Changes in the uterus after conception
After fertilization has occurred and the embryo has attached to the mucous membrane, the uterus undergoes the following changes:
- Consistency. During pregnancy, the cervix becomes softer to the touch. Sometimes this condition is compared with the softness of the lips, while in its normal state it is harder. The consistency of the uterus changes gradually.
- Color. In its normal state it is pink. But after fertilization has occurred, it begins to acquire a bluish tint. This is due to a sharp increase in blood circulation and the appearance of additional vessels that are necessary for the life support of the fetus.
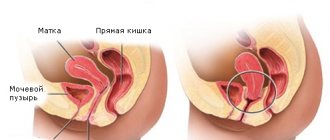
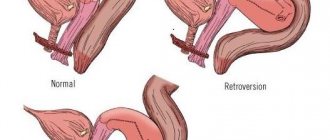
- Location. In order for sperm to penetrate into the cervical canal, the uterus rises. But after fertilization it drops below normal levels. This occurs as a result of the influence of hormones. It gradually rises throughout pregnancy.
The appearance also changes. In women who have not given birth, it has the shape of a cylinder, and in young mothers it has the shape of a cone.
Thus, during the examination, the gynecologist will be able to determine not only the pregnancy, but also its duration, the likelihood of miscarriage based on changes in the cervix. During pregnancy, the size of the organ is also of great importance. But it can only be determined by X-ray or ultrasound examination.
What changes are happening?
During the first trimester (12 weeks of pregnancy), the female organs are located in the pelvis. After approximately 3-4 weeks of absence of menstruation (8th week of pregnancy), the size of the uterus can almost double. At first, an asymmetrical increase may be observed due to the fact that the fetus is still very small compared to the volume of its future home.
After 13 weeks, the reproductive organ extends beyond the pelvis. It becomes possible to palpate the uterus through the anterior wall of the abdomen. Starting from this stage of pregnancy, the gynecologist constantly monitors the dynamics of changes in the height of the uterine fundus. In gynecology, this indicator is known as UHM (height of the uterine fundus). Thanks to this, it becomes possible to determine the growth rate of the uterus and fetus.
The height of the uterine fundus is measured using a tape or pelvis gauge when the girl is lying on her back. To ensure correct readings, you must empty your bladder before the procedure. It is considered that the pregnancy is proceeding normally if the indicators of the UMR correspond to the following parameters:
- the uterus at the 17th week of pregnancy (its bottom) is located in the middle between the navel and the pubic symphysis;
- starting from the 20th week, the fundus of the uterus drops below the level of the navel, the normative indicator is 2 cm below it;
- during the 24th week of pregnancy, the uterus is located just at the level of the navel;
- at the 28th week of pregnancy, the bottom of the female organ is approximately 2 cm above the level of the navel;
- During the 32nd week of pregnancy, the uterus is located at the bottom between the navel and the xiphoid process.
The measurements taken during the examination are recorded in the pregnant woman’s individual special journal.
Normal cervix during pregnancy
The course of pregnancy and the timeliness of delivery depend on how the organ changes and develops correctly. The organ is examined using ultrasound. This method of instrumental research allows you to accurately determine the size and condition of the uterus. Under normal conditions, during pregnancy the cervix is closed, and the entrance to it is blocked by a mucus plug. It is necessary to prevent infection, which can become a threat to the baby. Before labor begins, she comes out on her own.
When pregnancy reaches 24 weeks, it is important to determine the length of the cervix. This indicator is the most informative and helps to establish the likelihood of premature birth. In many cases, this helps to take timely measures and prevent miscarriage.
In rare cases, at this time the doctor will prescribe a transvaginal examination. It is necessary in cases where, during an ultrasound examination, the presence of a shortened neck is established, which does not allow its condition to be determined with high accuracy. The size of the organ is determined using a special vaginal sensor.
When pregnancy proceeds without complications, the size of the uterus at 24 weeks should not be more than 3.5 cm. The likelihood of premature birth increases depending on how much the indicator decreases. For example, the probability of miscarriage is up to 20%, with an indicator of 2.2 cm, and with 1.5 cm - 50%.
But do not panic if after 24 weeks the uterus shortens. This is a natural process as the body begins to prepare for childbirth. But at this time it has special significance.
In accordance with the duration of pregnancy, the size of the organ decreases smoothly and steadily. At 16-20 weeks, the length is from 4.5 to 4 cm. Then it gradually decreases and at 24-28 weeks it should not be more than 4 cm and less than 3.5. During examination at 32-36 weeks of pregnancy, the indicator is 3.5-3 cm.
Before birth, the length of the cervix is already about one centimeter. This is due to the fact that during this period the process of organ maturation proceeds much faster.
If during an ultrasound all indicators were normal, but after a certain time discharge is observed, you should immediately consult a doctor. The specialist will prescribe a repeat examination, as this sign may indicate the onset of premature labor.
Physiology
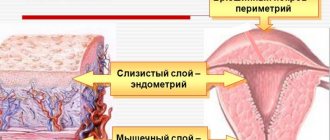
The cervix is a kind of entrance to the uterus. This organ is a continuation of the cervical canal. Normal cervical dimensions are very important. Deviations from the norm can lead to various pathologies occurring in a woman and her baby.
The location of the uterus and cervical canal is determined during an extended gynecological examination , which is performed on the expectant mother in a chair.
The size of the cervix in most healthy women ranges from 3 to 4.5 cm. A change in this indicator is a very important clinical sign of the development of many pathologies.
Even more interesting:
I infected my boyfriend with HPV
The ovary is enlarged and painful
Unstable hormonal levels cause the size of the cervix to change. This is especially clear in the second half of pregnancy.
If, when carrying a baby, a woman’s cervix is shortened in size, this is a manifestation of a pathology that requires correction.
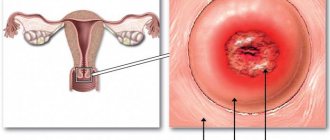
Cervical erosion during pregnancy
Erosion is a pathological condition when small wounds form on the neck. The cause may be various inflammatory pathologies, hormonal imbalances, or injuries resulting from the use of chemical or barrier contraceptives. Erosion most often occurs against the background of the development of papillomavirus. It is present in the body of many people, but begins to develop under the influence of external factors. These can be a variety of infectious and colds. In this case, it begins to bleed due to mechanical damage.
The resulting wound heals on its own after a certain time. But the overgrowth occurs with cells that line the inner mucous membrane, and not the outer surface of the organs. This is what poses a danger not only to the fetus, but also to the woman herself. During pregnancy, erosion is not treated. A course of therapy is prescribed after delivery.
IMPORTANT! It is very important to identify the pathology in the early stages, as it can lead to the development of serious consequences, such as infertility.
If fertilization has occurred, how to determine?
By 1 week, the baby is embedded in the epithelial tissues of the uterus.
Human chorionic gonadotropin begins to be produced. This is a clear sign of pregnancy. There are two ways to detect this:
- Take a clinical blood test for hCG.
- Take a pregnancy test yourself using morning urine, which contains the highest concentration of hCG after conception.
Then you can listen to changes in the body, internal sensations. With developed sensitivity, it is easy to understand what signals the body sends if a new life is born in it.
Polyp of the external os of the cervix
Polyps of the cervical canal may be detected by inflammation during examination. In some cases, they spread and extend beyond the cervical canal.
A polyp is a growth that is formed from pathological cells of mucosal tissue. Despite its small size, it poses a serious threat, as it can be injured, resulting in infection in the wound. This can cause premature opening of the pharynx or isthmic-cervical insufficiency. This defect negatively affects the development of the fetus and the course of pregnancy.
Polyps are removed when they grow, reach significant sizes, or combine into large growths. Surgery is performed only at 12-14 weeks. In cases where polyps do not pose a threat to pregnancy, it is left. After delivery, it may go away on its own.
Since a polyp consists of pathologically altered tissue, over time it can turn into cancer. But this change occurs in rare cases when the growth quickly grows and spreads.
Isthmic-cervical insufficiency
Not only the condition of the uterus can be dangerous when it exceeds normal levels.
A fairly short cervix also poses a threat to the baby. The degree of threat is determined by the results of ultrasound. The condition of the uterus is considered dangerous when the length of the cervical canal is 3 cm. The diagnosis of isthmic-cervical insufficiency is established when the indicator is 2 cm. The soft and very small cervix is not able to withstand the weight of the baby, and as it grows, the surface of the amniotic sac begins to disturb and the infection gets inside. In cases where the external pharynx opens quickly, this can cause prolapse of the fertilized egg.
But thanks to modern medicine, even with this diagnosis established, it is possible to carry and give birth to a healthy baby. Depending on how short the cervix is, surgical intervention is prescribed in which sutures are applied. This helps keep the organ closed.
In some cases, a gynecological pessary is installed. This is a special design consisting of a plastic or silicone ring. The pessary helps distribute the load and acts as a bandage. The structure or sutures are removed immediately before birth.
The cervix is an important organ that facilitates the fertilization process. In addition, it helps prevent infection from entering the appendages and uterus. It is the cervix that plays a major role in inflammation during pregnancy. Based on the changes that occur during fetal development, the doctor determines the risk of miscarriage or premature birth. It is for this reason that it is important to monitor the condition of the organ, especially during pregnancy.
What happens in 1 week of pregnancy?
After conception, the fertilized egg travels through the fallopian tubes to the uterus, which prepares to receive it. Pregnancy in the first week is a conditional time during which a woman’s body undergoes important changes and prepares for the development of the fetus.
The egg is in the crushing stage as it moves through the fallopian tubes, gradually increasing in size. They are helped to move by special cilia and contractions of the walls of the fallopian tubes.
Unfertilized eggs die after 12-24 hours, and a fertilized egg, when it enters the uterus, is implanted into it. Changes begin in the body, hormonal levels are rearranged.
Condition of the uterus
Changes at the beginning of pregnancy mainly begin in the uterus. At the early stage of the origin of life, structural changes begin in the female womb. Chemical processes occur that affect the entire body of the expectant mother.
The uterus has the following features:
- Practically does not change its location.
- It becomes soft and the neck thickens.
- A mucous plug forms in the area of the cervix, preventing pathogens from penetrating into the reproductive organ. This is how the fetus, while in the uterus, is protected from infection.
Slight nagging pain in the abdomen may occur as a result of relaxation of the pelvic ligaments. This is how the woman’s body prepares for the upcoming birth.
Breast
The mammary glands of the expectant mother become sensitive, and breast elasticity increases.
From 1 week, the breasts grow and increase in size.
But not all expectant mothers have it denser immediately after conception.
The thickening and growing breasts of the expectant mother require careful handling. You need to choose the right underwear so that it does not restrict breathing, is comfortable and is made from natural materials.
Stomach
At an early stage, a woman’s belly does not grow. A barely noticeable rounding appears only in mothers with experience, and even then not immediately. At the time of implantation of the egg or during the contraction of the fallopian tubes, when the embryo moves towards the uterus, mild nagging pain in the abdomen may occur.
If the pain goes away quickly and does not cause noticeable discomfort, there is no need to worry. This phenomenon is normal in the first week of pregnancy. When the nagging pain intensifies and heavy bleeding begins, this is a reason to consult a doctor.
What happens to the fetus?
There is no such thing as a fetus yet.
The unborn baby is just a fertilized egg that travels through the fallopian tubes to the uterus to be implanted in its walls. But he already carries half of his mother’s genetic material and half of his father’s. By the end of the week, the embryo is implanted into the epithelial tissue of the uterus.
The egg divides and becomes larger. The formation of the placenta and umbilical cord begins. At this moment, the embryo is still small, it cannot even be seen on an ultrasound, but it is closely related to the mother.
A woman can address the baby and talk to him. Such close contact has a positive effect on his further development.
Changes in the mother's body
The first changes indicate the very fact of pregnancy. Some of them are noticeable only during a gynecological examination, but most of the changes can be noticed by the woman herself.
These include the following:
- The uterus slightly enlarges, its surface softens.
- The vaginal mucosa turns a little blue.
- There is no menstruation and related processes.
The changes are due to the body’s preparation for pregnancy and the successful birth of a child. All systems and organs adapt to the process of fetal development.