The glands of the uterus and ovaries continue to produce characteristic secretions even after the onset of menopause. Under the influence of hormonal changes that occur in the female body during menopause, the volume of discharge may even exceed the usual amount. The serous consistency accumulates inside the uterus, supplemented by a small amount of fluid from the abdominal cavity. If there are obstacles to the outflow of secretion, it stagnates, stretches the organ, causes pain and other symptoms. Serozometra in postmenopause is a pathology that is eliminated in the hospital department.
Symptoms
At the initial stage of development, the pathology does not manifest itself with severe symptoms. As intrauterine mucus accumulates, a woman experiences:
- Dull pain in the suprapubic region, which the patient associates with hormonal changes. Discomfort increases during sexual intercourse.
- Copious vaginal discharge with an unpleasant odor. They have a yellow tint and look like pus.
- Impaired urine outflow caused by compression of the ureters by the enlarged uterus.
- In women with a thin build and large serozometers, a protrusion in the lower abdomen can be felt.
- Aching sensations in the lumbosacral region of the back. Discomfort decreases when changing body position.
- Constipation caused by serosometer pressure on the intestines.
If a woman does not seek medical help for a long time, suppuration of the uterine tissue occurs, and a number of signs complement the clinical picture. An increase in body temperature and all the symptoms of intoxication of the body are observed, the pain syndrome becomes more intense.
How to take Borovaya Uterus
For the treatment of various diseases, herbalists use Borovaya uterus in three types:
Borovaya uterus tincture: To prepare it you will need 0.5 liters of vodka and 5 tbsp. spoons of dry raw materials. Pour vodka over the medicinal herb and leave for 21 days; the solution should be stirred from time to time and stored in a dark place. How to drink Borovaya uterus? Usually the tincture is taken 15-30 drops 1 hour before meals.
Borovaya uterus decoction : 2 tbsp. spoons of raw materials pour 300 ml. water, boil for 5 minutes, let it brew for another half hour, strain. Use the decoction orally half an hour before meals, one tbsp. spoon 3 r/day.
Infusion of Borovaya uterus : Just like for a decoction, pour 2 tablespoons of chopped herbs into half a liter of boiling water, wrap, leave for 15 minutes, then strain. Drink half a glass of infusion 3-4 times a day half an hour before meals.
Any medicinal plant after infusion must be filtered; experienced herbalists recommend not using metal strainers, etc., it is best to strain through a linen cloth or cotton napkin. Prepared drinks cannot be stored for more than 2-3 days; it is best to pour the infusion or decoction into a glass container with a lid and put it in the refrigerator. Both the infusion and the decoction for gynecological problems can be taken not only orally, but also used for douching with the Borovaya uterus. To do this, pour two tbsp. spoons with a glass of boiling water, leave for at least 3 hours, strain.
Causes
Factors that cause serosometra are related to hormonal changes that occur during postmenopause and events in the patient's medical history. For example, if a woman has previously had multiple abortions, suffers from intestinal inflammation, or suffered a difficult birth. When visiting a doctor, the patient needs to inform him about the diseases that she had previously been diagnosed with, and clarify information about her obstetric and gynecological history. It includes the number and type of births, previous cases of curettage of the uterine cavity (including those performed for diagnosis).
Narrowing of the cervical canal
Pathology can be congenital or acquired - one that occurs throughout life due to the adverse effects of various factors. During the postmenopausal period, the serozometer is formed precisely because of 2 types of narrowing. Acquired stenosis of the cervical canal is a consequence of swelling of its mucous membranes, which is preceded by inflammation or an allergic reaction. For a long time, a woman may not be aware of the presence of a narrowing. One of the few signs of cervical canal stenosis is discomfort during intimacy.
The disorder is eliminated after the underlying pathology is relieved. Therefore, to eliminate the root cause of stenosis, you should:
- Stop allergies. For this purpose, antihistamines are used (they are only available with a doctor's prescription).
- Get rid of inflammation of the cervical canal. Undergo antibacterial or antiviral therapy, depending on the type of pathogenic microflora that caused cervicitis.
- Strengthen the state of local immunity (through the introduction of vaginal suppositories).
To prevent cervicitis from recurring, you must stop using pads with fragrances; if you are allergic to latex, do not use condoms. If inflammation of the canal is caused by frequent douching, you need to stop performing this procedure and allow the mucous membranes to fully recover.
Choose a specialist, read reviews and make an appointment with a gynecologist online
Endometriosis
Uncontrolled growth of the internal uterine layer, in which the membranes overcome the cavity of the organ and can block its pharynx. Due to the blockage, serous secretion is not released outside, and it accumulates inside the organ.
Signs of endometriosis:
- Lower abdominal pain
- Discomfort during intimacy
- Discharge of large blood clots from the vagina
During the postmenopausal period, intense hormonal changes occur in the female body. Therefore, against the background of menopause, endometriosis often develops. At the initial stage, the pathological process is rarely detectable. But provided that a woman regularly visits a gynecologist, endometriosis can be detected in the early phase of its development.
If the overgrown endometrium provokes serozometra during postmenopause, it is necessary to excise the excess membranes to restore the outflow of mucus from the uterine cavity. The woman then undergoes corrective hormone therapy. Conservative treatment for endometriosis, which caused serozometra, does not provide a positive result.
Benign or malignant neoplasms
Regardless of their origin, tumors represent a mechanical obstacle to the full release of secretions from the uterus. Small neoplasms only in rare cases provoke the accumulation of secretions inside the reproductive organ. Mainly if the tumors are located near the uterine pharynx. Most often, mucus stagnation occurs in patients with fibroids. Against the background of hormonal changes occurring in postmenopause, this type of neoplasm develops frequently.
Common reasons for the development of tumor processes:
- Hereditary predisposition
- Systematic stay near a source of toxic exposure
- Having suffered a traumatic birth
- Frequent cases of abortion
- A history of an episode of displacement or partial prolapse of the intrauterine device
- Uncontrolled use of hormonal drugs
- Being in a stressful environment
Serozometra can also provoke cervical cancer - if the neoplasm is localized near the pharynx and is characterized by a large size. Given the long period of asymptomatic progression, sometimes women find out about the presence of a tumor only during an examination for pain in the lower abdomen. The type of tumor elimination depends on many factors, including the presence of concomitant diseases. Surgery, chemotherapy, and the introduction of synthetic substitutes for natural hormones are prescribed.
Spikes
The adhesive process is a reaction of the immune system to the presence of inflammation or damage to organ tissue. Through the formation of synechiae, the body's protective properties limit healthy tissues from pathologically altered segments.
Characteristic adhesions form near the uterus and appendages due to many reasons - among them:
- Sluggish inflammation in the genitourinary system
- Frequent cases of abortion
- Previous injuries to the pelvic organs
- Damage to the uterus caused by uterine rupture
The presence of an adhesive process has a long period of latent development. In the majority of cases, diagnosis is made only after the appearance of complications caused by synechiae. Adhesions are removed surgically. Conservative prescriptions (for example, administration of Lidase) have a largely preventive effect, so the drug is administered after surgery.
Endometritis
Inflammation of the internal uterine layer can occur both during postmenopause and long before its onset. The causes of the pathology are hypothermia, intimacy with a partner who does not perform hygiene procedures, and sexually transmitted diseases. Endometritis also develops due to the presence of another inflammatory focus in the pelvis. For example, if the patient suffers from cystitis, adnexitis, cervicitis. In this case, the pathogenic microflora passes from the affected organ to the uterus, causing its inflammation.
Signs of endometritis:
- Increased body temperature. If the inflammatory process takes a chronic course, the indicators vary within the range of low-grade fever (up to 37.5°C). In acute endometritis, body temperature reaches high levels.
- Severe pain syndrome. Localization of discomfort is the lower abdomen, lumbosacral back.
- Weakness and dizziness (signs caused by general intoxication of the body).
- Vaginal secretions that have a putrid or purulent odor.
- Bloating.
- Neurological disorders caused by a general deterioration in health.
Due to inflammation, the uterine tissue is characterized by swelling. Therefore, the mucus present inside the cavity is not released outside, accumulates, and stagnates.
Physical inactivity
A sedentary lifestyle most likely leads to the accumulation of secretions secreted by the glands of the ovaries and uterus. The contractility of the reproductive organ is weakened, tissue tone changes and secretions accumulate, forming a serozometra. If, after the onset of menopause, a woman does not pay attention to moderate physical activity, behaves passively, congestion develops in the pelvis. To prevent problems with the outflow of serous secretion, it is necessary to abandon a sedentary lifestyle.
Abuse of hormonal drugs
This action contributes to hormonal imbalance. As a result of the imbalance, the glands of the ovaries and uterus function excessively, which contributes to the release of an increased volume of secretion. Not the entire amount of the produced mass may be released externally, and the remaining part stagnates inside the organ. If a woman is taking hormonal medications, she should be informed about this factor when she consults a doctor with complaints about signs of serozometra. Treatment begins with stopping the use of these drugs.
Cervical atresia
A pathological condition characterized by obstruction of the uterine pharynx, which prevents the flow of mucus from the organ cavity. The condition is preceded by endometritis, the presence of sexually transmitted diseases, traumatic uterine curettage, previous ablation or electrocoagulation. For a long time, a woman may not suspect the presence of atresia. But soon the narrowing of the female reproductive organ becomes a cause of complications. Atresia is treated mainly in a minimally invasive way - you will need to undergo bougienage (expansion) of the pharynx.
Ectopic pathologies
The formation of serozometra is not always associated with problems in the reproductive system, especially with the condition of the uterus. Not less often, the accumulation of secretion occurs due to a disorder localized outside the reproductive organs. Diseases such as colitis (inflammation of the intestines) and cystitis (damage to the bladder) can provoke inflammation of the uterus and cause serozometra during menopause. When colon disease occurs, dysbacteriosis progresses as a concomitant pathology. It interferes with the full activity of the intestines, causing the development of constipation, which leads to compression of the uterus.
The reproductive female organ cannot release the entire accumulated amount of secretion, which causes its stagnation. In this case, treatment begins with normalizing intestinal activity. Cystitis causes serosometra due to overcrowding of the bladder. Being inflamed, the organ does not function fully; urine can accumulate, stretching the cavity. Anatomically, the bladder is located in front of the uterus, and as it becomes full, it compresses it. In this case, treatment begins with eliminating cystitis.
Frequent abortions
If a woman regularly terminates her pregnancy before postmenopause, the inner uterine layer changes its structure. The endometrium swells, its glands do not function correctly. These factors serve as favorable conditions for intrauterine accumulation of serous secretion.
The aspect of contractility of the reproductive organ is of no small importance. In women who have previously undergone 2 or more abortions, the uterine tone is altered. The organ cannot contract strongly enough to release all the accumulated secretion. Its volume increases, the contents stagnate and cause a number of symptoms.
Diagnostic methods
A doctor will be able to determine the serosometer only after a thorough diagnosis and examination. Due to the significant accumulation of serous water in the uterus, it begins to increase in size. To determine an accurate diagnosis you need to:
- Additional examinations. A woman is recommended to have an ultrasound of the genitourinary system. The doctor can determine the size of the uterine cavity and the amount of accumulated fluid. Sonography makes it possible to identify the size of the enlarged uterus. Doppler ultrasound can establish the speed of blood circulation in the vessels of the uterus. Its change may indicate the processes of neoplasms occurring in the body.
- Histological examination of serous water from the uterus. To make an early diagnosis of cancer, a specialist can perform a uterine puncture. If there is a suspicion of the presence of serous waters inside the pelvis, a puncture is performed from the abdominal region through the back of the vagina.
- Analyzes. Urine and blood are examined for biochemical analysis. Blood examination for tumor markers and hormones. A smear is taken from the vagina to determine the microflora and diagnose possible sexually transmitted diseases.
Possible complications
The accumulation and stagnation of the serous mass can provoke pyometra and peritonitis: suppuration of the uterus and abdominal cavity is indicated.
Signs that are observed in both pathologies:
- Increased body temperature
- Pain in the suprapubic region and abdominal cavity
- Weakness
- Nausea, vomiting
- Dizziness
- Purulent vaginal discharge
- Severe bloating
Pyometra and peritonitis develop due to prolonged lack of treatment in the presence of serosometra. Intrauterine stagnation of secretion is a favorable environment for the entry of bacterial microflora and the subsequent development of the inflammatory process. From the uterus it moves to the tissues of the abdominal cavity, causing peritonitis: a condition that, if not treated in a timely manner, leads to mortality.
Skycloud's Diary
- Architecture (114)
- Bodyflex, yoga (70)
- Videos (1,901)
- All about coffee (492)
- Sunday coffee with newspaper (45)
- Knitting (224)
- My knitting patterns (7)
- Home cooking (616)
- Pancakes (57)
- Muffins (12)
- My recipes (174)
- Everyday (2,763)
- and talk? (259)
- Old wives' tales (163)
- Mirror (43)
- Good night picture (424)
- Wise thoughts (109)
- News of the day (7)
- Useful tips (685)
- Liked (172)
- Health (932)
- Internet, blogger, blog design (132)
- Interior (824)
- Interior things (149)
- Cats are my weakness (676)
- Cat housing (19)
- My cats (98)
- Culinary Podium (89)
- Restaurants (45)
- Literary cafe (92)
- Yellow Brick Road (13)
- Zhenya (9)
- Once upon a time there were people (11)
- Green hedgehogs (8)
- Master class (2,258)
- My MKs (11)
- Fashion, Beauty, Health (1,653)
- Shoes (66)
- Clothes (557)
- Scrub (34)
- Care products (266)
- Hand care, manicure (107)
- My works, floristry (71)
- News (402)
- Maidan, Ukraine, Crimea (109)
- General (5,513)
- Public people (116)
- From the world by thread (916)
- Interesting places on the planet (83)
- Interesting facts (52)
- Movie trivia (56)
- Poetry (71)
- Advertising (28)
- Contemporary art (223)
- Ukraine (256)
- Festivals, holidays, competitions (151)
- Tests, polls, horoscopes (124)
- Dedicated to those who have left us... (39)
- Floristry (311)
- Other materials (129)
- Fresh flowers (118)
- Photos (563)
- Handmade (2,504)
- Jewelry (115)
- Beading (25)
- Felting (17)
- Embroidery (35)
- Decoupage (70)
- Valentine's Day (111)
- For children's creativity (75)
- Ideas for a summer residence (132)
- From candies (14)
- Plastic products (68)
- Dolls (109)
- Modeling (44)
- Soap making (30)
- New Year (605)
- Easter (220)
- Alterations (197)
- Weaving from newspaper tubes (627)
- Gifts for men (22)
- Scrap (81)
- Sewing (231)
- Humor (469)
Even more interesting:
Causes of sores on the labia
Yarina with folic acid
Which doctor should I contact?
The appearance of symptoms characteristic of the development of serozometra in postmenopause is the basis for contacting a gynecologist. A doctor of this profile deals with the identification and subsequent elimination of diseases of the female reproductive system. Symptoms of serozometra resemble signs of pathologies of the intestines and parts of the urinary system. To exclude the presence of tumors of the gastrointestinal tract, bladder or ureters, you will need to contact a surgeon or urologist.
Choose a specialist, read reviews and make an appointment with a gynecologist online
Diagnostics
To identify intrauterine accumulation of secretion and determine its characteristics, you need to go through:
- Laboratory examination of blood, urine, smear from the cervical canal.
- MRI or CT.
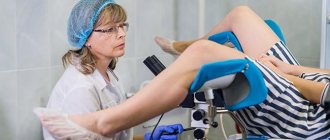
- Ultrasound of the pelvis. During the procedure, the size of the serozometer is determined, which serves as a determining factor in the preparation of treatment.
- Examination on a gynecological chair.
- Survey.
- Biopsy of the uterus followed by histological examination. Using special forceps (or a needle), a small piece of organ tissue is taken, after which the sample is examined under a microscope. This type of analysis allows you to exclude the presence of cancer.
Additional types of diagnostics depend on the characteristics of the clinical case. It is possible to prescribe a hysteroscopy and a blood test to determine estrogen and progesterone.
Therapy
The nature of therapy to eliminate this pathology depends on the size of the fluid formation, the rate of its accumulation and the cause of the disorder. Treatment of serous fluid is aimed at improving the outflow of serous fluid and reducing its formation.
In the absence of inflammation
In women of menopause and reproductive age, in the absence of an inflammatory process and a small volume of fluid (expansion of the uterine cavity up to 5 mm), you can do without any surgery. Recommended:
- control - pelvic ultrasound every 6-12 months;
- drugs - aimed at improving blood circulation in the uterus, increasing vascular tone and regeneration of the epithelium (Detralex, Dioflan, Avenue);
- vitamins - group B and ascorbic acid.
Curettage and hysteroscopy
If heterogeneity of the contents of the uterine cavity is established (echo signs of polyps, tumors, synechiae, remnants of the fertilized egg), diagnostic curettage or hysteroscopy is recommended.
The latter method is preferable, especially with recurrent serosometer, due to its greater information content and safety. During curettage or hysteroscopy, bougienage (dilation) of the cervical canal is performed; in the presence of submucous fibroids, myomectomy is performed. If oncological neoplasms are confirmed, treatment is carried out in accordance with the identified pathology.
In the presence of inflammation
If there are signs of an inflammatory process, the following drugs are additionally prescribed:
- antibiotics - ideally taking into account the sensitivity of the flora identified in the vagina and cervix or a wide spectrum of action;
- NSAID group - Diclofenac, Indomethacin, Ibuprofen in the form of rectal suppositories or tablets for oral administration;
- antiviral - in the presence of a viral infection, “Viferon”, “Kipferon”, “Ruferon”;
- eubiotics - to normalize vaginal microflora, “Narine”, “Acilact”, “Gynoflor”;
- immunostimulants - “Level”, “Amiksin IC”;
- products with estradiol - for local action in menopausal women, for example, Ovestin.
Auxiliary folk recipes
Treatment of serozometra with folk remedies is also best carried out under the supervision of a doctor after excluding serious diseases. You can use the following recipes.
- Cabbage . You should take five or six cabbage leaves, pour boiling water over them, pour in a liter of milk and bring to a boil. Strain. Pour into a basin and perform sitz baths.
- Mustard. Pour 5 g of mustard powder into a bowl of hot water. Stir. Used for sitz baths.
- Juniper. Chop 100 g of juniper, pour in 5 liters of boiling water and bring to a boil. Let it brew for several hours, then dilute with warm water for sitz baths.
- Borovaya uterus. Pour 10 g of herb into 200 ml of water, bring to a boil, let it brew for two to three hours. Take a tablespoon orally two to three times a day.
Impaired outflow of serous fluid from the uterine cavity most often develops due to hormonal imbalance and is a functional condition, not a disease. Women of menopausal age are at risk for the development of pathology. Treatment of serozometra in most cases includes curettage of the uterine cavity followed by ultrasound control once every six months to a year.
Treatment
Serozometra is rarely removed surgically: in the vast majority of cases, minimally invasive intervention is sufficient. It involves bougienage of the cervix followed by aspiration of stagnant secretions. The doctor uses an instrument to widen the opening of the organ and then gradually withdraws the serosometer from it using a syringe. The procedure is performed on a gynecological chair. To prevent bougienage from causing pain, the woman is first given anesthesia.
After minimally invasive manipulation, the patient is prescribed:
- Antibiotics. Prevents inflammation of the uterine membranes and promotes their rapid recovery after bougienage and aspiration.
- Hormonal agents. Compensate for the missing amount of estrogen in the female body.
- Analgesics. They relieve pain and help you recover faster after bougienage and aspiration of secretions.
- Antispasmodics. Eliminate discomfort that occurs after a gynecological procedure.
- Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (in the form of suppositories). Prevents the development of intrauterine inflammation, eliminates discomfort in the genital tract.
Additional types of medications depend on the characteristics of the clinical case. It is possible to prescribe vitamins, immunomodulators, and hemostatic drugs. If serozometra occurs during the postmenopausal period due to ectopic pathology, treatment begins with its elimination. For cystitis, the use of uroseptic drugs is indicated - Furazolidone, Furadonin or their analogues. If the accumulation of secretion is associated with the presence of colitis, the patient undergoes antibacterial therapy followed by restoration of the intestinal microflora.
Women with serozometra are treated in the gynecology department of the hospital. The indication for bougienage is the volume of secretion accumulation exceeding 10 ml (this factor is determined during ultrasound). Until the recovery period, the woman is in the department where doctors monitor her condition. The grounds for discharge of the patient are determination during ultrasound of complete cleansing of the uterus from contents.
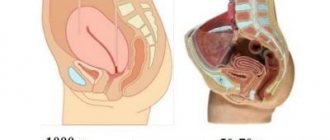
Definition of pathology
Serozometra is a female pathology in which the patient experiences free fluid in the uterine cavity. Between the muscles of the reproductive organ and the endometrium there is a serous membrane. It contains a huge number of blood vessels. Serous fluid is a transparent blood plasma that has a light yellow tint. It is this fluid that enters the uterine layer with blood vessels.
Due to the presence of a large number of scars in the walls of the uterus, the release of serous fluid is disrupted. This leads to the development of serozometra. Sometimes fluid begins to collect in the cervical canal area. This type of disease is called serozocervix. Both pathologies require immediate medical control, since a violation can lead to the development of severe complications.
Coding according to ICD-10 - other diseases of the uterus, not of an inflammatory nature, with the exception of the cervix - N85.
Prevention
To avoid the development of serozometra in postmenopause, it is necessary:
- Maintain intimate hygiene. During menopause, a woman experiences increased production of vaginal secretions. If it is not eliminated in a timely manner, inflammation of the uterus and cervical canal occurs, which serves as a favorable condition for the development of serozometra.
- Avoid hypothermia.
- Do not overuse douching.
- Balance your diet.
- Do not stop having sex, despite the onset of menopause.
- Avoid excessive physical activity.
- Do not take hormonal medications unless prescribed by a doctor.
- Avoid being in a stressful environment.
If a woman has undergone diagnostic curettage, to prevent the development of inflammation in the urogenital tract, you must follow the doctor’s recommendations. This avoids endometritis, which predisposes to intrauterine secretion accumulation. Serozometra in postmenopause is intrauterine mucus stagnation that occurs in women after menopause.
For a long time, the patient may not know that she has this pathology. When a large amount of serous fluid accumulates in the organ and it stretches, the woman experiences severe symptoms. These include pain above the pubis and in the sacral region, a feeling of general discomfort, discharge of pus from the vagina, and difficulty defecating. Serozometra is eliminated by bougienage and aspiration of the contents.
Forecast of the course of serozometers
A favorable outcome of the pathological condition depends on several factors. This is the timeliness of treatment, the main cause of the pathology, the presence of concomitant diseases. Timely conservative therapy with minor changes in the uterus and the absence of pronounced symptoms almost completely solves the problem.
There are no specific preventive measures to prevent the occurrence of serozometra. A healthy lifestyle, avoidance of harmful addictions, balanced nutrition, and sufficient physical activity for a woman’s age help reduce the likelihood of pathology.