Cervicitis: general information
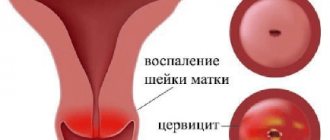
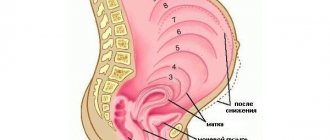
Photo of cervicitis
The cervix is a muscular tube about 4 cm long and about 2.5 cm wide, covered with epithelium. This is the junction of the vagina and the uterine cavity. The main function of this organ is to prevent the penetration of pathogenic infection into the uterine cavity, and then into the fallopian tubes and ovaries.
The cervical canal, located in the vaginal part of the cervix, is a fairly narrow formation. It prevents harmful microorganisms from penetrating into the uterine cavity due to the mucous plug that closes it, as well as due to the secretion secreted by the glands of the cervix. If such protection is violated, then the cervical canal can no longer perform its barrier functions and the process of inflammation of the cervix or cervicitis begins.
If inflammation occurs on the outer part of the cervix, which extends into the vagina, then exocervicitis is diagnosed; if the epithelium of the cervical canal becomes inflamed, then they speak of endocervicitis.
During the inflammatory process, the tissues of the walls of the cervical canal become swollen, the vessels of the cervix enlarge, and vasculitis occurs. With a prolonged course of the disease, vaginal varicose veins may also develop.
The lining of the cervical canal walls produces a large number of immune cells to fight infection. If they cope with this task, the disease goes away. If, for various reasons, this does not happen, then the process enters the chronic stage. In this case, it can last for years, periodically exacerbating.
Causes of cervicitis
Cervicitis is an infectious disease in which pathogenic microflora causes an inflammatory reaction. It can be
- infectious agents that enter the body exclusively through sexual contact. It is impossible to become infected with them if, for example, you sunbathe in a solarium without underwear or visit a sauna. This is a specific microflora: pathogens of gonorrhea and syphilis, as well as trichomonas, mycoplasma, ureaplasma, chlamydia and other pathogens of STDs.
- microbes that are commonly called opportunistic - nonspecific microflora; opportunistic microorganisms penetrate the cervix through the blood, lymph, or from the rectum. This could be staphylococcus, streptococcus, fungus of the candida family, E. coli, Klebsiella and others.
Cervicitis can have a different character
- Purulent, as a result of which the cervical canal is filled with pus. As a rule, the causative agent of this form of the disease is gonococci or opportunistic microorganisms.
- Productive when excess connective tissue, scars and septa occur during the healing process of inflammation.
- Proliferative, as a result of which the epithelium of the cervical canal grows and polyps form.
Factors that provoke inflammation of the cervix
Inflammation of the cervix can be caused by a variety of reasons. These are diseases that provoke the development of cervicitis, as well as the patient’s lifestyle itself.
- The main cause of inflammation of the cervical mucosa is sexually transmitted diseases. First of all, these are gonorrhea and trichomoniasis - they account for about 25% of cases of cervicitis. But, as mentioned above, inflammation can also be caused by other bacteria and viruses that enter the body during sexual contact. The disease can be provoked by ureaplasmosis, chlamydia and other similar diseases.
- The cause of the spread of the inflammatory process is also viral diseases, as well as diseases caused by staphylococci and streptococci. This may be a disease of the gastrointestinal tract of a bacterial nature and even sore throat or pneumonia.
- There is a risk of the onset of an inflammatory process on the surface of the cervix with a general weakening of the immune system and the resulting vaginal dysbiosis.
- The condition of the cervical mucosa and characteristics of sexual life are also affected: constant change of sexual partners, improper use of contraceptives, in particular spermicides, douching with acid-containing products.
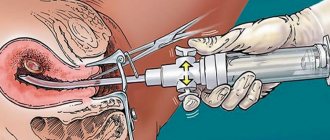
- There is a risk of cervicitis if the cervix is injured during an artificial abortion, a hysteroscopy procedure, or the installation and removal of an intrauterine device.
- Cervicitis can also develop in women during menopause. The so-called age-related inflammation of the cervix is due to the fact that the amount of estrogen in the blood of postmenopausal women decreases. As a result, the secretion of the cervical canal decreases, and it itself becomes thinner and therefore can begin to become inflamed.
- In rare cases, the cause of inflammation of the cervix may be an allergy to the latex from which condoms are made, as well as spermicides and lubricants used during sexual intercourse.
Why is cervicitis dangerous?
This disease does not directly threaten the patient’s life, but the following consequences may occur:
- The development of chronic inflammation of the cervix, which can subsequently spread to the uterus and appendages, affecting the peritoneum, bladder and kidneys.
- In advanced cases, adhesive disease of the pelvic organs develops, as a result of which the woman will not be able to become pregnant naturally.
- Sometimes inflammation in the uterus causes the development of cervical cancer.
Symptoms of cervicitis
Recognizing the disease can be quite difficult, especially if its course is chronic. A woman, especially a pregnant woman, can easily mistake minor changes in well-being for manifestations of psychosomatics.
You may suspect acute cervicitis if the following signs are observed:
- The nature of vaginal discharge changes, its quantity increases, and it acquires an unusual color and consistency. The nature of the discharge may vary depending on what caused the inflammation. So, with purulent cervicitis, they have an unpleasant odor, yellow-green color and thick consistency. With viral inflammation or chlamydia, cloudy yellowish or white mucus is observed.
- There may be nagging pain in the lower abdomen; sometimes a woman experiences pain during sexual intercourse. However, often inflammation of the cervix is not accompanied by pain.
- There may be a small amount of bloody discharge from the genitals before or after menstruation. Discharge becomes especially abundant after sexual intercourse.
- In the acute form of the disease, a sharp increase in body temperature to 38-39 degrees, enlargement of nearby lymph nodes, and signs of general malaise are possible.
Chronic cervicitis can occur with almost no symptoms. Often the only signs of the disease are white or yellow discharge from the genitals with virtually no odor, as well as uncomfortable sensations and pain during sexual intercourse.
In rare cases, if the cervical canal has completely lost its patency, a prolonged delay in menstruation may occur. In this case, women most often turn to gynecology regarding suspicion of pregnancy.
Symptoms of cervicitis during pregnancy
The main manifestations of cervicitis are:
- pain in the lower abdomen;
- bleeding or the appearance of brownish discharge;
- copious discharge of mucus and pus;
- the appearance of itching and burning in the vagina;
- pain during sexual intercourse.
It should be noted that if abdominal pain and bleeding occur in pregnant women, you should immediately call an ambulance, since these symptoms can be observed when a miscarriage begins.
Cervicitis and pregnancy
Many women wonder whether it is possible to get pregnant if they are diagnosed with cervicitis.
In most cases, the cervical canal retains its patency and does not create obstacles to the penetration of sperm. Thus, pregnancy can occur naturally.
If, during the process of inflammation, adhesions or scars have formed, or the walls of the cervical canal have become much thicker and denser, this creates an obstacle to natural fertilization and the woman is diagnosed with infertility. In this case, it is possible to restore the patient’s ability to conceive through surgery, restoring the patency of the cervix, or using in vitro fertilization (IVF).
Important:
Inflammation of the cervix can negatively affect the course of pregnancy and the results of childbirth:
- At the initial stage, an ascending infection from the cervical canal can affect the embryo, which will lead to its death or the occurrence of gross malformations.
- In late pregnancy, inflammation of the cervix can also lead to intrauterine growth retardation and cause fetal abnormalities.
- With this diagnosis, labor may begin prematurely, and when the child passes through the birth canal, there is a high risk of infection. In addition, the mother's postpartum period may be fraught with complications.
When planning a pregnancy, it is better to contact a gynecologist in advance to identify possible pathologies. If inflammation is detected when a woman is already pregnant, the doctor prescribes comprehensive treatment, taking into account the contraindications characteristic of this female condition.
Diagnosis of cervicitis
As a rule, the diagnosis of cervical inflammation is made during a routine examination or when visiting a doctor for other reasons.
The gynecologist makes a conclusion based on visual examination data, as well as test results.
During an examination in the mirrors, the doctor may detect the following signs of the disease:
- the cervix is enlarged due to inflammation;
- swelling is observed;
- a zone of erosion around the external pharynx is visible;
- there are various types of discharge from the cervical canal;
- There are pinpoint hemorrhages on it.
During the postmenopausal period, such a diagnosis can be made if there is thinning of the mucous membranes of the cervix and external genitalia.
Colposcopy helps clarify the diagnosis, as a result of which various complications of the disease can be identified.
As a rule, when inflammation is detected, a woman is given a number of concomitant diagnoses, including
- cervical erosion;
- colpitis - inflammation of the vaginal mucosa;
- vulvovaginitis - inflammation of the tissues of the vulva and vagina;
- bartholinitis - inflammation of the large gland of the vestibule of the vagina;
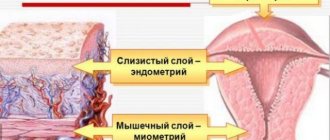
- endometritis – inflammation of the inner layer of the uterus;
- adnexitis - inflammation of the uterine appendages, etc.
This is explained by the fact that the causative agents of cervicitis are capable of inflaming not only the cervical area. They have an active effect on tissues and organs located in close proximity to it.
Laboratory diagnostic methods
The final diagnosis is made only after conducting and interpreting the results of a number of laboratory tests. The doctor may prescribe the following procedures:
- Swabs are taken from the vagina, urethra and cervix to determine the nature of the causative agent of the disease.
- The presence of sexually transmitted infections is checked using the PCR (polymer chain reaction) method. This test has a high degree of accuracy and does not produce false positive or false negative results.
- A cytology smear is taken from the cervix to identify possible pathological changes of a malignant nature, in particular dysplasia and other precancerous conditions.
- After examination in the mirrors, colcoscopy and cytological examination, the doctor may prescribe a histology test - a diagnostic procedure that allows you to most accurately identify the possibility of pathologies such as cervical cancer, dysplasia, endometriosis, fibroids, etc.
- Bacterial culture of vaginal discharge allows you to determine the causative agent of the infection.
- A blood test is performed for syphilis and HIV.
In order to correctly prescribe treatment, it is extremely important to identify the cause that caused the inflammation, since the same pathology can be caused by different pathogens. Thus, inflammation of the cervix is only part of the clinical picture of many diseases caused by completely different reasons.
How does cervicitis affect pregnancy?
Normally, the mucous membrane of the cervix acts as a boundary barrier between the uterus and the vaginal microflora. Cervical mucus helps create a protective plug that prevents infection from entering the uterine cavity.
The mucus produced by the uterine cervix has a pronounced bactericidal effect and also contains a large amount of immunoglobulins that prevent the development of infection and support local immunity. The development of the disease leads to a sharp decrease in the protective function of cervical mucus and creates favorable conditions for the development of infection.
For reference. Chronic cervicitis during pregnancy is often accompanied by the development of cervical ectopia (which increases the risk of miscarriage). Also, in patients with acute or untreated chronic cervicitis, pregnancy can trigger the progression of the disease.
In such patients, destructive processes in the mucous membrane rapidly progress, erosions develop, and the risk of developing cervical cancer (in the future) increases.
Treatment of cervical inflammation
To effectively treat cervical inflammation, an integrated approach is used, which includes
- taking anti-inflammatory and antimicrobial drugs;
- measures to restore normal vaginal microflora;
- taking immunomodulators;
- restorative therapy;
- physiotherapy.
During pregnancy, surgical methods are not used; conservative therapy is used to treat the disease.
Drug treatment
Various drugs are prescribed as conservative therapy, depending on which microorganisms are the causative agents of the disease.
- When the cervix is affected by chlamydial infection, antibiotics from a number of tetracyclines (doxycycline), quinolones (Tarivid), macrolides (erythromycin) and azalides (azithromycin) are used. For specific cervicitis caused by Trichomonas or gonococci, not only the patient, but her partner is treated.
- If the lesion is fungal in nature, use oral medications (flucostat and analogues), as well as local treatment in the form of rectal and vaginal suppositories and vaginal tablets (clotrimazole, isoconazole);
- When the cervix is affected by the human papillomavirus, cyclostatic drugs (5-fluorouracil) are prescribed.
- The indication for the use of suppositories containing hormones (ovestin) is atrophic age-related inflammation.
- When the cervix is affected by viruses, treatment takes a particularly long time. Taking antiviral drugs is combined with the prescription of multivitamins and immunomodulators. In this case, the drug genferon, which has immunomodulatory properties and has antiviral, antimicrobial and anti-inflammatory effects, is effective.
Treatment with antibiotics and antibacterial drugs is carried out in the second and third trimesters of pregnancy, taking into account that the drugs do not have a negative effect on the development of the fetus.
Antibiotics cannot be used in the first trimester of pregnancy, so local treatment is preferentially prescribed.
Before using any medicine, carefully read the instructions!
However, the acute stage of the disease - the so-called double inflammation of the cervix - is often observed in the first trimester of pregnancy. In this case, the drug indomethacin is indicated for use. Unlike traditional medicines, it does not contain hormones, while having an effective anti-inflammatory and anesthetic effect. Indomethacin drugs are recommended for use up to 32 weeks of pregnancy.
The effectiveness of this product is evidenced by the following review:
“They provide excellent pain relief and effectively relieve inflammation. They helped me out more than once"
Local therapy
Local treatment of cervicitis is effective if the inflammation is in the chronic stage. When acute phenomena subside, the vagina is treated with a solution of silver nitrate, 3% dimexide or 2% chlorophyllipt. It is also possible to douche with a weak solution of potassium permanganate, soda or boric acid.
Vaginal tablets and suppositories (Betadine, Terzhinan) are used as a local antimicrobial and anti-inflammatory agent.
Folk remedies
Traditional medicine is also used in the treatment of cervical inflammation as an auxiliary one.
It is recommended to douche with a decoction of oak bark or sage, or an infusion of chamomile or calendula flowers.
It will help to alleviate the course of the disease and use the following herbal infusions internally:
- Adonis, wormwood, mint, thyme, juniper berries and raspberry leaves.
- Oak bark, wormwood, bird cherry flowers, rose hips and strawberry leaves.
- Sage, yarrow and eucalyptus leaves, tansy flowers, juniper fruits and alder cones.
It is recommended to consume infusions 1/3 cup per dose three times a day.
Considering that inflammation of the cervix during pregnancy creates a certain risk for the health of the fetus and the woman, it is worth taking a responsible approach to your health. During pregnancy planning, it is necessary to undergo an examination by a gynecologist in order to identify all pathologies of the reproductive system and undergo the necessary treatment in advance.
Compliance with the basic rules of sexual life, having a regular sexual partner, and being attentive to your body will help prevent the risk of cervical inflammation or identify the problem in the early stages, preventing the serious consequences of this disease.
If you found this article useful, don't forget to share it with your friends on social networks. Perhaps it will help someone avoid serious problems while preparing for a long-awaited pregnancy.
Video: How to treat inflammation of the uterine appendages
How to treat inflammation of the uterine appendages
Video: treatment of inflammation
Treatment of inflammation