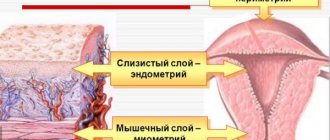
After pregnancy occurs, a woman’s body begins to undergo various transformations. For the most part, they affect the reproductive system, as the main organ prepares for gestation and birth of a child. The uterus has a complex structure and consists of three layers. Many girls wonder in the early stages of pregnancy what the endometrium should be like, because it plays a major role in this process.
An important feature is that this layer can change its thickness. At different periods of the menstrual cycle it can be greater or less, which is necessary for the successful attachment of the embryo in the event of fertilization of the egg. Let us consider in more detail what thickness of the endometrium should be for pregnancy, and under what parameters it is considered thin or thick.
Once the sperm has met the egg and fertilization has occurred, conception is considered to have occurred, so the embryo needs to attach to the inner layer of the uterus. Since the corpus luteum, produced by the ovaries, temporarily stops performing its functions, the body does not produce progesterone, and menstruation does not occur.
The main layers of the reproductive organ. Source: livewomen.ru
In early pregnancy, the endometrium gradually enlarges, depending on how the fertilized egg grows. It is this layer that currently performs the function of feeding the embryo, and in order for it to be complete, the body gives a signal to increase the number of blood vessels and glandular cells in this area. Thanks to this, the embryo receives the substances necessary for life, as well as a sufficient level of oxygen.
It is impossible to say for sure what the endometrium is like during early pregnancy, since these parameters change and are individual for each woman. Subsequently, this layer will be used to form the placenta, the condition of which determines whether the fetus will develop normally in the womb.
The size of the endometrium during early pregnancy is an indicator of how correctly this process occurs and whether there are any pathological abnormalities. In the first weeks, the fertilized egg cannot be detected by ultrasound, and there is also no opportunity to listen to the baby’s heartbeat; during pregnancy, the thickness of the endometrium determines whether the embryo has implanted.
Norm
During pregnancy, the size of the endometrium constantly changes, since due to fluctuations in the level of sex hormones in the body, the secretory function increases and the circulatory system grows. Many girls are interested in what indicators are considered normal, and this raises a natural question: if the endometrium is 7 mm, is pregnancy possible? Doctors say that this thickness is ideal for the attachment of the fertilized egg.
Normal endometrium and with hyperplasia. Source: climaxpms.ru
If the layer is smaller, then the embryo will not have enough opportunity for attachment and subsequent proper development. It is important to understand that the normal endometrium during early pregnancy is within the range of 8-14 mm, and by the end of 4 weeks its thickness will be 2 cm. In this case, we can say that the fetus is developing correctly.
When a doctor says that the thickness of the endometrium during early pregnancy is not normal, it means it is less than 8 mm, so spontaneous interruption of the fetal development process is possible.
The endometrium has a heterogeneous structure. What does it mean?
After taking Cyclodinone, my endometrium became heterogeneous and 16mm, but before everything was smooth. And although the doctor says that this drug should not give such an effect, I don’t really believe it, because the cycles themselves have lengthened, and M have become more abundant and painful.
Heterogeneous endometrium is NORMAL. This indicates that you are in the second phase of your cycle. The endometrium is homogeneous in the first phase of the cycle, then it is layered, i.e. grows and in the second phase becomes heterogeneous.
and the presence of corpora lutea in the ovaries indicates that you have ovulated. And the endometrial thickness is very good for fertilization, so GOOD LUCK with this cycle
It is possible that the stimulation provoked heterogeneity, or maybe it showed that you have a tendency towards hyperplasia. Maybe they will recommend you a diagnostic hysteroscopy to examine the uterine cavity; polyps are not always detected by ultrasound, and sometimes there are a lot of them and it is not visible that the endometrium is not good.
Oh listen, I didn’t understand, maybe you mean that it’s three-layered? which should be after O. In general, don’t panic! Let everything work out.
According to my ultrasound at 15 DC (1-2 DPO), the endometrium is heterogeneous 14 mm. G said that everything was very good, so I thought that it should be so (at 10 DC to O the endometrium was homogeneous 8 mm). So I think everything is fine with you, I wish you B in this cycle.
Plaksa, I definitely don’t have polyps. If they were, they would have been discovered long ago. I’ve been visiting all the gynecologists in the city for a year now. And I have already undergone so many examinations.
Heterogeneous endometrium in the second phase is normal. At this time, glands grow in the endometrium to nourish the baby - they are precisely hypoechoic areas that create heterogeneity and it’s very cool that they are expressed already on the 4th day after O. In the first phase
Hypoplasia
Also, girls often ask if the endometrium is 6 mm, is pregnancy possible. Experts say that the likelihood of implantation of the fertilized egg, although low, exists. In medical terms, this condition of the mucous layer is called hypoplasia.
In order to determine what kind of endometrium a woman has during early pregnancy, she needs to undergo an ultrasound examination of the pelvic organs. If deviations are identified, it is imperative to establish the reason why the thickness of this layer is less than normal. It is important to understand that although there is a positive answer to the question, if the endometrium is 5 mm, is pregnancy possible, the possibility of spontaneous miscarriage cannot be ruled out.
During pregnancy, the thickness of the endometrium depends on how well and fully sex hormones are produced. Accordingly, if these substances are in insufficient quantities in the body, then thinning of the lining layer will be noted. The mucous membrane may develop incorrectly if the woman has previously had abortions.
When a doctor sees that a woman’s endometrium is 3 mm, whether pregnancy is possible in this case, it is impossible to say unequivocally, because it is possible that this condition developed against the background of the progression of inflammatory diseases of the reproductive organs, these pathologies lead to disruption of the nutrition process and oxygen starvation in cells, therefore hypoplasia develops.
Also, in some patients, a thinned endometrium is an individual characteristic of the body that is inherited. When the thickness of the lining layer of the reproductive organ is too small, the likelihood of normal pregnancy is extremely low, so it is necessary to undergo qualified treatment and also be under the supervision of a gynecologist.
Treatment
Treatment of pathologies associated with endometrial heterogeneity is carried out depending on the underlying disease. In some cases, antibiotics may be prescribed in conjunction with hormones, especially if changes in the mucous membrane are detected against the background of an inflammatory process.
Antibiotics with a broad spectrum of action are best suited for the treatment of such pathologies. This group includes Amoxicillin and Ceftriaxone. It is mandatory to prescribe medications that enhance immunity and vitamin complexes.
If necessary, the doctor may prescribe non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs such as Ibuprofen and Diclofenac. The attitude towards physiotherapy for such pathology is ambiguous. All physiotherapy procedures are prescribed in the absence of fever and strictly according to indications.
Most gynecologists prefer not to use physical therapy due to fear of possible complications. If foci of inflammation are clearly visible with heterogeneous endometrium, doctors recommend surgical treatment. Particularly worth mentioning are the methods used in traditional medicine.
In nature, there are many plants that can have a beneficial effect on the condition of the endometrium. But not all of them may be suitable for treating a particular woman. Therefore, any decoctions and infusions of herbs can only be used with the permission of the attending physician. Any self-medication is strictly prohibited, since the result of taking unfamiliar drugs may be a further deterioration in health.
Hyperplasia
Another type of pathological condition of the mucous membrane is when the endometrium is 10 mm. Is pregnancy possible? Every patient diagnosed with hyperplasia is interested. If the size of the endometrium in the early stages of pregnancy is too large, then this requires adjustment so that the placenta subsequently has the opportunity to develop normally.
Hyperplasia indicates that the lining layer has grown excessively and its thickness has become large. The main reason for the development of this condition is the high level of concentration of the hormone estrogen in the woman’s body. But it is possible that the provoking factor was long-term use of combined oral contraceptives. In this situation, the attached embryo may also spontaneously separate and the pregnancy will be terminated.
Thick endometrium during pregnancy
Hyperplasia is an even more unpleasant condition. Excessive growth of the endometrium interferes with normal conception and gestation; its size matters during implantation of a fertilized egg and during pregnancy. It is difficult for a woman with this pathology to become pregnant. Conception is possible only with focal hyperplasia.
If you manage to get pregnant with this diagnosis, pregnancy often occurs with complications. These include miscarriages, pathologies of fetal and placental development, and the formation of tumors. In severe forms of hyperplasia, the doctor will insist on terminating the pregnancy.
Reasons for insufficient thickness
Thin endometrium is rarely diagnosed during pregnancy, since conception against this background is considered almost impossible. Women with insufficient thickness of the lining of the uterus suffer from infertility problems. Even if pregnancy occurs, it usually ends badly. Most often, it is interrupted during the next menstruation, and the woman does not even realize that she was pregnant.
Why does hypoplasia develop?
Experts have identified a number of predisposing factors:
- Insufficient thickness of the endometrium becomes a consequence of endocrine disorders.
- Congenital or acquired vascular disorders that affect blood circulation in the uterus.
- Complications resulting from surgical interventions and injuries to the uterus, for example, after induced abortions and curettage, which led to damage to the epithelium of the reproductive organ.
- Anomalies of uterine development, sexual infantilism.
- Infectious and inflammatory processes of a chronic nature in the area of the reproductive organ.
- Long-term hormonal contraception.
- Hereditary predisposition to insufficient growth of the endometrium.
Three-layer endometrium on ultrasound: what does this mean, causes and developmental features
Ultrasound examination of the pelvic organs in women can detect pathology not only of the ovaries and myometrium, but also of the uterine mucosa. In the descriptive part of the study protocol, the following phrase is often found - three-layer endometrium, which has its own meaning.
In the absence of pathology in the conclusion, the doctor indicates that there is a normal echo picture of the uterus and ovaries.
What is a three-layer endometrium
The endometrium is the mucous lining of the uterus, which consists of two layers: basal and functional. The last layer is constantly renewed, depending on the phase of the menstrual cycle, and is peeled off with the onset of menstruation. Consequently, its ultrasound picture is constantly changing.
The closure line is usually hyperechoic, that is, lighter in color in relation to the surrounding tissues. The endometrial layers themselves are darker - hypoechoic. In order to get the clearest picture of the condition of the uterus and ovaries on an ultrasound, a woman must properly prepare for the examination.
How is three-layer endometrium diagnosed by ultrasound?
The optimal method for diagnosing the endometrium is transvaginal ultrasound, because it is with such a scan that the border between the mucous membrane and the myometrium is most clearly visible. Preparation for the examination consists of preventing flatulence with a 2-3-day diet, maintaining intimate hygiene and emptying the bladder immediately before the procedure.
The examination is carried out lying on your back with your knees bent.
For transvaginal scanning, a special intracavitary sensor is used, onto which a disposable protective condom is placed for ultrasound.
The sensor is inserted into the vagina, thanks to which the most complete image of the internal organs of the female reproductive system is displayed on the device’s screen. Scanning is carried out in several planes.
To assess and measure endometrial thickness (M-echo), the following rules are used:
- obtaining a longitudinal section of the uterus with mandatory visualization of the cervical canal;
- measurement of the most thickened part of the “M-echo”, or the median complex (most often in the area of the uterine fundus);
- in the absence of contents in the uterine cavity, the thickness of only the posterior and anterior endometrial layers is measured.
If it is impossible to conduct a transvaginal or transrectal ultrasound, the examination is performed transabdominally - through the anterior wall of the abdomen. It is important for a woman to follow a diet for several days (limit fresh vegetables, legumes, fast food). If you have flatulence, the day before the procedure you can drink a sorbent that will absorb excess gases.
On the eve of the examination, approximately 1 hour before, you need to drink 700-1000 ml of water to fill the bladder. This will create an acoustic window and help to better remove the uterus and ovaries. Diagnosis is carried out with the woman positioned on her back, the sensor is applied to the abdomen in the pubic area. Endometrial measurement is also performed when the uterus is brought into a longitudinal position.
Causes and features of the development of three-layer endometrium
Each menstrual cycle begins with bleeding (desquamative phase), which lasts on average 4-5 days. During this phase, when scanning, the uterine mucosa is determined as a middle complex that is heterogeneous in structure, which has inclusions of low and high density.
Already in the proliferative phase of the cycle, pronounced growth and development of the glands of the inner lining of the uterus occurs. The endometrium has the following ultrasound signs:
- homogeneous structure;
- reduced echogenicity;
- clear hyperechoic border with the muscle layer;
- smooth hyperechoic line of closure of the posterior and anterior leaves.
In the periovulatory phase (before and after ovulation), the ultrasound picture of the endometrium changes somewhat. It becomes somewhat heterogeneous, thickens, and its echogenicity is equal to that of the unchanged myometrium.
What causes changes in endometrial thickness can be found in this video.
At the beginning of the secretory phase of the menstrual cycle, the mucous membrane retains its three-layer character for some time. The echogenicity of the M-echo increases and becomes equal to the echogenicity of the muscular membrane, the line of closure of the sheets gradually disappears.
Thus, it becomes clear that the three-layer endometrium is a physiological state of the inner layer of the uterus, which is observed during the following phases of the menstrual cycle (MC):
- proliferative (after the end of menstruation);
- periovulatory;
- early secretory.
If the ultrasound picture of the mucous membrane does not correspond to the day of MC, it can be assumed that there is a hormonal imbalance or dysmenorrhea of an inorganic nature.
Normal thickness of the three-layer endometrium depending on the phase:
- The average proliferative phase is 4-7 mm.
- Late proliferative phase – 6-10 mm.
- Early secretory phase – 13-18 mm.
In postmenopause, sex hormones are no longer produced, so the uterus stops undergoing cyclic changes. The echogenicity of the endometrium is increased, the structure is normally homogeneous. The boundary between the muscular and mucous membranes is erased. The M-echo size normally should not exceed 4-5 mm.