The process of culturing embryos directly relates to the procedure of artificial insemination. Today, the infertility of one of the partners is no longer the final verdict on the possibility of having children, since, thanks to advances in medicine, procedures for fertilizing eggs in artificial conditions are available, including the method of in vitro fertilization (IVF method).
It is IVF that is considered one of the most effective ways to conceive a child for couples in which, due to the presence of certain pathologies or diseases, the woman cannot conceive or bear a fetus, or the man has reproductive problems. This method is a method of overcoming infertility, but it does not cure it.
Theory
The penetration of the fertilized egg into the endometrium, which lines the inner surface of the uterine cavity, is called implantation. During the process of implantation into the mucous membrane, the embryo damages soft tissue, which can cause bloody discharge from the vagina. The rate of pregnancy on different days after ovulation (DPO) depends on:
- the degree of loosening of the endometrium and its nutrient content;
- the level of progesterone in the blood, which prevents the onset of menstruation;
- the presence of infectious agents and microflora in the reproductive organs in the body.
On the 5th day after embryo transfer, pregnancy is already possible, however, during the IVF procedure, early implantation is rare. This is due to the development of embryos outside the female body, and after transfer they require some time to adapt to new environmental conditions. Conception is not a one-step process; each stage in the IVF procedure is of great importance in the onset of the gestational period and normal development of the fetus.
Multiple pregnancy
Multiple pregnancies after IVF are quite common. According to medical indicators, the probability of implantation of two or more embryos after in vitro fertilization is 30 times higher than with natural conception.
A woman with a multiple pregnancy is at risk because the possibility of developing anomalies increases. The implantation of two or more embryos significantly increases the load on the body. At the request of the patient, reduction can be performed - reducing the number of fetuses. This procedure can be carried out up to 13 weeks.
Timing of embryo implantation
When male and female reproductive cells fuse, a diploid cell is formed, which begins to actively divide. First, a blastomere of 6-8 cells is formed, then a morula (16-64 cells) and only then a blastocyst, which is implanted into the uterine wall. Reproductionists distinguish three periods of embryo implantation:
- Early – 6 DPO or 3 DPO in case of IVF;
- Average – 7-8 DPO or 5 DPO for three days or five days in case of IVF;
- Late – 10 DPO or 7-8 DPO if undergoing IVF.
Average implantation occurs within 7-8 days after ovulation. During in vitro fertilization, a reproductologist collects a mature oocyte, after which he fertilizes the sperm in the laboratory. It takes an average of 3-5 days to grow blastomeres, after which viable embryos are implanted into the uterus. Implantation of the fertilized egg at 5 DPP is a fairly rare occurrence, which in 90% of cases occurs when using five-day embryos.
Blastomere stage
On days 2-4, the zygote fragments and blastomeres are formed. First, the cell is divided in half, then each of the resulting cells is divided in half again. But division occurs asynchronously, so the embryologist may notice an odd number of blastomeres.
During the cleavage period, the stage is determined by the number of cells. To assess the quality of the future embryo, the following indicators are taken into account:
- size and shape;
- number of nuclei, normally one in each blastomere;
- state of the cytoplasm: vacuoles (vac), granulation (gra), accumulation of organelles (serr), harmful substances (rb) - bad signs;
- the percentage of fragmentation is the number of nuclear-free structures, normally no more than 10%.
Based on the results of the examination, the embryologist makes an assessment and decides which zygotes are promising for further development.
Stage of embryo compaction
On the 3rd day after fertilization, the process of compaction begins. Blastomers develop processes that help them tightly cling to neighboring cells and establish contact. This occurs due to specific proteins and calcium ions.
Gradually, the cells spread out and a cytoskeleton is formed. If at this stage there is not enough calcium in the medium, the embryo will become uncompacted. Otherwise, a morula is formed - this is an embryo at the compaction stage.
Embryo at the morula stage
Morula gradually loses its dependence on calcium. But its quality is difficult to assess. In electronic photographs, the cells appear smoothed out, and their number is almost impossible to determine.
At the morula stage, a good embryo has at least 8 cells. It acquires an even spherical shape, without various protrusions and depressions. Poor prognosis is the presence of vacuoles and fragmentation.
Embryo at the cavitation stage
From the end of the 4th to the beginning of the 5th day, the morula enters the cavitation stage. The development of the embryo at the mcav stage involves the appearance of a cavity that divides it into two parts:
- Trophoblast.
- Interior of cells.
The cavity is formed by pumping liquid into it. This is a transition point after which we can say that the morula has become a blastocyst.
Embryo at the blastocyst stage
Due to the increase in fluid volume, the volume of the cavity begins to increase. After what time the morula turns into a blastocyst is determined individually. The process can last up to 12 hours.
At this stage, the blastocyst is assigned an alphanumeric designation that characterizes three parameters:
- the number from 1 to 6 indicates the stage of development;
- letters from A to C – quality of intracellular mass;
- the second letter A, B or C is the state of the trophoectoderm.
For example, a stage 4 embryo is an embryo of average quality that has a chance of implantation.
An assessment of the quality of the embryos is necessary so that the doctor can determine the timing of replantation, and when using vitrified embryos, the time of defrosting. In some cases, early defrosting and rearing of embryos is necessary.
Implantation during cryotransfer
In embryological practice, two methods of implanting embryos into the uterine cavity are used:
- Instant transfer - implantation of diploid cells into the uterus immediately after their cultivation in a nutrient medium;
- Cryotransfer is the transfer of embryos thawed immediately before IVF into the uterine cavity.
Cryotransfer is possible if the couple has previously used assisted reproductive technologies to conceive. To avoid repeated stimulation of ovulation if IVF is unsuccessful, it is recommended to freeze part of the fertilized eggs for subsequent attempts.
Conception on the 5th day after cryotransfer occurs infrequently, which is due to the need for embryos to go through an adaptation period when entering the female body. If a blastocyst is implanted into the endometrium, patients may experience objective changes in their health status.
Third trimester
The third trimester requires continued monitoring of the condition of the expectant mother and the development of the fetus. Women attend courses that teach preventive measures for premature birth. It is important to undergo Doppler blood flow monitoring monthly.
After 33 weeks, pregnant women again undergo ultrasound screening. Evaluated:
- condition of the placenta and blood flow;
- ratio of fetal size to gestational age;
- condition of the child’s internal organs.
If the expectant mother notices symptoms of premature labor that began before the 37th week, you should immediately call an ambulance. After hospitalization, the woman will undergo conservation therapy, which will allow her to carry the child to a safe term for birth.
Embryo development by day
With a successful IVF protocol, the implantation of embryos into the endometrium occurs according to the following scheme:
- 0 DPP – implantation of blastomeres into the uterine cavity or cryotransfer;
- 1 DPP - the embryo emerges from the protein shell;
- 2 DPP - the blastocyst attaches to the surface of the endometrium;
- 3 DPP – the process of implantation of the blastocyst into the uterine mucosa begins;
- 4 DPP – the process of implantation of the zygote into the uterus continues;
- 5 DPP – implantation is completed;
- 6 DPP – the developing placenta begins to produce hCG;
- 7 DPP – the content of hCG in the body increases significantly.
The above scheme is typical for early implantation of blastocysts into the uterus. If the implantation process occurs at 5 DPP of the five-day period, the sensation of pregnancy occurs several days later.
Second trimester
Maintaining a pregnancy after IVF is not always easy. Patients must be constantly monitored by a doctor and undergo appropriate examination. Women regularly donate blood to determine the concentration of free estriol, total hCG and alpha-fetoprotein hormones. This allows you to diagnose disorders at an early stage, for example, Patau syndrome, Down syndrome, etc.
Doctor's examination during IVF pregnancy
Between 20 and 24 weeks, all women should undergo a second-level ultrasound. This means that, in addition to examining the woman’s organs, an assessment of the child’s internal organs is carried out. The placenta is also visualized and the quality of blood flow in it is determined.
Signs of conception after IVF
After the IVF procedure, many women begin to “listen” to changes in the body in order to determine whether conception has occurred or not. Many of the sensations they describe are subjective and are more associated with excitement rather than with real physiological changes in the organs of the reproductive system.
Conventionally, reproductologists divided symptoms after IVF into two categories: subjective and objective. Subjective symptoms include:
- emotional lability;
- rapid fatigue;
- heaviness in the lower abdomen;
- tingling in the uterine area;
- frequent mood changes;
- vaginal discharge.
A few days after embryo transfer, changes characteristic of the beginning of a new menstrual cycle may occur: soreness in the chest, pain in the lower abdomen, nausea, etc. Reproductionists warn that if the embryo is successfully implanted into the uterus, they completely disappear and do not in any way interfere with the normal course of pregnancy.
Objective symptoms that occur when a blastocyst penetrates the endometrium include:
- increase in basal temperature;
- detection of hCG in blood serum;
- a general increase in temperature to 37.2 degrees Celsius.
It is possible that the mentioned sensations may occur at 5 DPO when five-day embryos are transferred into the uterus. Unlike the “three-day” ones, they contain more cells, and therefore the period for their subsequent division and transformation from a morula into a blastocyst, ready for implantation into the uterus, is reduced.
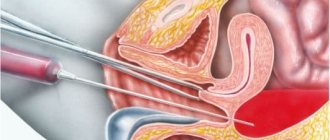
How to prepare for egg retrieval (puncture)
Embryo culture requires the physical removal of an egg from a woman's ovary. Such a procedure requires mandatory preparation, the rules of which the woman begins to follow in advance. For five days you should avoid sexual intercourse, stop drinking alcohol, fried, smoked, and fatty foods. It is forbidden to visit the bathhouse, sauna, or take hot baths.
On the eve of the procedure you should:
- refuse dinner (you are allowed to eat no later than 17:30);
- remove varnish or any coating from nail plates;
- do not drink liquid after 24:00.
In the morning before the puncture, it is forbidden to smoke, eat, drink, or chew chewing gum. If a woman wears contact lenses, it is better not to wear them during the operation.
The date of the procedure should correspond to the time of natural ovulation.
Postponement of five-day days
With IVF, blastocyst transfer is scheduled for 5 or 6 days. The procedure is performed in a clinic. Sometimes doctors use local anesthesia during the transfer. However, in most clinics, blastocyst transplantation is carried out without anesthesia.
Before the transfer, the woman lies down on a gynecological chair, as for a routine examination. A thin catheter is inserted into the cervix, through which cells pass from a container with a water base. The procedure takes no more than 15 minutes. After cell transfer, it is recommended to lie down.
In the next 2 weeks, you must follow your doctor's recommendations. The success of in vitro fertilization depends on this. The woman is prescribed maintenance hormonal medications. Until results are obtained, it is advised to avoid physical and emotional stress, and also to refrain from intimate relationships.
During IVF, you can do a double transfer. This procedure involves planting three-day-old trees. After two days, the procedure is repeated and the blastocyst is transferred. But the high risks associated with the possibility of terminating an ongoing pregnancy force doctors to abandon this technique.