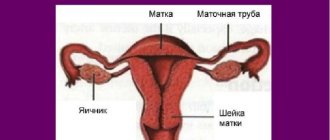
The uterus is the main female reproductive organ that performs reproductive functions and is intended for bearing a fetus. In order for pregnancy to occur and proceed normally, it must have the correct location. One of the variants of deviation from the norm is uterine retroflexion. The article discusses the causes, symptoms and possible complications of this pathology.
Description
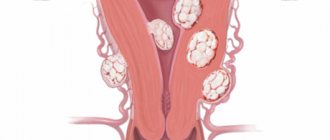
Retroversion of the uterus is a pathological condition that consists of deviation and non-standard location of the uterus. Occurs most often in virgins.
There are different degrees of backward deviation of the uterus. In case of slight displacement, the uterine fundus may be located at the level of the sacral promontory, and in case of more pronounced deviations, it may be lower than the cervix. As a result of this, formations that are palpated in the pouch of Douglas may be mistaken for another pathological process.
Retroversion of the uterus can be congenital or acquired. The congenital form of the disease occurs in 20-30% of cases. An acquired deviation often develops during childbirth due to weakening of the uterine ligamentous apparatus as a result of pathology such as endometriosis, salpingitis, ectopic pregnancy, trauma or mechanical displacement of the uterus by a tumor of the pelvic organs.
Symptoms
With mobile retroflexion, the uterus is able to move, and therefore the woman may not notice any symptoms. With a fixed type, accompanying disorders are observed, for example, adhesions and inflammation. And the organ itself remains motionless and incorrectly located, which changes and complicates its functioning.
The following symptoms of retroflexion are likely:
- disruptions of the menstrual cycle: frequent delays or decreased intervals between menstruation;
- scanty or, on the contrary, excessively abundant menstrual flow (when the uterus deviates posteriorly, the release of its contents is disrupted);
- copious vaginal discharge;
- pathological vaginal discharge of an abnormal color or having an unpleasant odor (the symptom is caused by inflammation or genital infections that caused retroflexion);
- discomfort that occurs during sexual intercourse;
- discomfort, heaviness and pain in the sacrum and lower abdomen;
- constipation (develops when the intestines are compressed by the displaced uterus);
- frequent urination.
Symptoms
Very often, retroversion of the uterus can occur asymptomatically (in the absence of concomitant disease). Some patients may experience minor symptoms: pain in the back and pelvic area, infertility, miscarriage or menstrual disorders.
Feelings of discomfort, pelvic pain or back pain may occur as a result of a displaced uterus. Signs of congestion in the pelvic area are often possible. Symptoms are worse after walking for a long time or towards the end of the day.
The occurrence of menstrual irregularities as a result of uterine displacement is difficult to explain. The most common cause is dysmenorrhea or prolonged menstrual bleeding.
It is unlikely that uterine retroversion can cause spontaneous abortion. Even with a large deviation, at 13-14 weeks of pregnancy, the uterus extends beyond the boundaries of the small pelvis. Sometimes the fundus of the uterus can linger in the sacral cavity and it is as a result of this that spontaneous abortion can occur.
There is no evidence that uterine retroversion contributes to infertility. But concomitant diseases of the pelvic organs, which arise due to retroversion of the uterus, can provoke infertility. These are uterine leiomyoma, salpingitis or endometriosis, which can result in dyspareunia.
Diagnostics
It can be quite difficult to diagnose uterine retroversion based on an analysis of symptoms. The most informative diagnostic method is the examination of the pelvic organs. The presence of a tumor on palpation in the pouch of Douglas and forward displacement of the cervix in the absence of a detectable forward deviation of its fundus indicate retroversion.
Sometimes difficulties may arise in excluding concomitant pathological processes that are located in the pouch of Douglas. This can be done on the basis of anamnestic data and a thorough examination of the pelvic organs. For example, if there is medical history that indicates endometriosis, you can palpate tumor-like formations that displace the uterus posteriorly, or nodes in the uterosacral ligament area. Laparotomy or laparoscopy may be necessary to confirm the diagnosis.
In some cases, other diseases can be mistaken for uterine retroversion. An ectopic pregnancy or dense inflammatory formations emanating from the appendages can adhere tightly to the posterior uterine surface and “simulate” its posterior displacement. Myomas of the posterior wall of the uterus are sometimes difficult to differentiate from its retroversion. Adnexal cysts that are located in the pouch of Douglas can be mistaken for a retroflexed gravid uterus.
Prevention
Prevention includes:
- Maintaining a healthy and active lifestyle, balanced nutrition.
- Moderate physical activity.
- Use of barrier contraceptives.
- Timely visits to the gynecologist, treatment of emerging diseases in the early stages.
Retroflexion of the uterus is often a minor and correctable pathology. But if it is not eliminated in time, problems with conception and the functioning of the reproductive system may arise. Therefore, it is important to consult a doctor and follow his recommendations.
(voted: 1, rating: 5.00 out of 5)
Share the news on social networks
Ask a Question! You have questions? Feel free to ask any questions! And our staff specialist will help you. Go>>
- Recommended Articles
- Treatment methods for ovarian cysts
- Cervical dysplasia
- How to treat acute and chronic cervicitis?
« Previous entry
Treatment
Treatment of uterine retroversion in the absence of concomitant diseases is rarely carried out. In some cases, the symptoms are as severe as possible. Mostly such manifestations occur in young multiparous women. In this case, there is a need for surgical treatment. There is a weakening of the supporting structures of the pelvis and it is sometimes difficult to determine whether symptoms arise from uterine retroflexion or weakness of supporting structures or congestion in the pelvis. The best treatment method in this case is hysterectomy of the vagina and plastic surgery of its walls. If the patient wants to preserve fertility, hysteropexy is performed, which immobilizes the uterus.
Surgeries that are performed due to adhesions in the pelvis, ectopic pregnancy or endometriosis may require hysteropexy to restore anatomical relationships and prevent the development of adhesions.
To ensure the correct position of the uterus, several methods are used (with abdominal access). The most common are a modification of the Gulliam operation, the Baldi-Webster method and the Olshausen method. But sometimes with any of these interventions it is impossible to keep the uterus in a physiological position. Often, in order to keep the uterus in anteversion, a duplication of the uterosacral ligaments is formed. If uterine retroversion is accompanied by severe dysmenorrhea, presacral neurectomy is sometimes performed with hysteropexy.
Retroversion of the uterus
Retroversion of the uterus (retroflexion, bending of the uterus)
- pathology consisting in a non-standard location, deviation of the uterus [1]. The main cause of uterine bending is a hereditary factor [2], but bending can also be caused by violations of the integrity of the uterine ligaments, weakness of the pelvic floor muscles, some inflammatory diseases of the pelvic organs, tumors, and endometriosis. In most cases, uterine retroversion is asymptomatic and is diagnosed only when visiting a doctor regarding infertility. A tilted uterus can cause pain in the lower abdomen during menstruation or spotting a few days before it. To diagnose this pathology, an ultrasound examination of the pelvis is sufficient. The main methods of treating uterine retroversion are physiotherapy, gynecological massage, therapeutic exercises; surgical intervention is adequate only in the most extreme cases [3] .
Diagnostic measures
Uterine retroflexion is a pathology that can be detected during a standard gynecological examination.
The vagina is palpated with one hand, and the abdominal wall with the other, through which the doctor can try to displace the uterus. Thus, the procedure makes it possible not only to detect the bend, but also to determine whether the retroflexion is fixed.
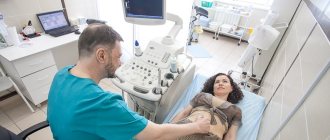
Additionally, an ultrasound examination and sometimes computed tomography are performed - such procedures make it possible to determine the presence of adhesions, inflammatory processes, and neoplasms.
Notes
- ↑
Curvature of the uterus on infomedical.ru. Archived from the original on August 14, 2012. Retrieved July 10, 2011. - ↑
“Retroverted Uterus”
Women's Health
, 2009, Web. 5 Mar. 2010. . - ↑
Deflection of the uterus on women-medcenter.ru. Archived from the original on December 10, 2012. Retrieved July 10, 2011.
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.
See what “Retroversion of the uterus” is in other dictionaries:
retroversion of the uterus - (retroversio uteri; retro + lat. verto, versum twirl, turn) the position of the uterus, in which its body is tilted posteriorly, and the cervix is anterior relative to the pelvic axis ... Large medical dictionary
Retroversion is an abnormal position of the uterus in which it deviates posteriorly and its base is located in the pouch of Douglas, opposite the rectum, instead of being located opposite the bladder. This arrangement of the uterus is observed... ... Medical terms
RETROVERSION - (retroversion) an abnormal position of the uterus in which it deviates posteriorly, and its base is located in the pouch of Douglas, opposite the rectum, instead of being located opposite the bladder. This location of the uterus... ... Explanatory Dictionary of Medicine
How to understand retroversion of the uterus
Many women with infertility are diagnosed with a “flexed uterus.” The vast majority of patients are diagnosed with retroposition. This is a pathological condition in which the organ moves towards the rectum. One of the bending options is the posterior deviation of the female organ - retroversion. If the uterus is deviated posteriorly and the cervix is additionally curved, they speak of retroflexion. In this case, the passage of sperm to the egg becomes difficult and fertilization does not occur. What causes this pathology, what are its main symptoms and causes of development?
Features of conception, how to get pregnant
Moderate physiological curvature of the uterus does not affect conception. Problems arise only with significant retroflexion. In this case, sperm simply do not enter the uterus that is tilted back, and conception does not occur. A favorable position for conception during uterine retroflexion is the knee-elbow position. After intercourse, it is recommended to remain on your stomach for at least 5 minutes so that sperm can easily penetrate the uterus and meet the egg.
Another cause of infertility with retroflexion is the adhesive process. If the bend of the uterus was not congenital, but formed as a result of inflammatory diseases, there is a high probability of developing obstruction of the commissural tubes. In this situation, retroflexion is not the cause, but only an indicator of problems in the reproductive sphere. In case of long-term infertility due to a bent uterus, you need to undergo an examination by a gynecologist.
The concept of retroposition
What is retroposition? This is a pathology in which the anatomical location of the organ in the pelvis is disrupted. Retroposition is one of the types of bending of the uterus, when it tilts back towards the rectum. Most often, this pathology is typical for girls who have not yet begun to be sexually active. The uterus can deviate to varying degrees; in the worst case, retroversion can reach the third degree and put pressure and change the physiological position of the rectum.
Like other forms of bending, retroversion can be congenital or acquired. In the first case, the pathology develops due to disturbances during intrauterine development of the fetus.
Also, the adhesive process can provoke a displacement of the body of the organ and its neck in relation to the bladder. With malignant or benign formations, the development of retroversion increases several times due to the constant pressure of the tumor on the organ.
Main symptoms of retroversion
As a rule, this pathology does not have characteristic symptoms. Very often, girls learn about the disease during their first examination by a gynecologist or when studying the cause of their infertility. However, if there are concomitant diseases with retroversion, a woman may experience the following symptoms:
- severe pain during menstruation;
- menstrual cycle disorders;
- pain during sex;
- different nature of discharge such as leucorrhoea (from scanty to very abundant);
- chronic infectious and inflammatory processes in the pelvis.
For retroversion, the most obvious symptom is nagging pain in the lumbar region; the process of regulating the act of defecation may also be disrupted (due to the strong pressure of the uterus on the rectal area, the process of moving feces is difficult, which causes frequent constipation).
Signs of uterine retroflexion - what is it? Description of the clinical picture
It’s worth saying right away that in most cases, the bending of the uterus is not accompanied by any special signs - often girls do not even suspect the presence of pathology. Retroflexion is often discovered accidentally during examination.
However, sometimes the disease is accompanied by a number of disorders, the list of which is worth familiarizing yourself with.
- The curvature of the uterus makes it difficult for blood to drain, so menstruation is often accompanied by heavy discharge and severe pain.
- Some patients complain of periodic pain in the sacrum and lower abdomen. Severe discomfort often occurs during sexual intercourse.
- Symptoms can also include heavy vaginal discharge, which, again, is associated with the accumulation of fluids in the uterine cavity.
- Sometimes the uterus puts pressure on the rectum, which leads to the development of chronic constipation, which does not disappear even with a change in diet.
- If the uterus puts pressure on the bladder, then patients note an increased urge to urinate.
Don’t forget about the symptoms of concomitant diseases (fibroids, endometriosis) - these include heavy and irregular periods, pain and heaviness in the abdomen. If there is any deterioration, you should definitely consult a doctor.
Diagnostics
Unfortunately, retroposition can be the main cause of spontaneous abortion in the early stages. This is due to a disruption in the flow of blood to the uterus due to its backward bending. The organ itself changes its location and can even extend beyond the pelvis, which provokes a miscarriage.
A doctor can diagnose retroposition during a simple examination. To do this, he inserts two fingers of one hand into the vaginal area, and with the second he probes the lower abdomen. With the help of such palpation, the correct position of the uterus can be determined. If the doctor diagnoses retroposition, that is, a posterior deviation, then an additional ultrasound examination of the pelvic organs will be required, thanks to which it is possible to accurately determine how much the body and its neck have deviated from the normal position.
In this case, the doctor may detect a slight displacement of the uterus towards the rectum due to inflammatory processes in the appendages or the fixation of a fertilized egg outside the body of the uterus. In such a situation, it is necessary to treat the root cause of the organ deviation.
Features of the pathology
The normal position of the uterus is anteflexio and anteversio. According to anatomical rules, the organ should be located in the center of the pelvis between the rectum and the bladder. The body of the uterus is tilted forward, forming an anteriorly open angle with the cervix (anteflexio) and vagina (anteversio). At the same time, it is physiologically mobile, and the position can change as the bladder or rectum fills.
The “correct” position is ensured by:
- muscles and ligaments of the pelvic floor;
- abdominal muscles;
- influence of surrounding organs.
If retroflexion is detected, this means that the body of the uterus deviates unnaturally towards the spine. The angle with the neck is open posteriorly. The pathology negatively affects the condition of the pelvic organs: the uterus puts pressure on the rectum and disrupts its functioning.
Under unfavorable conditions, uterine retroflexion can result in prolapse or loss of the internal genital organs.
In most cases, retroflexio is an obstacle to conception or successful pregnancy.