Every woman who has learned on an ultrasound that she has two corpus luteum maturing in different ovaries is interested in the likelihood of a multiple pregnancy. This phenomenon is actually rare, but it does not always indicate a one hundred percent probability that two mature eggs will be fertilized at once. To date, the reasons for this process remain poorly understood. It is also reliably impossible to answer the question why 2 corpora lutea are formed in different paired glands in the female body. According to research results, not one, but several follicles can mature in one cycle. Moreover, ovulation sometimes occurs in two ovaries at once. Thus, two corpus luteum can develop in one ovary at the same time.
Where does it come from?
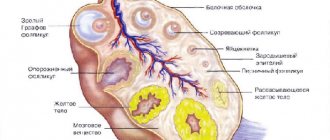
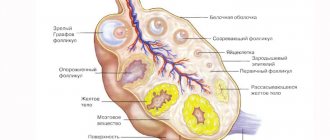
After the next maturation of the follicle, its contents with the egg are “poured” into the abdominal cavity (this process is called ovulation). When fertilized by a sperm, this egg develops into a fertilized egg. The outer layer of the ovary forms the so-called corpus luteum at the site of the burst Graafian vesicle (follicle).
The corpus luteum in the ovary is also called a temporary endocrine gland; it contains lutein. The fact of its appearance indicates that ovulation has occurred. During laparoscopy (examination of the contents of the abdominal cavity using optical instruments), it is distinguished by a yellow color. It produces the hormone progesterone, which is responsible for the development of the first months of pregnancy (10-14 weeks). If a woman does not become pregnant in this cycle, the lifespan of the gland is usually limited to two weeks. Normally, by the beginning of the next cycle (that is, by the beginning of menstruation), it disappears.
Is this pregnancy?
It is possible to determine that a woman has not one luteal formation in her ovary, but two, immediately after ovulation using an ultrasound.
We recommend you find out: What is a corpus luteum cyst of the left and right ovary?
The formation of a pair of objects is not yet a reliable sign of pregnancy. You can find out about the onset of conception only after a delay.
The corpus luteum is necessary for pregnancy. It is a source of progesterone, a hormone that maintains proper uterine tone and regulates the state of a woman’s immune system.
If conception occurs, the luteal sac continues to function for 3-4 months, after which it transfers its functions to the formed placenta.
It is logical to assume that two bags promise a multiple pregnancy. It will be possible to find out about this only at 5-7 weeks, when the heartbeat of the embryos is visualized.
The result of the examination cannot be predicted in advance.
If there are two corpora lutea and one fertilized egg, then only one egg has been fertilized, or there are twins in one fertilized egg, which the woman will find out about much later.
When there are two fertilized eggs in the uterus, we are undoubtedly talking about a multiple pregnancy. Even if a single luteal formation has formed in the ovary.
The presence of two corpora lutea does not guarantee that conception has taken place. If fertilization does not occur, then a few days before the next menstruation, the luteal formation begins to regress, and it gradually resolves.
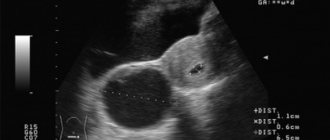
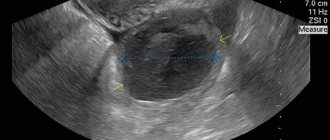
Corpus luteum on ultrasound
Possibilities of ultrasound (ultrasound) in monitoring the development of the luteal gland:
- Determination of size, quantity, localization.
- Identification of deviations from the normal development of the temporary gland during pregnancy.
On ultrasound, the luteal gland looks like a round liquid formation with a diameter of 12-30 mm. Its appearance in the middle of the menstrual cycle with a gradual decrease in size towards the beginning of menstruation is considered normal (for this reason the formation is called false). If pregnancy develops, the temporary gland exists for 10-14-16 weeks and is called “true”.
Features of multiple pregnancy
The woman who will soon become the mother of identical twins is to be congratulated. However, with multiple pregnancies, the following risks increase:
- premature rupture of amniotic fluid;
- the onset of labor before the due date;
- development of late toxicosis.
As a rule, in the case of carrying several babies, labor begins not at 40, but at 35-37 weeks. Sometimes a caesarean section is performed. Despite the potential risks associated with multiple pregnancies, with careful monitoring of the expectant mother by a gynecologist, problems can usually be avoided.
Two temporary secretion glands in one ovary do not guarantee that a woman will become the mother of two children at once. The conception of several babies at the same time is indicated by two fertilized eggs in the reproductive organ. This fact is most reliably determined at 13-14 weeks of pregnancy.
« Previous entry
Deviations in the development of VT
This gland produces the hormone progesterone, which stimulates the growth of the uterine mucosa for implantation and development of the fertilized egg before the formation of the placenta. The absence of a temporary gland occurs during the menstrual cycle without ovulation and is attributed to hormonal disorders that can cause infertility.
Large sizes (3-5 cm or more) of the temporary gland are considered cysts, not life-threatening; almost 5% of women have them. Cysts develop due to adverse effects on the fragile female body (stress, heavy loads). Such formations gradually disappear over 2-4 monthly cycles; they do not interfere with pregnancy. But all this time the woman should be observed by a gynecologist. After all, this formation, although very rare, can still cause complications (rupture of the cyst with bleeding, suppuration), and then surgery is necessary.
All these months in the second phase of the cycle, the uzist can see two temporary glands at once - the new and old corpus luteum (that is, the cyst left over from previous cycles).
The disappearance of the temporary gland during pregnancy before 16 weeks creates a threat of its interruption and requires observation and treatment.
Causes
The exact reasons for the formation of two corpora lutea in one menstrual cycle have not yet been clarified, but, according to recent research, this occurs under the influence of the following factors:
- spontaneous multiple ovulation;
- stimulation of follicle production;
- in vitro fertilization;
- hereditary predisposition (frequent cases of multiple pregnancies in the family);
- defects in the development of the uterus.
In the last few years, the presence of two corpora lutea and multiple pregnancies has most often been observed in women who have undergone in vitro fertilization (IVF).
The IVF program involves ovarian stimulation, which provokes so-called superovulation - the simultaneous maturation of several eggs. After fertilization, a woman is implanted with 2 to 6 embryos, which significantly increases the chances of a multiple pregnancy.
Spontaneous multiple ovulation is most often observed in women aged 35-39 years - doctors associate this with the hormonal “explosion” that occurs in the female body before the onset of menopause. Accordingly, the ability to conceive twins at this age is considered increased.
The hereditary factor also plays an important role in the development of multiple pregnancies - scientists have identified a special gene in the body of some women that is responsible for the maturation of several follicles.
Finally, another possible cause of double ovulation is the so-called uterine duplication.
It is a rather rare pathology in which there is a septum in the organ cavity that divides it into two parts.
It should be noted that, despite the increased likelihood of several eggs maturing, pregnancy with such a diagnosis is quite difficult and requires constant medical supervision.
Why are there two of them?
It is often possible to detect two corpus luteum during ultrasound examinations of the ovaries. This condition can be considered a variant of the norm. The following factors may be the reason:
- Genetic predisposition.
- “Solid” age of a woman.
- Hormonal stimulation of ovulation in preparation for IVF (in vitro fertilization).
If the expectant mother has had twins in her family, then the diagnosis of twins will not be surprising. This feature was confirmed by studies that discovered several genes responsible for this condition. In women with such “baggage”, two corpora lutea are often found in one ovary after ovulation. This means that two dominant follicles have matured in the ovary, and both have ovulated.
However, genetic predisposition does not mean that you will definitely become the mother of twins. It happens that only one of two eggs is fertilized. And then 1, not 2 fetuses develop (the “excess” corpus luteum gradually resolves).
Women close to the onset of menopause (over 35 years old) are accompanied by a “storm of hormones.” This leads to the simultaneous maturation of several follicles, nature urges the woman to continue the birth. Two corpus luteum may appear in different ovaries or in one. At this age, multiple pregnancies (usually children of different sexes) are more common, even in the absence of a genetic predisposition.
The use of hormonal drugs during the IVF preparation stage works in a similar way. The result is the appearance of many mature follicles, which are used for in vitro fertilization. As a result of manipulation of the eggs, a corpus luteum develops in one or both ovaries. Usually several embryos are placed in the uterine cavity, but their survival rate is unpredictable, as is the number of temporary glands that arise.
Causes
If previously such changes in the female body occurred for completely natural reasons, now the use of hormonal drugs can lead to a similar result, since when they are taken, the maturation of eggs is stimulated.
But modern medicine cannot accurately answer the question of why two eggs mature on two ovaries and two corpus luteum are formed at the same time. A similar process, according to scientists, can be caused by:
- Multiple spontaneous ovulation
- Ovulation stimulation
- In Vitro Fertilization
- Uterine malformations
- Genetic predisposition
If fertilization does not occur and pregnancy does not occur, the corpus luteum dissolves. The presence of two corpora lutea at once indicates that two sex cells have matured in the body at once. If both of them are fertilized, they speak of a multiple pregnancy. The result of such a pregnancy is the birth of twins.
It is usually believed that the appendages work alternately and the egg matures first on one side and then on the other. For example, the same in vitro fertilization in a certain way relates to the stimulation of ovulation.
With this method, a woman’s body can contain up to several dozen mature eggs, thus increasing the likelihood of pregnancy.
The likelihood of two eggs maturing at once is always higher in those women in whose family the birth of twins has already been recorded. In such mothers, such a property is already fixed at the genetic level.
A double pregnancy can also occur with such an anatomical feature of the uterus as its doubling. The peculiarity of this structure of the uterus is the presence of a septum, which is normally absent. According to statistics, multiple pregnancies most often occur in women whose age exceeds thirty-five years.
The reason for this is the high level of hormones, which leads to spontaneous ovulation with the maturation of several eggs at once. At this age, the level of hormones in the blood increases due to a “hormonal storm”, which always precedes the onset of menopause, when all the functions performed by the ovaries gradually fade away.
Two corpus luteum in the early stages of pregnancy make it possible to provide the body with all the necessary hormones and, accordingly, ensure the normal course of pregnancy for 10-16 weeks of their existence.
Cystic formation
Exceeding the size of the corpus luteum may be due to the formation of a cyst. Usually it appears at the site of a follicle that was unable to burst during the process of ovulation and an egg remained inside it. There are usually no symptoms, only some women with hypersensitivity complain of a pulling sensation in the lower abdomen. There is no need to be afraid of a luteal cyst - in the vast majority of cases it resolves on its own in 2-3 cycles, even if it is very large - up to 8 centimeters.
Also, do not panic if, along with the fact of a long-awaited pregnancy, the doctor also confirms the presence of a luteal cyst on the ovary. It does not affect the baby or the course of pregnancy. Usually, by the 20th week of gestation, such cystic formations resolve on their own; nothing needs to be treated. But we must not forget about possible complications - torsion of the cyst stalk and its rupture. The likelihood of this is low, but you should not ignore it. Therefore, a woman needs to visit her doctor more often and carefully monitor her own condition.
If sharp pain occurs, accompanied by bleeding, as well as a drop in blood pressure, you should immediately call an ambulance. It should be noted that in most cases, when emergency surgery is required, the operation is performed laparoscopically and the pregnancy can be saved.
Possible pathologies
In gynecology, pathologies of the corpus luteum in the ovary exist in small quantities. Most often they occur in women of reproductive age, less often in adolescence and during menopause.
Absence of gland
There is no VT due to the oocytes not being released. This requires adjustment of hormonal levels, and sometimes artificial stimulation of ovulation is used. If there is insufficiency or absence of the corpus luteum in the ovary after the release of the egg, the woman is prescribed drugs containing progesterone.
During artificial insemination, doctors often use drug stimulation to promote the formation of the gland.
Corpus luteum deficiency
Diagnosed with small sizes of VT. It is characterized by insufficient production of hormones of the second phase of the cycle against the background of normal ovulation. In this case, the study of progesterone levels is carried out additionally by drawing blood for analysis. Successful conception requires the prescription of progesterone-containing drugs, which the woman continues to take during pregnancy.
How is it formed?
The formation of a temporary gland occurs in accordance with certain stages. The entire lifespan of this temporary formation is called the corpus luteum phase. Here are the main stages of the life of the gland in non-pregnant women:
- Proliferation - follicular membranes, the integrity of which was disrupted at the time of ovulation, begin to “group” into a characteristic fold, and a gland is formed.
- Vascularization - gland cells divide, it begins to be actively supplied with blood due to the germination of the blood network.
- Heyday is the period of maximum productivity of the temporary gland, when the production of hormones occurs at an active pace in the highest concentrations.
- Regression - dystrophic changes begin inside the gland. It gradually decreases, reduces and gradually stops the production of hormones altogether, becoming whitish scar tissue, which eventually resolves on its own. The gland disappears, only to return in the next menstrual cycle.
If a woman has conceived a baby in the current cycle, then after the flowering stage there is no regression, and the temporary formation itself begins to be called the gravidate (corpus luteum graviditatis), or corpus luteum of pregnancy. It becomes such immediately after the embryo attaches to the endometrial layer of the uterus.
Immediately after implantation, the chorionic villi begin to produce a special active substance - human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG). The task of this hormone is to maintain the functionality of the corpus luteum, since the need for progesterone during pregnancy is high.
HCG keeps the temporary gland in working order until a full-fledged placenta is formed, which is capable of taking over the function of producing progesterone and a number of other active substances necessary to continue pregnancy.
Thus, outside of pregnancy, iron in the fair sex lives 10-13 days after the release of the egg. During pregnancy, the lifespan of the gravid corpus luteum increases; it is active until 11-14 weeks of pregnancy. At the end of the first trimester, the young placenta begins to work and already at the beginning of the second trimester the stage of regression for the gravid corpus luteum begins. It proceeds in the same way, the gland begins to decrease, the secretion of progesterone by it is reduced, a whitish body is formed and gradually no trace remains of it.
Viability of the gland
In the absence of conception, the lifespan of VT is no more than 10 days. After their expiration, the iron degenerates into scar tissue and stops producing progesterone, being rejected during menstruation along with the endometrial cells of the uterus. Before rejection, such a formation in the ovary is called the white body - it forms a scar after itself. Under the influence of regressed glands, the tissue of the appendage becomes scarred.
With successful fertilization of the egg and fixation of the fertilized egg in the walls of the uterus, the corpus luteum continues to function. Its viability period increases to three months - until the resulting placenta begins to fully produce progesterone. After this, the gland dies off as unnecessary.