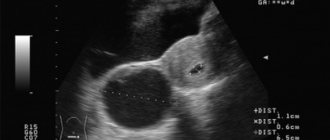
A hypoechoic formation in the ovary is a very alarming condition for many women.
However, this is not a diagnosis, but only an option for deciphering the ultrasound results. Quite a few such anomalies in the genital organs are detected today. They are formations of dense tissue, the cause of which can be various factors. For example, this may be a woman’s poor lifestyle, sexually transmitted infections, as well as the presence of a hereditary factor or the development of an ectopic pregnancy. These pathologies must be seriously treated, which is why it is impossible to do without modern medical care in such situations. It is important to carry out a timely diagnosis, as well as identify a hypoechoic formation in the ovary, what it is, in order to prevent its complications.
If you are worried about herpes on your lips, don't worry! There is a solution. By clicking on the link you will learn all the necessary measures to prevent herpes.
Diagnostic methods
Hypoechoic formation in the ovary, what is it and how is it diagnosed? This type of tumor is determined by ultrasound, which uses a special sensor that creates high-frequency vibrations and sends them to the examined tissues of the body. The same sensor receives back the frequencies reflected from the organs. An image appears on the device screen, which is displayed as a picture. This diagnostic method indirectly resembles an echo, which is why many doctors call this type of examination echography.
The results of the ultrasound examination must be deciphered by the doctor, who will make the diagnosis. To determine a particular disease, an ultrasound is performed along with a visual examination of the woman, collecting an anamnesis and analyzing symptoms and complaints. In addition, it is important to consider the characteristics of the ultrasound equipment. After a complete examination, the specialist determines the type of hypoechoic formation and, if possible, the cause of its appearance.
We recommend you learn: Anechoic inclusions in the ovary
Characteristic symptoms of the pathology
Most often (in 60% of cases) the anechoic formation turns out to be an ovarian cyst. Among them there are functional (these include follicular and luteal) and organic (endometrioid, dermoid).
Functional cysts
A follicular cyst forms in the follicle if ovulation does not occur. The wall stretches, the tumor can reach significant sizes, while there are no painful symptoms. Within 1-3 months, the cyst usually resolves as the cycle improves.
Luteal (corpus luteum cyst) can be detected in the 2nd half of the cycle. A sign of its appearance is the existence of an anechoic formation in the ovary immediately before menstruation. Unlike the corpus luteum of pregnancy, it is round, the diameter of the dark spot gradually increases.
In this case, the woman experiences an asymmetrical enlargement of the abdomen, and a slight nagging pain appears. The cycle becomes irregular, the functioning of the bladder and intestines is disrupted.
Addition: There is also another type of hypoechoic formations located outside the ovary. The paraovarian cyst is attached to it by a thin stalk. It is filled with liquid. Its development is not related to the processes of the cycle, but can complicate the functioning of the organ. When the leg is twisted, the cyst enlarges and severe pain occurs due to impaired blood supply and irritation of the peritoneum.
Organic cysts
These are benign tumor-like structures that do not disappear on their own within 2-3 months. Their appearance does not depend on the stage of the menstrual cycle, however, just like functional ones, they most often grow after the onset of puberty, giving various complications. In this case, inflammatory diseases of the uterine appendages, cyst ruptures, and tissue necrosis occur due to twisting of the base of the cyst. If neoplasms appear on both sides, the woman faces infertility.
Endometrioid (chocolate) occurs when cells of the overgrown endometrium fall on the surface of the ovary. They begin to divide, forming a cavity filled with menstrual blood. During menstruation, the walls of the cyst bleed. Menstruation becomes more abundant and longer. Further development of such cysts leads to infertility due to the formation of scars in the tissues, as well as adhesions between the appendages and other organs. Dysfunction leads to disruption of the general hormonal levels and malfunction of the thyroid gland.
Dermoid cyst (teratoma) is a congenital pathology. The dense round capsule contains the remains of organic tissue from which the embryo is formed. There is mucus inside it. The anechoic formation can reach a diameter of 15 cm.
Cystadenomas
On ultrasound they look the same as cysts.
The serous is filled with a yellowish liquid of protein origin (seeps through the internal membranes of the organs). The average size is 16-20 cm. There is no danger of malignant degeneration.
Mucinous. Its contents are thick mucus. The ultrasound image shows several cameras. The tumor can reach large sizes and can degenerate into cancer.
Papillary. Multi-chamber cavity, covered from the inside with papillae. The size of the tumor itself does not exceed 12 cm, but it often spreads to neighboring organs and degenerates into ovarian cancer (especially in women over 45 years of age).
Carcinoma (cancerous tumor)
It is an anechoic formation in the ovary, the appearance of which is indicated by the presence of a developed network of blood vessels. It does not have clear dimensions or a specific shape.
What does a hypoechoic neoplasm look like on ultrasound?
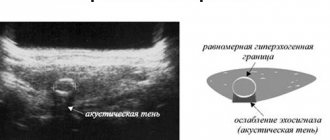
To understand what a hypoechoic formation in the ovary is, it is worth understanding how doctors see it during an ultrasound. On the monitor, areas with low echogenicity are visible as dark spots with low acoustic density. In contrast to the acoustic characteristics of healthy tissues of the appendages, tumor tissues are hypoechogenic. Such an area weakly reflects the ultrasonic signal directed at it by the device. Considering the structure of the neoplasm, we can say that it either contains liquid or contains a cavity. The formation on the screen can be visualized as dark gray, gray or black areas. To decipher the results, a special category scale is used, in which each pixel displayed on the monitor has a certain shade of gray. In this case, the color is determined by the strength of the ultrasonic signal that is returned to the sensor.
Important! Ultrasound interpretation is performed by gynecologists and diagnosticians specializing in this area of research. The results are necessarily compared with test results and other studies that the patient has undergone.
In some cases, to determine whether this is a benign hypoechoic inclusion in the ovary or a malignant neoplasm, in addition to ultrasound, other pathology examination methods are used. This may be an MRI, color Doppler, angiography or CT. In addition, if there is a suspicion of a malignant inclusion, a histological analysis of the biopsy specimens is prescribed.
We recommend you learn: What is ovarian hydatid?
More about the phenomenon of “hypoechogenicity”
The examination technique using ultrasound is that using special equipment, sound vibrations of a certain frequency are generated, sent to the organs, and then a response is received, that is, reflected sound, echo. The structure of organs can be judged by acoustic density (echogenicity).
Hypoechoic formations
Some formation in the body may show reduced acoustic density and appear darker on the screen than neighboring tissues. This phenomenon is called hypoechogenicity, that is, reduced density. In this area, ultrasound progresses more slowly. Most often, this phenomenon has a liquid structure: it could be, for example, a cyst. The doctor will not be able to immediately give an accurate diagnosis.
The fact is that the formation can be round or with uneven edges. Round can be:
- Cyst.
- A tumor.
- Parasitic cyst.
- A normal follicle, if we are talking about the ovaries.
- Galactocele if found in the breast.
What a formation with low echogenicity may be
Most often, hypoechoic formations that appear in the ovaries are cystic tumors with thin walls and clearly visible fluid inside. During an ultrasound examination, the doctor must indicate the size of the tumor, its shape and contours. Round type neoplasms can be:
- follicles;
- cysts;
- some types of tumors.
If the found hypoechoic area has uneven contours, it is most likely a fibroma, malignant tumor or cyst. In the ovaries, follicles, vascular tissue, the corpus luteum, and any type of cystic formation are characterized by low echogenicity. Only in rare cases does low echogenicity turn out to be a cancerous body. In reproductive age, heterogeneity of the ovary on ultrasound is considered normal. During menopause, when the appendages lose their functionality, the ovaries of a healthy woman should have a uniform structure.
Many patients are interested in the question of why doctors do not write the type of tumor in the diagnosis, but only mention the hypoechoic inclusion. The fact is that an accurate diagnosis can be made only after a more thorough examination and passing the necessary tests. Ultrasound examination gives only indirect results. Additional manipulations to confirm the diagnosis may include methods such as cystoscopy, biopsy or laparoscopy.
We recommend you learn: What is ovarian fibroid?
Symptoms of a dermoid cyst
While the dermoid cyst is small in size, it has no signs. When it increases, symptoms such as nagging pain in the lower abdomen may be observed. If you regularly visit a gynecologist, then such an echogenic formation in the ovary
is detected in the initial stages of development. The formation can also put pressure on neighboring organs, which can cause problems with the bladder (frequent urination) and intestines (constipation or diarrhea). If the cyst becomes inflamed, your body temperature may also increase.
The fact is that as the formation grows, it begins to displace healthy ovarian tissue. At first, no changes are observed, but then the tumor compresses the vessels, cutting off nutrition to the ovary. As a result, healthy tissue is replaced by scar tissue (connective tissue), which is more resistant to deficiency of nutrients and oxygen. At the same time, there may not be any changes in the body, because the second, unaffected ovary can easily cope with the load placed on it. Therefore, a dermoid cyst is often discovered when it almost completely replaces healthy ovarian tissue.
The danger of an ovarian dermoid cyst is also that it can twist, which is accompanied by sharp and severe pain in the lower abdomen. Occasionally, such a formation can become malignant.
The nature of inclusions with low echogenicity
Ovarian tumors account for about 25 percent of all hypoechoic pelvic tumors. Having discovered a tumor, the doctor is obliged to act quickly, without delaying the solution to the problem. Otherwise, a complication may develop that will threaten the woman’s health or even life. A cyst in the ovary can have a different nature. It can be a benign functional, endometrioid or dermoid tumor, or cystadenoma. When determining the type of cyst, it is important to be guided not only by ultrasound results, but also by the symptoms present in the female body. If the cyst is benign, hormonal and drug treatment is sufficient to eliminate it. After therapy, such cysts disappear on their own, but malignant neoplasms continue to be visible on ultrasound in the form of hypoechoic bodies.
In rare cases, benign cystic tumors with low echogenicity begin to develop, reaching significant sizes. However, if this happens, surgical intervention is required. To determine the nature of hypoechoic inclusions, their internal structure must be assessed. Education can be:
- homogeneous;
- heterogeneous;
- with hyperechoic elements.
Most often, homogeneous bodies with low echogenicity represent carcinomas, and heterogeneous formations indicate diffuse forms of cancer. If hyperechoic inclusions are present in a hypoechoic neoplasm, we can speak of an ovarian adenoma.
Please note: Ultrasound is required to examine the tissues surrounding the tumor with distal acoustic effects and features of lateral tissues. In addition, the specialist determines the presence or absence of blood vessels in the hypoechoic body. All this allows you to find out the nature of the ovarian tumor, as well as determine whether the patient will need additional examination.
It is important to remember that hypoechoic tumors are rarely prone to rapid development; however, it is not recommended to delay solving the problem, since even a benign tumor can turn into malignant without proper treatment. Therefore, you should not postpone your visit to the doctor. Many patients are interested in the question of how areas with low echogenicity are treated. In fact, it is not the detected tumors that require treatment, but the diseases that led to their appearance and changes in the density of ovarian tissue.
Features depending on the organ
Some cysts reach large sizes and can be seen during ultrasound examination as a round or oval inclusion filled with fluid. In such cases, specialists immediately resort to surgical intervention, prescribing hospitalization for the patient.
During the assessment of the internal structure of the inclusion, the nature of the formations is determined. They may have the following characteristics:
- uniformity;
- heterogeneity;
- the presence of hyperechoic elements.
Such an inclusion soon resolves in the body on its own and does not require special treatment, unlike a subchorionic hematoma. This formation can lead to the development of an ectopic pregnancy or prevent the fertilized egg from attaching to the uterus.
Hyperechoic formations appear in various organs of the human body. They are found in soft tissues or inside cavities. Formations are distinguished according to the following characteristics:
- form;
- size;
- contours;
- intensity of brightening in the image.
Based on these criteria, the specialist suggests a particular disease.
Liver
The hyperechoic neoplasm here is a tumor; more often it is malignant. Represented by a light spot of irregular shape.
Liver cysts can be detected due to the reverberation effect. Once in the cavity, ultrasound is reflected several times from its walls and attenuates. The image shows the light walls of the cyst with a darkening in the center.
Gallbladder
Hyperechoic formations of the gallbladder are located inside it or on the wall.
- Sludge is a thick hyperechoic suspension of bile at the bottom of the bladder. Represented by a white stripe along the bottom contour.
- Polyp. Formed by cholesterol deposits, it grows from the wall of the organ. It has a wide base and elongated shape. Size up to 4 mm.
- The stone is compressed bile salts. It looks like a bright white spot at the bottom of the bubble. There is always an acoustic shadow. The shape of the stones is often round.
It is easy to distinguish sludge or stone from a polyp. The stones move when the body position changes, but the polyp remains in place.
A hyperechoic focus in the uterine muscle is a fibroid or malignant tumor. With fibroids, an increase in the organ itself and its deformation are simultaneously observed.
A hyperechoic formation may be a uterine polyp or a menstrual blood clot. To confirm this, an ultrasound should be done 3-4 days after menstruation.
Breast
Dense neoplasms in the mammary gland occur against the background of hormonal imbalances or inflammation:
- fibrous mastopathy - rounded light formations with an acoustic shadow;
- mastitis - linear areas of clearing or nodes;
- malignant tumor is a formation with unclear contours.
Bladder
Most often, stones are found here - small light inclusions with an acoustic shadow. They have different shapes and sizes. At the initial stage of urolithiasis, sand is detected - a hyperechoic suspension.
The bladder is affected by the infectious disease schistosomiasis. Many pinpoint hyperechoic inclusions are found in its wall.
A kidney tumor is usually located on its surface. It is represented by a light, rounded growth. A benign tumor has an even lighter rim - the capsule.
Thyroid
The hyperechoic area is a tumor of the thyroid gland. A light, round formation with clear contours. Inside there may be even denser areas - calcifications.
Ovaries
A dense formation in the ovary with unclear contours and a dark border around it is cancer. A tumor with a capsule around it and a heterogeneous structure is a teratoma. This is a congenital ovarian cyst containing fat, hair, and teeth.
Ultrasound of the fetus
But sometimes it is a sign of chromosomal abnormalities. If a woman has risk factors, she undergoes additional examination. A needle is inserted into the amniotic sac and a small amount of water is taken for analysis.
The same examination can be done in the placenta. The analysis identifies any genetic abnormalities.
Description in different organs
Due to the fact that isoechoic formations correspond in density to organs, it is difficult to see them on an ultrasound image. The presence of an isoechoic neoplasm can be suspected by tissue compression or the presence of a capsule.
Formations with an isoechoic structure are detected everywhere:
- kidneys;
- liver;
- thyroid;
- liver;
- breast;
- ovary.
Kidneys
Kidney formations that are isoechoic are most often malignant tumors. They are characterized by strong compression of surrounding tissues and uneven outlines. The tumor often grows into the ureter.
Cysts and kidney stones are never isoechoic. Cystic formations contain fluid and are therefore represented by black areas. The stones are very dense and look like white uneven inclusions.
Ovaries
An isoechoic nodule with a hypoechoic rim is an ovarian cyst. It is formed by a greatly enlarged follicle. Cysts are discovered before ovulation. In the image, the cyst is presented as a rounded gray spot with a white rim around it.
Irregular isoechoic areas are a sign of ovarian cancer. Compression of neighboring follicles and their deformation are noticeable. Cancer is characterized by rapid growth.
Thyroid
An isoechoic node is a sign of goiter against the background of preserved hormonal function of the gland. You can determine it by changing the direction of grain in the image. A compaction zone also appears around the node.
Oncological alertness should be shown if white areas appear inside such a formation. This is a sign of calcification, which often accompanies cancer.
How nodes and cysts look on an ultrasound can be seen in the video:
Uterus
Isoechogenic formations are myomatous nodes or polyps. Myoma is located inside the wall of the uterus or protrudes into the cavity. The image shows a spot of heterogeneous density. Its size can reach tens of centimeters.
Polyps always protrude into the uterine cavity. They look like small oblong gray spots on a dark background. If you do an ultrasound during different phases of the menstrual cycle, you may notice a change in the size of the polyp.
Liver
Isoechogenic formations in the liver are most often hemangiomas. They are represented by gray spots with increased blood flow. They have rounded outlines and do not compress surrounding tissues. Hemangiomas are tumors from overgrown vessels.
Isoechogenic spots may turn out to be lipomas. This is a growth of adipose tissue. Formed as a result of poor nutrition and alcohol abuse. They have a round shape and clear boundaries.
Malignant neoplasms are less likely to be isoechoic. They can be distinguished by blurry outlines and compression of the tissue around them.
Breast
A spot with anechoic inclusions, that is, black dots, is a cystic adenoma of the mammary gland. This is a hormone-dependent neoplasm. It changes size depending on the phase of the menstrual cycle. A white capsule is clearly visible around the gray spot in the image.
Cystic adenoma is not dangerous to a woman’s health. But it can transform into cancer under certain conditions. Rapid growth of the adenoma and the appearance of discharge from the nipple are indications for surgical treatment.
Determination of hypoechogenicity
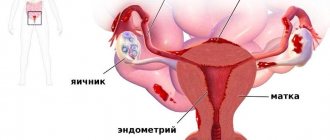
The sex glands in women are located asymmetrically, and the ovaries also differ in size - the organ located on the right is noticeably larger.
They are connected to the uterus through the fallopian tubes, performing the most important functions, without which the reproductive health of the body is unthinkable. Thus, the ovaries form eggs and produce female sex hormones, thereby the paired glands ensure not only the maturation of germ cells, but also the safety of pregnancy in a woman. During a medical examination, the ultrasound device sensor is directed to the organ area, and then the sound waves are reflected from it, transforming into an echo.