After cervical canal polyp surgery
After the operation, most women gradually return to a normal lifestyle. But some people experience certain complications. There are nagging pains, stagnation of fluid in the area of the cervical canal and an irreversible process of formation of adhesions. These processes arise as a result of violation of certain rules of the operation. Most often this is infection or insufficient removal of the tumor. Also, a typical symptom may be constant bleeding from the vagina, which gets bigger and bigger each time. To stop this process, it is necessary to remove the polyp that remains there again.
In the postoperative period, you must follow some doctor's recommendations. These are:
- It is prohibited to use drugs that thin the blood. This can cause bleeding at the site of the removed polyp.
- It is necessary to constantly monitor vaginal discharge. If bleeding does not stop within 7 days after surgery, you should think about a complication and consult a doctor.
- Lifting heavy objects and playing sports are strictly prohibited for the first three months.
- You should avoid sexual contact with your partner for about 2 months. It is also not recommended to insert tampons into the vagina.
If you follow the above recommendations, you can avoid a deterioration in your general condition. After surgery, removal of a polyp of the cervical canal, you should also prohibit drinking alcohol and tobacco. Polyps in the uterus - removal, how long to stay? It is advisable to observe bed rest in the first days of the postoperative period. After all, rest will allow the postoperative wound to recover normally.
Therapy after removal of a polyp of the cervical canal is based on restoring hormonal levels and relieving various discomforts after surgery. The most important goal in the postoperative period is to prevent the reappearance of a tumor, both in the cervical canal and in the uterus. The duration of recovery can vary from 2 to 5 months. This period of time must be used so that later you no longer return to the past problem. Using various medications, physiotherapeutic procedures, as well as other doctor’s recommendations, you can quickly recover and live a normal, full life. Having the opportunity to leave offspring is the main task of the mother.
Also, after the operation, the following drug regimens are prescribed:
- Antibacterial and antimicrobial therapy.
- Hormonal drugs.
- General strengthening therapy.
- Taking vitamins and minerals.
- Diet.
As for medications and dosages, this is prescribed exclusively by a doctor. Taken together, these prescriptions have a good effect on the rate of relief of the disease.
After surgery, every 3-4 months you need to visit a doctor and conduct ultrasound diagnostics. Also, dynamic monitoring of blood counts will make it possible to exclude or confirm the process of inflammation and infection.
Removal of the cervical canal polyp and the discharge that is observed should decrease and disappear within 6-7 days. If this does not happen, then you must notify your gynecologist. As mentioned above, success in the postoperative period is compliance with all doctor’s recommendations. After all, such a neoplasm as a polyp is an unpredictable disease. Some polyps do not change their size for years, and some increase several times in a month.
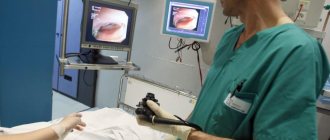
Endometrial polyps of the uterus are a common variant of the development of focal pathology of the organ mucosa. Pathology can occur both in reproductive and premenopausal ages. Several methods are used to remove a polyp in the uterus, hysteroscopy is one of them. The procedure is a surgical intervention and is one of the ways to get rid of pathology, which is carried out under general short-term intravenous anesthesia.
The duration of anesthesia is from 15 to 20 minutes. The use of high-quality products makes it possible to achieve complete pain relief during the procedure, and the drugs used for anesthesia are well tolerated by patients.
How to prepare
Before the operation, simple preparation for the intervention is required. It consists of taking tests before hysteroscopy of the uterus; if all the results are normal, then a day is set for the procedure.
The set of tests required to prepare for hysteroscopy of the uterus includes the following studies:
- blood and urine tests;
- determining the degree of cleanliness of the walls of the organ by taking a smear;
- ECG;
- determining the presence of chronic pathologies and consulting with a specialized doctor.
During the period of preparation for hysteroscopy, the doctor may prescribe antibiotics or hormonal drugs. This is required to reduce the risk of postoperative complications.
To prepare for the operation, a cleansing enema is performed before the procedure, hair is also removed from the genitals, and the bladder is emptied immediately before the procedure.
How are polyps treated?
After diagnosing the disease, the doctor can prescribe non-surgical treatment of polyps or conservative treatment (surgical method).
Non-surgical treatment:
- Hormonal drugs: COCs or gestagens. Combined oral contraceptives (COCs) contain estrogen and progesterone. They normalize the balance of these hormones in the body. Gestagens normalize the functions of the endocrine system. As a result of the work of these drugs, tumors stop developing, the risk of developing a cancer tumor decreases, and blood loss and pain are reduced.
- Anti-inflammatory drugs and antibiotics. Prescribed for genital infections and inflammatory processes in the pelvic area.
- Vitamins. Vitamins and minerals activate the body's immune system. Doctors recommend taking complexes containing B vitamins, iron, zinc, and magnesium. They help improve blood composition, stimulate cellular metabolism, metabolism and protein synthesis.
The surgical method of treating polyps is used in cases where there is a high probability of developing a cancerous tumor, when the tumor is large, when the recommended medications are not suitable for a particular patient. Polyps on the cervix are removed in the following ways:
- hysteroscopy;
- diathermocoagulation;
- cryodestruction;
- radio wave method;
- polypectomy;
- complete removal of the cervix.
Operations are performed under local or general anesthesia. To treat patients, doctors give preference to organ-preserving operations, but in some cases complete amputation of the uterus is necessary, especially with a high risk of cancer.
The most popular methods are polypectomy and hysteroscopy:
- Polypectomy - removal of a polyp by curettage or unscrewing.
- Hysteroscopy – removal of a tumor using an endoscope equipped with a microcamera.
After surgery, diagnostic curettage is required, followed by restorative treatment. During the recovery period, many women are bothered by spotting and spotting. Some of them are normal, others are signs of complications due to severe cervical spasm.
On what day of the cycle is the polyp removed?
In most cases, hysteroscopy is an elective procedure. Doctors do hysteroscopy on the 3rd day after menstruation. When choosing the moment for the procedure, gynecologists recommend focusing on the period from 6 to 9 days after the start of menstruation, which is associated with the occurrence of restoration processes in the mucous membrane during this period.
The choice of timing may influence the likelihood of postoperative recurrence of endometrial polyp.
Recovery after polyp removal
Despite the fact that the operation is performed through the vagina, without implying any incisions in the abdominal cavity, the woman faces a long rehabilitation period. It begins with bed rest in a hospital ward. The patient will receive antibiotics, anesthetics and anti-inflammatory drugs for 7-9 days.
Among the postoperative symptoms, the woman will feel nagging pain for the first week. She may also be bothered by copious discharge mixed with blood. During this period (and at least another 3-4 months), you should use only pads, and in no case tampons.
After being discharged from the hospital, the patient should “rest” at home for another week or two, especially if she has a hard job. After all, for the next month she cannot lift weights, bend over, or squat sharply. You will have to forget about sexual relations for 2 months, until the internal wounds are completely healed. Baths, saunas, swimming pools are also temporarily prohibited.
How to delete
In medicine, several methods are used to remove tumors of the uterine mucosa. The choice of technique depends on the clinical picture characteristic of the disease, the volume of the pathological formation, the type of tumor and its shape.
Removal of the tumor is carried out in the following ways:
- hysteroresectoscopy of the polyp using radio wave technique;
- surgery to remove polyps using a laser method;
- hysteroresection with curettage.
The latter method is called separate diagnostic curettage (SDC), which is used when it is necessary to perform a biopsy of mucosal material.
Polyps can be removed using an electric loop. Surgical removal of a polyp is a simple operation, but requires an appropriate level of training from the doctor, depending on the surgical method used.
Symptoms
Depending on what type of polyp a woman has and what size it is, different symptoms of the disease occur. At the same time, there are general symptoms characteristic of neoplasms in the uterine cavity. These include:
- the appearance of blood between menstruation (spotting or heavy bleeding reminiscent of menstruation);
- painful periods that are irregular;
- aching pain in the lower abdomen;
- pain (from mild to severe) during sexual intercourse;
- bleeding after sexual intercourse;
- the appearance of discharge with an unpleasant odor, which may have a yellowish tint (this symptom occurs when a polyp located in the uterine cavity becomes infected and inflamed).
Due to the fact that polyps can bleed, the patient usually develops anemia, which is characterized by pale skin, dizziness, general weakness and increased fatigue. Tinnitus and irritability may also occur.
In women after menopause, the symptoms of this disease are manifested by the appearance of uterine bleeding (resembling menstruation). The inability to get pregnant can also be one of the symptoms of endometrial polyposis. Therefore, women who are unable to conceive a child must undergo a full examination, including to exclude the presence of polyps in the reproductive organ.
If we talk about the symptoms of pathology in accordance with the type of polyps, it should be noted that each type has its own characteristics of clinical manifestations. So, if a woman has a glandular endometrial polyp or an adenomatous one, then they are formed against the background of endometrial hyperplasia and are hormone-dependent neoplasms. Accordingly, such women experience other symptoms characteristic of hormonal disorders, these are:
- obesity;
- hyperglycemia;
- uterine fibroids;
- polycystic ovary syndrome and other diseases.
Unfortunately, this type of polyp occurs in 70% of women with this pathology and, since they are prone to malignancy, after their detection, urgent removal of the endometrial polyp is required.
The second type is autonomous. These include fibrous and glandular fibrous endometrial polyps. The symptoms in this case are not complemented by other signs of disruption of the organs and systems of the body.
Endometrial polyps
Postoperative period
The postoperative period under normal conditions is calm. After 2-3 days, the unpleasant sensations disappear.
Recommendations after hysteroscopy during the recovery period depend on the individual characteristics of the body, the volume of pathological formation and the presence of concomitant diseases.
Recovery
When recovering from hysteroscopy, you should follow the regimen recommended by your doctor.
During the rehabilitation period, it is recommended to abstain from sexual intercourse, prevent overheating of the body, provide adequate nutrition, and also limit stress on the body.
Even more interesting:
Ulcers due to thrush in women
Pits on fingernails reasons photo
What not to do
No diet is required after polyp removal. The main prohibitions relate to sexual intercourse and physical activity, this is due to the high likelihood of heavy bleeding.
Restrictions should be observed for 2 months - the standard recovery period. Following the doctor's recommendations helps prevent infection of tissues injured during surgery.
How long to stay in the hospital
If there are no complications, the woman is kept in hospital for three days. When using a laser, the patient does not stay in the hospital.
Indications for interventions
A planned surgical operation is carried out if there is a history of:
- Large polyps (more than 10 cm) cause blockage of the fallopian tubes and cervical lumen, and can degenerate into malignant tumors. Their presence in the canal interferes with pregnancy or may be one of the reasons for spontaneous abortion.
- Age after 40 years - hormonal changes in this age period contribute to the occurrence of multiple polyposis.
- Ineffectiveness of conservative therapy - hormonal drugs, as a drug treatment, should stop the growth and spread of polyps. If this does not happen, surgery is recommended.
- Infertility – treatment consists of removing large polyps from the endometrial walls.
- Adenomatous polyps - almost always degenerate into cancerous tumors and are removed as a matter of priority.
Conservative therapy is powerless against these growths and always requires surgical intervention. Removal of a polyp of the cervical canal is a vital necessity.
Is it necessary to remove a polyp in the uterus?
As for excess weight, this is a factor that contributes to the occurrence of endometrial hyperplasia due to the fact that adipose tissue produces a certain amount of estrogens (female sex hormones produced by the ovaries in the first half of the menstrual cycle).
Surgical removal of the endometrial polyp is the only way to get rid of it. When discharged from the hospital after endometrial polyp surgery, the patient should receive detailed recommendations on further actions.
In some cases, if necessary, determined by a doctor, a pregnant woman may be prescribed polyp removal in the early stages of pregnancy. The shape of the polyp can be different: round, teardrop-shaped, flattened in the form of an almond, complex in the form of a cockscomb, etc.
However, some of the relapses (in our opinion, about 20%) can be attributed to non-radical removal of polyps. The final verdict belongs to the histological examination of the endometrial polyp, the information content of which is close to 100%.
However, the final diagnosis indicating the type of GPE is established after a histological examination of endometrial scraping.
But, knowing how curettage is done, doctors recommend replacing it with hysteroscopy.
From a morphological point of view, endometrial precancer includes hyperplasia with atypia (atypical hyperplasia) and adenomatous polyps.
Thus, fibrous polyps may resemble uterine fibroid nodes, and if such a formation is large, its surface may be mistaken for an atrophic mucous membrane.
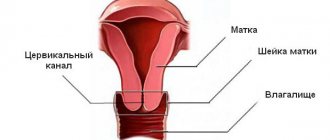
Uterine polyps are benign neoplasms that are formed due to the pathological growth of the endometrium - the mucous membrane of the uterus. Polyps can be of different sizes - from 1 mm to 3-4 cm. They have the shape of a mushroom and are a tubercle on a thin stalk.
Polyps can be isolated from each other or form groups of growths. In the case of multiple polyps, doctors diagnose uterine polyposis. Lack of treatment can lead to the spread of tumors to the cervix and vagina.
USEFUL INFORMATION: Sperm. How long do they stay in the egg?
The danger of uterine polyps is that over time they can turn into malignant tumors. Although the probability of this is only a few percent, the disease requires constant monitoring and timely treatment.
Removal techniques
Subtypes of surgical intervention are used:
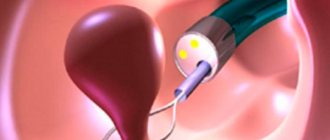
- Polypectomy – excision or twisting of a growth from the wall of the cervical canal, used for polyps up to 3 cm in size. The bed of the tumor is cauterized.
- Laser coagulation – excision of the stem of the growth due to laser radiation, while coagulation of the vessels feeding it occurs. The operation is performed with minimal risk of bleeding and is approved for use for formations of any size. It is better to remove a polyp of the cervical canal using this method.
- Cryodestruction - occurs by freezing the polyp stalk with liquid nitrogen, followed by its extraction. The technique is low-traumatic and does not leave scars.
- Diathermoexcision – destroys the base of the tumor using a loop with an electric current passed through it. The method is recommended in the presence of cervical deformity and wall dysplasia. There is a risk of formation of adhesions and erosions.
- Coagulation by radio wave method - using the Sugitron device, a safer option (3 times compared to the previous one).
After the manipulations, the cervical canal polyp is sent for histological examination, the waiting time for an answer is up to 14 working days.
Varieties
Polyps vary in shape and size, as well as in the tissues that form them. The shape of polyps can be oval or round. The size varies from a few millimeters to one to eight centimeters. Polyps of the cervical canal grow up to two to three centimeters.
Gynecologists distinguish the following types of polyps of the uterus and cervical canal depending on the forming tissues.
- A glandular polyp is formed due to glandular cells that predominate over stromal cellular elements. Quite often, such neoplasms form in young patients.
- Placental uterine polyp is formed from placental tissue after childbirth, pregnancy and miscarriage.
- A fibrous polyp is formed from connective tissue cells. The glands are single in nature. There is a small number of vessels that have sclerotic, thickened walls.
- Mixed or glandular fibrous polyp is a rare variety. Such neoplasms occur in women with a stable cycle. The glands are irregular in shape and vary in length. Stromal elements predominate in the structure. The vascular walls are distinguished by sclerosis and thickening. Glandular fibrous polyps often have signs of inflammation, as well as circulatory problems.
- Adenomatous polyp of the uterus is uncommon. Characteristics of this form are considered to be the spread of glandular tissue and focal proliferation with atypical cells. The glands are irregular in shape and small in size. Sometimes the formation of false papillae is observed. Cells have polymorphism and a violation of the ratio of nucleus and cytoplasm. In addition, pathological mitosis is noted.
From the point of view of malignant degeneration, glandular and adenomatous polyps of the uterus and cervical canal are dangerous.
Postoperative period
Does not provide a stationary regime. An hour after surgery, the patient goes home. The development of complications in the hands of the sick person - if certain rules are not followed, it is possible to independently provoke x occurrences.
The attending physician indicates the time of the next visit and explains in detail subsequent changes in the functionality of the female reproductive system, with a mandatory warning against possible side effects.
Observation
The patient is recommended to have a certain (depending on the type of polyp and the body’s response to the intervention) frequency of visits to the gynecologist, which is reduced to a scheduled examination every six months 3-4 months from the day the operation to remove the polyp was performed.
Strict adherence to prescribed procedures will speed up the healing process.
Medication prescriptions
They are carried out strictly according to indications and take into account the general condition of the patient’s body.
Correction of hormonal levels
When glandular (glandular-fibrous) tumors are removed, the doctor prescribes hormonal correction. The goal of treatment is to restore hormone levels and normalize the cyclicity of menstruation.
Hormone therapy includes:
- up to 35 years - estrogen-gestagen contraceptives (Yarina, Zhanin, Regulon) are recommended for use;
- after 35 years of age - drugs of the gestagen group (Norkolut, Duphaston);
- "Mirena" spiral - with installation for 5 years, the drug is considered a modern method of treating gynecological pathologies, without pronounced adverse reactions of the body (unlike hormonal drugs).
A polyp of the cervical canal cannot be cured with hormone therapy, but its further growth and spread can be stopped.
Antibacterial therapy
It is used as a prophylactic against possible infectious complications, with a duration of use ranging from 2 to 10 calendar days. It is prescribed according to indications; in some cases there is no need for it.
Indications for prescribing antibiotics are:
- chronic manifestations of genitourinary infections;
- excision of polyposis using a loop, unscrewing and gynecological curettage;
- when recurrent polyps occur against the background of chronic inflammation.
Lifestyle requirements
Polyp of the cervical canal, the treatment of which, in addition to surgery, requires additional measures. In the early postoperative period, there are a number of prohibitions, the exact implementation of which will not reduce the functionality of the autoimmune system and prevent the occurrence of complications:
- During the first month (one menstrual cycle), any sexual contact is strictly prohibited.
- Increased physical activity can provoke additional congestion to the pelvic organs or increase blood pressure, both options are provocateurs of bleeding from surgical wounds. During the calendar month, those undergoing surgery are prohibited from engaging in heavy physical labor and raising children.
- You should not go into a strict rest mode - reduced activity during this period will lower the overall tone of the body and delay recovery indefinitely.
- Any warming activities - saunas, baths, steam rooms, sunbathing and heating pads in the lower abdomen can develop an inflammatory process.
- For daily hygiene, showering and washing are recommended - baths, public ponds and swimming pools are strictly prohibited - to avoid introducing infection into the healing area.
- For hygiene purposes, use gynecological pads. Tampons are a source of third-party infection.
- Morning and evening temperature measurement, recorded in a notebook - for the attending physician.
- Avoid constipation - switch to a balanced diet.
- Do not ignore the urge to urinate and defecate.
Endometrial hyperplasia during pregnancy
The most common concomitant of endometrial hyperplasia is infertility. During examination of patients with primary infertility, endometrial hyperplasia is diagnosed in every fifth of them. Pregnancy against the background of diffuse endometrial hyperplasia of a hormonal nature is impossible.
For pregnancy to take place, two prerequisites are necessary:
— The presence of ovulation, which means readiness for fertilization;
— Endometrium “prepared” for the development of a fertilized egg. In the first phase of the cycle, under the control of estrogen, the functional layer of the endometrium grows, but, unlike hyperplasia, these changes are physiological. It is their patients who are sometimes mistakenly called endometrial hyperplasia.
Pregnancy will occur only if there is a two-phase cycle with a physiological change in the dominant hormones. In the overwhelming majority of cases, endometrial hyperplasia develops with severe hyperestrogenism and gestagen deficiency, there is no ovulation, and pathological changes occur in the endometrium that exclude the development of pregnancy.
A rare exception is the situation when endometrial hyperplasia has non-hormonal causes and occurs against the background of a two-phase ovulatory cycle. This applies to cases of focal hyperplasia, when a focus of pathological growth of endometrial tissue - a polyp - appears on an unchanged functional layer. The further scenario of events has two directions:
1. The fertilized egg enters the uterus and implants (takes root) in its healthy part. If the polyp is not large and does not interfere with the development of pregnancy, it is monitored, and after childbirth it must be removed. It is possible that a polyp threatens the normal course of a developing pregnancy, in which case a decision may be made to remove it. Situations like this happen extremely rarely. Endometrial polyps can only be removed in the early stages of pregnancy.
2. If the polyp is located on the way of the fertilized egg to the uterus, pregnancy will not occur. A similar ending will happen if the fertilized egg tries to “locate” in the area of the polyp - implantation will not occur, and pregnancy will not occur.
Large endometrial polyps can cause premature birth and uterine bleeding in pregnant women.
To avoid unwanted situations, it is necessary to undergo a gynecological examination before the desired pregnancy occurs.
The diagnosis of endometrial hyperplasia does not mean a death sentence for reproductive function; with timely adequate therapy and elimination of the causes, endometrial hyperplasia regresses.
USEFUL INFORMATION: What is ICSI
Discharge and menstrual cycle
Bleeding and discharge during the postoperative period
The discharge after removal of the polyp of the cervical canal is represented by slight bleeding and discharge of mucous contents. As a protective reaction of the body, mucus is secreted - it has specific disinfecting properties and prevents the development of infectious processes in the body of the uterus.
A modern operation that removes a polyp of the cervical canal of the cervix involves a slight release of cervical secretion. It contains a mixture of mucus, blood and ichor. With varying degrees of intensity, from smearing to mixed, after a short period it fades away.
In the absence of postoperative complications, normal discharge (blood) is present for no more than 7 days, the mucous membranes also return to normal levels within the specified time. The course of the period after surgery according to these criteria is the main sign of proper wound healing when removing growths.
All other discharge after removal of a polyp is a sign of unplanned processes occurring in the body in the form of complications.
Restoration of the menstrual cycle
Any operation is a serious stressful situation for the body, and interventions in the cervical canal area change the structural structure of the endometrium. The normative (habitual) menstrual cycle returns to normal levels within six months, and its regularity is restored. The arrival of the first cycle should occur 5-8 weeks from the date of surgery.
Half of the women undergoing surgery note that when the first menstruation arrives, the condition returns to normal - without deviations, with stable criteria. Those who remained noticed that after the removal of the polyps, the discharge changed in abundance, duration and volume. Changes go from abundant to meager and vice versa.
Warning is caused by heavy, prolonged periods (7-10 days), accompanied by sharp, debilitating pain in the lower abdomen, radiating to the lower back or back. If they appear, you need to contact a medical facility.
Pregnancy after removal of polyposis
Permitted by the attending physician no earlier than six months after the operation and completion of a course of drug therapy. After hormonal treatment, the desired pregnancy occurs within a few months.
Pregnancy after removal of a polyp of the cervical canal should be additionally observed by its leading gynecologist - in order to avoid recurrence of polyposis and the threat of miscarriage.
Complications in the postoperative period
During the period of planned rehabilitation, various complications may occur. Their appearance is a rather rare option, appearing for various reasons. The main root cause is considered to be an insufficient level of preparation for the operation itself - preventive measures were not used before the actual excision of the polyp.
In the preoperative period, the acute phase of diseases was not treated either in the pelvis or in the entire body. The pathogenic factor, against the background of a weak immune response, is transferred to the healing site along with the bloodstream. This creates a focus of inflammation in the previously operated area, which significantly worsens the rehabilitation process.
Due to these phenomena, surgery to remove polyps in the cervical canal is recommended to be performed routinely, rather than through emergency surgery. Planned operations are possible only if the sick are treated appropriately – undergoing examinations and paying close attention to their own health.
If obvious signs of complications appear, you should urgently contact a gynecologist:
- with an increased amount of bloody (mucus) discharge;
- pronounced unpleasant odor of discharge;
- the appearance of painful pulling sensations and their intensification in the lower abdomen;
- low-grade body temperature;
- general deterioration in general health;
- abrupt cessation of any kind of discharge.
In the normative state, none of these signs should be present; their appearance signals the beginning of the process and requires immediate contact with the local gynecologist. It must be remembered that any disease in the acute phase is easier to treat than the advanced form.
Major complications
- Inflammation of the uterus - occurs against the background of an untreated infectious disease, inflammatory processes and violation of septic and antiseptic rules during surgery (poorly sterilized instruments, insufficient treatment of auxiliary premises and equipment). Antibacterial therapy is recommended as treatment.
- Perforation of the uterine wall is an accidental puncture that occurs due to poor dilation, loose walls and low qualifications of the specialist. Large injuries are sutured, small ones are capable of self-healing. Treatment with antibiotics is also carried out.
- Hematometer - formed during spasmodic compression of the cervix, expressed in a sudden cessation of discharge and the occurrence of a pronounced pain syndrome. The associated infection is treated with anti-inflammatory drugs, and the pain is relieved by prescribing antispasmodics.
Possible complications and consequences
In rare cases, complications of the postoperative period occur during planned rehabilitation.
Most often, they appear due to insufficient preparation for surgery: if preventive measures were not taken before removing the polyp - treatment of acute diseases not only in the pelvis, but throughout the body. With the blood flow, the pathogenic factor under certain conditions can be transferred to the healing site. This causes a sharp deterioration in the rehabilitation process and creates a focus of inflammation in the operated area. Therefore, surgery to remove a cervical polyp is recommended not as an emergency procedure, but as a planned procedure, after serious preparation. This is only possible if the patient takes a responsible attitude towards her health: regular examinations by a gynecologist maintain women’s health at the proper level.
The following phenomena should cause caution:
- increased amount of mucous and/or bloody discharge;
- unpleasant odor of discharge;
- the appearance or intensification of pain in the lower abdomen, most often pulling;
- temperature rise to subfebrile level;
- abrupt cessation of all discharge;
- general deterioration of health.
Normally, none of this should happen. If at least one of these signs appears, you should immediately seek medical help. In the initial stage of inflammation it is much easier to cope with the situation than in an advanced case.
Important! If for some reason the operation was performed under general anesthesia using curettage, i.e. in a large volume, it may bleed a little more intensely and a little longer.
In the long term after surgery to remove a polyp, the cervical canal may bleed for many reasons, including those not related to the surgical intervention. In any case, unexpected bleeding of any intensity, with or without pain, should be a reason for a visit to the antenatal clinic.
Preventive actions
Prevention is aimed at preventing the formation of growths in the cervical canal area:
- It is recommended to undergo a medical examination at least twice a year by the attending gynecologist;
- promptly treat endocrine pathologies and various gynecological diseases;
- it is necessary to reduce the risk of injury to the cervix - do not resort to abortion using contraception;
- observe the minimum requirements of intimate hygiene;
- seek help for extramenstrual bleeding and primary signs of disease.
A cervical canal polyp is not a cosmetic defect, but a serious health problem. Refusal of medical care can lead to the development of cancer
Treatment of endometrial polyp
Diagnosis of the benign neoplasm in question, as a rule, does not present any difficulties for the doctor - it is enough to give the patient an ultrasound examination of the pelvic organs.
The main method of treating endometrial polyps is surgical intervention, when the tumor is simply removed from the uterine cavity. This operation is called hysteroscopy, it is carried out using a special instrument - a hysteroscope, inserted into the uterine cavity. During the work, the surgeon examines the uterine cavity and removes the polyp. During the operation, a scraping of the endometrium is required - this biomaterial is sent to the laboratory for histological examination, which makes it possible to determine the type of polyp.
Subsequent treatment tactics depend on the type of polyp and the age of the patient. If histological examination shows that the neoplasm has a fibrous structure, then no therapy is performed. If glandular fibrous or glandular polyps are detected, the patient is shown hormonal therapy, which will normalize and stabilize the menstrual cycle and the overall hormonal balance in the body.
Hormonal therapy is carried out over a long course (from 3 to 6 months), the doctor usually prescribes certain drugs:
- Yarina, Janine, Regulon - estrogen-gestagen contraceptives that are excellent for women under 35 years of age;
- Duphaston, Utrozhestan - gestagens, they are usually prescribed as postoperative therapy for women over 35 years of age;
- intrauterine system "Mirena" - it releases the hormone levonorgestrel into the uterine cavity, it is placed in women who do not plan a pregnancy in the next 5 years.
It is worth paying special attention to one point: if a histological examination of the biomaterial revealed an adenomatous form of the polyp, then radical treatment will be required, since this form of polyps is considered a precancerous condition. If a woman is already 45 years old, then doctors perform a complete removal of the uterus; in the case of a combination of the disease in question with endocrine disorders, it is recommended to remove the appendages as well
Women of reproductive age will have to undergo a long course of hormonal therapy, which will allow them to become mothers, but when menopause occurs, doctors will insist on surgical treatment.
Endometrial polyps, at first glance, are absolutely safe formations. But a woman must remember that under certain circumstances, such a benign formation can become malignant. Therefore, if even minor gynecological health problems arise, you need to contact a gynecologist who can diagnose the problem in a timely manner and prescribe effective, low-traumatic treatment.