What is an anechoic formation in the ovary?
Anaechogenic formation is not a diagnosis. This term is used in ultrasound diagnostics to determine the reflection of waves. The presence of pathology is indicated by cysts characterized by low echogenicity.
The echogenicity indicator is used in ultrasound diagnostics of the whole body. Formations with low echogenicity are not detected by an audible signal when the sensor is directed at them.
Echogenicity decreases if there is air, liquid, or dense tissue in the ovary. Reduced echogenicity is visualized as a dark spot. Increased echogenicity is displayed in a light color.
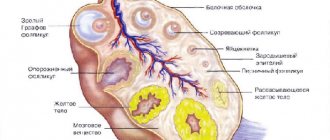
The following ovarian formations are distinguished:
- cysts;
- corpus luteum;
- embryo.
The ovary may contain a dark spot before and after ovulation:
- Follicle maturation. Before the egg is released, the follicle size can be up to 2.5 cm.
- Formation of the corpus luteum. It is formed after the integrity of the follicle is disrupted and the egg is released. The corpus luteum produces progesterone to initiate and prolong pregnancy. Before menstruation, this temporary gland dissolves and disappears.
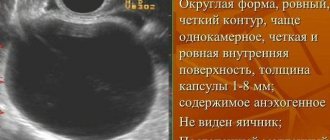
An anechoic ovarian cyst is a dark, rounded spot that the doctor sees on the screen. A cystoma is a cavity with exudate that disrupts the functioning of the ovary.
Anechoic formations of the ovaries often involve cysts, which may have oval and round inclusions and thick walls. Anechoicity also means exudate with a liquid consistency. Sometimes the cavity formation has a mesh, cobweb-like structure and includes septa, blood clots with high density and different shapes.
Ovarian cysts can be:
- single, multiple;
- single-chamber (safer), multi-chamber (presence of a partition).
Treatment tactics for anechoic cysts depend on their options:
- Endometrioid. A round anechoic formation in the right ovary or on the left side has a heterogeneous structure and a hard outer layer. Such a cyst is characterized by an increase during the cycle.
- Follicular. Cysts are formed as a result of follicle growth and lack of ovulation. The main cause of follicular formations is considered to be hormonal disorders, characterized by improper production of sex steroids. Such anechoic cysts in most cases resolve on their own. If there is no regression, medications are prescribed.
- Serous. The cyst can be single-chamber or multi-chamber. The formation is formed by serous tissue and filled with clear liquid.
- Paraovarian. This is a sedentary, dense formation around the perimeter of the ovary with transparent contents. The development of a cyst often provokes pain in the lower abdomen.
- Yellow body. Anechoic inclusions in the ovary up to 10 mm or more. This formation appears in the absence of regression of the corpus luteum with its subsequent increase.
- Dermoid. The variety implies a congenital formation, characterized by the presence of fragments of teeth, hair, and skin.
Cystomas and malignant tumors are also anechoic in nature. These formations have rapid growth and cell division.
The presence of blood vessels in anechoic cysts requires examination to exclude a malignant tumor. Cancers always have blood circulation.
Why do ovarian cysts form?
Today, the exact causes of the formation of ovarian cysts in the uterine cavity are not known, but some patterns have been identified:
- Congenital cyst (the girl already has it at birth): dermoid cyst.
- Cysts due to hormonal imbalance: corpus luteum cyst, follicular (functional) cyst.
- Benign ovarian cysts: cystadenomas.
- Cysts in other diseases: cyst in polycystic ovary syndrome, endometrioid ovarian cyst.
- Malignant ovarian cyst: carcinoma (oncology) of the ovary.
Causes
There are many factors that can lead to the occurrence of pathological formations. Among the causes of anechoic cysts are:
- hormonal dysfunction leading to an imbalance in the ratio of sex steroids;
- inflammatory processes of the reproductive sphere, infections;
- developmental anomalies of the paired organ;
- history of surgical interventions and abortions;
- endometriosis.
Cysts that are functional in nature occur when hormonal levels change.
Traditional methods
Traditional medicine offers a huge number of recipes that can help in the fight against anechoic formation on the ovary. The following tools are often used:
- Honey. It has beneficial properties that enhance immunity and activate the restoration of tissues and organs. To prepare the medicine, you need to take the core of the onion, pour it with honey, and leave it to infuse overnight. Then dip the tampon in this product and insert it into the vagina at night. Course - 10 days.
- Pine buds. Take a tablespoon of the plant, brew it with a liter of boiling water, and leave it to steep overnight. You can take this remedy 3 times a day, half a glass. The course is a month.
- Walnuts. They do an excellent job of regulating hormonal balance. The nut shells are poured with 250 ml of alcohol and left in a dark place for 3 days. Take the drink on an empty stomach, a large spoon once a day. Course – 7 days.
Before using alternative methods of treatment, you should definitely consult with your doctor.
Symptoms
Typically, anechoic cysts are detected in women in the reproductive cycle, which is associated with the hormonal activity of the ovaries. It is possible to detect formations in teenage girls. Anechoic formation in the ovary in postmenopausal women is uncommon.
Small ovarian cysts progress latently. The clinical picture appears when the formation reaches a significant volume:
- nagging pain, usually one-sided;
- feeling of fullness in the intestines;
- false urge to urinate due to compression of the bladder.
An anechoic fluid formation in the ovary can cause pain, which intensifies during sexual intercourse and physical activity.
What is endometrioma (endometrioid ovarian cyst)?
Endometrioma forms in women who suffer from endometriosis. Endometriosis is a female disease in which the endometrium (the inner lining of the uterus) begins to develop in other organs. When the endometrium begins to develop on the ovary, an endometrioid ovarian cyst may appear. Since the endometrioid ovarian cyst is filled with dark brown fluid, it is often called a chocolate cyst.
Endometrioma (chocolate cyst) is treated exclusively with surgery.
Consequences
In most cases, anechoic cysts are benign. However, their growth can cause serious complications:
- Torsion of the legs and rupture of the formation. These pathologies can lead to the development of tissue necrosis, intra-abdominal bleeding and are accompanied by signs of an acute abdomen. Treatment involves surgery.
- Compression of the pelvic organs. Typically, as the cyst grows, there is a frequent urge to urinate and defecate.
Endometrioid cysts are often found in cases of infertility and severe pain. About 20% of cysts are malignant.
Diagnostic methods
When contacting a doctor, the first step is to study the clinical picture of the disease and the woman’s medical history.
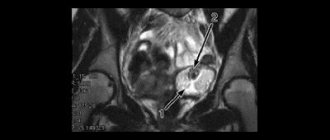
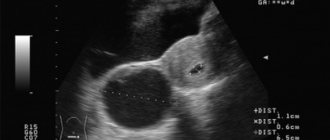
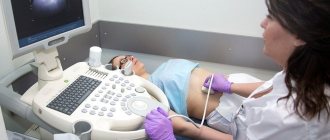
Next, a gynecological examination is performed on a chair. If the size of the cyst is small, the doctor may not notice it. In this case, a study using an ultrasound sensor will help make a diagnosis. It shows neoplasms of any parameters, allows you to determine their type, location, structure. An examination is carried out through the vagina, which allows you to get closer to the ovaries and get a larger picture. On the monitor, an anechoic ovarian cyst appears as a dark spot.
Diagnostics
Cysts are detected during a gynecological examination and ultrasound examination. Large cysts are palpated during the use of the bimanual method. In some cases, when determining an anechoic formation, a series of ultrasound scans is required.
The occurrence of neoplasms is often noted with hormonal imbalance, which is an indication for diagnosing the level of sex steroids. To exclude the malignant nature of the pathology, it is necessary to determine the concentration of the tumor marker CA-125.
A puncture or puncture of the posterior vaginal vault is required if there are signs of blood or fluid in the abdominal cavity. The method is used in case of suspected complications of a benign neoplasm.
Computed tomography is used for differential diagnosis. Laparoscopy allows you to diagnose and remove the cyst during surgery.
To exclude an inflammatory process, you need to perform general blood and urine tests.
Is a corpus luteum cyst dangerous during pregnancy?
No, such a cyst is not dangerous. Corpus luteum cyst is not a rare occurrence in the early stages of pregnancy. It not only does not interfere with the development of the fetus, but also helps maintain pregnancy by producing the pregnancy hormone - progesterone. When the need for progesterone disappears, the cyst resolves on its own. Often, this occurs after the twelfth week of pregnancy (in some cases at the eighteenth or nineteenth week).
Again, in extremely rare cases, there is a possibility of the cyst rupturing or torsion. In this case, the pregnant woman will feel severe pain in the abdomen. If this happens, emergency surgery may be needed.
Treatment
The choice of treatment tactics depends on the type of tumor, its size and morphological characteristics. Gynecologists use:
- observation tactics;
- conservative treatment;
- surgical intervention.
The woman’s age and her reproductive plans are also significant.
Waiting tactics
Observation of cystic neoplasms is possible if they are benign in nature and do not progress. As a rule, expectant management is carried out in relation to functional, luteal, and paraovarian cysts.
Conservative therapy
Treatment consists of the use of hormonal drugs, the choice of which depends on the type of tumor:
- estrogen-progestin drugs;
- progestogens;
- antiestrogens;
- androgens;
- antigonadotropins;
- anabolic steroid.
Treatment is supplemented by taking anti-inflammatory drugs and vitamins. Physiotherapy has a good effect.
Surgical intervention
For some types of cystic tumors (dermoid, serous), treatment involves surgery:
- cyst removal;
- excision of part of the affected ovary;
- removal of the organ (with the fallopian tube);
- electrocoagulation.
Operations are performed both laparoscopically and laparotomically. If a malignant process is suspected, removal of the appendages and uterus is possible.
Echogenicity
Echogenicity is used in ultrasound diagnostics of the whole body. On inclusions of low echogenicity there is no sound when directed by the sensor. The morphological data of the organ under study play an important role. The organ being examined contains fluid, air, and dense tissue—reduced echogenicity. On ultrasound, the body appears as a dark spot. Inclusions with increased echogenicity are shown in light color. Formations in the ovaries:
- corpus luteum;
- follicular, endometrioid, serous cyst;
- embryo
After an ultrasound, a woman needs to see a gynecologist to rule out reasons for worry.
Based on the ultrasound examination, the doctor shows the patient the reflection on the spectrogram. Studying the formations in detail, additional research is carried out to reveal the full picture of the condition of the ovaries.
An anechoic ovarian cyst is a dark round spot visible to the doctor on the monitor screen. Cystomas are cavities with accumulated exudate that interfere with the functioning of female paired glands and disrupt the hormonal balance.
Reasons for education:
- lack of estrogen;
- inflammatory diseases of the uterus, ovaries;
- infectious diseases;
- inferiority of the uterine appendages;
- surgical consequences on the rectum, bladder, vagina;
- adhesive process
Ovary on ultrasound
The anechoic cavity in the ovary has different sizes. The work of a healthy ovary during the menstrual cycle: after menstruation, follicles grow in one or two ovaries. In the first 14 days, the anechoic body in the ovary, measuring 1-3 mm, increases to 7-8 mm. The dominant follicle with the emerging egg grows 16-30 mm. By releasing the egg, the anechoic structure becomes smaller, turning into a specific endocrine gland. The corpus luteum does not work, it ruptures 2-3 days before menstruation, the fluid leaves. From the first to the last day of menstruation, a healthy woman has no anechoicity in the ovary. With the onset of pregnancy, a round yellow body on one ovary is mistaken for an anechoic formation.
Prevention
Often, a thin-walled anechoic formation in the ovary is a consequence of hormonal disorders and inflammatory processes. If signs of diseases of the reproductive system occur, you must contact a gynecologist and undergo an examination.
Experts emphasize that it is necessary to monitor menstrual function and thyroid function. Pathological symptoms are not an indication for self-medication. Incorrect therapy can lead to progression of the disease and deterioration of the general condition.
Women with a history of benign tumors should not sunbathe or visit a solarium or sauna. Any thermal procedures or physical exercises aimed at the lower abdomen can provoke the growth of a tumor.
Corpus luteum cyst and its treatment
When ovulation ends (the rupture of the follicle and the release of the egg), a piece of tissue appears in the ovary that produces progesterone, the pregnancy hormone. This area of tissue is called the corpus luteum. If pregnancy does not occur, the corpus luteum should normally resolve. But there are situations when the corpus luteum does not disappear, but fills with blood or fluid, thereby forming a corpus luteum cyst.
Typically, a corpus luteum cyst does not require treatment, since it resolves on its own within one to two months. To speed up the process of resorption, the gynecologist may recommend taking contraceptive medications that help reduce the size of the cyst.
In rare situations, a corpus luteum cyst reaches a large size (more than five to seven centimeters in diameter), spins around its axis or ruptures. In this case, the woman experiences severe pain in the lower abdomen, which intensifies with exercise or sex. If any complication of a corpus luteum cyst develops, urgent surgery must be performed.
Liver deformity
As in the case of the kidneys, the foreign structure is almost always represented by a cyst.
- An hydatid cyst is a round formation characterized by echogenic walls and the presence of calcifications inside.
- Hepatic artery aneurysm. The formation is subject to pulsation, echo-negative.
A simple variation of the cyst is characterized by septations, an oval or round shape, casting shadows along the contour.
Preventive actions
Echo-negative cysts are often encountered in medical practice. It is impossible to completely protect yourself from their occurrence, but you can reduce the risk of developing pathology with the help of preventive measures.
First of all, you need to monitor your hormonal levels. Its violations cannot be ignored. After all, failure is the main cause of the formation of cystic inclusions.
Doctors also advise the following:
- Take vitamins regularly to strengthen the immune system;
- to live an active lifestyle;
- to refuse from bad habits;
- Healthy food;
- avoid stressful situations;
- observe the work and rest schedule;
- undergo a preventive examination with a gynecologist at least once a year.
An anechoic mass in the ovary is a diagnosis but should not be a cause for concern. If therapy is started in a timely manner, the prognosis is favorable. Modern medicine offers many methods for treating cysts, so getting rid of them is not difficult.
Fragile women's health is constantly exposed to attacks from harmful bacteria, stress, and suffers due to poor ecology. What is an anechoic formation, and how can it affect a woman’s body?
One of the most unfavorable consequences of all negative effects on the body is the appearance of dark spots on ultrasound.
Even if a woman is completely healthy, she is not immune from the appearance of cysts in the uterus and follicles or near them, and if the immune system is weakened by constant stress and past illness, then a tumor may appear even faster.
The tumor or cyst, which contains fluid and changed tissue, can be located not only in the ovaries, but also in the thyroid gland, kidney, uterus, or near any organ.
The concept of anechoic formation in the ovary characterizes the pathology of the female reproductive system. This is one of those symptoms of the disease that requires careful diagnosis and several types of research before diagnosis.
Ultrasound diagnostics is used to detect pathology.
A pathological or benign avascular echogenic formation will appear different on diagnosis from healthy organ or gland tissue.
An anechoic formation is called if, during diagnosis, there are no reflected ultrasound waves in the organ. The very concept of “avascular echogenic formation” is not a diagnosis, and depending on the circumstances, the fluid it contains, and the organ being diagnosed, it can be normal or pathological.
Ultrasound has a high frequency that is not audible to the human ear. When a specialist conducts a study using it, ultrasound is generated due to the transducer sensor. Using the same sensor, information is read from the sound reflected from the surface of the organ, that is, the echo.
Depending on the frequency of sound during the study, a string of data on the monitor is built into a whole image. If the sound is not reflected, then this option will be called “anechoic”, that is, unable to reflect sound.
As a rule, ultrasound does not pass through bones during diagnosis. If the body has cavities with air, for example, the intestines, bladder, stomach, then during the study the ultrasound will be scattered as it passes through the air. Capsules that contain liquids conduct radiation well, and on the monitor during diagnosis they will appear as denser, darker areas. Such capsules are usually called cysts. Depending on what tissue the neoplasm consists of and what tissues or fluids it contains, it can be either echogenic or non-echoic.