A placental polyp is a neoplasm inside the uterus, which was formed from placental tissue that did not leave the organ cavity for one reason or another. This happens after a difficult birth, miscarriage or abortion. Polyps have the form of a small rounded and elongated growth located on the surface of the uterine mucosa.
By nature, this neoplasm is benign, but without proper treatment it can be accompanied by severe complications. A polyp from the placental tissue must be removed surgically, since it is not able to resolve on its own.
What it is?
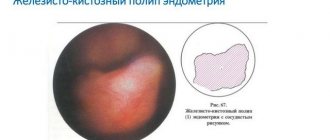
Polyps are fairly common abnormal formations that occur in any part of the body where there is mucous membrane. They are formed from cells of surrounding tissues. So, in our case today, the material for construction is the remains of the placenta, which for some reason remained in the uterine cavity. Single polyps can reach large sizes, which complicates the normal functioning of the organ in which they are located. The uterine formation grows up to 8-10 cm. Externally, it is a process, sometimes long and thin with a lump of tissue at the end, or a tubercle with a wide base. The surface often matches the color of the surrounding mucosa, but sometimes they are brown, red, or yellowish. There are also cases of polyposis, when there are many formations. This type of pathology is no less dangerous. The mucous membrane covered with growths cannot function normally.
Interesting fact! Polyps even grow in the nose and ears, as well as in the intestines, stomach, bladder, throat and other places.
What is medical abortion and what are the complications after the procedure?
Abortion is the termination of pregnancy, either due to external intervention or due to natural causes. The procedure is classified as early abortion if the pregnancy is less than 12 weeks, and late abortion if the pregnancy is more than 12 weeks.
If the pregnancy is less than 7 weeks, a medical abortion is performed using a special hormonal drug. Although the procedure is performed at a short stage of pregnancy and is considered uncomplicated, the risk of complications after an abortion remains high.
Placental polyps are a fairly common complication of medical abortion.
What are placental polyps and their symptoms?
The placenta consists of many “lobules” (lobular structure) that are well supplied with blood. Some placental tissue may be retained in the uterine cavity after an abortion, spontaneous miscarriage, or childbirth. Parts of the placenta that remain in the uterus can form a polyp. From the very beginning, the remainder of the placental tissue has a loose structure, but then this area grows with connective tissue cords, becomes denser and is firmly connected to the wall of the uterus. The formation can be located on a stalk or attached in a wide layer to the wall of the uterus.
Most often, polyps manifest themselves in the form of uterine bleeding 2 weeks after a medical abortion. A fully formed polyp may manifest itself in the form of bleeding at a later date - 4-5 weeks after the intervention. The woman will notice spotting from the genitals. Usually the patient does not experience any pain, but this depends on the size of the formation and the degree of capture of the uterine wall. A large polyp in the uterus can bleed very heavily, which can cause anemia in a woman.
Bleeding may stop and then resume again, exhausting the body.
If, after a long period of time after intrauterine exposure, intense pain in the lower abdomen appears, then this is a very bad sign, with the appearance of which you need to run to your doctor. Because in addition to severe bleeding, formations are also dangerous due to some complications:
- Polyps in the uterus can become infected over time and become a source of acute septic conditions and chronic infections
- There may be concomitant dysfunction of the ovaries with subsequent infertility.
Why do placental formations appear in the uterus?
Factors that caused polyps to form:
- Doctors paid insufficient attention to the patient after childbirth;
- Incomplete curettage during abortion;
- Leaving parts of the placenta during cesarean section;
- Antenatal death of a child;
- Miscarriage;
- Abortion by any method in which the uterine cavity was not completely cleaned.
The question remains: why the fragment is not rejected or is not in a calm state, but begins to grow. The fact is that the placenta is nourished by many blood vessels, so having a supply, the cells begin to divide, leading to an increase in formation. Blood adheres to the surface and becomes overgrown with connective tissue.
Interesting fact! Sometimes a polyp is an isolated additional piece of placenta, which is covered with a membrane and has its own blood supply. This is an anomaly of intrauterine development.
Causes of placental polyp formation and methods of its treatment
A placental polyp is a neoplasm inside the uterus, which was formed from placental tissue that did not leave the organ cavity for one reason or another. This happens after a difficult birth, miscarriage or abortion. Polyps have the form of a small rounded and elongated growth located on the surface of the uterine mucosa.
By nature, this neoplasm is benign, but without proper treatment it can be accompanied by severe complications. A polyp from the placental tissue must be removed surgically, since it is not able to resolve on its own.
Other types of polyps as a result of pregnancy
In addition to the placental one, there are 2 more types of growths, the formation of which is directly related to bearing a child:
- Chorionic polyps are formations from cells of the villous chorion - the fetal membrane at the site of attachment to the wall of the uterus. This layer is one of the first to form and initially covers the fertilized egg completely to ensure connection when approaching the walls of the organ. In the place where the junction with the uterus occurs, the villous chorion provides attachment, nutrition and excretion. Then, in this area, the placenta itself appears from the chorion and other components. This type of formation forms after an abortion or miscarriage in early pregnancy.
- Decidual polyps are formations from cells of the lining of the uterus, which forms during pregnancy between the wall and the fetal bladder. This is a special pathology that does not require any treatment. Polyps are a consequence of hormonal changes during pregnancy. They provoke the growth of this membrane, which is sometimes excessive, which is why polyps appear. Decidua leave the uterus during childbirth.
Diagnostics and treatment at ON CLINIC
To maintain health and identify the disease at the earliest stage of development, even a healthy woman needs to undergo regular gynecological examinations - at least once a year.
.
If any alarming symptoms appear that indicate disorders in the reproductive system, you cannot hesitate - you should immediately seek help from specialists.
Over many years of practical experience, the ON CLINIC medical center has acquired a reputation as an advanced clinic with a progressive diagnostic base and an excellent team of professionals of the highest level. In their work, our gynecologists use proven and effective methods for diagnosing and treating any female diseases, including neoplasms of various types.
Ultrasound diagnostics with volumetric scanning allows you to accurately determine the presence and localization of the formation, and the layer-by-layer laser removal method allows you to perform surgery with minimal damage to healthy tissue, which promotes rapid regeneration and recovery.
Treatment of placental polyps is carried out in our center with minimal discomfort for the patient. Our specialists are not only highly qualified gynecologists, but also trusted doctors - your advisors on the most delicate topics related to women's health.
ON THE CLINIC: trust the professionals!
Source: www.OnClinic.ru
Clinical picture
The growth does not form immediately, so the symptoms begin to bother the patient 3-5 weeks after the end of pregnancy, in one way or another. Signs of polyps from the placenta are:
- First, spotting appears;
- They intensify;
- Bleeding begins;
- The patient is weak, pale, and dizzy;
- Pain in the lower abdomen may be present.
Carefully! If you notice an unpleasant odor, your body temperature rises, and symptoms of fever and intoxication occur, this indicates a serious infection. Lack of medical care will lead to sepsis and death of the woman.
Diagnosis of pathology
A polyp in the uterine cavity can be identified through a combination of a number of studies:
- At the appointment, the doctor will learn about the duration and nature of the bleeding and accompanying symptoms. A patient's history of recent childbirth, abortion, or miscarriage will suggest a suspected diagnosis.
- When examined on the chair, the gynecologist sometimes sees a formation hanging through the cervix.
- An ultrasound will show the internal condition of the uterus.
- Hysteroscopy allows you to visually examine the polyp and surrounding tissues and take a fragment for histological analysis.
- A vaginal smear to detect or rule out infection.
Such symptoms may hide other complications after completion
pregnancy, so ultrasound is required. In addition, standard tests for CSR, HIV, and hepatitis will be prescribed.
If ovarian pathology is detected during diagnosis, the question of treatment before or after surgery is decided by the doctor individually for each case.
Diagnostics
Before diagnosing a placental polyp, the doctor interviews the patient and collects anamnesis. The disease can be suspected if no more than 5 to 7 weeks have passed after a medical abortion.
Then the doctor conducts the following tests:
- Gynecological examination using speculum. A painless enlarged uterus and a gaping of the uterine pharynx are detected. Sometimes a dense elastic formation can be palpated.
- Ultrasound examination of the pelvic organs. This method allows you to visualize the presence of a polyp, determine its location and size.
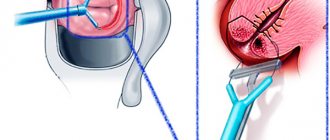
- Hysteroscopy. A special device (hysteroscope) is inserted into the uterine cavity and the integrity of the mucous membrane is examined.
- Diagnostic curettage. Mandatory after a medical abortion. The biomaterial obtained during manipulation is sent for histological examination.
- Colposcopy. Using a colposcope, the walls of the vagina and cervix are examined.
Gynecological examination is a method for diagnosing a placental polyp after a medical abortion.
It is necessary to carry out a differential diagnosis of a placental polyp after a medical abortion with a decidual polyp, an exophytic form of uterine cancer, cervical papilloma, and chorionic polyp. This disease is also differentiated from injuries to the internal genital organs, endometrial hyperplasia, and uterine fibroids.
Why are polyps in the uterus dangerous?
The appearance and development of placental formations without the necessary treatment leads to the following consequences:
- Iron deficiency anemia due to constant blood loss. As a result, the woman becomes weakened, fainting may occur, and mental and physical performance decreases.
- Inflammation of the organ mucosa, which impairs its functionality and can cause endometriosis, a dangerous disease. If all this is not treated, the result will be uterine cancer.
- Pathologies of the ovaries, which leads to endocrine disorders, and, consequently, weight gain, changes in the cycle and other troubles.
- Infertility. The altered mucous membrane is unable to adhere to the fertilized egg or rejects it in the first weeks. Ovarian dysfunction leads to follicles not maturing, which means pregnancy is impossible.
- Sepsis occurs as a result of the death of polyp cells, or when an infection enters the damaged formation. Pathogenic microorganisms quickly spread through numerous vessels.
- Death due to infection or severe bleeding. When a woman suffers from constant blood loss, she weakens and becomes vulnerable to any kind of infection. Therefore, these 2 factors can play together.
The patient's reproductive system changes greatly during pregnancy, even if it lasts only a few weeks. After childbirth, the body is weakened by the process itself, and a miscarriage or abortion is a sharp change and stress. Therefore, it is so important to follow your doctor’s recommendations and monitor your condition.
What is a placental polyp and can it come out on its own?
A growth that forms from placental tissue is called a placental polyp. The pathology is accompanied by menstrual cycle disorders and bleeding. If treatment is not treated in a timely manner or treatment is refused, the tumor is complicated by consequences and disrupts the functioning of the reproductive system. You can prevent this, the main thing is to contact a medical facility at the first alarming symptoms.
Types of placental polyps
The trigger for the formation of a growth is considered to be pregnancy, with different outcomes. Formations are:
- Decidual. A tumor formed from the endometrial lining. A polyp appears during pregnancy between the baby's place and the wall. This pathology does not require therapy. During childbirth, the polyp will come out with the baby.
- Chorionic. Formed from cells of the villous chorion. The occurrence of the disease is caused by miscarriages and abortions.
There are the following types of placental polyp: with preserved villi, destructive ones - they remain when the contents of the uterus are not completely removed during labor, and isolated lobules (a complication of cesarean section).
Factors influencing the formation of polyps:
- heredity;
- formations in the uterus, cervical canal.
After childbirth
Tumor formation is provoked by retention of placental tissue in the uterus. The more of them remain, the faster the polyp grows. This is due to a violation of the separation of the placenta from the uterine wall, or the presence of other anomalies of the child’s place.
It is possible to prevent the occurrence of a placental polyp after childbirth. To do this, it is recommended to examine the uterus after the birth of the child, and if the placenta is not completely separated, remove it manually. If you notice pain in the lower abdomen or bleeding, you should consult a doctor.
After a medical abortion
Placental growth is caused by incomplete removal of the membranes of the fertilized egg, which is why villi are retained in the uterine cavity. Against the background of incomplete curettage, infection, and excessive accumulation of blood, the formation of a polyp is possible.
The appearance of a polyp is also caused by:
- injuries;
- hormonal imbalance.
During pregnancy
During pregnancy, due to increased production of progesterone and other female hormones, excessive growth of the cervical canal mucosa and the appearance of a decidual polyp are possible. Such growths are not dangerous and do not require therapy.
Complications of placental polyposis
The disease requires adequate treatment. If you do not undergo therapy on time, the growth will lead to the following consequences:
- The occurrence of anemia due to severe blood loss. Accompanied by a deterioration in general condition, fainting, decreased mental and physical activity.
- Endometriosis. Untimely treatment of the pathology is fraught with uterine cancer.
- Ovarian diseases, endocrine disorders, weight gain, cycle disorders.
- Infertility. Due to changes in the mucosa, the egg cannot attach. Against the background of ovarian dysfunction, the follicle does not mature, which means that pregnancy is impossible.
- Sepsis due to cell death or infection entering the injured polyp.
- Death due to large-scale bleeding or infection.
Treatment tactics
A guaranteed method of therapy is surgery to remove the placental polyp. Only a decidual neoplasm can go away on its own. All other types require surgery. There is a whole range of measures to help eliminate symptoms and stop the development of the tumor.
The treatment regimen and the need to take medications are determined by the doctor after a thorough diagnosis.
Drug treatment is prescribed to alleviate the woman’s condition, and also as preparation for surgery.
Table 1 - Drug correction
| Drug group | Effect |
| Vitamin and mineral complexes, dietary supplements | Increases the body's protective properties |
| Antibiotics | Eliminate or prevent an infectious process |
| Antispasmodics | Minimize pain |
| Products with iron | Fighting anemic syndrome |
| Anti-inflammatory | Reduce inflammation |
If the growth is small in size, is not accompanied by unpleasant symptoms, and does not lead to a worsening of the condition, the doctor takes a wait-and-see approach.
The main method of treating tumors of any location is surgery. There are many ways to excise a polyp.
Table 2 - Surgical treatment
| Methodology | Description |
| Scraping | Standard method for removing multiple growths. The procedure is traumatic and is performed like an abortion. |
| Vacuum aspiration | It involves inserting a negative pressure aspirator into the uterine cavity. This allows you to remove the tumor along with the upper layer of the uterus, which is effective for small tumors |
| Polypectomy | The placental growth is excised, and the area where it is localized is sealed with an electrode |
| Laser removal | The safest method. The mucous membrane heals in a couple of days after surgery, there are no scars or scars left on it |
| Electrocoagulation | Consists of cauterizing the formation, its body and legs |
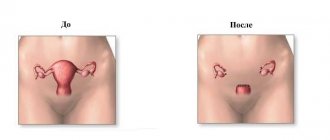
| Resection | When a placental polyp transforms into a cancerous tumor (and its severe growth), an operation is performed to remove a section of the uterus or the entire organ |
After surgery, the growth is sent to the laboratory for histological examination and to rule out the risk of cancer. To restore the body after surgery, the following is recommended:
- Analgesics and NSAIDs (non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs) - relieve pain, minimize swelling and inflammation.
- Antibiotics - to prevent secondary infection.
- Vitamins - strengthen the immune system, normalize metabolism.
- Blood-stopping medications.
The first few days after surgery, bloody spotting and pain of varying intensity are noted. In order for the recovery period to pass without complications, it is recommended to exclude sexual activity, hypothermia and overheating, taking a bath, and drinking alcoholic beverages. You can't play sports yet. You can return to your normal life in a month.
Monitoring your well-being, discharge, temperature, as well as visiting a doctor and maintaining intimate hygiene - all this contributes to a successful recovery.
Prevention measures
Not a single girl is immune from the appearance of a polyp from the placenta. Pathology can be prevented; for this it is recommended:
- Monitor the condition of the uterus after abortion and labor.
- Take medications to contract the uterus (remove the remaining placenta).
- Only contact a certified specialist for an abortion.
- Avoid self-termination of pregnancy.
conclusions
The formation of a placental tumor almost does not depend on the girl. Pathology can be detected in time through regular examinations, including ultrasound.
The symptoms of the disease can be so pronounced that it is difficult not to notice them. If there is bleeding, aching pain in the abdomen, or fever, you should visit a doctor.
Timely detection of a placental polyp and adequate treatment is the key to preserving women’s health and reproductive functions.
Source: https://ginekologius.ru/placentarnyj-polip
Treatment
It is impossible to force placental fragments or polyps to resolve with drug therapy. However, drugs are still used:
- Antibiotics to stop the infectious process;
- Injections to relax the uterus, as a result of which the formation may fall off;
- Anti-inflammatory drugs;
- Medicines to reduce bleeding when needed.
Subsequently, if the polyp is not rejected, you need to have surgery. There are several removal methods, each with its own pros and cons.
Methods for eliminating polyps from the uterine cavity:
- Curettage or curettage. A traumatic method that is widely used in public medical institutions. This is dangerous not only for the uterus, weakened by previous events (abortion, childbirth or miscarriage), but also for the organ of a completely healthy woman.
- Vacuum aspiration is a more gentle removal method available in any clinic. The equipment used for abortions is used to clean the uterus. The operation is not always effective. A polyp firmly attached to the wall may remain in place. But if everything went well, the uterus remains intact and will recover within a month.
- Classic polypectomy through a hysteroscope. The formation is cut off, and its location is sealed with an electrode. As a result, a small scar is formed, which will interfere with reproductive function in the future.
- Laser polyp removal is the safest method. The surface of the mucous membrane heals in a matter of days without scars, so the method is suitable for women who are planning a pregnancy in the future. Radio wave equipment has the same advantages.
- The doctor can remove a polyp that is located close to the opening of the cervix using a forceps - a tool similar to scissors with ends in the form of forceps. It's fast and free, however, it's not always possible.
The most modern and effective methods are polypectomy through a hysteroscope, laser and radiosurgery. Equipment for such operations is available either in large government institutions, which are difficult to get into, or in private clinics, where it will cost 5-15 thousand rubles, and sometimes more.
Attention! Uterine curettage and vacuum have a high risk of relapse; more than half of patients return to the doctor after a few months with a new polyp.
The procedure is often performed without anesthesia, but, according to women, the sensations are not pleasant. Therefore, if in doubt, it is better to discuss the issue of pain relief in advance. Anesthesia can also be done in a regular hospital. All manipulations are available on an outpatient basis, so a long stay on sick leave is not necessary.
The removed lesion is sent for histology to study the nature of the tissue. It happens that microscopic analysis reveals cancer cells.
What is a placental polyp after a medical abortion, can it be cured without surgery?
A placental polyp after a medical abortion is formed from the remnants of the placenta remaining in the uterus. This pathology occurs in 0.9% of cases after medical termination of pregnancy. Today, there are several treatment options for such a polyp.
What is a placental polyp
This type of neoplasm is formed from placental parenchyma that is not completely removed during an abortion.
The polyp has exophytic growth, that is, it grows inward, into the uterine cavity. This neoplasm has a round shape, a wide base or a thin stalk, with which it is attached to the mucous membrane. The surface of the polyp is flat, smooth, pale pink, red or yellow.
A single location of the tumor is common. It can reach 9–12 cm. In some cases, the formation of several polyps is possible. This pathology is called polyposis. In this case, the function of the organ is disrupted, which can lead to adverse consequences.
Reasons for the formation of placental polyp
The main reasons for the appearance of a polyp after a medical abortion are:
- Incomplete removal of the placenta.
- Atony of the uterus.
- Insufficient curettage during abortion.
- Infection.
- Difficulty in the passage of blood clots from the uterine cavity.
Infection is a possible cause of placental polyp after medical abortion
The pathogenesis of polyp formation is as follows: a piece of placental tissue remaining in the uterus grows into its wall. It is then covered with blood clots, fibrous and connective tissue. The placenta is well supplied with blood, so the cells of this formation begin to actively multiply. A polyp is formed that rises above the surface of the endometrium.
Clinical manifestations
The main manifestation of a placental polyp after medical abortion is the occurrence of uterine bleeding. Its cause is the fusion of the placenta with the mucous membrane. This prevents the normal contraction of the uterus and the narrowing of blood vessels.
Bleeding does not appear immediately. In the first days after an abortion, the hormone oxytocin is still present in the woman’s blood. It is valid for 3 – 4 days. Under its influence, the vessels of the uterus spasm, the uterus actively contracts, and blood flows out.
Therefore, after any termination of pregnancy, spotting and bloody discharge is observed. Normally, they go away within a week after the abortion.
When a placental polyp forms, bleeding does not decrease over time. They can be stored for a month.
Thus, pronounced clinical symptoms appear 3–4 weeks after the manipulation. The released blood is scarlet in color, does not clot well, and does not mix with vaginal discharge.
Against the background of prolonged bleeding, the patient develops signs of anemia:
- Weakness, increased fatigue, rapid fatigue.
- Headaches, staggering when walking.
- Paleness of the skin and sclera.
- Dizziness, lightheadedness, tinnitus.
- Poor appetite.
- Irritability, difficulty concentrating.
When a secondary infection occurs, the woman’s temperature rises, nagging pain in the lower abdomen, itching and burning in the external genital area appear.
Diagnostics
Before diagnosing a placental polyp, the doctor interviews the patient and collects anamnesis. The disease can be suspected if no more than 5 to 7 weeks have passed after a medical abortion.
Then the doctor conducts the following tests:
- Gynecological examination using speculum. A painless enlarged uterus and a gaping of the uterine pharynx are detected. Sometimes a dense elastic formation can be palpated.
- Ultrasound examination of the pelvic organs. This method allows you to visualize the presence of a polyp, determine its location and size.
- Hysteroscopy. A special device (hysteroscope) is inserted into the uterine cavity and the integrity of the mucous membrane is examined.
- Diagnostic curettage. Mandatory after a medical abortion. The biomaterial obtained during manipulation is sent for histological examination.
- Colposcopy. Using a colposcope, the walls of the vagina and cervix are examined.
Gynecological examination - a method for diagnosing placental polyp after medical abortion
It is necessary to carry out differential diagnosis of placental polyp after medical abortion with decidual polyp, exophytic form of uterine cancer, cervical papilloma, chorionic polyp. This disease is also differentiated from injuries to the internal genital organs, endometrial hyperplasia, and uterine fibroids.
Methods of therapy
The main treatment method for placental polyp after medical abortion is surgery. Before the operation, possible complications are prevented and concomitant chronic diseases are treated. In the preoperative and postoperative periods, drug therapy is mandatory.
Medication
Drug treatment involves the use of the following groups of drugs:
- Antibacterial. Prescribed to reduce inflammation in the uterus.
- Iron-containing. Recommended for concomitant anemia.
- Antispasmodics. They affect the smooth muscles of the uterus and eliminate spastic manifestations.
- Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. Used to prevent inflammation and reduce pain.
If necessary, symptomatic treatment is recommended: antipyretics, painkillers or hormonal agents. When hemoglobin decreases below 60 g/l, the patient is given transfusions of blood components: plasma, red blood cells, blood replacement solutions. General strengthening medications, vitamin therapy and homeopathic medicines are also used.
Surgery
The most common methods for removing a placental polyp include:
- Scraping. It is performed under intravenous anesthesia. The manipulation lasts no more than 30 – 40 minutes. The polyp is removed mechanically.
- Electrocoagulation. A wire loop is used through which an electric current is passed. After the procedure, a small defect remains on the surface of the mucosa, which then becomes covered with a crust.
- Laser therapy. The most gentle method of treatment. After it, scars and connective tissue growth do not form. This method is suitable for treating young women of reproductive age.
- Radiosurgery. The pathological formation is affected using radioactive waves. After removal of the polyp, a fibrinous film is formed on the surface of the mucosa, under which rapid healing of the wound occurs.
- Cryodestruction or treatment of the polyp with liquid nitrogen. This manipulation must be performed carefully, trying not to touch the surrounding healthy tissue. This method of removing polyps is rarely used. It is mainly used when the tumor is localized in the cervix.
Radiosurgery is a method of treating placental polyp after medical abortion
For small polyps, they are removed or resected. In case of large or multiple tumors, the uterus is completely removed (extirpation).
Possible consequences
Possible consequences of a placental polyp are:
- Infertility.
- Chronic anemia.
- Endometritis.
- Sepsis.
- Dishormonal disorders.
- Attachment of a secondary infection.
- Chronic miscarriage.
- Development of hemorrhagic shock.
A polyp can also contribute to the development of endometriosis, ovarian pathology, or lead to death.
Prevention of pathology
The main preventive measures include:
- Adequate contraception, planning pregnancy, avoiding abortion.
- Compliance with personal hygiene rules.
- Regularly scheduled gynecological examinations.
- Compliance with all medical recommendations prescribed after an abortion.
To prevent complications after surgery, it is necessary to
Observe sexual rest for 2 weeks, avoid physical activity and thermal procedures (visits to baths, saunas).
Prevention of placental polyp is also a thorough gynecological examination of the woman after an abortion, checking the placenta for integrity.
The formation of a placental polyp is one of the possible complications of a medical abortion. This pathology can lead to serious consequences.
Timely seeking medical help will help you take the necessary measures in time and avoid reproductive dysfunction.
Source: https://oonkologii.ru/platsentarnyj-polip-posle-medaborta-01/
Recovery after polyp removal
The first 1-3 days there is a bloody smear. Sometimes contractions of the uterus are felt. Rehabilitation lasts until the onset of menstruation for about a month or a little more. During this period you cannot:
- Be sexually active;
- Bask;
- Take a bath and, in general, immerse yourself in water;
- Drink alcohol;
- Be physically tense;
- Supercool.
For successful recovery you need:
- Take vitamins and iron supplements if anemia occurs;
- Visit a doctor for preventive examinations;
- Maintain genital hygiene;
- Monitor your condition, the nature of discharge and body temperature.
Symptoms
The main symptom of placental polyp is bleeding. In the first two weeks there may be slight spotting. During this period, a woman may not immediately suspect the presence of a pathology, since after childbirth, including after a cesarean section, as well as after a miscarriage and medical abortion, such discharge may be normal for some time. But normally, the volume of such secretions gradually decreases, while with a polyp they, on the contrary, increase. Therefore, a prolonged cessation of lochia, as well as an increase in the volume of bloody discharge, is a reason to consult a doctor.
If a woman did not know that she had a miscarriage, a sign of the disease may be too long periods that came earlier than usual.
At 4-6 weeks, uterine bleeding often occurs, which can be very massive and life-threatening.
Nonspecific signs of the disease, which still often occur against its background, are: weakness, increased fatigue, drowsiness, headache. They occur against the background of prolonged blood loss.
Dangerous symptoms are:
- high body temperature;
- purulent discharge: green, yellow, cloudy, foamy;
- specific putrid unpleasant odor;
- stomach ache;
- itching, burning;
- discomfort.
These are signs of inflammation and infection.
Prevention of pathology
The main preventive measures include:
- Adequate contraception, planning pregnancy, avoiding abortion.
- Compliance with personal hygiene rules.
- Regularly scheduled gynecological examinations.
- Compliance with all medical recommendations prescribed after an abortion.
To prevent complications after surgery, it is necessary to
Observe sexual rest for 2 weeks, avoid physical activity and thermal procedures (visits to baths, saunas).
Prevention of placental polyp is also a thorough gynecological examination of the woman after an abortion, checking the placenta for integrity.
The formation of a placental polyp is one of the possible complications of a medical abortion. This pathology can lead to serious consequences.
Timely seeking medical help will help you take the necessary measures in time and avoid reproductive dysfunction.
Placental polyp is a neoplasm formed from endometrial mucosa and remnants of placental tissue. Pathological growth of mucous membranes rushes into the cavity, has a wide base or a thin stalk (mostly without a stalk). Treatment of the disease is always surgical, with long-term restorative drug treatment. When the first symptoms appear, you should immediately contact a specialist.
Predisposing factors
Placental polyp after abortion occurs in only 1.7% of all clinical complications. Predisposing factors are a hereditary predisposition to polyps of any location, as well as the presence of pathological growths in the uterus, cervical canal, and lumen of the cervical canal.
There are two main types of medical abortions:
- Surgical or instrumental - curettage followed by vacuum aspiration up to 12 weeks of pregnancy and up to 22 weeks for special indications;
- Medicinal or “velvet” - miscarriage under the influence of drugs up to 6-8 weeks.
In both cases, the woman must be monitored by a gynecologist for several months.
The placenta begins to form immediately after conception, and completes its formation by 14-15 weeks of pregnancy. After this period, the process of aging begins. The later the abortion is performed, the greater the risk of fragments of the placenta, along with blood clots, attaching to the wall of the uterus and their subsequent formation into polyps.
The main causes of polyp during medical abortion are:
- Incomplete curettage or expulsion of the placenta during a “velvet” abortion;
- Infection:
- Increased accumulation of blood in the uterine cavity;
- Prolonged bleeding (as a result of injury to the uterus, hormonal imbalance);
- Insufficient qualifications of the doctor (including clandestine abortions in undeveloped or highly religious countries).
It is important ! Incomplete abortion or prolonged bleeding is a life-threatening clinical situation that requires urgent hospitalization of the woman and subsequent instrumental cleaning of the uterine cavity.
In the case of a medical abortion, a woman may have a low level of hormonal levels, which cannot ensure normal contraction of the uterine cavity and remove the remains of the placenta.
Fragments of placental tissue grow into the connective tissue layer of the endometrium, actively grow with the vascular component and form something like an elevation above the inner layer of mucous membranes, which is called a polyp.