Many women do not always know and clearly imagine the processes that occur in their body every month throughout their reproductive years. Many people learn about the formation of the corpus luteum during pregnancy only after they hear or read the results of an ultrasound.
An ultrasound examination, as a result of which a woman makes a discovery about the existence or absence of her corpus luteum, is carried out for various reasons. Someone has the task of confirming pregnancy. Some people just can’t get pregnant and need an ultrasound to check.
Both of them ask questions:
- what it is;
- what condition does its presence indicate?
- what does the change in its size indicate?
- why gynecologists pay so much attention to this indicator;
- what is a corpus luteum cyst, and what is the danger in it.
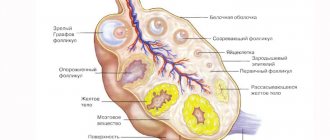
Corpus luteum in the ovary: what does it mean?
If a woman goes for an ultrasound in the second half of the cycle, the doctor should see the temporary luteal gland. Its presence indicates that the egg has already matured and has left the follicle.
Luteal formation appears under the influence of luteinizing hormone, which is secreted in the anterior lobe of the pituitary gland. During this period, the vascular system actively grows in the granulosa cells and the corpus luteum of the ovaries is formed, which produces progesterone. This hormone is required to prepare the endometrium for egg implantation and support the development of pregnancy in the first weeks.
Important! The absence of a luteal glandular structure in the 2nd phase of the menstrual cycle indicates that there was no ovulation.
The opinion that endocrine formation appears only during pregnancy is erroneous. It is formed from the cells of the ruptured follicle (its granular layer) after the release of the egg.
What it is?
All women of different ages, races, and heights have one thing in common - their menstrual cycle follows the same laws, the phases of which are sequential. After menstruation, follicles begin to mature, one of which will become dominant. In it, like in a cozy pouch, the egg matures, in the middle of the cycle the follicle ruptures, ovulation occurs. The egg leaves its “shelter” and enters the abdominal cavity, and from there into the fallopian tube, where within a day and a half it can be fertilized.
Ovulation calculator
Cycle duration
Duration of menstruation
- Menstruation
- Ovulation
- High probability of conception
Enter the first day of your last menstrual period
Ovulation occurs 14 days before the start of the menstrual cycle (with a 28-day cycle - on the 14th day). Deviation from the average value occurs frequently, so the calculation is approximate.
Also, together with the calendar method, you can measure basal temperature, examine cervical mucus, use special tests or mini-microscopes, take tests for FSH, LH, estrogens and progesterone.
You can definitely determine the day of ovulation using folliculometry (ultrasound).
- Losos, Jonathan B.; Raven, Peter H.; Johnson, George B.; Singer, Susan R. Biology. New York: McGraw-Hill. pp. 1207-1209.
- Campbell NA, Reece JB, Urry LA ea Biology. 9th ed. - Benjamin Cummings, 2011. - p. 1263
- Tkachenko B. I., Brin V. B., Zakharov Yu. M., Nedospasov V. O., Pyatin V. F. Human physiology. Compendium / Ed. B. I. Tkachenko. - M.: GEOTAR-Media, 2009. - 496 p.
- https://ru.wikipedia.org/wiki/Ovulation
In place of the follicle, a temporary formation is formed from the remains of its shell - a gland that produces progesterone. Due to the color of the pigment inside it, it is called the yellow body. It is difficult to overestimate its importance for a woman, because this education allows the female body to prepare for a possible pregnancy. Of course, the gland cannot “know” whether the egg is fertilized or not, but the production of progesterone occurs in any case. This hormone helps prepare the endometrium for possible implantation. While the fertilized egg moves into the uterus within a week after ovulation, the endometrium becomes looser to make it easier for the embryo to implant.
Progesterone also reduces a woman’s immunity so that immune cells do not kill the embryo, mistaking it for a foreign body, since the baby’s genetic makeup is only half related to the woman.
The corpus luteum cannot exist for long if there has been no conception. If implantation of the embryo does not occur, after 10-12 days it dies and dissolves, and the production of progesterone in large quantities stops. In a woman’s body, estrogen begins to control everything and menstruation begins. Before menstruation, the corpus luteum ceases to be such and is transformed into a whitish body that has no functional load, and then disappears altogether.
After conception and successful implantation, the chorionic villi begin to produce the more understandable and familiar hormone hCG (this is why pregnancy tests become “striped”). Human chorionic gonadotropin prevents the corpus luteum from ceasing to exist, so the gland continues to function until the end of the first trimester of pregnancy. Then the placenta is formed, the functions of the progesterone “factory” fall on it. The corpus luteum regresses as unnecessary after the 11th pregnancy.
When does the corpus luteum form in the ovary?
The corpus luteum becomes visible in the ovary after ovulation is complete. After the egg is released, the follicular fluid is poured out and the follicle cavity closes. A glandular endocrine structure is immediately formed in it; in the first days it is small in size.
This temporary formation increases gradually. Its diameter is directly related to hormonal activity. The larger the size, the more progesterone it produces.
Why is iron needed?
The main function of the gland is to produce progesterone. The latter is considered a hormone of the third phase of the cycle, necessary for the movement of the egg through the fallopian tube, thickening the endometrium for easier attachment of the fertilized egg to the walls of the uterus. VT reaches its peak activity 3-4 days after ovulation. In the absence of pregnancy, it undergoes regression.
Signs of the corpus luteum in the left ovary
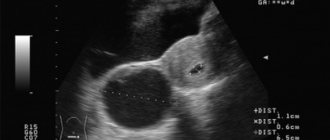
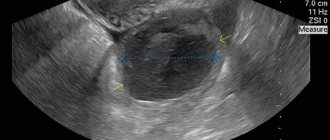
Only with the help of ultrasound can one determine the presence of a corpus luteum in the ovary. It is impossible to determine on your own whether it appeared in the 2nd half of the cycle. The temporary structure responsible for the production of progesterone forms and disappears asymptomatically, no visible changes occur.
If during ovulation a woman felt pain or tingling in the left lower abdomen, then we can assume that a temporary hormonal gland will appear on the left.
If an ultrasound shows that the corpus luteum in the left ovary is 18 mm in diameter, this means that the egg has emerged from the left female reproductive gland. This size corresponds to phase 2 of the cycle. When planning pregnancy, it is better that its diameter is more than 20 mm. This is an indirect confirmation that progesterone is produced in sufficient quantities. When the size of the hormonal formation is less than 16 mm, they speak of phase 2 insufficiency.
Can the corpus luteum in the ovary hurt?
The endocrine gland formed at the site of the ruptured follicle should not provoke pain. Although some gynecologist patients report the appearance of pulsation and discomfort in the lower abdomen, which are concentrated on one side.
Severe pain usually occurs when a cyst forms. This condition is characterized by the fact that by the time menstruation begins, the temporary organ does not decrease in diameter, but continues to grow. Intracellular fluid begins to accumulate in it. Cysts can reach 8 cm in diameter. In 90% of cases, they resolve on their own within a few months.
Sudden sharp pain may indicate that the corpus luteum in the ovary has burst. This is a pathology that doctors call apoplexy. The condition requires immediate hospitalization and surgery during which resection or complete removal of the problem organ is performed. Due to the rupture, blood begins to accumulate in the abdominal cavity, and the lack of timely medical care provokes the development of serious consequences.
Corpus luteum in the ovary and delay
If a delay in menstruation occurs during an ultrasound, the doctor must evaluate the size and structure of the formation that appears in phase 2. The absence of menstruation on time in the presence of the luteal gland may be due to pregnancy. Normally, its size should be 20-30 mm. On ultrasound it looks like a hyperechoic formation with heterogeneous content.
If menstruation is delayed, on ultrasound the doctor may see an anechogenic round formation with a homogeneous structure - a cyst. Its diameter varies from 30 to 80 mm. To normalize the condition, patients are prescribed progesterone drugs in a short course. A few days after their cancellation, menstruation should begin.
Reference! If, during a delay in ultrasound, the corpus luteum in the ovary is not visualized, this indicates a possible endocrine pathology or disease of the reproductive organs.
A situation is possible in which the delay is caused by the persistence of the corpus luteum in the right or left ovary. Persistence of an immature hormonal gland is characterized by a decreased level of luteinizing hormone. The temporary organ cannot fully mature, because of this, phase 2 of the cycle is lengthened.
When a mature gland persists, it does not decrease in size by the beginning of menstruation, but moves into the next cycle. In this case, a full follicular phase and an extended luteal phase are observed. It lasts 20-25 days and is accompanied by hyperproduction of progesterone.
About sizes
Unlike the follicle, which, when tracked by ultrasound, changes its size every day in the first half of the cycle, the corpus luteum has a fairly stable size, normally ranging from 10 to 30 mm. A slight decrease by day of the cycle is noticeable only in the regression stage, when the gland is absorbed. Therefore, you should not worry if the doctor determines the diameter of the corpus luteum to be 11-12 mm, 13-14 mm, as well as 15-16 or 17-18 mm. Everything that fits within the range of 10 to 30 mm is normal size.
Based on the size of the corpus luteum, the doctor will not be able to find out when ovulation occurred, given that the range of normal sizes is still quite large. It is believed that during the first week after ovulation, on average, the corpus luteum reaches a size of 17-19 mm, 10 days after ovulation - 20-27 mm, and in the last five days of the cycle it (if there is no pregnancy) begins to decrease to 15 mm. Therefore, it is a stretch to say that a diameter of 21-22 mm corresponds to the period of ovulation of 7-9 days, and a diameter of 23-24 mm indirectly indicates ovulation about 10-11 days ago. In the flowering stage of the gland, when its size is maximum, there may be values of 25, 26-27 and 28-29 mm, but in this case it will be difficult to calculate when ovulation actually took place.
Considering that in women the size of the corpus luteum can initially be within the normal range, both small and large, it is possible to say about the date of ovulation only if the doctor assesses the size of the corpus luteum at least every other day. In practice, there is no need for such a survey.
If the size of the gland is only 8-9 mm or less, this indicates insufficiency of the corpus luteum. With it, the pregnancy of the child is in serious danger of being interrupted, because the small gland produces little progesterone. If the highest level of the norm is exceeded (31, 32, 40 mm or more), they speak of a possible cystic formation, the so-called luteal cyst or corpus luteum cyst. Its diameter can reach up to 80 mm.
Corpus luteum in the ovary without pregnancy
If there are no problems with reproductive health, and ovulation occurs regularly, then in the 2nd half of the cycle a temporary endocrine structure should form in one of the gonads. In the absence of pregnancy, it decreases in size and degenerates by the beginning of menstruation.
What does the corpus luteum mean in the right ovary?
When performing an ultrasound, the doctor can detect the luteal gland. By seeing a 22 mm corpus luteum in the right ovary, the doctor will be able to confirm that ovulation occurred on the right.
What does the corpus luteum mean in the left ovary?
The detection of a hyperechoic round formation on the left indicates that ovulation has occurred in the left gonad. In the absence of problems with the reproductive organs, it makes no difference which side the egg comes out from. If a woman has had one of her fallopian tubes removed or blocked, then it is important to track ovulation. Pregnancy can occur provided that the egg is released from the side where the healthy fallopian tube is located.
Two corpora lutea in one ovary
Quite rarely, in natural cycles without stimulation of ovulation, a situation occurs in which 2 eggs are released. After all, normally, 1 dominant follicle should form and burst in the body.
If 2 eggs are released in a cycle, then 2 temporary glandular organs will be formed in their place. This situation often occurs in cases where ovulation is stimulated with the help of special drugs.
When stimulated or in a natural cycle, two corpus luteum may appear in different ovaries. In the absence of pregnancy, they regress towards the onset of menstruation. If a delay occurs, their presence may indicate the development of a multiple pregnancy. This situation occurs in cases where 2 eggs are fertilized at once.
White body in the ovary: what is it
If fertilization does not occur, the stage of reverse development of the temporary hormonal gland begins before menstruation. The cells of this formation die, and the connective tissue, which is located in the central scar, resolves. As a result, a whitish formation remains in its place. It exists for about 5 years, then it begins to gradually dissolve, degenerating into a scar made of connective tissue.
Absence and underdevelopment after conception
If the presence of a cyst does not pose a great threat to the female body and the fetus, then the underdevelopment of the corpus luteum or its absence may be a cause for concern. Such pathologies are easy to diagnose in the first weeks after conception. They can lead to complications such as the threat of miscarriage. Such diagnoses are made only after an extensive examination of the patient. In this case, the following procedures are prescribed:
- ultrasound diagnostics;
- blood sampling for analysis of hormone levels;
- thorough gynecological examination;
- studying basal temperature charts, if present.
IMPORTANT! Many pregnant women are afraid to do an ultrasound, thinking that this diagnostic method has a negative effect on the fetus. In fact, this informative method cannot harm either the child or the expectant mother. Ultrasound is allowed to be performed the required number of times at any stage of pregnancy.
If a diagnosis is made indicating insufficient development of the luteal body, do not fall into despair. Thanks to modern pharmacology, women even with this pathology are able to conceive and bear healthy children. Some patients are faced with another deviation in which a neoplasm important for the development of the fetus is not visible on ultrasound, although conception has already occurred.
If there is no corpus luteum in the ovary, what is it like during pregnancy: this question worries every woman with a similar diagnosis. The visual absence of this neoplasm indicates that its size is too small for it to perform its main function of maintaining fetal development. In this case, deviations in the woman’s hormonal background should be determined as quickly as possible and drug therapy should be started. If this is not done, an insufficient amount of hormones will enter the expectant mother's body, which will lead to the threat of miscarriage.
If the temporary luteal organ is not visible in the later stages, there is no need to worry, as this is the norm. Its disappearance indicates that the placenta has formed sufficiently to ensure normal development of the fetus. At this stage, the function of the neoplasm is to prepare the uterus for implantation and subsequent placental development of the fetus. To ensure that your pregnancy proceeds without pathologies, it is important to visit your doctor regularly. This will allow pathological processes to be identified in a timely manner and eliminated before the threat of miscarriage occurs. The ovaries must be examined after childbirth to ensure the absence of VT.
We recommend you learn: How to palpate the ovaries
Corpus luteum in the ovary: dimensions
The process of formation of a glandular structure from granulosa cells of a ruptured follicle starts after ovulation. When the follicle ruptures and the mature egg is released, blood is released from the damaged blood vessels. It accumulates in the center of the developing temporary gland. In the same place, a stigma is formed - a connective tissue scar, around which the cells of the granular layer begin to multiply. They are covered with a dense network of capillaries. This stage is called proliferation and vascularization. The size of the hormonal formation during this period is 12–15 mm.
Then the granulosa cells begin to accumulate lutein (a pigment that gives the characteristic yellow color) and degenerate into glandular cells - granular luteocytes. Theca luteocytes are formed from cells of the internal folder. This stage is called ferruginous metamorphosis.
Progesterone production begins at the 3rd stage of flowering. At this time, the temporary organ reaches a diameter of 24 mm. During this period, doctors call the formed glandular structure cyclic or menstrual.
2-3 days before menstruation, it decreases to 12-15 mm, and scar tissue forms from it. This leads to a decrease in progesterone production and the onset of menstruation.
If fertilization has occurred and an embryo has formed, then the flowering stage lasts 10-16 weeks. The hormone produced by the corpus luteum of the ovary is required for the maintenance and normal development of the fetus.
During pregnancy, the size of the corpus luteum in the ovary reaches 30 mm. Over time, its functions are transferred to the placenta, and it begins to regress.
Development of neoplasm during pregnancy
The corpus luteum is constantly changing in the early stages of pregnancy and can function up to fifteen weeks. When the process of placenta formation begins, the need for this temporary organ disappears, as the placenta begins to take over the functions of producing progesterone in the required quantities. In subsequent months, the placenta provides the synthesis of female sex hormones. In some cases, the neoplasm does not disappear after the placental period and remains in the ovary until birth.
The corpus luteum may vary in size during pregnancy. It all depends on what stage the fetus is in development. The luteal neoplasm is in the process of growth throughout its entire existence after conception. This is due to the fact that he needs to provide the woman’s body with the hormones necessary for the development of the fetus. Normally, the size of such a temporary organ is 10-30 millimeters. This value will remain until the tenth to fifteenth week. Then a gradual decrease and complete resorption begins. In rare cases, it remains until labor. But this should not cause concern, because the neoplasm loses its functionality and does not have a negative effect on the development of the fetus.
We recommend you learn: Development of a luteal cyst of the left ovary
How long does the corpus luteum live in the ovary?
If there are no problems with reproductive health, then a temporary hormonal formation appears immediately after the release of the egg and continues to develop for 12-14 days. If during this period the egg is fertilized and begins to implant into the wall of the uterus, then it will continue to develop. The lifespan of the corpus luteum in the left ovary during pregnancy can last 16 weeks.
Changes and pathologies of the organ
Pathological changes in the corpus luteum of the right ovary most often do not have specific symptoms, are not accompanied by any discomfort and are diagnosed only by ultrasound.
There can be many reasons for the malfunction of the gland:
- infectious and inflammatory diseases of the female reproductive system and related organs;
- hormonal imbalance caused by stress, sudden changes in weight, disruption of the ovaries, thyroid gland or pituitary gland, etc.;
- use of hormonal contraceptives;
- blood supply disorders in the ovaries;
- bad habits, unhealthy lifestyle;
- polycystic ovary syndrome and other causes.
The determining indicator of pathologies of the corpus luteum is its size. If during pregnancy the iron level is less than 10 mm, then they speak of functional deficiency. This situation means that hormone production is not at full strength and there is a risk of miscarriage or fetal death. The woman is recommended to take maintenance hormonal therapy. Sometimes it is enough to drink synthetic progesterone only until the second trimester, in some cases - throughout the entire period of bearing a child.
When the corpus luteum on the right ovary exceeds 28 mm in diameter, a cyst forms. Most often, this condition during pregnancy does not pose a great danger, as it resolves on its own within 2-3 months.
Both of these conditions require constant monitoring by a doctor for the threat of interruption.
Drug therapy is not prescribed in all cases, but diagnosis should be carried out regularly. Diagnostic measures for pathologies of the corpus luteum during pregnancy include:
- ultrasound examination to monitor the size of the corpus luteum. Ultrasound does not cause any harm to the fetus and the expectant mother (as some women mistakenly believe), and it can be performed an unlimited number of times throughout the entire gestation period, if indicated;
- a blood test to determine the amount and ratio of hormones that are necessary to maintain pregnancy;
- general examination by a gynecologist;
- basal temperature indicators.
When is an examination necessary?
Pathologies are quite rare. You can suspect them based on the following symptoms and signs:
- cycle failure,
- prolonged delay of menstruation,
- increase or decrease in the amount of bleeding, pronounced premenstrual syndrome, etc.,
- long absence of conception,
- deterioration of skin, hair, nails is a symptom of hormonal imbalance.
In these cases, it is necessary to undergo an examination. It should be remembered that over time, VT pathologies and other abnormalities in women’s health, if left untreated, can lead to infertility.
Education mechanism
The luteal gland develops immediately after ovulation. A ruptured follicle that releases an egg into the fallopian tube leaves a membrane from which VT is formed. It has a characteristic yellow color. Its appearance is accompanied by a sharp change in hormonal levels - the level of estrogen, which predominates in the first half of the cycle, rapidly falls, at this time the concentration of progesterone in the blood gradually increases.
VT is equally likely to occur in both appendages - it depends on which organ ovulation occurred in.