An early miscarriage is a spontaneous termination of pregnancy before 13 weeks. At the same time, the internal and external pharynx of the uterus opens, the embryo is separated, violating the integrity of the blood vessels. Heavy bleeding is a sign of his final death. Women faced with this problem need to know what discharge is considered normal after a miscarriage, how many days the blood flows, and how to prevent complications.
What is a miscarriage?
Unfortunately, pregnancy does not always go well for many women, and giving birth to a child is a big problem for many. A situation where pregnancy ends before 37 weeks is called miscarriage. In this case, a break in the period up to 21 weeks inclusive is called a miscarriage, and beyond this period - premature birth. The period of pregnancy up to 12 weeks is an early miscarriage, and from 12 to 21 weeks is a late miscarriage. Up to 15% of all pregnancies end in miscarriage, and approximately 7% end in premature birth.
Symptoms during abortion can vary greatly: for example, with an early miscarriage, a woman complains that her lower abdomen hurts and notes the appearance of pink or brown discharge. The clinical picture may vary depending on whether cleaning was performed after a miscarriage or not. If the miscarriage passed without complications, then in the absence of cleaning the bleeding lasts within 5-10 days, and after cleaning this period extends to 14-20 days.
The reason is that during cleaning, part of the endometrium is removed and the vessels of the uterus are damaged to a greater extent, which leads to later discharge. The nature of the discharge after a miscarriage without cleaning is usually light, which is due to the fact that the fertilized egg comes out without rupture, entirely, it is small in size and its separation in the early stages does not injure the uterus so much. The cleaning procedure is more traumatic, although necessary in some cases, and leads to longer and more profuse bleeding.
conclusions
Uterine curettage is a medical procedure that has some side effects. In particular, after cleaning there is a rather long recovery period. If you do not follow all the rules and violate the recommendations, recovery will take several months, and complications after a miscarriage may worsen.
Thanks to modern equipment, specialists from the abortion and contraception department of the MGO “Diana” will perform curettage after a miscarriage as carefully and safely as possible, without injuring the walls of the uterus. This will allow you to quickly restore health after the loss of a child, avoid complications and return the woman’s reproductive system to an active state.
Share link:
Causes of miscarriage
The reasons for miscarriage can be very diverse:
- genital and extragenital pathology of the mother;
- genetic disorders of the embryo and fetus;
- stress;
- endocrine disorders.
Genital pathologies include abnormalities of the uterus (bicornuate, saddle uterus, presence of a septum in the uterus), uterine fibroids, inflammatory processes in the female reproductive system, hypoplasia and isthmic-cervical insufficiency.
Extragenital pathology includes arterial hypertension, diabetes mellitus, renal, liver failure and other pathologies. Genetic disorders on the part of the embryo, chromosomal aberrations can lead to structural abnormalities, which leads to the expulsion of the fetus from the uterine cavity.
In the list of immune pathologies, causes such as histocompatibility antigens and Rh factor incompatibility play an important role. The so-called antiphospholipid syndrome (APS) is extremely common, when antibodies are formed to the phospholipid membranes of fetal cells and its membranes. This activates the coagulation process, leading to DIC (disseminated intravascular coagulation). Thrombosis occurs in the vessels of the placenta and decidua, fetal nutrition is disrupted, hypoxia occurs, the fetus dies and is rejected.
Hormonal levels play a major role in miscarriage: especially ovarian failure, leading to a decrease in progesterone levels; and hyperandrogenism of adrenal and ovarian origin. Infectious diseases are also of great importance in initiating miscarriage. General somatic infectious pathology, as well as genital pathology associated with sexually transmitted diseases (chlamydia, ureaplasma, toxoplasma, etc.) can involve the tissues of the embryo and fetal membrane.
Stress and psychogenic factors in themselves can be the cause of miscarriage, which is confirmed in real life. An increased emotional background can activate the contractile activity of the uterus, causing the fertilized egg to move away from the walls.
Why does fetal rejection occur?
The cause of spontaneous abortion is associated with many factors:
- Hormonal disorders in the body. When there is a deficiency of female progesterone or an excess of male androgen, the expectant mother is prescribed hormonal drugs that minimize the risk of losing the child.
- Genetic disorders of the embryo.
- Stress, weakened immunity.
- Wrong lifestyle.
- Concomitant diseases, in particular from the field of gynecology.
- Injuries, physical and psychological stress.
Clinical symptoms of miscarriage
According to the severity of the process of expulsion of the fetus from the uterus, they are distinguished:
- threatened miscarriage;
- beginning miscarriage;
- abortion is in progress;
- complete abortion;
- incomplete abortion.
A distinctive feature of a threatened miscarriage will be aching pain in the lower abdomen or sacrum, which is a manifestation of activation of the contractile activity of the myometrium. However, the unborn child can still be saved, since the fertilized egg remains connected to the uterus.
When a miscarriage begins, cramping pain, bloody discharge appears, and detachment of the fertilized egg occurs. Examination on the chair allows you to detect the opening of the external os of the uterus.
Abortion in progress means detachment of the fertilized egg, which completely loses contact with the wall of the uterus and moves to its lower sections. At this time, severe cramping pain begins, the cervix opens and the fetus is expelled: either completely (complete abortion), when only fragments of the decidua remain in the uterus; or partially (incomplete abortion), when part of the segmented fertilized egg remains in the uterine cavity and can subsequently create problems.
The severity and range of symptoms depends on the trimester: the first trimester is characterized by pain and bleeding, while the second trimester is characterized by bleeding at first, which is not typical, but occurs after the fetus is delivered; the process of expulsion itself is accompanied by very severe attacks of pain.
In the case of placenta previa, all stages may be accompanied by severe bleeding. All stages can be characterized by the presence of nagging pain when there is a threat of miscarriage; the addition of cramping pain. The discharge during a miscarriage is bloody at the beginning. The contractions are strong. In the case of an incomplete abortion, contractions may subside due to bleeding.
Possible discharge during the post-abortion period
Most often, women consider the resumption of menstruation after an abortion to be the main sign of recovery after an abortion. In part, they will turn out to be right. After all, a restored cycle means that reproductive health is normal. However, the condition of all organs of the pelvic region and the woman’s mental state should also be normal. But, before we talk about the complete recovery of the body after...
Abortion before what period is the safest? Abortion is the only operation that is performed to stop the normal functioning of the body. Of course, there are cases when termination of pregnancy is necessary for medical reasons, but in most cases, according to statistics, women decide to terminate a completely healthy pregnancy. Regardless of a woman’s personal reasons, if she already...
Pregnancy by the end of the second trimester is characterized by a fully formed child, who only needs to get stronger before being born. There is no longer any talk about late-term abortion at the woman’s request, as well as medical abortion. Since February 2012, a law has been in force in Russia according to which there is only one social reason for terminating a pregnancy...
Which discharge should be alarming, and which are considered normal? Many girls and women panic at first without trying to understand the situation. But a regular consultation with a doctor about the possible consequences can eliminate many unnecessary questions. What to expect? Is discharge possible after an abortion? How much bleeding is abnormal? Yellow discharge after an abortion, brown discharge signal what? This article is dedicated to answering these questions. But, you should remember, only a doctor can give qualified medical information.
After an artificially terminated pregnancy, the female body weakens to one degree or another. The environment for new and strengthening of existing infections is created by a combination of reduced immunity and injuries to the internal genital organs. To prevent complications from the development of infections, a woman after an abortion needs to monitor vaginal discharge. They appear on about 3 days. Yellow discharge after an abortion with a pungent smell of rot is especially dangerous. This is a clear sign of a sexually transmitted infection. You should consult a doctor immediately. The earlier treatment is started, the greater the likelihood of a successful outcome in preventing complications.
Diagnosis of threatened miscarriage
Diagnosis is made based on the patient’s complaints, the results of a gynecological examination and laboratory tests for hormones. A gynecological examination reveals a moderate opening of the uterine pharynx, through which the lower part of the fertilized egg can be palpated.
A frozen, undeveloped pregnancy is suspected when the size of the uterus and fetus lags behind the gestational age.
Tests for progesterone and human chorionic gonadotropin, the levels of which for the first trimester should range from 40,000 IU/liter, and for the second trimester - 70,000-100,000 IU/liter, can be helpful in establishing a frozen pregnancy. A lack of progesterone indicates poor secretion of the hormone by the corpus luteum of pregnancy and the placenta. The level of estrogen matters: it must fit within the standards characteristic of each period of pregnancy - this hormone ensures normal growth of the placenta.
If there is a suspicion of hyperandrogenemia, then an analysis is performed to determine 17-ketosteroids in the blood and urine. Exceeding the normal level threatens miscarriage. In APS, antibodies to cardiolipin, markers of blood coagulation activation, and lupus anticoagulant are detected.
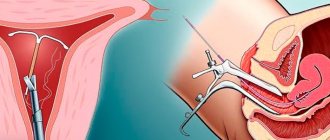
Yellow discharge after cleaning the uterus
If, after curettage of the uterus, a woman has atypical yellow discharge, this indicates an infectious process occurring in the reproductive organs. The process of uterine curettage and preparation for it require a number of measures aimed at preventing infectious and inflammatory complications in the postoperative period. When sanitary and epidemiological requirements are violated during gynecological intervention, the risk of developing an infectious pathology increases. The same is observed during an emergency intervention, when the patient underwent a cleaning procedure without specifying her infection status. If the circumstances preceding the cleansing are favorable, the woman undergoes an examination and if inflammatory changes or disease are detected, she undergoes sanitation.
The most common complications of curettage are:
- cervicitis;
- endometritis;
- endocervicitis;
- salpingo-oophoritis;
- metroendometritis.
Yellow discharge after curettage can occur with cervicitis. The pathology is an inflammation of the cervical canal. The reason may be:
- injury to the cervix during cleaning;
- the presence of genital infections and vaginal dysbiosis before surgery;
- violation by the woman of the recommendations of the postoperative period;
- failure by doctors to comply with the rules of asepsis and antisepsis when performing uterine curettage.
The following types of cervicitis that form after curettage are distinguished.
- Purulent. The causative agents are most often bacteria: gonococci, trichomonas, ureaplasma, mycoplasma, chlamydia. With the development of a purulent form, the columnar epithelium of the cervix is affected. The discharge is copious and purulent, yellow in color with an unpleasant odor.
- Serous-purulent. The cause of the disease is opportunistic flora of the genital tract. With dysbacteriosis, E. coli, staphylococci, streptococci and other microorganisms actively multiply in the vagina, which during the operation penetrate the endocervix and trigger the process of inflammation. It is also accompanied by yellow discharge.
- Atrophic. It does not form immediately after cleaning. Characterized by a decrease in the thickness of the mucous membrane of the cervix.
In general, the disease can be asymptomatic. The appearance of yellow purulent discharge after curettage indicates an acute form of inflammation.
The woman also receives the following complaints:
- nagging pain in the lower abdomen;
- pain in the lumbar region;
- yellow discharge may contain blood;
- frequent and painful urination.
In some cases, after cleaning and the development of cervicitis, an increase in temperature may be observed.
During a gynecological examination, the doctor, in addition to yellow discharge, notes swelling and redness of the part of the cervix that extends into the vagina. Minor hemorrhages and ulcerations may also be detected.
If left untreated, the pathology becomes chronic. The yellow discharge becomes less abundant, but contains blood. A woman feels a constant aching pain in the lumbar region during sexual intercourse.
Cervicitis is diagnosed based on vaginal examination and smear cytology.
How to prevent miscarriage?
To prevent miscarriage, a set of measures is carried out, the scope of which depends on the specific cause leading to the threat of miscarriage. It is necessary to provide the woman with complete emotional and physical rest (bed rest) and a balanced diet. Provide drug therapy based on possible teratogenic effects and predominant symptoms. Thus, when the contractile activity of the uterus increases, antispasmodics (Baralgin, No-shpa, 25% magnesium sulfate) are indicated. Sometimes beta-agonists (Ritodrine, Partusisten, etc.) help well.
For hypofunction of the corpus luteum during pregnancy and placental insufficiency, Utrozhestan and Duphaston are prescribed. For abnormal development of the uterus, estrogens are added, and for ovarian hypofunction, choriogonin is added. For hyperandrogenism, small doses of glucocorticoids can be prescribed to suppress their function by reducing the activity of adrenocorticotropic hormone.
In case of isthmic-cervical insufficiency, a pessary is installed to compensate for the insufficient tone of the cervix. In case of antiphospholipid syndrome, disturbances in the coagulation system are corrected (Heparin, Trental, Curantil, etc.), and plasmapheresis is performed to reduce the concentration of antibodies. Physiotherapeutic methods are added to reduce the drug load on the pregnant woman and fetus (sinusoidal stimulation of the uterus, endonasal galvanization, etc.).
The nature of the first menstruation
The first menstruation after a miscarriage in 95% of cases changes its characteristics in comparison with menstruation before conception. Often a new cycle coincides with the previous schedule, but its shift is also considered normal. A change in the volume of blood released, the presence of PMS and other criteria are not a violation if the indicators fit into the medical standard.
Normal first menstruation and cycle after a miscarriage:
- duration of menstruation – 3─7 days;
- amount of blood – 90─150 ml (about 4 changes of pads per day);
- the composition of the discharge is dark red or red-brown in color with no clots larger than 1.5 cm, without an unpleasant odor;
- restoration of the cycle - within 3 months after spontaneous abortion;
- PMS – moderate or moderate severity of symptoms;
- the duration of the follicular and luteal phases is 14-16 days each;
- ovulation is complete.
How long it will take for menstruation to appear depends on the severity of the woman’s condition after a miscarriage. According to the standard, gynecologists take the day of spontaneous complete abortion as the beginning of the follicular phase. With a favorable prognosis, the first menstruation occurs 24-35 days after pregnancy failure. Deviation of the nature of the following cycles from the norm is regarded by doctors as a sign of functional disorders and pathologies.