Causes of infantilism
There are the following degrees of underdevelopment of the uterus: - rudimentary uterus; - infantile uterus; - hypoplastic uterus.
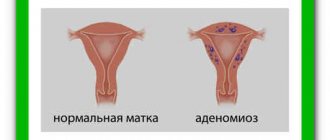
Uterine infantilism, otherwise uterine hypoplasia, is an underdevelopment of the female reproductive system and the centers that regulate its functions. In general, women who have a delicate appearance, that is, small stature, thin, are prone to infantilism of the uterus. In addition, there is a high probability of developing uterine infantilism in those girls who abuse diets in adolescence. This disease is caused by diseases such as measles, rubella, rheumatism, as well as surgery on the ovaries.
Sure symptoms of uterine infantilism are scanty menstruation or no menstruation at all, pain in the premenstrual period and during menstruation, underdevelopment of the labia majora and minora. This disease occurs when the chain “hypothalamus – pituitary gland – ovaries – uterus” is disrupted. The cause of uterine infantilism is often hereditary diseases, as well as serious diseases suffered in childhood.
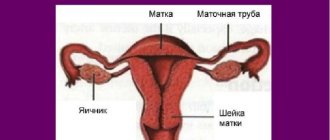
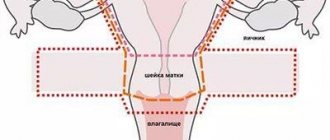
Women suffering from uterine infantilism, as a rule, have a narrow vagina, a long cervix, but a flattened body of the uterus. The angle between the body and the cervix is practically absent. The contractility of the uterus is reduced. The ovaries are located much higher than required. The fallopian tubes are thin and tortuous. In general, there is poor circulation in the genitals. The infantile uterus is the size of a 9-10 year old girl. This is fraught with problems with conception, possibly infertility.
During pregnancy with infantilism, the uterus can be in constant tone, therefore the threat of miscarriage, as well as premature birth, increases.
It is possible to diagnose uterine infantilism using ultrasound. Sometimes the initially diagnosed infantilism may not be confirmed later. It is worth knowing that there are several degrees of uterine infantilism. Sometimes the infantile uterus is called “children’s.”
Complications
The infantile uterus is fraught with infertility, habitual miscarriages, cervicitis and endometritis due to the low resistance of the reproductive sphere to pathogenic microorganisms complicated by childbirth (labor weakness, incoordination of contractions). It is also possible that ectopic pregnancy may occur due to excessive tortuosity and elongation of the oviducts, tubal obstruction, and the occurrence of early postpartum hemorrhage.
Abnormalities of the uterus
Abnormalities of the uterus
- a change in the location, shape, size, or proportions of an organ resulting from developmental disorders in the prenatal period. It is often accompanied by functional disorders of the reproductive system and can be combined with malformations of other genital organs. Infertility, miscarriage and pregnancy complications are possible. In some cases, uterine developmental anomalies are asymptomatic. The diagnosis is made taking into account complaints, medical history, results of a gynecological examination and additional research data. Therapeutic tactics are determined depending on the type and severity of the defect.
Diagnostics
A gynecologist and a doctor who performed ultrasound diagnostics can determine that a woman or girl has uterine hypoplasia. The main symptom is the discrepancy between the size and functional characteristics of the main reproductive organ from the established norm.
But with an infantile uterus, concomitant pathologies are often detected. In women, during a gynecological examination and ultrasound, you can see the following:
- underdevelopment of the labia minora, their hypoplasticity;
- inflated location of the ovaries, their underdevelopment;
- excessively narrowed vagina;
- the head of the clitoris is not covered by the labia;
- vaginal vaults are weakly expressed.
When conducting a comprehensive diagnosis, some patients find that the fallopian tubes are very narrowed and their patency is impaired. This pathology prevents the conception of a child and increases the likelihood of developing an ectopic pregnancy.
When identifying an infantile uterus, it is necessary to understand why this deviation arose and decide on treatment tactics.
General information
Anomalies of uterine development are changes in the anatomical structure of the organ due to disorders of intrauterine development. They make up 1-2% of the total number of congenital anomalies of the female genital organs. They differ significantly in the manifestations and degree of functional impairment. Often combined with malformations of the vagina and fallopian tubes. Anomalies in the development of the uterus are often asymptomatic and are detected only during an ultrasound or gynecological examination. They can provoke menstrual irregularities and cause infertility and miscarriage. Increase the likelihood of complications during pregnancy and childbirth. Treatment of abnormalities of the uterus is carried out by specialists in the field of gynecology.
Description:
Sexual or genital infantilism, detected over the age of 15 years in individuals with the female genotype, is characterized by anatomical and histological underdevelopment of the genital organs and their hypofunction. If sexual infantilism is accompanied by general infantilism (and this happens in half of all observations), then it becomes possible to establish this diagnosis at an earlier age (13-14 years).
This pathology is found in 4-16% of girls who have undergone a preventive examination.
There are two types of genital infantilism:
A) accompanied by ovarian failure,
B) not accompanied by ovarian hypofunction.
With sexual infantilism, cases of congenital refractoriness or decreased sensitivity of the ovaries to gonadotropins, and derivatives of the paramesonephric ducts to steroid hormones are not at all uncommon.
Causes of uterine development abnormalities
The uterus is formed from the middle part of the paired Müllerian canals fused together. The canals are formed in the first month of pregnancy, their fusion occurs during the second month of pregnancy. In this case, the lower parts of the canals also merge, forming the vagina, while the upper parts remain separated and are subsequently transformed into the fallopian tubes. Violation of the fusion process entails all sorts of abnormalities in the development of the uterus in the form of partial or complete duplication. It is also possible that one of the canals is underdeveloped with corresponding asymmetry of the organ. A fairly common pathology is general underdevelopment of the uterus, caused by later effects on the process of mutual regulation of the maturing endocrine and reproductive systems of the fetus.
Diagnosis of a child's uterus
Diagnosis of a child's uterus or infantilism includes a full gynecological examination, a blood test for the level of female hormones - estradiol, testosterone, progesterone; as well as thyroid hormones.
During a visual examination, a specialist diagnoses:
- Insufficient hair growth of the labia;
- Physiologically small labia;
- Protruding glans of the clitoris;
- Narrow vagina.
The physiological dimensions of the uterus are confirmed by ultrasound and x-ray examination.
Types and symptoms of uterine abnormalities
Agenesis
(complete absence of the uterus) is a rare pathology and is mainly diagnosed during the autopsy of non-viable fetuses with multiple birth defects.
Unicornuate uterus
is formed when the growth of one Müllerian duct stops or slows down and the other develops normally. It accounts for approximately 13% of the total number of uterine developmental anomalies caused by impaired development of the Müllerian ducts. In almost half of the cases it is combined with congenital defects of the urinary system. There are four main variants of this anomaly of uterine development: without a rudimentary horn; with a horn without a cavity; with a horn, the cavity of which communicates with the uterine cavity; with a horn having an isolated cavity.
Usually accompanied by primary algomenorrhea. Amenorrhea or uterine bleeding may occur. Some patients with this anomaly of uterine development complain of pain during intercourse. Some patients experience infertility. In other women, pregnancy is possible, but the outcome of gestation depends on the size of the uterus. According to statistics, in half of cases pregnancy ends in spontaneous abortion.
Premature birth is observed in 15% of patients with this anomaly of uterine development. Fetal survival rate is approximately 40%. Intrauterine growth retardation and malpresentation are often diagnosed. Emergency conditions with a one-horned uterus can occur when blood accumulates in the horn, which does not communicate with the uterine cavity. Another danger of this anomaly of uterine development is pregnancy in a rudimentary horn. Due to the small size of the horn, such a pregnancy ends with uterine rupture and massive bleeding.
To clarify the characteristics of the abnormal development of the uterus, invasive studies are used - simultaneous hysteroscopy and laparoscopy, which make it possible to assess the shape, volume and condition of the internal cavity of the uterus, determine the presence of a non-communicating horn, identify concomitant pathology of the fallopian tubes and other disorders. Non-traumatic MRI and high-resolution ultrasound are becoming a modern alternative to invasive examination for this anomaly of uterine development.
Bicornuate uterus
is formed by incomplete fusion of the middle part of the Müllerian ducts. It has two cavities and one neck, less often two necks, connecting to one normal vagina or to a vagina separated by a partial septum. In 20% of cases of uterine anomalies, a complete bicornuate uterus is detected - an organ with two separate cavities. An incomplete bicornuate uterus resembles a symbolic image of a heart, has a common cavity and a modified bottom, separated by a more or less pronounced protrusion.
Saddle uterus
makes up 23% of the total number of developmental anomalies of the uterus; it is an organ with a saddle-shaped depression in the fundus. It can be separated by a complete or partial intrauterine septum. It is often asymptomatic. Some patients experience a normal pregnancy and successful delivery. In other cases, with this anomaly of uterine development, miscarriage, breech presentation of the fetus, pathology of the placenta, premature birth, weak or discoordinated labor are observed. The diagnosis of uterine anomaly is established on the basis of ultrasound, hysteroscopy, MRI and other instrumental studies.
Duplication of the uterus and vagina
- a case of the most striking duplication of the female genital organs. A more common variant of this anomaly of uterine development is simultaneous duplication of the uterus and vagina; less often, two uteruses are detected with a common vagina. The organs are usually more or less closely in contact with each other or partially fused, but cases of uteruses separated by the bladder have been described. The degree of maturity of organs with this anomaly of uterine development can vary significantly - from two equally mature uteruses and vaginas on both sides to extremely uneven development (a full pair of organs on one side and rudimentary ones on the other). With sufficient development of both pairs of organs, menstruation and pregnancy can occur in both one and the other uterus. If there are two vaginas, the pathology is preliminarily diagnosed at the stage of a gynecological examination. To clarify the diagnosis, ultrasound, hysteroscopy and other studies are prescribed.
Pregnancy with an infantile uterus
The prognosis for a slight deviation in the size of the organ from the norm (children's or teenage uterus) is favorable, especially after hormonal and corrective treatment. It is possible to achieve pregnancy on your own and carry it safely to term under medical supervision. The presence of a rudimentary uterus excludes the independent possibility of becoming pregnant; in this case, they resort to assisted reproductive technologies (surrogacy).
Prevention of the disease consists of eliminating unfavorable factors that negatively affect the formation of the female reproductive system. It is important to provide the girl with adequate nutrition, avoid strict diets, promptly treat and prevent the occurrence of infectious diseases, and reduce the number of traumatic and stressful situations.
Sozinova Anna Vladimirovna, obstetrician-gynecologist
3, total, today
( 56 votes, average: 4.38 out of 5)
Synechia: types, causes, symptoms and general principles of treatment
Uterine prolapse: symptoms and treatment
Related Posts
Treatment of uterine abnormalities
The tactics for treating uterine anomalies are determined by the gynecologist individually, taking into account the type and severity of the anomaly, the age and condition of the patient’s body, her desire to have children and other factors. Indications for emergency surgical intervention are pregnancy in the rudimentary uterine horn, accumulation of menstrual blood in the atretic vagina or in the isolated cavity of the uterine horn.
Indications for elective surgery for abnormalities in the development of the uterus are usually disorders of reproductive function (miscarriage, infertility). With a one-horned uterus, the rudimentary horn is removed, followed by fixation of the fallopian tube to the corner of the uterus. With a double and bicornuate uterus, the walls of the organ are dissected along the internal rib and then connected, forming a single cavity. Surgical intervention is usually performed through an open approach (Strassmann procedure), less often using hysteroscopy. For a saddle uterus, metroplasty is usually performed through natural channels during hysteroscopy.
Prognosis for abnormal development of the uterus
The prognosis is determined by the type of pathology, the degree of maturity of the uterus and the volume of the organ cavity. There is an increased risk of spontaneous abortion, miscarriage and premature birth. Management of pregnancy with abnormalities of the uterus includes the prevention of miscarriage, bleeding and isthmic-cervical insufficiency. If there is a threat of termination of pregnancy after 26 weeks, a caesarean section is indicated.
In other cases, the tactics of obstetric care for anomalies of the uterus are determined taking into account the position and condition of the fetus, the presence of endocrine and somatic diseases in the mother and other factors. Surgical interventions can increase the likelihood of a successful pregnancy from 30-40 to 90 percent or more. Women with abnormal development of the uterus, who previously complained of painful menstruation and disturbances in their general condition during menstruation, note the disappearance of pain and improvement in well-being.
In case of gross anomalies in the development of the uterus and miscarriage, a woman can resort to the use of surrogacy. Artificial insemination using the ICSI, IMSI or PIXI method is carried out using the patient’s own egg and the husband’s sperm (or donor sperm). Then the embryos are cultured. After selection and full examination of the surrogate mother, embryos are implanted into her uterus.
Infantility (hypoplasia) of the uterus
Anomalies of the uterus and vagina are observed in 4.3-6.7% of all women of childbearing age. They cause infertility in every eighth case, and in 12.6-18.2% they cause recurrent miscarriage, placental abruption, abnormal fetal position and other complications.
One of the most common anomalies of the uterus is its infantility (also called hypoplasia) - a defect associated with the small size of the main reproductive organ.
With a slight decrease in the size of the uterus, the anomaly does not manifest itself with any symptoms, but a significant degree of hypoplasia can be suspected even in adolescence - by the late appearance and extreme pain of menstruation.
Signs of an infantile uterus
If the teenage uterus does not manifest itself in any way, and a woman can only find out about this anomaly during pregnancy or even after childbirth, then more severe degrees of hypoplasia have their own symptoms:
- late onset of menstruation (after 16 years);
- painful periods;
- irregular periods;
- decreased libido;
- difficulty achieving orgasm;
- infertility or recurrent miscarriage.
Uterine hypoplasia is often combined with other gynecological pathologies: mainly endometriosis, frequent inflammation of the vagina and cervix. They can mask the manifestations of uterine hypoplasia.
Often, girls with uterine infantility have a characteristic appearance: they are short, thin, with very small breasts and a narrow pelvis. Upon examination, the gynecologist sees a small amount of pubic hair, underdeveloped labia and a small vagina.
Preventive measures and forecasts
When diagnosing the fertile type of uterine infantility, the possibility of conception is excluded. In this case, pregnancy is possible only with the use of assisted reproductive technologies (ART). If the generative function of the gonads is preserved, in vitro fertilization (IVF) is used using oocytes ready for insemination.
The course of pregnancy in patients with severe endometrial hypoplasia is associated with a high probability of spontaneous abortion and complicated delivery.
In women with miscarriage syndrome, intracytoplasmic sperm injection (ICSI) is performed as part of surrogacy. With minor changes in the structure of the reproductive organ and normal secretion of steroid hormones by the ovaries, the chances of conception and successful pregnancy increase by 45-50%.
Conclusion
Full development of a woman’s reproductive system is possible only if unfavorable endogenous and exogenous factors are eliminated during puberty.
Prevention of pathology consists of timely treatment of infectious diseases (tonsillitis, pharyngitis, herpes, meningitis), prevention of stressful situations and proper nutrition.
Preventive measures help prevent the development of hypovitaminosis and endocrine disorders, which increase the likelihood of genital infantilism.
Source: https://klinika.k31.ru/napravleniya/vazhno-znat/infantilnost-gipoplaziya-matki/
Uterine infantilism
Author of the article
Zakharchenko Ekaterina Olegovna
Congenital malformations of the genital organs of varying degrees occur in approximately 5% of sexually mature women. Abnormalities of the uterus are most often expressed in the form of its underdevelopment. This pathology is called uterine infantilism or hyperplasia. Its dimensions correspond to the uterus of a pre-teen girl. Significant underdevelopment of the reproductive organ causes infertility. But the less pronounced uterine infantilism is, the greater the woman’s chances of conceiving and carrying a child and the lower the likelihood of developing complications during pregnancy. The degree of underdevelopment of the uterus directly affects the production of sex hormones, which in turn determine the formation of secondary sexual characteristics and are responsible for sexual desire and reproductive functions.
Infantilism in gynecology
That is, an adult woman has a uterus, the size and functionality of which corresponds to the uterus of a small or teenage girl.
This condition can present certain difficulties in treatment, as well as in conceiving and carrying a pregnancy.
Since with an infantile uterus there is usually also underdevelopment of the ovaries, the level of sex hormones in a woman’s body is significantly reduced.
How does underdevelopment of the genital organs manifest?
In medicine, infantilism is usually divided into two types. Experts define general infantilism (a condition in which all human systems and organs are delayed in development) and partial infantilism (there is a lag in the development of one of the systems, for example, underdevelopment of the reproductive system).
Source: https://o-kak.ru/infantilizm-v-ginekologii/
Causes of pathology
The formation of the internal genital organs, including the uterus, begins in utero. In a newborn girl, this organ is already fully formed, but is small in size. Until the age of 9-10 years, the uterus in girls grows very slowly, but after this age the growth accelerates sharply. By the age of 14, with proper sexual development, the organ increases to the physiological norm, reaching a total length of 5-6 cm, and the cervix is 3-4 cm. Depending on the constitution and height of the girl herself, the size of her uterus at puberty may differ slightly from the specified norm , which is not considered a pathology and does not affect fertility. If the organ remains in an infantile state, then this could happen for several reasons.
Firstly, the intrauterine factor of underdevelopment is considered. This situation could have occurred due to a gene failure or the occurrence of severe intoxication of the mother’s body during pregnancy.
Secondly, the harmful effects on the girl’s body in childhood, which led to the anomaly, are considered. The following factors could be the reason:
- viral damage to the hypothalamus, pituitary gland, ovaries;
- tumors of the endocrine parts of the brain;
- all types of intoxication;
- lack of nutrition;
- severe emotional and physical stress;
- frequent sore throats, bronchitis, ARVI;
- previous surgical operations on the ovaries.
Causes of uterine underdevelopment
The pathology can be congenital, which is caused by triggers that acted on the mother’s body when carrying a girl. Acquired uterine hypoplasia cannot be excluded if the organ's growth retardation occurs for reasons affecting the development of the reproductive system in childhood and puberty. Congenital factors include:
- chromosomal aberrations, genetic diseases;
- the impact of occupational hazards (working with poisons, toxic substances, under radiation conditions) on the body during pregnancy;
- smoking, drug addiction, alcoholism;
- placental insufficiency leading to intrauterine growth retardation;
- acute infectious diseases during gestation;
- taking a number of medications.
Hypoplasia of the uterus is provoked by the following factors in childhood:
- toxic, infectious damage to the pituitary gland, hypothalamus in childhood, or their trauma, which leads to a disorder in the functioning of the hypothalamic-pituitary system;
- tumors of anatomical structures of the brain;
- complicated childhood infections (measles, mumps and others);
- chronic general diseases (liver and kidney pathology, heart defects, diseases of the bronchopulmonary system);
- endocrine diseases (hypothyroidism, increased prolactin, diabetes mellitus);
- autoimmune pathology (lupus, autoimmune thyroiditis, rheumatoid arthritis);
- gynecological pathology (ovarian dysfunction, previous surgical interventions on them, underdevelopment of the gonads, cysts, tumors of the gonads);
- lack of vitamins);
- alcohol, nicotine, drug addiction;
- excessive physical and mental stress, chronic stress, nervous disorders (neuroses, depression);
- weight deficiency (lack of nutrition, debilitating diets, starvation, anorexia);
- frequent ARVI;
- heredity.
note
Parents whose close relatives suffered from uterine infantilism should pay careful attention to the formation of the child’s body in childhood and adolescence, and, if possible, reduce the number of factors that provoke underdevelopment of the uterus. The presence of pathology in the family increases the risk of developing a child's uterus several times.
Degrees
There are three degrees of hyperplasia (infancy) of the uterus. Classification occurs according to the size of the organ and the ratio of the size of the uterine body to the cervix:
In the embryonic stage, the uterine cavity is extremely small, and the organ itself is mainly formed by the cervix and has a total length of up to 3 cm.
The length of the organ is from 3 to 5.5 cm and the ratio of the cavity to the cervix is 1:3 - signs of a child’s uterus. The teenage uterus has normal proportions, but is reduced in size compared to the mature organ, with a total length of 5.5-7 cm.
Types of pathology
During the examination and ultrasound, the gynecologist determines the degree of infantilism. It will depend on the size of the reproductive organ.
Infantile uterus of the 1st degree is diagnosed mainly in those girls who developed this pathology during the prenatal period. The length of the uterus together with the cervix does not exceed 3 cm, while the cervix is usually elongated. With such a degree of infantilism, the internal cavity of the main reproductive organ is practically not formed. This condition is extremely rare.
Infantilism of the uterus of the 2nd degree is spoken of in cases where the size of this organ is within 3-5 cm. Doctors diagnose that a woman has a child’s uterus.
With grade 3 infantilism, the length of the main reproductive organ varies between 5-7 cm, including the neck. It is not difficult to normalize the condition if you choose the right treatment tactics. With this degree of infantilism they say that the uterus is teenage. Many women with a stage 3 infantile uterus can become pregnant and carry a baby to term on their own.
Normally, in nulliparous women, the length of the reproductive organ should be at least 7 cm; in women who have given birth, it reaches 8 cm. In this case, the length of the cervix can be 2.5-3 cm.
Signs and symptoms
The presence of uterine anomalies, in particular infantilism, may be indicated by such signs as:
- delay in the onset of first menstruation,
- manifestations of dysmenorrhea,
- irregularity of the menstrual cycle,
- lack of sexual desire,
- rare orgasms or anorgasmia,
- difficulty conceiving.
Mild pathology, in which it is classified as third degree, tends to be asymptomatic. A girl with this diagnosis is capable of conceiving if other pathologies do not interfere with this. Her uterus increases to normal size after childbirth.
More pronounced degrees of hyperplasia have pathological symptoms and even determine the appearance of a woman. Underdevelopment of the organ of the second and first degrees causes a lack of sex hormones. As a result, women with this pathology are usually short in stature, with a narrow chest and small breasts; have scant hair on the pubis and under the arms.
Symptoms and manifestations of infantilism
Women of short stature with an elegant and thin skeletal system, a narrow pelvis, and narrow shoulders may suffer from genital sexual infantilism. Also, patients experience a late onset of menstruation, the discharge is characterized by scarcity, pain and irregularity, with the presence of headaches, weakness, fainting and nausea.
Disproportion of the external genital organs (predominance in size of the small lips over the large lips), enlargement of the clitoris, and openness of the gap are also diagnosed. The size of the uterus is seriously inferior to normal; a forward bend is visible. It is the size of the uterus that underlies the determination of the degree of infantilism.
In the first degree of infantilism, the uterus has fetal (rudimentary) dimensions. But doctors rarely encounter such an anomaly, and they cannot help the patient in any way; with genital infantilism of the second degree, the uterus is three centimeters in size - this is the norm for a ten-year-old girl.
High location of the ovaries, the presence of long and convoluted tubes. In the third degree of infantilism, the uterus has a length of 6-7 cm. This degree is the easiest; it is possible for the hypoplastic uterus to reach normal sizes. Sexual life and pregnancy have an influence on this process.
Treatment of infertility with a small uterus
In order to normalize hormonal levels and compensate for missing hormones, patients with this diagnosis are prescribed hormone replacement therapy. Unfortunately, in advanced stages, treatment does not guarantee restoration of reproductive functions. The treatment strategy and prognosis can only be given by the attending physician after examination. Patients are prescribed hormonal medications, a special diet, massage, and physical therapy.
To overcome infertility in women with a small uterus, assisted reproductive technologies, in particular IVF, are successfully used. In case of critical organ failure, but preservation of ovarian function, a surrogate mother can carry an artificially fertilized maternal egg.
Sources:
https://www.kakprosto.ru/kak-877084-chto-takoe-infantilizm-matki https://www.krasotaimedicina.ru/diseases/zabolevanija_gynaecology/uterine-abnormalities https://krmed.ru/articles/infantilizm_matki. html
Treatment
Patients must understand that an infantile uterus is not a death sentence. Only in the first degree it is not possible to restore the normal size of the uterus. Hormone therapy allows you to increase the size of the organ. Gynecologists also recommend:
- review the diet; the menu should contain a higher content of proteins and foods rich in phytoestrogens;
- periodically carry out vitamin therapy, consuming B vitamins, calcium and vitamin D supplements;
- perform special exercises aimed at increasing blood circulation in the pelvis;
- undergo physiotherapy courses (electrophoresis, UHF and magnetic therapy, laser procedures).
Sometimes, even with normal physical condition, a woman cannot become pregnant. In severe cases, surrogacy is used. They also resort to the help of professional psychologists, because for many, infantilism leads to the appearance of a lot of complexes, including a feeling of inferiority. Women with infantilism must plan pregnancy and bear a child under the supervision of a doctor.