Most of the women who have encountered this problem know what the corpus luteum is in the ovary, but few have heard about the white body. Therefore, if the doctor told you about it during the ultrasound, do not rush to sound the alarm. The white body of the ovary is a residual manifestation of a neoplasm during physical resorption in a woman’s body. It appears every time after the corpus luteum of the ovary has gone through the entire cycle from maturation and development to regression.
The nature of the development of the white body
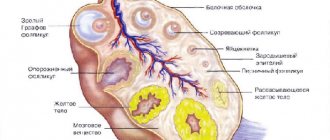
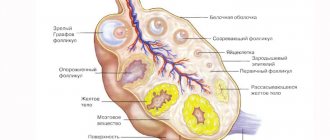
The corpus luteum of the ovary is a temporary secretion gland formed in the second phase of the menstrual cycle.
It appears after ovulation. During the course of the last of the bursting walls of the follicle, an egg is released, entering the peritoneum, and then into the fallopian tubes. The luteal gland is necessary to ensure the movement of the female cell to the uterus for conception and to maintain further pregnancy by producing progesterone. In the absence of fertilization, it regresses. The white body is a scar that remains after the disappearance of VT.
Stages of gland formation from proliferation - the first stage of development - to complete regression:
- Proliferation. 14-16 days of the cycle. Active division of cells necessary for the formation of the future luteal gland. This occurs on the walls of the ruptured follicle, less often - immediately before the moment of its rupture. At this time, the maximum level of luteinizing hormone is determined in the woman’s body.
- Vascularization. Days 16-18 of the cycle. Development of blood vessels of the corpus luteum of the ovary. The latter continues to grow. Progesterone begins to be produced, the level of which gradually increases.
- Bloom. 19-24 days of the cycle. VT functionality reaches its peak. At this time, the maximum concentration of progesterone in a woman’s body is observed. Due to active blood supply, iron acquires a burgundy hue.
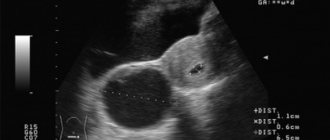
- Regression. 24-28 days of the cycle. In the absence of conception, the corpus luteum gradually decreases in size - its cells experience dystrophic changes, and hormonal function decreases. At this time, a white formation forms - a scar left by the luteal gland. It is detected using an ultrasound examination performed a few days before menstruation, which determines the presence of a small scar on the ovary - this is the white body.
The normal functioning of VT can be determined by the appearance of yellowish discharge in the second phase of the cycle, which does not cause discomfort.
When pregnancy occurs, the yellow gland does not regress. It begins to produce even more progesterone to maintain the viability of the fetus and is called the gravidar luteal formation. Its full functionality lasts up to 12 weeks, and by 20 weeks it completely disappears. The production of hormones by this time is carried out by the placenta. A white body does not form in one of the ovaries during pregnancy.
Reasons for appearance
To understand why the corpus luteum forms in the ovary, you need to know what it is, as well as what the corpus luteum is and what are the stages of its formation. Neoplasms can occur when the membrane lining the uterus prepares for gestation by producing oxytocin, relaxin, estrogen and inhibin. These hormones are needed in sufficient quantities for the pregnancy to develop normally.
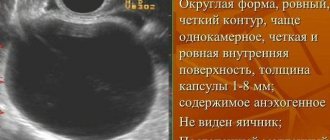
The ovarian gland contains lutein, which is yellow in color. Its size ranges from 10 to 27 mm and depends on the luteal phase of the cycle. If the corpus luteum of the ovary is significantly smaller or, conversely, larger in size, then there are deviations from the norm. In this case, they talk about problems in the functioning of the gland or the presence of a cyst in it.
The development and functioning of this endocrine gland is influenced by the immune system, pituitary gland and ovaries. The gland goes through 4 stages:
After the level of the hormone lutein increases, and after the egg is released into the peritoneum, folds form on the walls of the follicle, and blood is released into the cavity. The cells that line this cavity begin to divide rapidly. But it doesn't always happen this way. It happens that the formation is not preceded by the process of maturation and development of the endocrine gland, that is, ovulation, but it is formed in the process of luteinization of the follicle, which dominates.
At this stage, blood vessels form in the follicle. As a result of this process, the gland continues to develop, its functioning is complete, thanks to good blood circulation. According to experts, this gland is the only organ in a woman’s body that has the strongest blood flow.
- Bloom.
At this stage, the hormones of the corpus luteum are most active. The gland becomes larger, extending beyond the ovary, and turns burgundy. If conception does not occur, then this ovarian body remains moderately active for approximately 10-12 days, and then its activity declines.
At this stage it turns into a white body. If pregnancy does not occur, the cells undergo dystrophic changes, decrease in size and, ultimately, a scar is formed, which is called the white body. After some time it will disappear. Next, the level of hormones will decrease, the mucous membrane of the uterus, containing a large number of blood vessels, is exfoliated (rejected) and the woman begins her menstrual cycle. The follicle begins to mature in a new way.
Possible pathologies of white formations on the ovaries
The absence of the white body of the ovary is possible due to disruption of the luteal gland. This happens for reasons:
- hormonal imbalance;
- formation of an ovarian cyst;
- inflammatory or infectious processes in the appendages;
- lack of ovulation - white and yellow bodies do not have the opportunity to form;
- the onset of menopause is the cessation of a woman’s reproductive function.
Symptoms of dysfunction of the ovarian VT:
- pain in the left or right lower abdomen;
- Irregularity of the menstrual cycle - long delays in menstruation or their onset too early;
- change in the nature of menstruation - an increase or decrease in the amount of bleeding, the appearance of pain in its first days;
- the formation of acne on the face, deterioration of the condition of the skin, hair and nails - a sign of a violation of hormone levels;
- pathological vaginal discharge.
The most common occurrence is the ovarian VT cyst. This occurs due to hormonal imbalance or against the background of inflammation of the genital organs. The appearance of a white body does not occur in the cycle in which the pathology arose.
The white body may also be absent if there is insufficient yellow formation in the ovary. It is manifested by a small amount of progesterone produced and a short menstrual cycle - its duration ranges from 22-25 days. Pregnancy occurs extremely rarely against the background of VT insufficiency. If it occurs, there is a high probability of spontaneous miscarriage.
Is it dangerous
Lack of progesterone leads to inadequate functioning of the corpus luteum, as a result of which a woman cannot become pregnant, she experiences miscarriages and fetal death.
The most common pathology is a corpus luteum cyst. It can be temporary or functional. As a rule, it does not grow more than 6 millimeters. Pronounced symptoms are pain in the lower abdomen and lower back, or a feeling of some discomfort. Such a cyst is not dangerous and can go away on its own as the period increases, or after the menstrual cycle if fertilization has not occurred.
White body of the ovary. What is this? As mentioned above, it does not pose a danger, since it is not a disease or neoplasm, but a consequence of the extinction of the corpus luteum. It forms in place of this body in the form of a scar and gradually disappears. If pregnancy occurs, the white body is not formed at all.
Is medical intervention required?
To assess the functioning of the appendages, diagnostics of the body is necessary. The gynecologist prescribes several types of ovarian histology to determine the functionality of the corpus luteum and the regularity of the appearance of the white body:
- donating blood for progesterone concentration on days 22-24 of the cycle;
- vaginal smear – assessment of local microflora, identification of inflammatory and infectious processes;
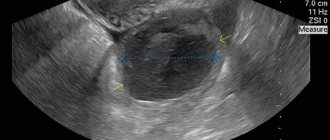
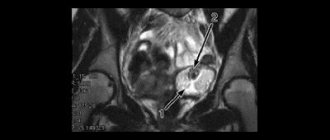
- Ultrasound of the genital organs - the study must be carried out several times in the second phase of the cycle to determine the correct stages of formation of the luteal gland, ending with the appearance of the white body.
It is impossible to identify the white formation remaining on the tunica albuginea of the ovary in the previous cycle, because the entire surface of the appendage consists of similar scars.
A woman can independently determine the nature of the menstrual cycle using a basal temperature chart. At the same morning time, she should measure the temperature in the rectum without getting out of bed. Normally, at the time of ovulation, the lowest values are observed, which increase sharply when the luteal gland begins to function. Regression of the latter and the appearance of a white body in the right or left ovary is determined by a decrease in temperature immediately before the onset of menstruation.
The presence of a temporary endocrine gland in the ovary does not always guarantee the formation of a white body due to the possibility of pregnancy or degeneration of the gland into a cyst.
When pathologies are detected, the following types of means are used:
- hormonal drugs - prescribed for failure of the endocrine function of the ovaries, restore the course of the menstrual cycle, support the performance of VT;
- antibacterial - necessary when identifying infections;
- anti-inflammatory – eliminate the source of inflammation in the genitals;
- vitamins – help regulate the monthly cycle, saturate the body with useful substances;
- absorbable – contribute to the disappearance of the luteal cyst;
- folk remedies based on herbal decoctions - normalize the course of the phases of the cycle.
What to do
If all your attempts to get pregnant and carry a child to term have not been successful, this may indicate that you have problems with the balance of hormones, as a result of which the endocrine gland of the ovary does not function as it should. The first step is to do an ultrasound. Also quite informative methods for determining hormonal imbalances and malfunctions of these bodies are measuring basal temperature, as well as taking blood for analysis. Blood sampling occurs on the seventh or eighth day after ovulation occurs. Thus, the level of the hormone progesterone is determined. Cells are also collected from the uterus by scraping.
Recommendations from experts
Every woman should know that white formation is not a disease - it indicates the correct course of the menstrual cycle. To maintain health, experts recommend:
- visiting a gynecologist with an ultrasound scan every six months;
- refusal to take medications without a doctor’s prescription;
- control of your own health;
- timely treatment of all detected pathologies.
Leading a healthy lifestyle is considered a good way to prevent diseases of the ovaries and the entire reproductive system. Every woman needs to organize proper rest, regular moderate physical activity, and proper nutrition. This will eliminate possible irregularities during the menstrual cycle.
A white body in the ovary is not a disease, but a scar formed during the regular course of menstruation. It indicates the imminent onset of menstruation. A white formation does not form during pregnancy; in other cases, its absence is considered a pathology and requires diagnosis by a gynecologist.
Function [edit | edit code]
The ovaries produce steroid hormones. The ovarian follicular apparatus produces mainly estrogens, but also weak androgens and progestins. The corpus luteum of the ovaries (a temporary endocrine gland that exists only in the luteal phase of a woman’s cycle), on the contrary, produces mainly progestins, and to a lesser extent, estrogens and weak androgens.
A woman's ovaries work cyclically. During maturation, one of the follicles becomes dominant and inhibits the maturation of the others. The egg matures in the dominant follicle. When the follicle is fully mature, it bursts, and a second-order oocyte (egg is a more common term, but less correct) exits it into the abdominal cavity. This process is called ovulation. It is then captured by the fimbriae and the fluid flow created by the peristalsis of the fallopian tube enters the fallopian tube, through which it migrates to the uterus. If within 3 days (limitation is the lifespan of sperm) before ovulation and 1 day after ovulation (limitation is the lifespan of the egg), a woman had vaginal intercourse with a man, which led to the entry of a sufficient number of motile sperm into the vagina, then fertilization is likely oocyte of the second order (it occurs in the abdominal cavity or the lumen of the fallopian tube). If fertilization has taken place, then the embryo migrates.
The burst follicle undergoes transformation into the corpus luteum, which begins to secrete progestins. Then the corpus luteum undergoes resorption and reverse development, as a result of which the secretion of progestins drops sharply and menstruation occurs. After menstruation, the maturation of the follicles begins again, one of them becomes dominant - a new menstrual cycle begins.
The menstrual cycle in women normally lasts on average 28 days (individual variations are possible, considered normal - from 25 to 31 days).
Throughout a woman's life, the ovary undergoes age-related changes. The number of germ cells in the ovary of a female fetus at the 10th week of intrauterine development is about a million. This is their maximum number. Throughout the rest of life, the eggs are gradually used up. The reproductive (childbearing) period for women is shorter than for men, lasting on average from 15 to 45 years. During this period, eggs mature cyclically and pregnancy is possible. It is fundamentally important that new eggs in women (unlike sperm in men) do not appear, and only the existing ones are used up all the time. Thus, a woman’s reproductive health begins to develop in the womb.
Possible complications
With a low level of progesterone, the temporary secretion gland cannot function normally (accordingly, the white body does not appear), so pregnancy does not occur, or ends in freezing or spontaneous termination.
If there are hormonal imbalances, a temporary gland cyst appears, often having a diameter of no more than 6 mm. In this case, pain occurs in the lower abdomen or in the lumbar region. The cystic formation usually regresses spontaneously over several cycles.
The reason for miscarriage lies in the insufficient function of the luteal formation. Conception may not occur if a woman has a thickened tunica albuginea (ovary) caused by PCOS.
Is treatment necessary?
The corpus luteum prepares a woman for possible conception. If it does not cope with its function, then problems with fertility are observed.
In case of absence of pregnancy (for a long time and for unknown reasons), it is advisable to:
- be examined for hormonal levels (it is necessary to donate blood for progesterone concentration 7-8 days after ovulation);
- do an ultrasound of the pelvic organs;
- analyze the basal temperature chart;
- undergo treatment prescribed by a gynecologist.
Your doctor may recommend other tests. First of all, the hormonal levels are assessed, because with a lack of progesterone, the corpus luteum does not cope with its task and the corpus luteum is not formed upon completion of ovulation.
A pregnant woman suffering from pathology is prescribed Utrozhestan or Duphaston. Therapy continues until the 12th week of the period, but is extended at the discretion of the gynecologist. If you have a possible cyst, you should see a doctor. It often regresses spontaneously after a few cycles or during pregnancy.
The corpus alba in the ovary is the last stage of development of the corpus luteum (CL), which transforms into a scar on the tissue of the epididymis. Over time, it is covered with new similar scars. The ovarian membrane is not perfectly smooth - it is covered with a huge number of almost disappeared white bodies.