Concept, diagnosis and types of avascular anechoic formation
The ability of tissues to absorb ultrasound is called echogenicity. An ultrasound sensor is used to read the echo data reflected from a specific organ. The totality of the information obtained is displayed on the monitor screen and built into a single image, the analysis of which allows the specialist to draw a conclusion.
Sometimes, during an ultrasound, anechoic formations are detected in the appendages, that is, those from which sound is not reflected. On the monitor screen they appear as dark spots. Most often, cysts are anechoic because there is fluid inside them, which does not allow echoes to form.
Avascular formation of the ovary: what is it? This is the name of a neoplasm of the appendage in which circulatory processes do not occur. Since malignant tumors have a blood supply, an anechoic avascular lesion of the ovary is a benign cyst that does not have a blood supply and is filled with fluid inside. To find out what specific pathology we are talking about, you need to consult a doctor.
A benign cyst of the appendage, filled with liquid contents, usually gradually grows. At first, it does not remind you of itself in any way or causes nagging pain in the lower segment of the abdomen, as well as disruptions in the menstrual cycle.
Anavascular anechoic formations are:
- functional ovarian cysts,
- paraovarian formations.
This type of avascular neoplasm of the ovary includes:
- Follicular cyst. Usually it does not pose a threat to a woman’s health and disappears spontaneously after 1-3 cycles. Such an abnormal inclusion appears due to the failure of ovulation and a further increase in the size of the follicle. It produces estrogen, which interferes with progesterone production and conception. A formation that is of impressive size or leads to a deterioration in a woman’s well-being requires removal, otherwise it may become twisted.
- A corpus luteum cyst appears because fluid accumulates in its center. The presence of such an abnormal inclusion is a common cause of epididymal apoplexy. On the echogram it is localized behind, to the side of or above the reproductive organ. Dimensions range from 3 to 6.5 cm. As a rule, the corpus luteum cyst undergoes reverse development after 2-3 months from the moment of formation. It must be removed when it exceeds the permissible size and worsens the woman’s well-being.
A paraovarian avascular formation in the ovary has a diameter of 0.5 to 2.5 cm, and on ultrasound is defined as an abnormal inclusion of an ovoid or round shape with thin walls, filled with anechoic homogeneous contents or a fine suspension. The presence of a paraovarian cyst can be assumed by visual assessment of an intact ovary. You need to be able to distinguish it from ectopic pregnancy and a number of other pathologies.
Paraovarian formation in the ovary does not spontaneously resolve. It usually grows over time. In this case, the woman from time to time feels pain in the lower abdomen or sacrum, which becomes more pronounced when playing sports, but suddenly disappears. An abnormal inclusion can put pressure on the bladder and intestines, causing disruption in their functioning. The occurrence of torsion of the pedicle of the neoplasm, accompanied by the clinical picture of an acute abdomen, cannot be ruled out.
The paraovarian cyst is almost immobile and progresses very slowly. It increases due to the accumulation of fluid and stretching of the walls. Typically, such a formation measures from 8 to 10 mm, but in rare cases it can increase to the size of a newborn baby’s head. Inflammatory diseases of the reproductive system, metabolic disorders, early entry into puberty, multiple abortions, infectious venereal diseases, constant use of hormonal contraceptives, local overheating of the genitals, and pregnancy contribute to an increase in its diameter.
Anechoic avascular inclusions in the cervix
An anechoic object can be defined as a neoplasm caused by various diseases. Such elements can be detected using an ultrasound machine. When using the technology, the doctor can easily make the correct diagnosis using the data from the echo signal receiver.
Nature of formations
In accordance with ICD-10, formations of the low echogenicity type are a variant of the non-inflammatory process of female internal organs.
The phrase anechoic formation means that the ultrasound emitted by the equipment does not pass through the tissue of the object. Thus, only a dark echo structure with possible inhomogeneous inclusions will be visible on the screen. This may mean that the device is aimed at a fluid, a blood clot, or tissue that has undergone a structural change.
When detected, an anechoic structure is not put forward as a diagnosis, but only the fact of the presence of pathology in the organ is stated. Such neoplasms can be located in the cervical canal of the cervix, uterus, and ovaries. If a woman has given birth to children, inclusions up to 5 mm in size, an anechoic formation in the cervix, are considered within normal limits.
Reasons for changes due to anechoic single inclusions
A single anechoic variant of the formation may appear, in addition to the cervix, in the area of the ovaries, uterus, and the space surrounding the pelvis.
The main factor due to which such neoplasms appear is the cystic nature of the inclusion. The course of events is also affected by the proliferation of endometrial tissue.
Also the cause of the appearance is endometriosis. A special layer that covers the inside of the uterus creates foci that do not transmit the ultrasonic spectrum of the ultrasound machine. In this embodiment, such areas look like spots, the size of which does not exceed 1 cm, with a chaotic arrangement. On the monitor, such formations have a heterogeneous appearance. Therefore, to the question: “what is an anechoic formation in the cervix up to 5 mm?” a common answer is endometriosis. With this diagnosis, diathermocoagulation (melting tissue with electric current) can be effectively used.
Other factors in the formation of anechoic inclusions:
- The uterus contains cancer or another tumor. In this embodiment, the formation appears on the monitor as a heterogeneous shape, with varying degrees of echogenicity. In this case, the organ can change in shape, becoming more massive
- Uterine leiomyoma is a benign type of tumor that is dependent on secreted hormones. Such pathologies can be supplied through the bloodstream. Such formations are typical for older women.
- The corpus luteum is an anechoic body and is the gland that produces progesterone during the ovulation period. The absence of a separately isolated gland during the initial stages of pregnancy indicates an insufficiency of secreted hormones.
What to do with an anechoic avascular formation of the appendage
The decision about the need for conservative or surgical treatment is made by the doctor.
If the abnormal inclusion is small, has a tendency to disappear spontaneously, does not cause discomfort and does not disrupt the functioning of the patient’s body, then the specialist can limit himself to dynamic observation. If there is a threat of infection of the formation, a rapid increase in its size, or a risk of its malignant transformation, the woman needs surgery. Functional cysts usually resolve spontaneously within a few months, so if they are small and do not affect the patient’s well-being, the doctor chooses a wait-and-see approach. Paraovarian formation does not go away on its own. If it is small, then observation is allowed. Otherwise, enucleation is carried out. Surgical intervention is also necessary when the patient plans IVF or natural conception.
A large ovarian cyst not only interferes with the normal functioning of neighboring internal organs, but also often leads to reproductive dysfunction, including infertility. In addition, torsion of her leg may occur with all the ensuing consequences that are dangerous to the life and health of the woman. Therefore, if the doctor insists on the need for surgical intervention, then you should listen to his opinion.
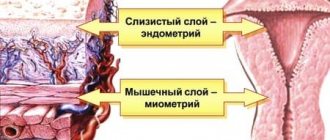
Endometrium of the uterus
The structure of the endometrium changes throughout the menstrual period. Closer to the regula it reaches its maximum thickness. If fertilization does not occur, then part of the uterine mucosa is rejected along with blood during menstruation. And the glands begin to actively grow again. Along with the uterine epithelium, the unfertilized egg also leaves the body. Therefore, the regularity and volume of menstruation in women also depend on it.
Let's figure out how the structure of the endometrium changes over the course of a month and what it depends on. In the first and partially in the second phases of the menstrual cycle, the inner lining of the uterus becomes three-layered . And on ultrasound, all layers and the boundaries between them are clearly distinguished.
Since in the study all layers are visualized in the form of straight, clearly distinguishable lines, such an endometrium is called linear. In a normally functioning female body, a similar phenomenon is present immediately after menstruation and partially in the second half of the cycle. This means that the woman is able to become pregnant. But if this type of mucous membrane is located at another time, then this is a sign of pathology.
Avascular endometrium is the lining of the uterus without blood vessels or poorly supplied with blood. This condition can lead to thinning of the inner lining of the organ responsible for reproduction. And as a result, a woman will not be able to get pregnant or carry a child. If such words are present in the ultrasound report, then you need to consult with your local gynecologist. The doctor will tell you what measures need to be taken in this regard.
Features of neoplasm in the ovary
An avascular formation in the ovary is a formation that does not have a blood supply. From this characteristic it turns out that we are talking about a functional cyst. Let's try to figure out what to do in this case.
During the menstrual cycle, fluid may accumulate in the ovary, which causes the formation of a cyst in the ovary, which can increase in volume. A functional cyst occurs in accordance with certain days of the cycle and has different sizes. The reason for its appearance is an unruptured follicle that continues to grow. Typically, such a cyst is treated conservatively; after a while it disappears on its own if the hormonal background changes.
Functional cysts can be of several types:
- follicular;
- corpus luteum cysts;
- paraovarian.
Most often, such an anechoic avascular formation in the ovary does not have pronounced symptoms and is accidentally discovered during a routine ultrasound of the reproductive system. Rarely, a woman may be bothered by irregular menstruation.
Avascular formation in the ovary: what is it, color circulation, ultrasound
Avascular formation of the ovary is a pathological neoplasm in which there is no blood circulation. Ultrasound examination can detect various abnormalities in the structure of the ovaries and uterus.
The patient can receive a conclusion in her hands, which will indicate something like the following: “an avascular formation was detected during CDK with homogeneous anechoic content.”
What is it and should I worry? Let's try to answer this and other questions.
Is a follicular cyst dangerous?
The follicular type of cyst has the appearance of a single-chamber formation and can reach a diameter of up to 10 cm. As a rule, it is a single anechoic avascular formation with a thin capsule and liquid contents of uniform consistency. They have a characteristic feature of arising without specific reasons and, just as unexpectedly, after some time they resolve on their own. But if such a formation is diagnosed, it is better to regularly monitor its changes through ultrasound monitoring.
When a woman’s body prepares for ovulation, a special internal secretory gland is formed in it, designed to synthesize female sex hormones. It is she who is the yellow body. Both the formation itself and the functional cysts that arise on it are not capable of harming a woman’s health. They usually begin to regress 2-3 months after their appearance. It is recommended to remove such an anechoic avascular formation in the ovary, determined by ultrasound, only if its size exceeds the maximum permissible norms.
Anechoicity - what is it?
During an ultrasound, ultrasound waves pass through the patient's body.
Internal tissues either absorb them or reflect them. Reflectivity, called echogenicity, is directly proportional to tissue density. On the monitor of an ultrasound machine, tissues with different echogenicity appear as light, gray and dark spots. Bones are the densest tissues and are hyperechoic. On the monitor they appear white. The softer the tissues and the more fluid they are filled with, the darker the picture on the monitor.
Hollow organismal formations filled with liquid, serous or bloody contents look like dark spots limited by a light border. Liquid contents absorb ultrasound. Formations with low-density contents are called anechoic.
According to ICD-10, anechoic formations in the ovaries are coded N-83.
Do we treat or remove?
The final conclusion regarding the nature of the formation and the method of its treatment can only be given by a gynecologist after careful diagnosis and tests. If the cyst does not cause discomfort, surgery is not necessary. But when there is a threat of infection, a rapid increase in size, and the risk of malignancy, surgery is inevitable.
It should be understood that not every cyst disappears on its own; most of them require treatment, sometimes surgery. Otherwise, the formation can grow to enormous sizes and interfere with the functioning of neighboring organs. In addition, some cysts look like a mushroom on a stalk, on which, under certain conditions, they can twist. The consequences of such a process can be disastrous and even fatal if you do not consult a doctor in time.
Women often hear from their gynecologist that they have an anechoic formation in the ovary. Not all patients know what this is. Tumors are detected using ultrasound. Neoplasms have their own characteristics and varieties.
Diagnostics
Large neoplasms are easily identified by palpation of the lower abdomen. Small cysts and tumors are detected only through instrumental diagnostic studies.
Diagnostic procedures include:
- Transvaginal ultrasound. The sensor is inserted through the vagina, due to which it is located as close as possible to the ovaries.
- Ultrasound of the uterus. It is carried out to determine the phase of the cycle based on the size of the endometrium lining the organ.
- Pregnancy test. Necessary to exclude the possibility of an ectopic pregnancy, in which the embryo remains in the ovary.
- Blood test for tumor markers. It is carried out to exclude or confirm the presence of malignant cells in the body.
What is an anechoic formation?
Anechoic is a structure that absorbs and reflects ultrasound.
It often manifests itself in the form of a cyst, which is a neoplasm with a round shape and thickened walls. Liquid forms inside the growth. Sometimes it may contain blood impurities. The internal part of the neoplasm is not only completely anechoic, but also has a mesh structure and irregularly shaped partitions. Hyperechoic inclusions are also present.
Why is an endometrioid cyst an avascular but not anechoic formation?
Endometrioid (“chocolate” cyst, endometrioma) is one of the types of external genital endometriosis and has a diameter of 3 to 20 cm. In 1/3 of cases, such neoplasms form on both appendages. Most often, endometrioid cysts are located behind the reproductive organ. They are motionless and, as a rule, single-chambered, however, sometimes they are so close to each other that they look like two or three-chambered.
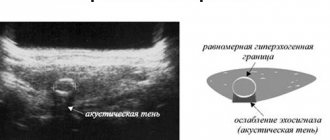
Endometriomas appear differently on ultrasound. Most often, their internal contents have a low or medium degree of echogenicity, which creates a “frosted glass” effect. The walls are usually quite thick; with CDK, the internal contents always appear avascular, and isolated areas of vascularization are detected along the periphery. Thus, an endometrioid abnormal inclusion is considered an avascular lesion but is not anechoic.
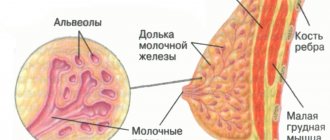
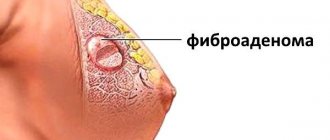
What is avascular formation in the mammary gland and what are its consequences? The female breast consists of glandular structures and subcutaneous tissue. In the absence of pathology, the mammary gland has a homogeneous structure and smooth, clear contours. However, on an ultrasound examination of the breast, a specialist can diagnose black shadows. These are hypoechoic formations. It is important to understand that avascular formations are just a description of the diagnosed picture. This is not a diagnosis of a disease or a symptom of it.
Types of cysts
Cystadenomas of an anechoic structure that occur inside or near the ovary are of the following types:
- follicular. Formed from a follicle. This element must rupture, then during ovulation the egg is released. In the presence of a follicular ovarian cyst, rupture does not occur;
- formation of the corpus luteum. Appear when fluid accumulates at the site where the egg exits the follicle;
- serous. They are smooth-walled growths formed from serous tissue that covers the ovaries and contains fluid inside;
- paraovarian. These forms of ovarian cysts are dense, form near the reproductive organs, and can reach large sizes.
Single and multiple, single-chamber and double-chamber cysts are also identified. The type of tumor is determined by performing an ultrasound of the pelvic organs.
Causes
There are certain factors that provoke changes in the structures of the mammary gland. Experts often associate the appearance of tumors with hormonal imbalances.
The outbreak occurs in the female breast for the following reasons:
- excess estrogen production
- long-term use of hormonal contraceptives
- hormone replacement treatment
- thyroid diseases
- inflammation in the fallopian tubes
- ovarian diseases and dysfunction
- operations
Reasons for appearance
An anechoic cyst most often occurs in women of reproductive age than after menopause. Ovarian tumors are less common during menopause because estrogen levels drop. Most of them are benign. The reasons for the formation of formations can be different. The doctor is not always able to say exactly what caused the disease.
Hormonal imbalance is considered the main culprit in the development of pathology. It negatively affects the activity of the ovary. During menopause, thin-walled anechoic formations in the ovaries appear more often due to inflammatory processes in the reproductive organs, the appearance of adhesions after surgery, and damage to the ovaries.
Encyclopedia of Ultrasound and MRI
Recently, ultrasound diagnostics has taken a leading position among diagnostic methods in gynecology. This is due to the accessibility, information content and safety of the method. However, ultrasound in gynecology has a number of difficulties due to the variability of the ultrasound picture depending on the day of the menstrual cycle, the number of previous pregnancies, and the duration of menopause.
In this regard, high professionalism and clinical thinking are required from the doctor conducting the study.
It should be understood that the sensitivity of the method is variable and depends on the pathology being diagnosed. Even conducting a study using an expert-class device does not guarantee an unambiguous diagnosis.
There are groups of pathological processes that have a similar ultrasound picture. Therefore, a high-quality examination should be comprehensive and include laboratory, instrumental research methods, as well as examination and medical history data.
The uterus is the largest organ of the female reproductive system, which is well differentiated by transabdominal and transvaginal ultrasound.
Organs of the female reproductive system
This allows you to diagnose space-occupying formations of even small sizes. Based on the visualized picture, all formations can be divided into three groups: hypoechoic, isoechoic and hyperechoic.
Isoechogenic formations have the same acoustic density as the surrounding uterine tissue.
Hypoechoic formations have a lower acoustic density and, during ultrasound examination, appear darker against the background of the main tissue of the organ. Hyperechoic inclusions have a high acoustic density and are visualized lighter against the background of uterine tissue.
To describe focal pathology of the uterus, the terms inclusion and formation are used. There is no fundamental difference in their use and the use of both terms is legal and acceptable in relation to any focal process.
Hyperechoic formations in the uterus have a different nature. The main reasons for their appearance are:
Intrauterine contraceptives . One of the most common types of contraception today, although complications of use are common (inflammatory processes, perforation of the uterine walls, menstrual irregularities). The ultrasound picture is different and depends on the type of intrauterine contraceptive device. The most commonly used is the T-shape. When placed correctly, it is visualized as a linear hyperechoic structure during longitudinal scanning and as a rounded formation with rough contours when the transducer is positioned transversely.
Intrauterine contraceptives, cysts – Uterus and appendages – Ultrasound
When positioned correctly, the hyperechoic inclusion reaches the bottom of the uterine cavity and does not protrude beyond the internal os. When using a Lipps loop as an intrauterine contraceptive, the ultrasound picture is characterized during transverse scanning by the detection of a solid hyperechoic line and individual inclusions of increased echogenicity during longitudinal scanning. When the uterus is perforated by an intrauterine contraceptive, a hyperechoic inclusion is determined, partially located in the thickness of the myometrium. Most often this occurs in the fundus of the uterus.
Chronic endometritis . This process is caused by endometrial hyperplasia and can occur in any age group. The ultrasound picture of hyperplasia is variable, most often it looks like hyperechoic inclusions of small size (2-7 mm) with clear contours, irregular shape, and possible expansion of the uterine cavity. In women of reproductive age, endometrial thickening and hyperechoic inclusions persist during all phases of the menstrual cycle.
Chronic endometritis. B-mode. Dilation of the uterine cavity
Endometrial polyps. In most cases, polyps have an isoechoic structure, but if there are a large number of fibrin strands in the structure of the polyp, this leads to an increase in the echogenicity of the formation. Fibrous polyps have a similar ultrasound picture to endometritis. Distinctive features are the presence of clear, even contours and a round shape during transverse scanning. There is a violation of the closure of the mucous membranes, its contours become wavy and intermittent. Color Doppler sonography reveals the vascular pedicle of the polyp, which consists of newly formed vessels that feed the formation.
Small endometrial polyp (arrows). TV scanning.
In reproductive age, the study is optimally carried out in the proliferative phase of the menstrual cycle.
- Air bubbles. These formations in the lumen of the uterus can appear as a result of curettage of the uterus, as well as during a long course of chronic endometritis. Ultrasound visualizes a hyperechoic formation with clear contours, often multiple and small in size. Sometimes an acoustic “comet tail” effect is observed, which is visualized as many echogenic bands behind the formation.
- Remains of the fertilized egg. The echographic picture is variable and depends on the stage at which the termination of pregnancy occurred. If chorion tissue remains, then the ultrasound picture is characterized by heterogeneity of structure and increased echogenicity. If termination of pregnancy occurs at a later stage, then fragments of bone structures are visualized in the form of hyperechoic formations with clear contours and acoustic shadows.
- Hematometra. Blood clots in the lumen of the uterus may remain after surgery or delivery. The examination visualizes an enlarged uterus with hyperechoic heterogeneous inclusions without signs of blood flow using Doppler. On ultrasound, they have a similar picture to the remains of the chorion. When carrying out differential diagnosis, dynamic observation is important. Over time, blood clots undergo destructive changes and are displaced in relation to the walls of the uterus. The components of the chorion practically do not change their structure and location over time.
- Uterine perforation and uterovesical fistula. The visualized picture is characterized by the detection of a cord 4-6 mm thick with increased echogenicity passing through the uterine tissue. It is characterized by its communication with the uterine cavity. No acoustic shadow will be detected. With a prolonged course, endometritis may occur with a corresponding ultrasound picture.
- Inflammation of postoperative sutures. The inflammatory process is manifested by an increase in the thickness of infiltration in the area of postoperative sutures on the uterus. Also, due to the deposition of fibrin threads, a plaque of increased echogenicity appears, often linear in nature.
Rarer causes of the occurrence of foci of increased echogenicity, which are often not taken into account, are submucosal myomatous node and lipoma.
Myomatous nodes have a hypoechoic structure, but submucosal nodes are prone to degenerative processes and the formation of calcified areas. It is these areas that look like inclusions of increased echogenicity against the general background of a hypoechoic or isoechoic node.
myomatous focus of altered and uneven echogenicity
Lipoma is a benign tumor of adipose tissue cells. It is considered extremely rare, partly due to its occurrence at an older age (after 50-60 years) and the asymptomatic course of the disease. The ultrasound picture is characterized by the presence of a formation with clear contours, increased echogenicity and the absence of blood flow during color Doppler mapping.
hyperechoic focus – lipoma from adipose uterine tissue
When hyperechoic formations are detected in the uterus, it is not always possible to make an unambiguous diagnosis based on the ultrasound picture. If there are doubts about the nature of this formation, a full examination is necessary. The following are important when carrying out differential diagnosis:
Anamnesis data (previous operations to diagnose hematometra and inflammation of postoperative sutures, the use of intrauterine contraceptives in their diagnosis and diagnosis of complications, termination of pregnancy to identify chorion remains and skeletal fragments).
- Clinical data and complaints of the patient (pain syndrome, menstrual irregularities due to endometritis, polyps and remnants of the fertilized egg).
- Diagnostic laparoscopy (if uterine perforation is suspected and the presence of a uterovesical fistula).
- Hysteroscopy (in the presence of polyps and myomatous nodes).
- Magnetic resonance imaging in case of difficulties in differential diagnosis and the impossibility of making a diagnosis based on already conducted studies.
When carrying out diagnostics, it is necessary to take into account the day of the menstrual cycle; if the ultrasound picture is questionable, it is necessary to repeat the study in another phase of the cycle, which will allow a more accurate interpretation of the data obtained. Ultrasound diagnostics of the pelvic organs, and in particular the uterus, requires high professionalism and experience of the doctor conducting the examination.
Main symptoms
Most women do not even suspect that they have a cyst. Structures with a thin capsule less than 1 cm in size do not manifest themselves in any way. Symptoms appear as the growth increases.
Patients are concerned about the following signs:
- feeling of heaviness in the stomach;
- dull pain in the lower abdominal cavity. Pain can intensify with physical activity, sexual contact;
- false urge to bowel movement and urination;
- pain when urinating.
If such symptoms occur, you should urgently see a gynecologist.
Diagnostic methods
When contacting a doctor, the first step is to study the clinical picture of the disease and the woman’s medical history.
Next, a gynecological examination is performed on a chair. If the size of the cyst is small, the doctor may not notice it. In this case, a study using an ultrasound sensor will help make a diagnosis. It shows neoplasms of any parameters, allows you to determine their type, location, structure. An examination is carried out through the vagina, which allows you to get closer to the ovaries and get a larger picture. On the monitor, an anechoic ovarian cyst appears as a dark spot.
Ovarian cyst CDK avascular what is it – Women's health
An avascular formation of the ovary is a pathological neoplasm in which there is no blood circulation. Ultrasound examination can detect various abnormalities in the structure of the ovaries and uterus.
The patient can receive a conclusion in her hands, which will indicate something like the following: “an avascular formation was detected during CDK with homogeneous anechoic content.”
What is it and should I worry? Let's try to answer this and other questions.
How is the treatment carried out?
If the patient is in good health, the cyst is small in size and does not cause any discomfort, then treatment of the anechoic formation may not be necessary. As the disease progresses, doctors often resort to surgery.
Depending on the degree of development of the tumor, the doctor chooses one of the following types of treatment:
- Waiting tactics. It is used exclusively for the functional type of cyst. Typically, such an anechoic formation in the ovary disappears on its own within a few months. If this does not happen, medication is prescribed.
- Conservative treatment. Consists of hormone therapy using oral contraceptives. They help suppress the production of female sex hormones, restore the menstrual cycle, and rehabilitate the activity of the ovaries.
- Surgical method. It is prescribed if no other treatment methods bring the desired result or in case of malignant degeneration.
- Aspiration therapy. Used when the cyst has no signs of a tumor. It is carried out as follows: a sensor with a puncture tip is inserted into the vagina and the contents are removed. Then ethyl alcohol is poured into the growth, destroying it.
The choice of treatment method for avascular ovarian formation is based on the results of an ultrasound examination and depends on the severity of the pathology, the woman’s age, and the presence of concomitant diseases for which any methods of therapy are prohibited.
Medications for cysts include the following:
Along with them, doctors advise taking medications that stimulate the immune system, namely vitamin complexes.
Avascular ovarian cyst with CDK what is it – Feminine hygiene
Women often hear from their gynecologist that they have an anechoic formation in the ovary. Not all patients know what this is. Tumors are detected using ultrasound. Neoplasms have their own characteristics and varieties.
What is an anechoic formation?
Anechoic is a structure that absorbs and reflects ultrasound. It often manifests itself in the form of a cyst, which is a neoplasm with a round shape and thickened walls.
Liquid forms inside the growth. Sometimes it may contain blood impurities. The internal part of the neoplasm is not only completely anechoic, but also has a mesh structure and irregularly shaped partitions.
Hyperechoic inclusions are also present.
Types of cysts
Cystadenomas of an anechoic structure that occur inside or near the ovary are of the following types:
- follicular. Formed from a follicle. This element must rupture, then during ovulation the egg is released. In the presence of a follicular ovarian cyst, rupture does not occur,
- formation of the corpus luteum. Appear when fluid accumulates at the site where the egg exits the follicle,
- serous. They are smooth-walled growths formed from serous tissue that covers the ovaries and contains fluid inside,
- paraovarian. These forms of ovarian cysts are dense, form near the reproductive organs, and can reach large sizes.
Single and multiple, single-chamber and double-chamber cysts are also identified. The type of tumor is determined by performing an ultrasound of the pelvic organs.
Reasons for appearance
An anechoic cyst most often occurs in women of reproductive age than after menopause. Ovarian tumors are less common during menopause because estrogen levels drop. Most of them are benign. The reasons for the formation of formations can be different. The doctor is not always able to say exactly what caused the disease.
Hormonal imbalance is considered the main culprit in the development of pathology. It negatively affects the activity of the ovary. During menopause, thin-walled anechoic formations in the ovaries appear more often due to inflammatory processes in the reproductive organs, the appearance of adhesions after surgery, and damage to the ovaries.
Main symptoms
Most women do not even suspect that they have a cyst. Structures with a thin capsule less than 1 cm in size do not manifest themselves in any way. Symptoms appear as the growth increases.
Patients are concerned about the following signs:
- feeling of heaviness in the stomach,
- dull pain in the lower abdominal cavity. The pain can intensify with physical activity, sexual contact,
- false urge to have bowel movements and urination,
- pain when urinating.
If such symptoms occur, you should urgently see a gynecologist.
Diagnostic methods
When contacting a doctor, the first step is to study the clinical picture of the disease and the woman’s medical history. Next, a gynecological examination is performed on a chair. If the size of the cyst is small, the doctor may not notice it.
In this case, a study using an ultrasound sensor will help make a diagnosis. It shows neoplasms of any parameters, allows you to determine their type, location, structure.
An examination is carried out through the vagina, which allows you to get closer to the ovaries and get a larger picture. On the monitor, an anechoic ovarian cyst appears as a dark spot.
How is the treatment carried out?
If the patient is in good health, the cyst is small in size and does not cause any discomfort, then treatment of the anechoic formation may not be necessary. As the disease progresses, doctors often resort to surgery.
Depending on the degree of development of the tumor, the doctor chooses one of the following types of treatment:
- Waiting tactics. It is used exclusively for the functional type of cyst. Typically, such an anechoic formation in the ovary disappears on its own within a few months. If this does not happen, medication is prescribed.
- Conservative treatment. Consists of hormone therapy using oral contraceptives. They help suppress the production of female sex hormones, restore the menstrual cycle, and rehabilitate the activity of the ovaries.
- Surgical method. It is prescribed if no other treatment methods bring the desired result or in case of malignant degeneration.
- Aspiration therapy. Used when the cyst has no signs of a tumor. It is carried out as follows: a sensor with a puncture tip is inserted into the vagina and the contents are removed. Then ethyl alcohol is poured into the growth, destroying it.
The choice of treatment method for avascular ovarian formation is based on the results of an ultrasound examination and depends on the severity of the pathology, the woman’s age, and the presence of concomitant diseases for which any methods of therapy are prohibited.
Medications for cysts include the following:
- "Duphaston". A hormonal agent, which is a synthetic analogue of natural cyst progesterone,
- Marvelon. A combination medication containing estrogen and progesterone,
- "Janine." Low-dose combination drug with estrogens and progesterone.
Along with them, doctors advise taking medications that stimulate the immune system, namely vitamin complexes.
Traditional methods
Traditional medicine offers a huge number of recipes that can help in the fight against anechoic formation on the ovary. The following tools are often used:
- Honey. It has beneficial properties that enhance immunity and activate the restoration of tissues and organs. To prepare the medicine, you need to take the core of the onion, pour it with honey, and leave it to infuse overnight. Then dip the tampon in this product and insert it into the vagina at night. Course 10 days.
- Pine buds. Take a tablespoon of the plant, brew it with a liter of boiling water, and leave it to steep overnight. You can take this remedy 3 times a day, half a glass. The course is a month.
- Walnuts. They do an excellent job of regulating hormonal balance. The nut shells are poured with 250 ml of alcohol and left in a dark place for 3 days. Take the drink on an empty stomach, a large spoon once a day. Course – 7 days.
Before using alternative methods of treatment, you should definitely consult with your doctor.
Anechoic formation during pregnancy
There are formations that are not echogenic even during pregnancy. Most often, expectant mothers are diagnosed with a corpus luteum cyst. It is not dangerous, it resolves on its own. Along with a delay in menstruation, the doctor can make an assumption about conception. The gynecologist will advise you to take a pregnancy test.
If it shows a positive result, ultrasound reveals the presence of an anechoic inclusion in the ovary, but does not see the fetus, then this indicates the formation of the luteal body. Its purpose is to create favorable conditions for the development of the baby.
It persists for 4 months, after which the functions of the luteal body begin to be performed by the placenta.
Sometimes pregnant women also find pathological cysts in one of the follicles. The danger of neoplasms is that under pressure from the uterus they can be damaged, causing twisting of the leg, tissue death, and rupture of the growth. These conditions are dangerous to a woman's health.
When diagnosing a malignant ovarian cyst, which develops rapidly and acquires sizes from 16 to 17 mm, the gynecologist resorts to surgical intervention. During pregnancy, the most gentle surgical techniques are chosen so as not to harm either the mother or the fetus.
If the tumor does not grow, then the operation can be rescheduled for another time after the baby is born.
Possible complications
The danger of a cyst lies in its complications. If the pathology is not treated, the anechoic formation in the ovary will grow, causing harm to the woman’s body.
The most serious complications requiring immediate medical attention and surgery are the following:
- torsion of the cyst stalk. Patients suffer from severe acute pain in the lower abdomen. Due to twisting, the tumor does not receive nutrients, which leads to the death of the tumor tissue, and then the appendages,
- education gap. During this process, the entire contents of the cyst are released into the ovarian cavity. This causes the development of peritonitis. Due to the fact that the fluid may contain blood inclusions, an inflammatory process may occur in the ovary,
- infertility or termination of pregnancy. Long-term absence of therapy for the tumor leads to disruption of the ovaries, which take a leading part in conceiving a child,
- neoplastic cancer. Not so often, but there are cases of a cyst transforming into oncology, which subsequently affects other organs.
These pathological conditions require urgent surgery.
Preventive actions
Echo-negative cysts are often encountered in medical practice. It is impossible to completely protect yourself from their occurrence, but you can reduce the risk of developing pathology with the help of preventive measures.
First of all, you need to monitor your hormonal levels. Its violations cannot be ignored. After all, failure is the main cause of the formation of cystic inclusions.
Doctors also advise the following:
- Take vitamins regularly to strengthen the immune system,
- to live an active lifestyle,
- to refuse from bad habits,
- Healthy food,
- avoid stressful situations,
- observe the work and rest schedule,
- undergo a preventive examination with a gynecologist at least once a year.
An anechoic mass in the ovary is a diagnosis but should not be a cause for concern. If therapy is started in a timely manner, the prognosis is favorable. Modern medicine offers many methods for treating cysts, so getting rid of them is not difficult.
Source: https://castlegal.ru/avaskuljarnaja-kista-jaichnika-pri-cdk-chto-jeto.html
Traditional methods
Traditional medicine offers a huge number of recipes that can help in the fight against anechoic formation on the ovary. The following tools are often used:
- Honey. It has beneficial properties that enhance immunity and activate the restoration of tissues and organs. To prepare the medicine, you need to take the core of the onion, pour it with honey, and leave it to infuse overnight. Then dip the tampon in this product and insert it into the vagina at night. Course - 10 days.
- Pine buds. Take a tablespoon of the plant, brew it with a liter of boiling water, and leave it to steep overnight. You can take this remedy 3 times a day, half a glass. The course is a month.
- Walnuts. They do an excellent job of regulating hormonal balance. The nut shells are poured with 250 ml of alcohol and left in a dark place for 3 days. Take the drink on an empty stomach, a large spoon once a day. Course – 7 days.
Before using alternative methods of treatment, you should definitely consult with your doctor.
How to treat
Therapy is prescribed only after a complete examination. For cysts and benign formations, comprehensive drug treatment is advisable. The following are used in therapy:
- anti-inflammatory drugs
- hormonal drugs
- herbal collections
To eliminate fibrocystic formation, the drugs Indinol and Fitonol are prescribed. They can be used for all types of tumors. Among hormonal drugs, medications containing gestagen and estrogen are prescribed - Duphaston, Estrogel, Utrozhestan.
To saturate the body with useful substances, various vitamin and mineral complexes are used. It is also important to provide adequate nutrition. It is recommended to eat a large amount of vegetables and fruits.
Effective homeopathic remedies are widely used as adjuvant therapy. Cyclodinone or Mastopol are taken for one month. Surgery is recommended when diagnosing a malignant tumor.
Traditional medicine can be used in complex treatment. Leaves of coltsfoot are applied to the lesion overnight. Then the chest is wiped with burdock oil in the morning.
You can prepare a healing mixture of honey, burdock rhizomes and castor oil. The compress with this homogeneous mass is left overnight. It is also recommended to make compresses on the chest with crushed pumpkin. To relieve pain and inflammation, a whole cabbage leaf is applied to the chest at night.
avascular osteonecrosis - rus avascular necrosis (m) of bone, aseptic osteonecrosis (m); avascular osteonecrosis (m) eng aseptic bone necrosis fra ostéonécrose (f) aseptique deu aseptische Knochennekrose (f) spa necrosis (f) ósea aséptica ... Occupational safety and health. Translation into English, French, German, Spanish
Avascular - without blood vessels or having poor blood supply. This term is usually used in relation to cartilage. Source: Medical Dictionary ... Medical Terms
avascular osteonecrosis - (o. avascularis; Greek negative prefix a + vascular) see Aseptic bone necrosis ... Big medical dictionary
aseptic bone necrosis - (osteonecrosis aseptica; synonym: avascular osteonecrosis, aseptic osteonecrosis) ischemic N. part of the bone: develops more often in the epiphyses of tubular bones ... Large medical dictionary
Anechoic formation during pregnancy
There are formations that are not echogenic even during pregnancy.
Most often, expectant mothers are diagnosed with a corpus luteum cyst. It is not dangerous, it resolves on its own. Along with a delay in menstruation, the doctor can make an assumption about conception. The gynecologist will advise you to take a pregnancy test. If it shows a positive result, ultrasound reveals the presence of an anechoic inclusion in the ovary, but does not see the fetus, then this indicates the formation of the luteal body. Its purpose is to create favorable conditions for the development of the baby. It persists for 4 months, after which the functions of the luteal body begin to be performed by the placenta.
Sometimes pregnant women also find pathological cysts in one of the follicles. The danger of neoplasms is that they can be damaged by pressure from the uterus,
causing twisting of the leg, tissue death, and rupture of the growth. These conditions are dangerous to a woman's health. When diagnosing a malignant ovarian cyst, which develops rapidly and acquires sizes from 16 to 17 mm, the gynecologist resorts to surgical intervention. During pregnancy, the most gentle surgical techniques are chosen so as not to harm either the mother or the fetus. If the tumor does not grow, then the operation can be rescheduled for another time after the baby is born.
Treatment methods
If an ultrasound shows the presence of anechoic inclusions on the cervix, the woman needs to undergo colposcopy, ultrasound and, if necessary, a puncture biopsy. The gynecologist will conduct an examination on the chair using mirrors and palpate the formation. Most often, such cysts do not cause danger, but occasionally an anechoic inclusion in the cervix can lead to infertility and infection.
Conservative and surgical methods are used in treatment. If the formation is less than 1 cm in size, the woman is advised to wait and undergo a re-examination after 2 months to track growth dynamics.
For a cyst whose size exceeds 1 cm, a puncture is prescribed - a needle is inserted into the cavity of the cyst, the contents are pumped out, and the liquid is sent to the laboratory to study the composition. Then a solution is injected into the cavity, which destroys the walls of the formation.
Drug treatment is carried out for endometriosis, endometrioid cysts in the cervix - for this, hormone replacement therapy is used for 6-9 months.
List of effective drugs.
- Marvelon. A combined hormonal drug with a high content of progesterone, helps slow growth, reduce endometrioid cysts in the cervix;
- Duphaston is a synthetic analogue of progesterone, eliminates hormonal deficiency, which reduces the risk of growth of anechoic formations;
- Janine. A combined hormonal agent that promotes the destruction of cysts in the cervix, reproductive organ, and ovaries;
- Anteovin is a two-phase drug that eliminates hormonal imbalance and starts the process of regression in anechoic inclusions.
Additionally, you should take medications that help strengthen the immune system - vitamin A, C, E. Physiotherapy - iontophoresis, electrophoresis with analgesics and anti-inflammatory drugs, exposure to formations with sinusoidal currents - helps well with anechoic inclusions.
If endometriosis affects the cervix, vagina, in addition to hormonal agents, use tampons that are soaked in hyaluronic, lactic acid, and herbal extracts. This method of treatment allows you to restore the functionality of the glands of the cervical region and reduce the manifestation of pain during sexual intercourse. Duration of therapy is 1–1.5 months.
If there are myomatous nodes, a woman should regularly visit a gynecologist and have an ultrasound scan. If the anechoic formation begins to increase in size, it is removed surgically. Immediate surgical intervention is necessary for ectopic pregnancy: laparoscopic surgery is performed.
Treatment of cervical cancer is carried out surgically, with additional radiation and chemotherapy prescribed.
Possible complications
The danger of a cyst lies in its complications. If the pathology is not treated, the anechoic formation in the ovary will grow, causing harm to the woman’s body.
The most serious complications requiring immediate medical attention and surgery are the following:
- torsion of the cyst stalk. Patients suffer from severe acute pain in the lower abdomen. Due to twisting, the tumor does not receive nutrients, which leads to the death of the tumor tissue, and then the appendages;
- education gap. During this process, the entire contents of the cyst are released into the ovarian cavity. This causes the development of peritonitis. Due to the fact that the fluid may contain blood inclusions, an inflammatory process may occur in the ovary;
- infertility or termination of pregnancy. Long-term absence of therapy for the tumor leads to disruption of the ovaries, which take a leading part in conceiving a child;
- neoplastic cancer. Not so often, but there are cases of a cyst transforming into oncology, which subsequently affects other organs.
These pathological conditions require urgent surgery.
Prevention and prognosis
To reduce the likelihood of cystic formations in the gonads, a woman should:
- maintain intimate hygiene;
- undergo routine examinations with a gynecologist;
- control the course of the menstrual cycle;
- control sexual life, try not to lead the situation to abortion.
With timely diagnosis and proper treatment, the prognosis is favorable. It should be borne in mind that cystadenomas tend to turn into malignant tumors, so these tumors must be surgically removed immediately after detection.
Preventive actions
Echo-negative cysts are often encountered in medical practice. It is impossible to completely protect yourself from their occurrence, but you can reduce the risk of developing pathology with the help of preventive measures.
First of all, you need to monitor your hormonal levels. Its violations cannot be ignored. After all, failure is the main cause of the formation of cystic inclusions.
Doctors also advise the following:
- Take vitamins regularly to strengthen the immune system;
- to live an active lifestyle;
- to refuse from bad habits;
- Healthy food;
- avoid stressful situations;
- observe the work and rest schedule;
- undergo a preventive examination with a gynecologist at least once a year.
An anechoic mass in the ovary is a diagnosis but should not be a cause for concern. If therapy is started in a timely manner, the prognosis is favorable. Modern medicine offers many methods for treating cysts, so getting rid of them is not difficult.
Fragile women's health is constantly exposed to attacks from harmful bacteria, stress, and suffers due to poor ecology. What is an anechoic formation, and how can it affect a woman’s body?
One of the most unfavorable consequences of all negative effects on the body is the appearance of dark spots on ultrasound.
Even if a woman is completely healthy, she is not immune from the appearance of cysts in the uterus and follicles or near them, and if the immune system is weakened by constant stress and past illness, then a tumor may appear even faster.
The tumor or cyst, which contains fluid and changed tissue, can be located not only in the ovaries, but also in the thyroid gland, kidney, uterus, or near any organ.
The concept of anechoic formation in the ovary characterizes the pathology of the female reproductive system. This is one of those symptoms of the disease that requires careful diagnosis and several types of research before diagnosis.
Ultrasound diagnostics is used to detect pathology.
A pathological or benign avascular echogenic formation will appear different on diagnosis from healthy organ or gland tissue.
Ultrasound has a high frequency that is not audible to the human ear. When a specialist conducts a study using it, ultrasound is generated due to the transducer sensor. Using the same sensor, information is read from the sound reflected from the surface of the organ, that is, the echo.
As a rule, ultrasound does not pass through bones during diagnosis. If the body has cavities with air, for example, the intestines, bladder, stomach, then during the study the ultrasound will be scattered as it passes through the air. Capsules that contain liquids conduct radiation well, and on the monitor during diagnosis they will appear as denser, darker areas. Such capsules are usually called cysts. Depending on what tissue the neoplasm consists of and what tissues or fluids it contains, it can be either echogenic or non-echoic.
Prevention
Prevention of the appearance of anechoic inclusions in the cervix and ovaries is nonspecific.
Basic methods of prevention:
- compliance with the rules of intimate hygiene (for care it is better to use neutral products with a minimum amount of fragrances and other aggressive ingredients);
- using condoms when having sex with new sexual partners;
- pregnancy planning;
- annual preventive examinations with a gynecologist;
- the use of hormonal oral contraceptives according to one’s own hormonal status;
- abstaining from sexual intercourse during menstruation;
- healthy lifestyle, regular exercise, proper and balanced nutrition.
To prevent the appearance of cysts, you can drink propolis tincture - dissolve 20 drops in 50 ml of water, drink after breakfast for 20 days, then take a ten-day break. In total, you need to take 3 courses in a row, and preventive maintenance should be done every year.
If unpleasant symptoms appear, you should not postpone a visit to the doctor; any disease is easier to cure if it was diagnosed in the early stages of development.
Anechoic inclusions are often diagnosed in women of different ages; there are many reasons for the appearance of formations, so only a gynecologist can make an accurate diagnosis. Timely treatment will help avoid complications, and adherence to simple preventive measures will help prevent relapse of diseases.
The cervix is the lower part of the uterus and is shaped like a hollow cylinder. The normal size reaches no more than 3-4 cm. The histological meaning of the organ is represented as a connecting link between the uterus and vagina. The organ is divided into the supravaginal zone and the vaginal element. A gynecologist can examine the cervix using a speculum. On the side of the vagina you can find depressions called the external os. This element is the cervical canal. Such an organ in a nulliparous woman has a rounded appearance, and in a woman who has given birth, the canal takes on a slit-like shape.
Similar article - How to determine bad cholesterol
Symptoms and causes
When diagnosed by ultrasound, an anechoic formation is displayed on the monitor in the form of darkened zones. If we talk about the ovary, uterus or follicles, then such areas, as a rule, should be filled with fluid. The appearance of formations indicates the presence of cysts.
Statistics show that on average up to 60% of women of childbearing age suffer from the appearance of cysts in the uterus, follicles or near them, while more than 85% suffer from the appearance of benign formations of various sizes and origins. Especially often, signs of the disease and avascular echogenic formation are detected during pregnancy, during prenatal diagnosis.
The formation of tumors in the uterus, kidney or thyroid gland occurs for various reasons. These can be various kinds of disorders that are associated with problems in the functioning of the hormonal system, as well as during the ovario-menstrual cycle. In addition, a formation near the ovary can occur against a background of inflammation, due to the appearance of adhesions, as well as due to abdominal injuries or inflammatory processes in the genitourinary system. In addition, endometrioma, that is, a tumor near the ovary, occurs in older women.
Typically, endometrioma is a concomitant neoplasm, that is, it appears with an advanced disease of the genitourinary system.
The development of anechoic formations in the ovaries suggests the presence of cysts and cystomas. A cyst is a benign neoplasm. As a rule, it has a thin wall, while its cavity is completely filled with liquid, which begins to form due to a secretion that is produced in large quantities and does not have time to be eliminated from the body. Depending on a number of reasons, the cyst has different sizes - from a few millimeters to several centimeters. The cystoma is large in size and pathological in nature.
What is an anechoic formation, types:
- Follicular. This avascular anechoic formation appears in or near the ovary in the form of a sphere with a thin shell in which fluid accumulates. As a rule, the reason for the accumulation of fluid is a violation of the rupture of the follicle when the egg is released, and this leads to the accumulation of fluid inside the resulting cavity. This accumulation begins to be secreted over time, and upon diagnosis it looks dense, with thick contents;
- Paraovarian. This neoplasm appears due to the accumulation of fluid in the fiber. A formation of this kind most often forms near the ovary;
- Dermoid cysts are usually congenital. Its development is a consequence of a disrupted process of ontogenesis;
- Corpus luteum cyst. This cyst characterizes the second phase of the menstrual cycle and forms in the uterus or follicle after incomplete destruction of the corpus luteum.
Cystomas have a slightly different development. Their structure is not homogeneous, that is, the neoplasm consists of several chambers. Cystoma can be:
- Mucinous. This type is formed during the process of proliferation of glandular epithelial cells. As a result, mucin is formed in the cavity - a viscous mucous substance. These types of tumors form in the thyroid and mammary glands, in the uterus, in the kidney and near these organs;
- Cystadenoma. Such a cyst can also be called papillary, since it is formed from the papillary epithelium. Due to the abundance of proliferating cells, it does not have a homogeneous structure. Of all other neoplasms, this type is the most dangerous due to its complications;
- Serous cystoma. This avascular echogenic formation is distinguished by the rate of cell proliferation, within and next to which fluid accumulates.
It is generally accepted that the provocateur of an echogenic neoplasm is a cyst or cystoma.
At the same time, the patient, as a rule, does not consult a doctor even if there are alarming signals - abdominal pain, anxiety, discharge from the breast, enlarged breasts, chronic diseases and others.
Most often, the presence of a cyst in the uterus or near the ovary disrupts the normal course of the menstrual cycle, and both delayed periods and spotting in the middle of the cycle and prolonged heavy bleeding can be observed. Such failures and signs of illness are associated with the fact that the release of the egg into the uterine cavity cannot be accomplished. Due to the fact that the cyst prevents its normal separation from the follicle, menstruation does not occur. This process also affects hormonal levels; as a rule, with this course of events, the level of hormones decreases.
Another characteristic of a neoplasm is the level of blood supply. As a rule, it is avascular, that is, not supplied with blood.
If the formation is avascular, that is, without a network of capillaries, then it is considered less dangerous than one that is surrounded by vessels, and if a tumor or cyst grows with fluid contents, it can be quickly and safely removed.
Dense formation on the cervix
A dense formation on the cervix most often appears as a benign polyp. The lump may be large or appear as a small, hard lump or lump. Such seals can be movable or remain static.
With 5% of variants, submucosal nodes may appear. It is also possible to register another type of disease - for example, fibroids.
To find out exactly what kind of dense object is in the cervix, you should undergo a test. Symptoms of neoplasms may include bleeding and the presence of other discharge from the genitals. It is especially worth focusing attention if there are inclusions of purulent formations.
To establish a diagnosis, the following steps are taken:
- Gynecological examination using speculum.
- Hysterography (x-ray of the uterine cavity).
- Examination of the pelvis using ultrasound.
The most common is a minimally invasive method - hysteroscopy. This method allows the doctor to quickly determine the exact location and type of tumor. The doctor can take biomaterial for analysis, which is also convenient in the presence of tumors.
Specialists resort to hysterography if it is necessary to detect an uneven surface of the cervix. Contrast is introduced into the pelvic cavity, the function of which is to create a high-quality image. The method can help in establishing the nature of the dense formation in the uterine cervix.
Prevention of the appearance of anechoic formations
A woman should adhere to simple rules of personal hygiene:
- organization of pregnancy planning.
- systematic medical examinations with a doctor
- using a hormonal contraceptive according to your hormonal status.
- physical activity, healthy eating and lifestyle
- using condoms during sexual intercourse
Also, to prevent the formation of cysts, it is possible to use propolis tincture - up to 20 drops per 50 ml of water. This mixture can be drunk every day for 20 days with a 10-day break. A total of three such cycles are necessary.
Anechoic formations can be detected at any age. Only a qualified doctor can accurately indicate the pathological nature of the formations and make the correct diagnosis.
The hyperechoic nature of the formation suggests that a homogeneous area does not transmit ultrasound.
Possible complications and consequences
The main option for the development of pathology in the uterus is bleeding from an endometrioid cyst. If a cyst bursts in the cervical area, urgent medical and anti-inflammatory treatment is necessary. There are also cases of the appearance of a myomatous node. Such a solid case requires differential diagnosis. In addition, anechoic formations can be caused by adhesions or tubal resection. These phenomena may occur during medical operations.
Similar article - What are the types of liver diseases?
Underneath an anechoic avascular neoplasm in the cervix, a uterine cyst most often appears. This formation has thin walls and contains a liquid solution inside. The diameter of such an object can reach from 3 mm to several centimeters. The term “avascular” should be understood as a neoplasm that is not supported by the body’s bloodstream. Such a symptom can serve as an excellent factor for determining pathology. Endometrioid cyst variants also acquire an avascular character.
As soon as a woman feels pain in the lower abdomen or other ailments, she should immediately contact a gynecologist. Some pathologies can develop quickly and progress to malignant stages. If an anechoic formation is detected in a person, the woman should be systematically checked to monitor the dynamics of the development of the pathology.
During pregnancy
As a rule, an avascular achaevo formation can be detected during ultrasound diagnostics, which women undergo during the first trimester of pregnancy. The appearance of anechoic formations with fluid contents during pregnancy is not uncommon, since a complete restructuring of the body to meet the needs of the unborn child leaves a significant mark on the mother’s body.
It is important to note that an echogenic formation is not a pathology as long as it is not large. However, it can be detected in the first trimester of pregnancy. Often the formation of the fertilized egg in the uterus and education have similarities, and that is why it is difficult to diagnose pregnancy in the early stages. When hCG rises, we can talk about pregnancy. If it is not confirmed, the doctor needs to monitor the patient in order to notice and stop the development of an endometrioid tumor.
Avascular with CDK what is it
An avascular formation of the ovary is a pathological neoplasm in which there is no blood circulation. Ultrasound examination can detect various abnormalities in the structure of the ovaries and uterus.
The patient can receive a conclusion in her hands, which will indicate something like the following: “an avascular formation was detected during CDK with homogeneous anechoic content.”
What is it and should I worry? Let's try to answer this and other questions.
In other organs
In addition to the uterine follicles, cysts or small nodules most often appear in the thyroid gland. This organ consists of fairly dense but heterogeneous tissue, which is noticeable on ultrasound. Often during the diagnostic process, the laboratory technician notes that there are bubbles in the thyroid gland, which can be either large or very small.
A small avascular echogenic neoplasm in the thyroid gland is often not life-threatening, and endocrinology deals with the study and treatment of the disease.
In addition to the thyroid gland, cysts with fluid may appear in the kidney. Due to their structure and function, the kidneys often suffer not only from the appearance of bubbles with fluid contents, but also from many other neoplasms that are more difficult to treat. An avascular formation of high echogenicity can be determined by performing an ultrasound examination. Most often, an avascular neoplasm in the kidney is a symptom of a more serious disease.
What does avascular ovarian cyst mean - Health and hygiene
Avascular formation of the ovary is a pathological neoplasm in which there is no blood circulation. Ultrasound examination can detect various abnormalities in the structure of the ovaries and uterus.
The patient can receive a conclusion in her hands, which will indicate something like the following: “an avascular formation was detected during CDK with homogeneous anechoic content.”
What is it and should I worry? Let's try to answer this and other questions.