Pathological formation in the pelvic area
Many people get scared if they suddenly find a tumor in their body. For some reason, most patients associate these formations only with cancer, which certainly leads to death. However, in reality everything is not so sad.
Among the many types of tumors, there are also completely harmless ones that do not have a significant effect on life expectancy. Such “good” tumors also include cystic-solid formations. What it is is not known to every person not connected with medicine.
Some people associate the word “solid” with the concept of “large, voluminous,” which causes even greater anxiety and fear for their lives.
In this article, we will clearly and clearly explain what the above-mentioned pathology means, how and why it appears, what the symptoms are and much other useful information.
How life-threatening is a cystic-solid formation?
To begin with, we note that all the diverse types of tumors known at the moment can be divided into two categories:
- Benign (does not form metastases and is therefore not cancerous).
- Malignant (forming single or multiple metastases, which almost always spread throughout the body, which is one of the main causes of death of the patient).
In approximately 90% of cases, it can be said about a cystic-solid formation that this tumor is benign, that is, safe for life. Of course, this forecast comes true only if the patient does not refuse the treatment proposed by the doctor and scrupulously follows all the recommendations.
Only a small percentage of such pathologies are malignant. In this case, we are not talking about the degeneration of a benign tumor into a malignant one. In those few patients who are “lucky” to fall into that fateful 10%, the pathology is initially diagnosed as malignant.
Cystic-solid formation - what is it?
Both “good” and “bad” tumors are classified according to their morphological characteristics. Among the neoplasms there are:
- Cystic. The safest ones are usually easily curable. They vary in shape and tend to grow, shrink, and disappear completely for various reasons. They are a cavity filled with a viscous substance.
- Solid. The most dangerous, in a neglected state, incurable. They are characterized by a hard shell, which entails the immutability of shapes and sizes, that is, they do not increase, decrease or disappear. Solid tumors are filled with tissue fragments inside.
- Cystic-solid. They are a cross between the first and second types of tumors. They can appear in any organ, which determines the nature of the substrate in their cavity. In most cases they contain both parts of tissue and liquid.
Neoplasms in the brain
Brain tumors cause the greatest concern for patients. A cystic-solid formation (even a benign one) always compresses neighboring areas of the brain, which causes unbearable headaches in the patient.
The reason for such difficult sensations lies in the fact that the brain is enclosed in a hard shell (skull), so any tumor simply has nowhere to go. A neoplasm in soft tissues has the ability to protrude outward or occupy body cavities. Compression forces the brain tumor to put pressure on neighboring cells, preventing blood from reaching them.
In addition to pain, this is fraught with disruption of the functioning of all body systems (digestive, motor, reproductive, and so on).
What is pelvic education?
The occurrence of tumors in the pelvic area in the female body is considered a common gynecological problem.
According to statistics, in recent years the number of cases of detection of benign or malignant tumors of the vulva, reproductive organs, bladder and rectum has increased significantly.
Such diseases are diagnosed in approximately every fifth woman on the planet.
Various types of pathological formations can be detected at any age - from newborns to the elderly.
At their core, tumors in the pelvis are atypical lesions in which the process of cell division is disrupted.
Causes of tumor formation
Pelvic tumors can develop in the organs of the female reproductive system, also in the intestinal tract, bladder, bones, ureter, and skeleton.
Source: https://g-women.ru/yaichniki/tazu-chto-eto-2.html
Forecasts
Of course, the appearance of a tumor in any organ should be taken seriously. If the patient consults a doctor on time and follows all his instructions, then a solid cystic formation in the kidney, thyroid gland, genitourinary system and some other organs can be cured completely and without complications. The outcome of treatment for such a pathology in the brain is less favorable, since surgical intervention almost always affects neighboring tissues, which can lead to a number of complications. A tumor in the spinal cord or medulla oblongata is the option with the least favorable outcome. But even in these cases, timely treatment can save the patient’s life.
In most cases, the source of solid formations
, localized in the pelvis, is the uterus, not the ovaries. Therefore, echographic assessment of their internal structure can only be indirectly useful in the differential diagnosis of the origin of the tumor.
Uterine fibroids are the most common pelvic tumor
, which has a solid structure during ultrasound examination. Usually its nodes have a hypoechoic structure and are located within the boundaries of the myometrium. However, with subserous localization, the nodes can connect to the body of the uterus only in the area of a narrow base, and in some cases they can even be determined practically separately, which, when located in the area of the broad ligament, among the intestinal loops or in the area of the omentum, can lead to a false impression of the absence of connection node with the uterus.
Solid ovarian tumors
. Compared with uterine fibroids, solid ovarian tumors are much less common. This structure is usually observed in adenocarcinomas, fibromas and ovarian thecomas. Some fast-growing epithelial ovarian tumors, such as cystadenofibromas, can also give the appearance of solid tumors on ultrasound.
Tecoma formation
or fibroids are sometimes accompanied by an increase in the amount of fluid in the abdominal cavity, the genesis of which is not associated with the dissemination of tumor cells throughout the peritoneum (the so-called “benign ascites”).
In case of incomplete torsion
the ovary may also look like a solid structure. This is due to severe swelling of its tissues, caused by impaired venous outflow. Ovarian fibromas are tumors of a solid nature, the structure of which has reduced sound conductivity due to a large amount of fibrous connective tissue.
Solid appearance of cystadenofibromas
is created due to the presence in them of areas with calcification phenomena, similar to those that can be observed during calcium deposition in myomatous (usually subserous) nodes. Other types of more rarely encountered solid ovarian tumors are metastases from gastrointestinal neoplasms, lymphomas, and other tumors.
Other formations
solid structure, found in the small pelvis. During ultrasound examination, a tumor with a solid structure may appear as a rare tumor such as fallopian tube carcinoma, for the detection of which it is better to use transvaginal scanning.
For some extragenital diseases
, such as lymphoma or intestinal tumors, neoplasms, also having a solid structure, can be localized in the pelvic cavity. The diagnosis of lymphoma is established based on identifying the typical location of pathologically changed lymph nodes in the iliac and/or para-aortic regions.
Visualization of lymph nodes
during an echographic examination, it is possible only when conglomerates of significant size are formed from them, which will have the appearance of hypoechoic formations of a lobular structure, localized in the area where the chain of lymph nodes is located. Solid tumors arising from the intestine can be suspected when a characteristic hyperechoic area is detected in its central part, which is a reflection from the contents located in the intestinal lumen. In pelvic dystopia, the kidney is usually located anteriorly and above the bottom of the bladder, has a characteristic shape, and a hyperechoic pyelocaliceal complex is visualized in its central part.
- 6 minutes to read
Cystic-solid formation - what is it?
Many people get scared if they suddenly find a tumor in their body. For some reason, most patients associate these formations only with cancer, which certainly leads to death. However, in reality everything is not so sad.
Among the many types of tumors, there are also completely harmless ones that do not have a significant effect on life expectancy. Such “good” tumors also include cystic-solid formations. What it is is not known to every person not connected with medicine.
Some people associate the word “solid” with the concept of “large, voluminous,” which causes even greater anxiety and fear for their lives.
In this article, we will clearly and clearly explain what the above-mentioned pathology means, how and why it appears, what the symptoms are and much other useful information.
Cystic-solid formation - what is it?
Both “good” and “bad” tumors are classified according to their morphological characteristics. Among the neoplasms there are:
- Cystic. The safest ones are usually easily curable. They vary in shape and tend to grow, shrink, and disappear completely for various reasons. They are a cavity filled with a viscous substance.
- Solid. The most dangerous, in a neglected state, incurable. They are characterized by a hard shell, which entails the immutability of shapes and sizes, that is, they do not increase, decrease or disappear. Solid tumors are filled with tissue fragments inside.
- Cystic-solid. They are a cross between the first and second types of tumors. They can appear in any organ, which determines the nature of the substrate in their cavity. In most cases they contain both parts of tissue and liquid.
Symptoms
This pathology can manifest itself in different ways, depending on its location. Thus, for a cystic-solid formation of the medulla oblongata (remember, this section is located in the occipital part of the head and is a continuation of the spinal cord) the following manifestations are characteristic:
- Dizziness.
- Deafness (usually develops in one ear).
- Difficulty swallowing, breathing.
- Sensory impairment in the trigeminal nerve.
- Impaired motor activity.
Tumors in the medulla oblongata are the most dangerous, as they are practically untreatable. When the medulla oblongata is injured, death occurs.
In general, cystic-solid formations in various parts of the brain are characterized by the following symptoms:
- Headaches, even vomiting.
- Dizziness.
- Insomnia or drowsiness.
- Deterioration of memory, spatial orientation.
- Impaired vision, speech, hearing.
- Loss of coordination.
- Frequent mood changes for no apparent reason.
- Muscle tension.
- Sound hallucinations.
- Feeling like there is some inexplicable pressure in the head.
If a cystic-solid formation of the spinal cord occurs, this is manifested by pain, aggravated in the supine position and at night, descending lumbago, impaired motor function, and paresis.
If at least some of the signs from the above list appear, you should immediately go to the doctor.
Cystic-solid formation in the thyroid gland
As a rule, a cystic-solid formation in the thyroid gland is a cavity limited by a dense membrane, filled with cells of the thyroid gland itself. Such cavities are observed single and multiple. The reasons for this may be the following:
- Hereditary factor.
- Frequent stress.
- Hormonal disorders.
- Iodine deficiency.
- Infectious diseases.
Symptoms
A cystic-solid formation of the thyroid gland may not manifest itself at all and may be discovered by chance during a routine examination of the patient. In such cases, the doctor palpates small lumps on the thyroid gland. Many people with this pathology have complaints:
- Difficulty and even pain when swallowing.
- Shortness of breath (which was not there before) when walking.
- Hoarseness of voice.
- Pain (uncharacteristic sign).
The occurrence of a cystic-solid formation in the left or right lobes of the thyroid gland is felt approximately the same. More often they are very small in size (up to 1 cm). However, cases of very voluminous cystic-solid formation (more than 10 cm) have been recorded.
Cystic-solid formation in the kidneys and pelvis
Kidney tumors occur with approximately equal frequency in men and women. But in women much more often than in men, cystic-solid formations appear in the pelvis.
What can this bring to patients? Since this pathology is mainly observed in women of childbearing age, without timely treatment it can lead to infertility.
The main cause of the disease is hormonal disorders caused by:
- Pregnancy.
- Climax.
- Abortion.
- Taking birth control pills.
Tumors manifest themselves as pain in the lumbar region and/or lower abdomen, headaches, and menstrual irregularities.
Cystic-solid formations appear on the kidneys for the following reasons:
- Organ injuries.
- Tuberculosis (developing in the kidneys).
- Infections.
- Operations.
- Stones, sand in the kidneys.
- Hypertension.
- Congenital anomalies of the organ.
Patients complain of pain in the lumbar region, difficulty urinating, and unstable blood pressure.
Cystic-solid formations of any location are diagnosed using the following methods:
- Examination by a doctor, palpation.
- Blood analysis.
- CT.
- Ultrasound.
- MPT.
- Biopsy.
If cystic-solid formations occur in the spinal cord, additional radiography of the spine, electroneuromyography, and spinal angiography are performed.
Treatment
The discovery of a cystic solid tumor is not a reason to prepare for death. In the vast majority of cases, this pathology is successfully treated. According to indications, the doctor may prescribe drug therapy or surgery. This mainly depends on the location of the tumor.
Thus, with a cystic-solid formation on the medulla oblongata, operations are not performed; only treatment with tablets and radiotherapy is practiced. If the tumor is localized in other parts of the brain, surgical intervention using laser and ultrasound is usually prescribed.
Chemotherapy and radiation therapy are prescribed only if the tumor is inoperable. For this pathology in the thyroid gland, treatment methods depend on the size of the formation. Small nodules (up to 1 cm) are treated with tablets.
If larger formations appear, a puncture may be prescribed followed by removal of the affected part of the thyroid gland.
Forecasts
Of course, the appearance of a tumor in any organ should be taken seriously. If the patient consults a doctor on time and follows all his instructions, then a solid cystic formation in the kidney, thyroid gland, genitourinary system and some other organs can be cured completely and without complications.
The outcome of treatment for such a pathology in the brain is less favorable, since surgical intervention almost always affects neighboring tissues, which can lead to a number of complications. A tumor in the spinal cord or medulla oblongata is the option with the least favorable outcome.
But even in these cases, timely treatment can save the patient’s life.
Source: https://FB.ru/article/359628/kistozno-solidnoe-obrazovanie—chto-eto-takoe
Treatment
The discovery of a cystic solid tumor is not a reason to prepare for death. In the vast majority of cases, this pathology is successfully treated. According to indications, the doctor may prescribe drug therapy or surgery. This mainly depends on the location of the tumor. Thus, with a cystic-solid formation on the medulla oblongata, operations are not performed; only treatment with tablets and radiotherapy is practiced. If the tumor is localized in other parts of the brain, surgical intervention using laser and ultrasound is usually prescribed. Chemotherapy and radiation therapy are prescribed only if the tumor is inoperable. For this pathology in the thyroid gland, treatment methods depend on the size of the formation. Small nodules (up to 1 cm) are treated with tablets. If larger formations appear, a puncture may be prescribed followed by removal of the affected part of the thyroid gland.
Solid ovarian mass: what is it, diagnosis
A solid ovarian mass is a benign or malignant tumor. To identify pathology, ultrasound of the pelvic organs and histological examination are performed.
Solid foreign inclusions of the ovaries are less common than fibroids of the reproductive organ. They often present as adenocarcinomas, thecomas, and adnexal fibromas.
According to ultrasound results, rapidly growing epithelial tumors (cystadenofibromas) are similar to solid formations.
When a fibroma or thecoma appears, the volume of fluid in the peritoneal area increases, i.e., benign ascites occurs.
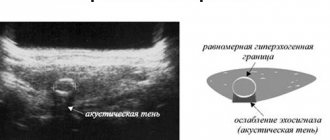
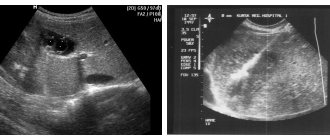
Ultrasound image. Cystic-solid formation of the ovary. Click to enlarge
Classification
All types of solid tumors can be divided into two types - benign and malignant.
Benign tumors
Benign neoplasms are clearly separated from neighboring tissues by their own membrane. Negative symptoms in patients occur only when the solid tumor increases in size and compresses nearby anatomical structures.
Its development is slow. Sometimes such nodes stop growing, decrease in size, or completely resolve without any external influence. They do not metastasize, and malignancy occurs only in rare situations.
If, in addition to dense tissue, the growth contains fluid content, it is called a voluminous cystic-solid formation. In 90% of cases it is benign, that is, it does not harm the patient’s health.
Malignant tumors
This group includes pathological foci formed from modified cells that are constantly dividing. For this reason, the tumor can reach significant sizes.
Solid cancer is aggressive, grows quickly and metastasizes in the early stages of the disease.
With the spread and necrosis of atypical cells, the body is poisoned and the functioning of tissues and organs is disrupted. The negative impact on nerve bundles causes severe pain syndromes, which can sometimes be eliminated only through drugs containing narcotic substances.
Advanced stages of cancer often lead to death.
Congenital, cerebellar cyst
If such a diagnosis is not detected in a timely manner, a person’s cyst may increase, which will cause the following changes:
- Cystic - brain;
- Excessive influence on dead tissue;
- Epidermoid;
- Right maxillary sinus;
- Impaired blood circulation;
- Death of a large area of tissue as a result of a stroke;
- Infection after encephalomyelitis;
- colloidal;
- atrophy of the vascular system.
In cases where the diagnosis was not carried out in a timely manner or time was lost in establishing an accurate diagnosis, the consequences can be dangerous:
- Violations in the implementation of movement;
- Deterioration in the ability to see and hear;
- Constant accumulation of excess fluid;
- Biological death;
Porencephalic cyst - what it is and how to treat it should also be known in order to prevent the onset of consequences. Usually, minor formations are identified during examination for the presence of another disease. In such cases, drug therapy is appropriate. For larger porencephalic brain cysts, the bubble is removed by surgery.
Source: https://gpk1.ru/mammologiya/kistopodobnoe-obrazovanie.html
Causes
Science does not yet know for certain all the reasons that cause the appearance of tumors, both malignant and benign. In the case of the occurrence of cystic-solid formations of the brain, the following reasons are distinguished:
- Irradiation.
- Prolonged exposure to the sun.
- Stress.
- Infections (especially oncovirus).
- Genetic predisposition. Note that a hereditary factor can be called the cause of a tumor in any organ, not only in the brain, but experts do not consider it a priority.
- Influence of carcinogenic factors (working with reagents, living in environmentally unfavorable areas). For this reason, tumors of various types most often occur in people who, by virtue of their profession, work with pesticides, formaldehydes, and other chemicals.
Cystic-solid formation in various organs
For many patients, medical terminology is unclear and diagnoses cause panic, even if in fact the complex name hides the common cold.
Nowadays, it is not uncommon to hear about a diagnosis of cystic-solid formations in a person. In fact, this is not a rare and quite successfully treatable disease.
Knowing what a cystic-solid formation is and that it is curable, the patient stops panicking and recovers faster.
What is a cystic-solid formation?
All cystic formations are a cavity filled with either liquid or tissue contents. From this, three types of formations in organs are distinguished.
- A formation whose cavity is filled with a viscous substance is classified as a benign tumor. It can appear, disappear, increase or decrease in size throughout life. This type of tumor is a benign cystic formation and rarely degenerates into a malignant tumor.
- In medical terminology, a solid formation is understood as a tumor that has a hard shell and clear boundaries. The formation contains a tissue component. This formation does not disappear and does not change size. As a rule, such a tumor is malignant.
- Formations that contain both fluid and parts of tissue are considered cystic-solid. Their location matters. This largely determines what content will prevail inside the cavity. Such formations in most cases are benign. In rare cases, the tumor is initially malignant.
Cystic-solid formations in organs
Such formations can occur in almost any organ. Their occurrence may be indicated by work disturbances or concomitant diseases.
But cases are not uncommon when the development of pathology occurs practically asymptomatically, and the patient learns about its presence by chance.
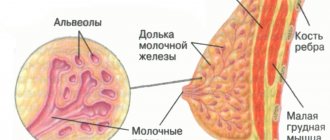
Most often, cystic-solid formations are detected during examination of the thyroid gland, genitourinary system, and brain.
Thyroid formations
Cystic-solid formations on the thyroid gland are particles of tissue from the organ itself, which are limited by a dense membrane. Such formations can be either single or multiple. Experts identify several causes of thyroid nodules, which are the main ones:
- genetic predisposition;
- previous illness caused by infection;
- constant nervous tension and frequent stress;
- hormonal disorder.
The iodine content in the body has a great influence on the normal functioning of the thyroid gland. When there is a shortage of it, this organ begins to fail, which is felt by the entire body.
Even if the patient does not suspect that he has this pathology, this does not mean that it does not manifest itself in any way. Symptoms of the disease include constant drowsiness and a feeling of fatigue. It is also reflected in the patient’s appearance.
Hair becomes brittle and begins to fall out. The skin becomes dry, prone to peeling, and has an unhealthy appearance.
Education of the pelvic organs and kidneys
The kidneys and ovaries are precisely the organs on which cystic formations most often appear. Even if they are benign, their untimely treatment can lead to serious complications.
Women between the ages of 20 and 50 are most susceptible to pathologies such as ovarian cysts. The main reason for its occurrence is hormonal imbalance.
There are a number of factors that lead to its failure and increase the likelihood of cystic-solid pathology.
- Puberty period.
- Pregnancy and postpartum period. Abortion.
- Menopause in women over 50 years old.
- Various diseases leading to hormonal imbalance, including diseases of the endocrine system.
- Taking hormonal drugs.
- Insufficient level of personal hygiene.
Cysts affecting the kidneys are a fairly common occurrence in medicine. Formations on the organ can be of various types, such as cystic, solid, and mixed types.
Despite the fact that the kidneys are a paired organ, disruption of the functioning of at least one of them leads to serious consequences. Medical statistics show that people over 40 years of age are most susceptible to pathology.
Typically, the disease affects one of the kidneys, much less often - both. The formation of a cyst is influenced by a number of factors, which include:
- various injuries and bruises of the kidneys;
- kidney damage due to an infectious disease;
- organ tuberculosis;
- operations or other surgical interventions;
- predisposition to stone formation in the organ or the already presence of them;
- high blood pressure;
- organ pathology at birth.
Renal cysts include both congenital anomalies of the organ and those acquired during life. Regardless of this, the symptoms of a cystic-solid formation are largely similar. Typically this is:
- pain in the lower back;
- "jumps" in blood pressure;
- difficulty urinating
Constant pain always indicates kidney disease. It can be sharp or dull and aching.
Brain Education
The main reason for the occurrence of a mixed cyst of the brain, like any other organ, is the impact of unfavorable factors on it. These include:
- ion radiation;
- prolonged exposure to sunlight on the body;
- constant contact with aggressive liquids and vapors;
- viruses and genetic predisposition.
Cystic-solid pathology of the brain is very dangerous due to its complications. The tumor affects any part of the organ and compresses it, thereby disrupting its blood supply. This means that part of the brain is not receiving adequate nutrition.
As a result, this can affect a person’s ability to move normally, and the functioning of the digestive system and reproductive system is disrupted. Symptoms of brain disease can vary widely. They depend on the location of the cyst and its size.
But as practice shows, the presence of a large formation does not always manifest itself with vivid symptoms.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=d1ZZQQc9cfE
The main symptoms of a solid cystic brain tumor are increased intracranial pressure, headache, dizziness and vomiting.
Diagnosis of pathology
Today, there are several methods that help diagnose mixed type cysts.
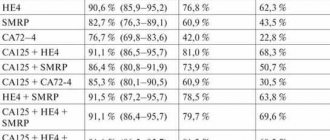
- Ultrasound diagnostics. During the study, it is possible to accurately determine the structure of the formation, its size and location. Ultrasound also allows you to see which structure predominates inside the cyst and make a conclusion about whether it belongs to one of the types. But this type of study does not allow us to determine whether a tumor is benign or malignant. It is this information that allows you to prescribe effective treatment.
- A biopsy is used to determine the malignancy of the tumor. Taking material for analysis from the cyst capsule is quite simple and painless. A thin needle is inserted into the tumor and the contents are drawn into a syringe. Next, it is sent to the laboratory for analysis.
- A blood test can also help diagnose a solid cystic tumor. Based on the results of the analysis and the content of hormones and the ratio of blood components, a specialist can make a conclusion about the presence of pathology and its nature.
- Computed tomography is the main diagnostic method before surgery as a treatment. Using this diagnostic method, you can determine the location of a large tumor in an organ and obtain accurate information about the nature of the pathology.
Depending on the diagnostic results, the doctor prescribes appropriate treatment. It can be either traditional or operational. The method of treatment depends on the size of the tumor and possible complications associated with it.
Source: https://vseokiste.ru/drugoe/kistozno-solidnoe-obrazovanie.html
Symptoms
This pathology can manifest itself in different ways, depending on its location. Thus, for a cystic-solid formation of the medulla oblongata (remember, this section is located in the occipital part of the head and is a continuation of the spinal cord) the following manifestations are characteristic:
- Dizziness.
- Deafness (usually develops in one ear).
- Difficulty swallowing, breathing.
- Sensory impairment in the trigeminal nerve.
- Impaired motor activity.
Tumors in the medulla oblongata are the most dangerous, as they are practically untreatable. When the medulla oblongata is injured, death occurs.
Types of knot formations
All neoplasms of the thyroid gland are divided according to their course into benign and malignant; by quantity into single (solitary) and multiple. Solitary nodes are more dangerous than multiple small ones, as with diffuse goiter.
According to the activity of hormones: toxic and calm non-toxic. The appearance of nodes increases with age. Benign nodes account for 95% of cases. This suggests that when nodes are discovered in you, you do not need to immediately prepare for death. Based on the structure of nodules, they are divided into cystic (liquid), solid and mixed:
- if the cystic component occupies ≤10%, it is a solid node;
- if from 11 to 50% - mostly solid;
- predominantly cystic – the cystic component occupies from 51 to 90%;
- with purely cystic – cysticity more than 90%, truly cystic nodes are rare; they are always benign.
The larger the cyst, the softer it is. This is an anechoic formation. Solid and predominantly solid are more common.