites for their formation are laid during the period of intrauterine development. They are cavities filled with sebaceous secretions including hair, particles of the epidermis, hair follicles, etc. Their inner shells are rough, and their outer shells are smooth.
As a rule, the size of dermoid cysts does not exceed the size of a walnut. But such neoplasms grow constantly, although quite slowly. They can be dense or soft, which is determined by the nature of the inclusions they contain.
Dermoid cysts are one of the most dangerous neoplasms of this kind, since in 8% of cases they degenerate into malignant tumors and cause the development of squamous cell carcinoma!
conclusions
Otherwise, the cysts can fester and rupture, which will lead to the development of life-threatening complications. In addition, some types of neoplasms have a peculiar stalk that can twist. This is an indication for emergency surgery. Therefore, if an ovarian cyst is detected, you should not neglect preventive examinations and strictly follow all the doctor’s recommendations.
Causes of ovarian cyst rupture
Rupture of a left ovarian cyst can be caused by the following factors:
- hormonal imbalance, manifested in disruption of ovulation processes;
- accession, exacerbation of chronic inflammatory process of the appendages;
- physical overexertion, lifting heavy weights;
- rough sexual intercourse;
- injuries, falls, blows to the lower half of the abdominal cavity;
- ectopic pregnancy;
- pathology of the blood coagulation system.
In some cases, the tumor bursts without any special triggers: at rest, during sleep.
Attention! Patients with adnexal growths need to avoid the main causes leading to rupture of the formations.
Symptoms of a ruptured ovarian cyst in women
Signs of ovarian cyst rupture vary depending on the strength and severity of the complaints. Main symptoms:
- sudden sharp pain in the lower abdomen, often on the affected side, the attack of pain is stronger;
- discomfort spreads to nearby structures: perineum, rectum;
- Tension of the abdominal wall is noted;
- intestinal motility is disrupted;
- false urge to urinate or defecate appears;
- pulse increases, blood pressure decreases;
- nausea, vomiting;
- weakness, dizziness;
- bleeding from the vagina;
- loss of consciousness.
Most symptoms are associated with blood and tumor contents entering the abdominal cavity. Without timely help, inflammation develops - peritonitis.
How to understand that an ovarian cyst has burst
Symptoms of a ruptured ovarian cyst vary depending on the severity and severity of the lesion. A rupture of a neoplasm of the appendages can be suspected when a stabbing pain appears on one side, gradually intensifying and spreading to the entire peritoneum. Typically, tissue tearing is provoked by physical activity, sexual activity, and injury. In any case, if uncharacteristic symptoms appear, it is necessary to seek consultation to diagnose the process and timely treatment.
Who should I contact?
With the clinical picture of this disease, you need to visit a gynecologist. If he suspects that the development of the cystic process is complicated by cancer, the patient will be referred to an oncologist.
If there are indications for laparoscopy, the main one of which is severe pain in the lower abdomen, the patient is sent for a consultation with a surgeon.
Diagnostics
Adnexal cysts can lead to serious consequences for reproductive health, so treatment must be started promptly, before complications occur. When the first signs of a neoplasm appear, you should immediately seek help from a gynecologist. Examination and questioning help the specialist make a diagnosis. The cyst and tumor rupture are clearly identified with the help of additional studies:
- Ultrasound of the pelvis;
- puncture of the posterior vaginal fornix;
- laparoscopy.
Important! Apoplexy of the right ovarian cyst occurs more often and is more complicated, which is associated with the blood supply to this area by a vessel extending directly from the aorta.
What to do if an ovarian cyst bursts
A ruptured capsule of an ovarian cyst cannot be treated at home. If you have symptoms reminiscent of rupture of tumors on the appendages, you should seek help. Some women report some improvement after the sharp pain when the tumor bursts. In fact, this phenomenon is temporary; doctors call this symptom a “light period”. The body initially copes with the bleeding, and health improves. Afterwards, a breakdown in compensatory capabilities occurs, the condition worsens sharply, without assistance at the moment there is a high risk of death.
Important! If you suspect a ruptured vesicle on the appendages, seek medical help immediately.
Emergency care for a ruptured ovarian cyst
Usually, when a painful attack occurs, which is the main symptom of rupture of a neoplasm of the appendages, patients take antispasmodics and painkillers at home. If a woman knows about the diagnosis and is warned about the possibility of rupture, these drugs are always in the medicine cabinet. However, it is advisable to refrain from taking medications, ensure rest and take the woman to the nearest hospital for treatment.
With an ovarian cyst, rupture with hemorrhage into the abdominal cavity is especially difficult. In this case, it is necessary to lay the patient down and give cold to the stomach. It is not advisable to take medications until the ambulance arrives. Drugs can distort the clinical picture and make it difficult to assess a woman’s condition.
Paraovarian cyst on the left during pregnancy
This neoplasm is located between the uterus and the appendage, on the left side. During the period of gestation, it stretches, which provokes severe gastric discomfort.
Gynecologists recommend removing the left-sided cyst at the stage of planning motherhood, as it can rupture or twist.
The main indication for surgery is the size of a neoplasm on the body of the ovary more than 5 cm. The risk of miscarriage, if present, increases.
Treatment of ruptured ovarian cyst
To prescribe therapy, it is necessary to establish the presence of a rupture, determine the predominant symptom, and the severity of hemodynamic disturbances. The main criterion that determines the patient’s management tactics is the amount of blood loss. The more massive the bleeding a woman has, the more pronounced the symptoms of the disease. To confirm the severity of the condition, special studies are carried out.
Conservative methods
If an ovarian cyst ruptures, treatment without surgery is carried out exclusively with a confirmed painful form of apoplexy. In most cases, the main symptom of the disorder is pain; bleeding in this case is minor. The wound is small and quickly closes with a blood clot.
Conservative therapy is reduced to taking antispasmodics, painkillers and hemostatic agents. During the treatment period, the patient adheres to strict bed rest. If there are positive dynamics, treatment is continued until the symptoms disappear. If signs of deterioration appear, the patient is prepared for surgery.
Surgical methods
In most cases, if there is a rupture of the ovarian tissue tumor, surgery is performed. The scope of surgical care is mainly determined immediately at the time of the procedure. If the damage is minor, tissue can be sutured and the tumor capsule can be peeled off. If it is not possible to stop the bleeding and the organ becomes saturated with blood, it is necessary to remove the affected ovary. A ruptured right ovarian cyst is usually repaired laparoscopically.
Important! If signs of rupture appear, you should not self-medicate. Even conservative therapy is carried out in a hospital setting under the close supervision of a doctor.
Benign ovarian neoplasm (D27)
Representatives of this group include cysts:
- endometrioid;
- paraovarian.
Endometriotic cysts
Such neoplasms are the result of the development of endometriosis. When endometriotic lesions merge, cysts are formed, which often contain menstrual blood.
They have a dense capsule and mainly occur in women aged 12–50 years. The size of endometrioid cysts usually ranges from 1–10 cm, and they can affect one or both organs at the same time. Although, due to the more active blood supply to the right ovary, a cyst more often forms in it, receiving the same ICD 10 D27 code.
Quite often, the formation of an endometrioid ovarian cyst is preceded by medical manipulations on the internal genital organs, including abortions and diagnostic curettages. But in some cases it occurs against the background of complete health, and a thorough examination reveals endocrine pathologies or banal exhaustion of the nervous system due to frequent stress.
An increase in tumor size often leads to the destruction of follicles, the appearance of follicular cysts and adhesions between the pelvic organs and the walls of the fallopian tubes. If this process is not stopped in time, the woman risks facing the problem of infertility.
Paraovarian cysts
Cavities located in the tissues of the appendage, that is, between the ovary and the fallopian tube, are called paraovarian cysts. They are found quite often (15–20% of all benign ovarian tumors), and mainly in women 20–40 years old, since it is during this period that the maximum development of the appendages is observed.
The only reason for the formation of such neoplasms is the occurrence of disturbances during embryonic development. They grow due to the accumulation of liquid secretion, which is facilitated by overheating of the body, observed, for example, when taking excessively hot baths, visiting saunas, baths, etc.
Paraovarian ovarian cysts can grow to gigantic sizes - more than 30 cm in diameter. In such cases, the appearance of abdominal asymmetry is often observed, which is especially noticeable in thin women. But at the same time, they are absolutely safe for women’s health and extremely rarely provoke the development of infertility and menstrual irregularities.
What is the danger of a ruptured ovarian cyst?
When a tumor bursts, the contents of the capsule and blood enter the abdominal cavity, irritating the nerve endings and causing inflammation of neighboring structures. Bleeding and peritonitis are the most severe conditions that occur when a woman does not seek treatment at the hospital.
Consequences of a ruptured ovarian cyst
With timely assistance provided when the formation bursts, serious violations can be avoided. When a cyst on the ovary ruptures, the consequences may be as follows:
- peritonitis;
- hemorrhagic shock;
- sepsis;
- increased formation of adhesions;
- higher risk of ectopic pregnancy;
- infertility;
- death.
Diagnostic scheme for suspected ovarian diseases
The reason for a visit to the doctor is a disruption in the menstrual cycle or the appearance of pain in the lower abdomen. To determine the diagnosis, an examination is carried out:
- Examination by a gynecologist. With a special examination, the doctor can determine the size of the ovary, assess the degree of their enlargement and palpate the round formation in the projection of the appendages;
- Laboratory tests: blood and urine tests. They are not indicative of ovarian pathology, but serve to assess the general condition of the patient;
- Tests for tumor markers: CA-125, CA-19-9, HE4 (ROMA index). An increase in tumor markers highly likely indicates a malignant tumor. It is important to remember that CA-125 is also elevated in endometrioma;
- Ultrasound examination with Doppler. Helps to visually assess the size and location of the formation, determine the thickness of the capsule and the number of chambers, identify changes in blood flow and suggest the type of tumor. A cyst is defined as a hypoechoic or anechoic structure in or adjacent to the ovary;
- Computed and magnetic resonance imaging. Used in controversial situations;
- Diagnostic laparoscopy. It is prescribed in terms of differential diagnosis and allows you to distinguish an ovarian mass from an ectopic pregnancy and other conditions.
Scheme of examination when a mass is detected on the ovary.
According to reviews of women who have been diagnosed with an ovarian cyst, this pathology can be confused with other conditions. Differential diagnosis is carried out with the following phenomena:
- Uterine pregnancy. Before visiting a doctor, a corpus luteum cyst can be confused with pregnancy. In both cases, there is a delay in menstruation, and dubious signs of gestation are noted (weakness, drowsiness, nausea, mood swings, sensitivity to smells, perversion of taste, etc.). The hCG test helps resolve doubts. With a cyst, hCG is not detected, but increases during pregnancy. Ultrasound provides additional information;
- Ectopic pregnancy. Upon palpation, the gynecologist identifies a rounded formation in the projection of the appendages, which can be either a cyst or a fertilized egg. A blood test for hCG and ultrasound help clarify the diagnosis;
- Salpingo-oophoritis. During a gynecological examination, it is defined as a rounded formation of the appendages. Detected by ultrasound;
- Ovarian cancer. Ultrasound, Doppler, and laparoscopy help confirm the diagnosis. The final conclusion is given by histological examination.
On a note
In the medical history of women with an identified ovarian cyst, there is often more than one diagnosis. Pathology of the appendages is often combined with uterine fibroids, hyperplasia and endometrial polyps . These diseases are based on similar developmental mechanisms, and sometimes they are detected simultaneously.
An ovarian cyst is often combined with uterine fibroids.
It is also useful to read: Nuances of IVF for polycystic ovary syndrome and single cyst
Recommendations and tips
Rupture of an ovarian cyst, the symptoms of which vary depending on the degree of damage to the tissue of the appendages, can occur in any woman. To avoid complications, it is necessary to be constantly monitored by a gynecologist, promptly treat cycle disorders, and diagnose growths on the appendages. If a cyst is detected, it is advisable to follow all the doctor’s instructions and avoid things that provoke rupture. If symptoms appear that the tumor has burst, you should immediately seek help from a specialist. In most cases, treatment is surgical.
Source
Classification of other types of cysts
Not all ovarian cysts are directly related to the functioning of the internal genital organs. In some cases, it is impossible to identify the cause of their appearance, although both the menstrual cycle and the symptoms that appear have an influence. This ovarian cyst has ICD 10 code N83.2. This code includes the following types of entities:
- Endometrioid, which appears due to the proliferation of tissue of the uterine mucosa into the ovary;
- Dermoid cyst containing particles of teeth, hair, skin;
- Paraovarian, originates from the epididymis;
- Mucinous - a cyst filled with mucus, has rapid growth and a tendency to degenerate into a malignant neoplasm.
The specialists of the oncology department of the Yusupov Hospital differ from other hospitals in their European quality, international experience and cooperation with foreign colleagues. This hospital employs highly qualified specialists in their field who use innovative technologies in the diagnosis and treatment of ovarian tumors. Individual selection of medications, taking into account the characteristics of the course of the disease, contributes to effective relief from the disease. Polite medical staff are always ready to help their patients solve any difficulties. The Yusupov Clinic provides a rehabilitation program aimed at a speedy recovery and return to their previous lifestyle. You can make an appointment and consultation by phone.
Author
Obstetrician-gynecologist, oncologist, candidate of medical sciences