Removal of the Bartholin gland or extirpation is a radical surgical method that surgeons do not like to use because of its complexity and “bloodyness.” But sometimes complete excision of the gland becomes the only correct solution. Women who have had their Bartholin gland removed must undergo a course of rehabilitation therapy. Its features are discussed in the article.
Services table
| Service name | Price |
| Initial consultation with a gynecologist | 2,300 rub. |
| Ultrasound gynecological expert | RUB 3,080 |
| Insertion of an intrauterine contraceptive device | 4,500 rub. |
| Hysteroscopy | RUB 22,550 |
| Repeated consultation with a gynecologist | 1,900 rub. |
| Taking a smear (scraping) for cytological examination | 500 rub. |
| Laparoscopy (difficulty category 1) | 61,000 rub. |
| Program "Women's Health after 40" | RUB 31,770 |
| Treatment of the cervix (medication) in 1 procedure | 800 rub. |
| Diagnostic curettage | 12,000 rub. |
When is surgery necessary?
If the tumor is small (no more than 2.5 centimeters), then surgical intervention is not necessary. In this situation, the patient should be constantly monitored by a gynecologist, who uses ultrasound to monitor the development of the disease. In some situations, the cyst can resolve on its own without pharmacological action. However, cystic neoplasms that have reached large sizes are always removed surgically. It is pointless to hope that a tumor measuring 7-10 cm will resolve.
Drug therapy is mandatory if, during diagnosis, the patient is found to have:
- fungal and sexually transmitted infections;
- E. coli infection;
- other inflammatory and infectious pathologies.
After identifying the causative agent of the disease, the gynecologist must prescribe appropriate medications. Basically, broad-spectrum antibiotics and antimicrobial agents are used to prevent the development of a purulent inflammatory process. Local treatment is also carried out using disinfectant solutions and antiseptic ointments.
Large cyst
Surgical intervention is necessary in cases where the size of the cystic formation has greatly increased, since a large tumor prevents the patient from leading a normal lifestyle. With frequent exacerbations of this pathology, the cyst is removed regardless of the size of the benign neoplasm. Surgical treatment is carried out in various ways, depending on the degree and form of the pathological process, the presence of complications and the general well-being of the patient.
In what cases is removal of a Bartholin gland cyst indicated?
How is a Bartholin gland cyst removed?
First of all, surgical intervention is indicated for purulent inflammatory processes. The specialist may prescribe antibacterial therapy. In some cases, such a therapeutic regimen allows non-surgical elimination of the manifestations of the inflammatory process of the excretory duct, as well as restoration of its patency.
Classical opening of a benign tumor and cleaning with disinfectant medications is not always an effective method, since in many cases women experience relapses. Various infections enter a woman’s body through the genital tract. If the excretory ducts of the gland are not restored, then negative consequences are inevitable. After surgical manipulations, physiotherapy and immunostimulating therapy are necessarily prescribed.
Bartholin cyst and pregnancy
When such a diagnosis is made to a woman carrying a child, she has serious concerns about the health of the unborn baby. What you need to know about the disease during pregnancy:
- decreased immunity contributes to tumor development;
- the infection can reach the fetus through the blood or amniotic sac;
- a disease complicated by an abscess threatens miscarriage or premature birth;
- developmental deviations are possible, for example, growth retardation;
- there is a risk of contracting intrauterine pneumonia;
- the ingress of pathogenic organisms sometimes causes damage to the organs of vision.
A child can also become infected while passing through the birth canal, this is especially dangerous for premature babies, their immunity is unable to cope with the disease on its own.
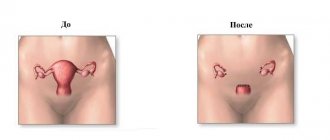
Complete removal of the gland
In some cases, experts recommend resorting to extreme measures, which include complete removal of the gland, this allows 100% to avoid exacerbations.
Extirpation of the gland is the most radical type of surgical treatment.
Surgery to remove a gland cyst is prescribed if other types of therapeutic interventions do not produce positive dynamics. With the help of extirpation, you can forget about this problem once and for all. However, after the operation, a significant decrease in the quality of sexual life is possible: dryness of the vaginal mucosa due to the poor functioning of the only gland, which entails unpleasant sensations and discomfort during sexual intercourse.
In addition, the suture may be bothersome after removal of a Bartholin gland cyst.
After removal of the cyst, a large scar remains in the surgical area, and a fistula or hematoma may occur. Damage to the venous walls during manipulation is fraught with the development of bleeding. Removal is carried out under general anesthesia, so operations are performed only on women who can tolerate anesthesia well. Hospitalization in a medical facility lasts approximately a week; if complications occur, the postoperative period can last up to a month. Considering the above consequences, the Bartholin gland should be completely removed only in severe cases with regular relapses of the pathological process.
Operation
Radical methods are also used to treat this pathology. They, as doctors note, are more effective and efficient. But each case is individual, and therefore the doctor, when making a diagnosis and prescribing therapy, must choose the most optimal method of treatment.
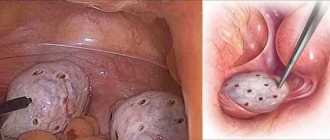
Enucleation of Bartholin gland cyst
This is the method preferred by most doctors when eliminating such pathology. But if the gland is completely removed, it can cause some harm to the woman, although she will never become inflamed again.
The gland is designed to secrete lubricant for the vagina during sex. When the gland is removed, the woman will experience discomfort and pain during sex. It can also completely put an end to her sex life.
During the operation, a large loss of blood may occur, since the cyst is located in a place where there are many vessels, and therefore such intervention should be resorted to rarely.
When a cyst is peeled, blood loss is also possible, but less. It is worth remembering that after removal of the cyst, there may be relapses.
The essence of the operation is as follows:
- An incision is made.
- The cyst is released from other tissues without rupture.
- The bed is sutured in layers.
Marsupialization of Bartholin gland cyst
The highest quality and optimal operation. It is often used to treat such pathology. It is carried out both during remission and during exacerbation. Usually, after such a procedure, a woman ceases to experience negative symptoms.
The flow of the operation is as follows:
- After making an incision, the contents of the cyst are removed.
- Sutures are placed on the incision in such a way as to allow a new channel to drain the fluid to form independently.
After such an operation, you will need to follow special rules of care and hygiene.
Also, during these two operations, the doctor places sutures, which can dissolve on their own over a certain period of time. They do not require removal. Such sutures are preferred in gynecology to prevent tissue inflammation.
- In the first time after surgery, swelling of the vagina is possible. This will cause some discomfort. At this stage, to reduce negative symptoms, you can apply cold to the organ.
- In order for the wound to heal well, it must be carefully treated initially and then monitor the hygiene of the organ. The seams need to be lubricated with septic tanks a couple of times a day.
- Turunda will have to be changed every day.
- The underwear should not be tight and should be made from natural material. Since access to air in the wound is necessary.
In chronic form
In the chronic form of the disease, relapses often occur, and abscesses may open on their own and secondary infections may occur. Opening of the formation should be carried out only in a hospital setting, where proper antiseptic treatment, cleansing of the cavity from purulent contents, and proper wound care are carried out.
It is not possible to completely empty the cavity of pus at home. And when an infection enters the blood, sepsis can develop, which, without timely medical assistance, can provoke the death of the patient. The most popular is laser removal of Bartholin gland cysts.
Gentle methods of surgical treatment
There are several methods of surgical treatment of cysts, which are aimed not only at opening the formation and removing pathological secretions, but also at developing a new excretory duct. The main methods of performing surgery to remove a Bartholin gland cyst can be as follows:
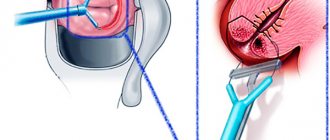
- Marsupialization of a cyst is a method aimed at the formation of a new excretory duct. This operation lasts approximately 30 minutes. Everything is done on an outpatient basis using anesthesia. After anesthesia, the doctor incises the labia, removes the pathological formation along with its contents, and rinses the cavity with an antiseptic solution. A catheter is inserted to drain the fluid. If the surgical area is very swollen, then an incision is made both on the mucous membrane and on the cyst. After this, the cyst shell is sutured, forming a new excretory duct. Subsequent rehabilitation takes place without drug therapy. This technique allows you to normalize the functioning of the gland, eliminate the inflammatory process, and prevent the development of an abscess.
- Enucleation of a cyst is a manipulation in which the cystic formation is opened with subsequent drainage of the gland. The cyst is removed and treated with antiseptic agents. After surgical treatment, a drainage is inserted, through which the accumulated fluid flows out of the cavity. After complete healing, the catheter is removed, and a new excretory duct develops in its place. This is a rather complex operation that requires great care. During the procedure, the specialist cuts the tissue in the area of the labia minora, being careful not to touch the cyst so that it does not rupture, otherwise its contents may enter the wound, causing an infectious process. The operation to remove a Bartholin gland cyst is performed on an outpatient basis under local anesthesia. After its completion, the patient is prescribed antibiotics, physiotherapy and immunomodulators.
Carrying out surgery for bartholinitis and recovery after it
The occurrence of pathological changes in the female reproductive organs indicates that surgery is needed for bartholinitis. This is a last resort measure that is decided to be taken when drug treatment does not produce results.
Indications for surgical treatment
Removal is necessary if:
- inflammation led to the formation of large bulges;
- there is discomfort in the genital area;
- During intimacy, a woman experiences sharp pain.
Indications for the surgical procedure include:
- the abscess is acute;
- the cyst deforms the entrance to the vagina;
- relapse of the inflammatory process;
- cyst in the Bartholin gland;
- the beginning of the process of suppuration in the gland duct;
- lack of healing of the fistula tract after spontaneous opening of the formation.
Even if the abscess has broken out on its own, you need to make an appointment with a surgeon. The doctor will see if the patient has a small cyst. The tumor becomes chronic and does not cause discomfort, but over time, when exposed to a number of factors, there is a risk of enlargement, which will lead to inconvenience and require expensive long-term treatment.
Surgical techniques
There are several treatment options if Bartholin's glands are inflamed:
- Drainage. To do this, the specialist uses a tube through which the outflow of stagnant secretions is established. The technique is not effective enough, since after it, if you read the reviews, there are frequent relapses. If cysts appear several times, the result may require removal of the gland.
- Marsupialization. This is the removal of a tumor by surgery. It involves the formation of an artificial excretory duct, which will take 2 months. The glands are preserved, but in case of relapse, extirpation will have to be performed.
- Catheter placement. An incision is made on the convexity, and the stagnant secretion is removed through it. A tube made of silicone material with a small balloon at the end is placed at the wound site. The patient needs to walk with such a catheter for several weeks until a new duct is formed.
- Puncture of the cyst. A puncture is made in the cyst. The contents are removed through the resulting hole.
If pus occurs in the neoplasm, the pathological contents are first removed, and only then further treatment is started.
If the patient has an abscess of the Bartholin gland (bartholinitis), the cavity must be opened and drained.
The doctor makes an incision along the inner surface of the labia majora in the place where the greatest fluctuation is present. When the pus drains, it is taken for bacteriological and bacterioscopic analyses.
The cavity is treated with disinfectants, and a turunda containing a hypertonic solution is introduced. The device is changed 2 times a day.
If the patient has been diagnosed with a Bartholin gland cyst, removal is necessary when it is not an exacerbation, in the “cold” period.
If an abscess occurs in the large gland of the vaginal vestibule, an incision is made. The manipulation is carried out under short-term anesthesia or under infiltration anesthesia.
The incision line is parallel to the labia minora, outside of it. When the opening is wide enough, drainage is performed using a strip of gauze. Then the entire cavity is packed.
After a day, the tampon is removed and drainage is performed with a tube made of rubber material.
What is included in the cost of the operation for enucleation of a cyst of a large gland located in the vestibule of the vagina:
- preparatory activities;
- carrying out infiltration anesthesia;
- incision of the skin, subcutaneous base;
- desquamation of tumors, glands;
- ligation of vessels that begin to bleed;
- suturing the tumor bed;
- alignment of the edges of the wound.
Postoperative period
When the abscess is opened, the patient feels better. The temperature returns to normal, other symptoms of the pathological process disappear. At the acute stage, bartholinitis is cured forever, but sometimes it becomes a chronic form of the disease. In this case, it is necessary to carefully monitor your health, avoid hypothermia, and observe personal hygiene rules.
To make recovery easier, patients are prescribed to attend physiotherapeutic procedures and use medications that have an immunostimulating effect.
After opening and draining the cavity, therapy is prescribed: antibiotics, sedatives, and painkillers are indicated. Desensitizing procedures and physical therapy may be prescribed. A set of measures is necessary for healing to proceed faster.
After removal of the cyst, the doctor recommends measures that strengthen the immune system:
- vitamins;
- herbal immunomodulators;
- balanced diet.
In order for recovery to proceed faster, it is important to follow a number of rules:
- use antibacterial hygiene products recommended by your doctor to wash yourself twice a day;
- use a weak solution of potassium permanganate or chamomile decoction for treatment only if the doctor has authorized it;
- choose loose-fitting underwear made from natural fabrics;
- do not use panty liners to avoid bacteria that form on their surface during the day;
- refrain from intimate contacts and masturbation until the wound is completely healed.
To prevent the process from becoming chronic, it is important to use antiseptics and antibiotics to speed up the healing of the wound. Antibiotic medications after surgery help prevent new infections from developing. Therapy is also prescribed for the sexual partner so that the woman does not become infected again.
Possible consequences
If bartholinitis occurs during pregnancy, it is difficult to tolerate. If infected before 22 weeks, the risk of miscarriage increases. If you get sick in the second half of pregnancy, the infectious agent can get to the baby.
Consequences of this:
- lung damage;
- eye infections;
- inflammation of the umbilical ring;
- premature birth.
Contraindications
A small cyst does not require surgical intervention. Such neoplasms disappear spontaneously over time if the outflow of secretions is normalized. They are removed only if it is necessary to prevent relapse, or for cosmetic purposes.
If there is an inflammatory process, then the cyst cannot be removed. It is necessary to wait for the complete cessation of inflammation. This can be understood through analysis of vaginal discharge. If there is no admixture of pus in them, then surgery can be performed.
Only a doctor can decide which surgical method to eliminate the pathology, taking into account a number of factors.
It depends on the stage of the inflammatory process, clinical picture, medical history and other features.
If a woman is tormented by constant painful sensations, the labia is very swollen, there is a ball above the skin, and the temperature has risen, you should not self-medicate. It's better to make an appointment with a doctor.
Source: https://venerologia03.ru/prochie-bolezni/operatsiya-pri-bartolinite.html
Postoperative period and recovery
After removal of a Bartholin gland cyst, the postoperative period proceeds differently for everyone.
To reduce the likelihood of postoperative complications, the patient is prescribed anti-inflammatory medications, as well as physiotherapy. Until the wound heals, you must abstain from sexual intercourse.
Recovery after removal of a Bartholin gland cyst is usually quick.
If the gland is completely removed, the postoperative period is prolonged for a long time. Severe hematomas and swelling appear in the vulva area, which disappear very slowly.
Recovery after removal of the Bartholin gland, as in the case of cyst excision, is associated with the elimination of pathogenic microorganisms that caused the pathology. Antibiotics are prescribed to achieve the following goals:
- reducing the risk of infection spreading throughout the body (for example, women with immunodeficiency or pregnant patients);
- elimination of symptoms of systemic infection (heat, fever);
- fight against pathogens of gonorrhea, chlamydia, methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus, discovered during the study of pus from a cyst.
The most appropriate method of surgical treatment is selected by the treating specialist, after which consultation with the patient is carried out.
Prevention
For preventive purposes, women need to use barrier contraceptives, observe the rules of personal hygiene, including during and after intimate relationships, fully treat inflammatory and infectious diseases, and visit gynecologists every six months. In addition, young girls and women of reproductive age need to ensure that their feet are always warm and avoid hypothermia, which is the most common cause of this disease. What happens after surgery to remove a Bartholin gland cyst? Below are reviews from women who have undergone surgery.
Reviews
Bartholin gland cysts today occur in approximately 9 women out of 100, and these are very high rates. Doctors do not yet know for sure what causes such a frequent development of this pathology, but clinics can currently offer patients several ways to quickly resolve this problem.
There are quite a lot of reviews about the removal of Bartholin gland cysts, and they are very diverse. Judging by the information contained in them, extirpation of the gland is most often performed. Women who have undergone such surgical treatment say that this is the most radical method of therapy in particularly advanced cases. Relapses do not occur after it, but many other negative consequences are observed. The main complication is that in patients the removal of secretions from the gland is disrupted, which is why the vaginal mucosa constantly dries out, which causes inconvenience not only during sexual intercourse, but also during life.
The most optimal method, according to patients, is laser treatment. After removal of the Bartholin gland cyst in this way, as women say, health is quickly restored, relapses are extremely rare, and there are no negative consequences. According to patients, this is the most gentle method of therapy and the most painless.
Removal of the Bartholin gland or extirpation is a radical surgical method that surgeons do not like to use because of its complexity and “bloodyness.” But sometimes complete excision of the gland becomes the only correct solution. Women who have had their Bartholin gland removed must undergo a course of rehabilitation therapy. Its features are discussed in the article.
Postoperative period of Bartholin gland cyst
Inflammation of the Bartholin gland associated with the formation of a cyst can only be treated surgically. The operation is carried out in the so-called “cold” period, when the stage of exacerbation of the inflammatory process passes. If the situation is not too advanced, gynecologists try to save the gland by performing marsupialization or enucleation of the cystic neoplasm itself. After surgery to remove a Bartholin gland cyst, the following measures must be taken:
- bacterial culture of the purulent contents of the cyst, its examination in the laboratory in order to identify pathological microorganisms that need to be treated with antibiotics;
- therapy with antibacterial drugs;
- taking vitamins and mineral complexes;
- attending physical therapy;
- daily replacement of gauze turundas in the wound, treatment of sutures with antibacterial solutions and healing ointments;
- taking medications that strengthen the immune system.
A woman should take care of herself after surgery, avoid sex, and avoid serious physical activity. A new penetration of infection into the ducts of the Bartholin glands, weakened by inflammation and disease, will lead to the formation of another abscess. Constant relapses of the pathology deplete the female body, and can even lead to blood poisoning. To prevent this problem, the gynecologist recommends removing the Bartholin gland completely. Excision of an organ requires careful actions by the surgeon, since there is a high risk of impaired hemostasis and severe bleeding.
By secret
- Incredible... You can cure a cyst without surgery!
- This time.
- Without taking hormonal drugs!
- That's two.
- Per month!
- That's three.
Follow the link and find out how Irina Yakovleva did it!
Representatives of the fair part can have a Bartholin gland cyst for a long time and not cause them any concern. Inflammation of the Bartholin gland can develop in a woman at any age. This happens due to injury, inflammation, or just like that.
A pregnant woman can have such formations, but she can give birth to a normal child. This disease does not affect the fetus in any way. Also, a woman can lead a normal sex life without any unpleasant symptoms.
A cyst is a cavity that is usually round in shape. There is usually liquid inside it. Education can be formed for the following reasons:
- Due to swelling or inflammation. As a result, fluid will accumulate in the tissues and a cyst may form.
- With a tumor of the genital organ. In some cases, such processes can occur without inflammation.
Removing a Bartholin gland cyst may not always be advisable, but doctors recommend carrying out such an event when pathology appears. Bartholin gland cyst can be treated without surgery. Bartholin gland cyst surgery is performed when such a formation poses a threat to the patient’s health.
But usually such a pathology is almost harmless and does not interfere with a woman’s life. If it is small in size, then you shouldn’t pay attention to it. Some women with this pathology may not have problems until old age.
But there are also times when surgery to remove a Bartholin gland cyst must be carried out without fail. This:
- Inflammation occurs and the gland begins to show unpleasant symptoms. In this case, surgical intervention is a necessary measure.
- When inflammation occurs periodically, you can try methods of medication and alternative treatment. Including when a Bartholin gland cyst appears during pregnancy.
- When the formation is large and it brings discomfort to the woman. She cannot have normal sex and puts a strain on the body.
- When, together with such a formation, there are also tumors of the labia. Then such material is removed comprehensively.
- At the request of the girl herself, when the tumor causes her discomfort.
If the manifestations listed above are observed, then the cyst can lead to more serious complications, and therefore it is recommended to immediately contact a gynecologist upon its detection for an examination and risk assessment. If ordinary inflammation occurs, it can cause more serious manifestations.
Recovery after removal of Bartholin's gland
If the Bartholin gland is completely removed, the postoperative period is prolonged for a long time. Severe hematomas and swelling appear in the vulva area, which disappear very slowly.
Recovery after removal of the Bartholin gland, as in the case of cyst excision, is associated with the elimination of pathogenic microorganisms that caused the pathology. Antibiotics are prescribed to achieve the following goals:
- reducing the risk of infection spreading throughout the body (for example, women with immunodeficiency or pregnant patients);
- elimination of symptoms of systemic infection (heat, fever);
- fight against pathogens of gonorrhea, chlamydia, methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus, discovered during the study of pus from a cyst.
If a woman has had her Bartholin gland removed, her postoperative period is associated with antibacterial treatment. The gynecologist prescribes the following groups of antibacterial drugs to such a patient to relieve inflammation:
In addition to antibiotics, a local treatment regimen is being developed using ointments and solutions that promote rapid healing of the surgical wound (Levomekol, Vishnevsky, Ichthyol). The doctor takes into account that postoperative antibiotic therapy disrupts the vaginal microflora, and therefore prescribes multivitamin supplements with Linex to support and restore it.
How to restore the functions of the Bartholin gland that remains?
Typically, a gynecological surgeon removes only one gland affected by cysts, fistulas and scars. A healthy Bartholin gland is preserved after surgery and continues to perform its functions “for two.” The woman’s task is to protect the organ from pathological bacilli. Antibiotic therapy helps her significantly with this. Additionally, you need to work on strengthening your immune system, changing your nutritional rules, and developing a diet. The following tips will tell you how to restore the Bartholin gland and its functions.
- Take care of the hygiene of the external genitalia. Wash yourself at least 2 times a day, using for this purpose a solution of potassium permanganate, antiseptic Citeal or a decoction of chamomile flowers. Cosmetics for intimate hygiene are also suitable for washing during the postoperative period.
- Give preference to loose underwear made not from synthetic materials, but from natural cotton.
- After surgery to remove one of Bartholin's glands, you should not wear pants or jeans that are too tight.
- During the rehabilitation period, do not use daily sanitary pads, as they are an ideal breeding ground for pathological bacteria. If you cannot do without pads, change them as often as possible (ideally every 2-3 hours).
- During menstruation, you cannot do without pads or tampons. A patient who has recently had her Bartholin gland removed should change her intimate hygiene products every 4 hours on her menstrual days. It is recommended to wash yourself before changing gaskets.
- During postoperative rehabilitation, it is better to give up sexual contact and masturbation.
Folk recipe
All recipes are aimed at using them to relieve inflammation and prevent tissue damage. Also, such remedies help relieve swelling and unpleasant symptoms. They can also be used to strengthen the immune system.
Recipe 1
Take nuts, hazelnuts and dill. Pour all this with honey product. Leave for 2-3 days. Take 5 milligrams per day.
Recipe 2
Take elderberry and nettle in equal proportions. Pour boiling water over and leave. Use for rinsing.
Recipe 3
Mix marigolds and chamomile. Pour boiling water over it. Cool the mixture and make baths. It is possible to add potassium permanganate to increase the effect.
Tips for patients
A cavity with problematic fluid does not always make itself felt immediately after its inception. If the stage of suppuration has not yet occurred, then the girl may simply feel a lump or unusual swelling in the intimate area. But since suppuration sometimes develops in a matter of days or even hours, it is better to immediately make an appointment with a gynecologist rather than wait for the worst development of events.
As soon as the immune system begins to weaken, this will indicate the start of a secondary infection. The cavity with biological material will begin to fill with purulent formations, raising body temperature, as well as signaling a sharp deterioration of the situation with other signs. When the suppuration mechanism starts, the woman will already be faced with an abscess of the Bartholin gland, which in the medical classification indicates a complicated form of the disease.
The fact that the patient has a high chance of encountering a cyst in a short period of time is evidenced by several indirect factors. They are not one hundred percent precursors to the collection of secretions in the formed cavity, but they are called high-risk aspects. The list includes the following diseases:
- infection with gonococci;
- urogenital candidiasis, which is popularly called simply thrush;
- ureaplasmosis;
- trichomoniasis;
- chlamydia.
Another high-risk item is poor genital hygiene. It is this nuance that expands the circle of potential patients, since even teenage girls can become victims of cysts.
It is not at all necessary that after the discovery of even a large cyst, the victim will be redirected to the oncology center. As soon as it is confirmed that the tumor does not carry an oncological plaque, there is no need to worry. When performing a planned surgical intervention, additional tests and other examination options are required if necessary. Only after the doctor is convinced that surgery is the optimal solution will the cyst be excised.
Moreover, different clinics offer their own package of basic services on a given issue. Today, most private medical centers use laser removal of an overgrown cavity that has an internal capsule with prolonged treatment. Radio wave treatment has proven itself to be successful and is less traumatic than the classic procedure with a scalpel.
Ladies who have undergone manipulation note that modern technologies not only provide less pain, but also guarantee a more aesthetic final result without loss of sensitivity of part of the genital organs. Innovative techniques also guarantee a shortened postoperative period, which will appeal to those victims who cannot leave work for a long time.
The price of the operation directly depends on what format of excision was chosen, as well as the type of anesthesia, included preliminary examination, and consulting services for the period after removal. The cost also varies depending on the reputation of the chosen medical center and the qualifications of the gynecologist-surgeon.
Laser
This is a modern technique for removing such formations, which has many advantages. But not all clinics perform such an operation, but only those that have special equipment and professional doctors.
This operation is carried out on the same principle as a regular one, but a laser beam acts as a scalpel. The advantage of this method is the following:
- Does not affect entire tissues.
- The operation is bloodless.
- It is carried out quickly (5-10 minutes).
- Does not require long recovery.
- Low chance of relapse.
Alarming symptoms
Signs of the formation of a problem cavity are most clearly visible in the area of the gland itself. If the cyst is still small, then it does not cause significant discomfort even during sex. But during the suppuration stage, it can grow literally before our eyes.
The most typical symptoms that indicate that you should immediately contact your gynecologist are:
- swollen labia;
- round bump of any size;
- pain when moving or staying in a stationary sitting position for a long time.
Things get worse when the Bartholin gland becomes susceptible to infection, which leads to the rapid development of bartholinitis. Such a turn becomes possible if pathogenic microorganisms have entered the already diseased area, negatively affecting the microflora of the vagina and external genital organs.
When the cyst becomes infected and begins to collect pus, the labia swell several times, and when palpating the unsightly-looking area, the victim experiences acute pain. Walking, even slowly, becomes almost impossible. Some patients note that in a supine position everything becomes even worse.
The appearance of an abscess is accompanied by a sharp increase in temperature by several degrees simultaneously with a rapid increase in the cyst up to eight centimeters in diameter.
At the final stage, there is a high percentage probability of self-opening of the lesion with accumulated secretions and purulent accumulations. Such an outcome threatens possible infection of nearby organs and tissues, so in emergency situations the patient may even be hospitalized by ambulance in intensive care.
Diagnostics
To confirm the diagnosis, it is necessary to undergo examinations by specialists such as:
- blood biochemistry and general analysis;
- antibiotic sensitivity smear;
- culture to determine microflora;
- microscopy of vaginal discharge;
- analysis for infections.
An examination by a gynecologist will show whether there is unilateral swelling of the labia, as well as their asymmetry, inflammation of the inguinal lymph nodes, and changes in tissue in the area of the cyst.
Postmenopausal women need a biopsy to rule out the development of malignant processes.
Classification of operations
There are several ways to get rid of a cyst. Moreover, they both often rely on local anesthesia. The only contraindication here is increased pain, which automatically indicates the need to use general anesthesia. But most women prefer to endure rather than subject their cardiovascular system to increased stress during general anesthesia. The surgeon has the final say.
Schematically, all approaches to getting rid of a cavity with secretions are divided into:
But sometimes it’s not possible to cope with gentle workarounds. If there are serious complications, it will be more productive to remove the entire organ. The doctor removes the duct along with the gland. Since the technique has several side effects, such as the lack of lubrication, it is practiced extremely rarely only in matters of preserving the life of the patient.
Most often, patients manage with marsupialization. The measure works well in situations where the victim faces regular relapses. Surgical intervention is based on the new formation of the duct along with the opening.
Marsupialization is necessary to further restore the patency of the excretory duct in order to effectively improve the functionality of the gland in the future. It is also aimed at eliminating possible post-inflammatory consequences that lead to the formation of abscesses in the cyst cavity.
When operating on the area that appears to be the most swollen outwardly, an incision is made on the mucosa. An identical action is performed on the cyst. After that, rinse the cavity with special solutions, so that the cyst shell can then be sewn to the area of the labia mucosa. Such scrupulousness is the key to the construction of a new excretory duct.
Some gynecologists, under the guise of classical marsupialization, open the cyst without any additional measures. This means that the contents are cleaned out and then rinsing is prescribed. The epithelium simply does not have time to form a protective film.
Experienced experts insist that this is not only harmful, but also almost always leads to a repetition of the picture: the duct will become clogged; the cyst will grow back.
It is much more effective to install a catheter that contains a bubble inside. It is designed to stand for several weeks, which is quite enough for a bypass channel to form with minimal chances of relapse even after several years.
For all of the above, local anesthesia is relevant. And if, after completing the procedure, the woman feels normal, then she is not kept in the hospital, but is sent home. A mandatory precaution here is to avoid sexual contact for at least a month.
It is much more difficult technologically to remove a Bartholin gland cyst. First, the surgeon makes an incision that is directed away from the labia minora. Making an incision in reverse order is a rather dangerous undertaking, since in this part of the body the mucous membrane is especially sensitive. The entrance to the vagina, which is lined with a mucous layer, quickly becomes thinner due to the negative impact of the disease. When cut correctly, the borders of the edges diverge only a couple of millimeters.
Next, the dehusking algorithm is saved as follows:
- The incised tissue is pushed back using Pean clamps and gauze swabs.
- The contents are squeezed out carefully.
- The risk of cyst rupture is controlled, which is easy to do by monitoring the situation, making an accurate cut and maintaining the same tempo of the operation.
If you reduce the set rate, then the likelihood of contamination of the open wound surface increases significantly. The final stage involves stitches, which are applied in the amount of two pieces.
It is extremely important to pay attention to the fact that during enucleation the victim loses a lot of blood, so it is important to constantly monitor the situation. To reduce the load, it is enough to simply bandage the branches that are weakening from hemorrhage. For venous wounds, tourniquets are used, which must completely cover the bed.
After applying the tourniquets, you will need to remove the immersed sutures, and at the very end the Peana clamps are removed. All that remains is to wait for the epidermis to retract so that the wound becomes smaller.
The doctor secures the incisions and the wound itself with vicryl.
You should prepare for a fairly long rehabilitation period. In addition to the standard swelling of the vulva, you will have to come to terms with the fact that the external genitalia will be surrounded by a hematoma. There may be pain and slight discharge.
In the future, you will need to adhere to preventive measures to prevent a recurrence. We are talking about a general increase in immunity, as well as redoubled efforts devoted to personal hygiene.
Clinical picture
Symptoms of bartholinitis are expressed to varying degrees, depending on the intensity of the inflammatory process. They appear acutely, often after hypothermia, menstruation, childbirth, abortion or unprotected sexual intercourse. First, a woman feels tingling, pain, heat, heaviness in the labia, which intensifies with movement and makes sexual intercourse painful or impossible. Along with this, general health worsens: body temperature rises to 38 degrees C, appetite disappears, headaches, and general weakness occur. Gradually, the pain in the perineum increases, becomes pulsating, the woman finds it difficult to walk and sit, and night sleep is disturbed.
Acute bartholinitis in most cases develops on one side. The labia majora at the site of the gland swells, increases in size, and its skin turns red. In the thickness of the lip, a painful lump ranging in size from one to several centimeters is felt - the gland itself. If the inflammatory process does not involve the surrounding tissues, then the skin above it is mobile and easily moves. When subcutaneous fat is involved, the epidermis becomes fused with it and loses its mobility. Often the inguinal lymph nodes react to inflammation; they increase in size and become visible in the form of round, dense formations under the skin. After some time from the formation of an abscess, it may burst outward with the flow of yellow-green pus.
After acute inflammation subsides, the disease enters the chronic stage. At first, the symptoms completely disappear and the woman feels healthy. This period of calm lasts from several months to several years, but any decrease in immune defense leads to an exacerbation of bartholinitis. Pain and swelling in the labia area, discomfort when walking, sitting, and sexual intercourse reappear. The temperature does not always rise and does not reach high values. As a rule, general health does not suffer.
Sometimes the inflammation is mild and occurs unnoticed by the woman or with minimal symptoms that are easy to miss. If, as a result of the disease, the patency of the gland duct is disrupted, then the gradual formation of a cyst begins. In the thickness of the labia majora, at its base, a subcutaneous volumetric formation of a round shape appears, painless to the touch, not fused with the surrounding tissues. It bulges outward, partially covering the entrance to the vagina. If both Bartholin glands are affected, the vestibule can be completely blocked, and sexual intercourse becomes painful due to the dryness of the external genitalia.