Doctors call curettage curettage, and patients in gynecological departments call it cleansing. Some doctors believe that such manipulations for diagnostic purposes have no right to exist. Others easily prescribe and perform such mini-operations. There are cases when one woman undergoes 12 diagnostic cleanses in a year, causing irreparable harm to her health.
p, blockquote 1,0,0,0,0 —>
p, blockquote 2,0,0,0,0 —>
Complications
Everyone knows that the uterus is an important organ that is found only in a woman’s body.
It performs a vital reproductive function. The uterus is located in the pelvic area, between organs such as the intestines and bladder. This is where the embryo (fertilized egg) attaches, after which the fetus develops over the course of nine months. If conception does not occur, then at the end of the monthly menstrual cycle the inner layer of the uterus peels off and leaves the woman’s body. This is how menstrual bleeding occurs.
What is this organ? Externally, the uterus is very similar to a small inverted triangle (the size of which does not exceed seven centimeters). The upper part of the organ is called the bottom, through which the egg enters.
The body is the side walls of the organ in which the cavity is located, where the embryo develops.
The lower part of the uterus is the cervix. This is a thin tube two to three centimeters long that connects the organ cavity and the vagina and in which the cervical canal is located.
The uterus consists of several layers:
- The external (or perimeter) is the so-called peritoneum, which protects the organ from external irritants.
- The middle (or myometrium) is a layer of smooth muscle, which is a kind of dense wall.
- Internal (or endometrium). It is a mucous membrane abundantly supplied with blood vessels. It is this layer that interests doctors when it comes to separate diagnostic curettage of the uterine cavity.
Naturally, pharmacological medications will be prescribed to you by your attending physician. He will describe in detail the dosage and regimen. Below are general recommendations regarding which medications are most often prescribed.
First, painkillers. These include “Diclofenac”, “Renalgan”, “Baralgin”. The drugs not only eliminate pain, but also slightly reduce bleeding. Most often, doctors recommend taking pills after meals. For the first couple of days, take one pill orally three times a day. Then take one tablet before bed for another two days.
“No-shpu” is taken as an antispasmodic. It enhances uterine contractions and accelerates the removal of bloody discharge remaining in the organ cavity. Take one tablet two or three times a day for three days.
To prevent the occurrence of postoperative infection, antibacterial therapy is prescribed. Most often, doctors prescribe Cedex or Cefixime tablets. Antibiotics can be taken four hundred milligrams once a day. The course of treatment is at least five days.
Sometimes the attending physician may consider it appropriate to prescribe suppositories that contain iodine. These may be drugs such as Betadine or Iodoxide. Suppositories are used to prevent inflammation and infections in the uterus. The specialist may prescribe one suppository per day for a week. It is best to insert a suppository into the vagina at night.
Antifungal drugs prescribed to prevent thrush are also often recommended for patients after curettage. “Fluconazole” or “Futsis” can be taken orally in a one-time dosage of 150 milligrams.
They occur extremely rarely, but undesirable manifestations can still occur, and you need to be aware of them. Complications after curettage include:
- stagnation of blood in the uterus, provoking an inflammatory process;
- tear or damage to the walls of the uterus with instruments (the doctor sews up the resulting wound);
- damage to the inner layer of the endometrium, which can cause infertility.
Such undesirable postoperative consequences are extremely rare and most often do not pose a threat to the life or health of the patient.
When curettage of fetal remains there is a possibility of complications. Such an operation can provoke the following consequences:
- Surgical manipulations can result in rupture of the uterine walls. The cause of this complication is mainly defects in the uterine cavity.
- After completion of the procedure or after a short period of time, there is a possibility of bleeding. This complication occurs against the background of weak uterine contractions. It is worth considering that excessive bleeding can cause anemia, so if such a problem occurs, you should urgently seek help from a doctor.
- Since the uterine mucosa after surgery is a wound, you can notice the appearance of an inflammatory process on it - endometritis. This pathology can be recognized by the following symptoms: pain in the lower abdomen, increased body temperature, weak uterine contractions, copious vaginal discharge, accompanied by an unpleasant odor.
- Since curettage is carried out blindly, remnants of the membranes may remain in the uterus. The problem can be recognized by bloody discharge, which is characterized by increased duration. In this case, the size of the uterus will not decrease to the levels observed before pregnancy. The presence of residues can be confirmed using ultrasound. If they are found, repeated cleaning will be required.
- Curettage involves removing the top layer of the endometrium along with the membranes. Because of this, there is a possibility of damage to the basal layer of the reproductive organ. This mainly happens when the procedure is carried out carelessly. The consequence of such an operation may be the occurrence of adhesions and fusion. These formations can subsequently interfere with the process of attachment of the fertilized egg to the uterine walls, which causes infertility.
To minimize the risk of these complications, a woman needs to carefully prepare for the operation and follow all the recommendations of the attending physician. Also, if alarming symptoms appear, you should immediately contact a specialist to diagnose the causes of its occurrence.
Bleeding after endometrial polyp removal
Occurs within 2-3 days after removal. Minor bleeding and blood clots should not be a cause for concern at this time. A cause for concern should be copious bleeding, as well as the appearance of scarlet blood. In this case, you need to consult a doctor as soon as possible, or call an ambulance.
Bleeding occurs as a result of damage to the mucous membrane and surrounding tissues. It can also occur as a result of insufficient healing of the vessel. Often it is cauterized. The risk of bleeding is high during curettage and abdominal surgery, and is almost completely eliminated during hysteroscopy and laparoscopy.
[15], [16], [17], [18], [19]
Are there any contraindications to the procedure?
This is a very important question. Scheduled cleaning is not carried out if the patient suffers from infectious diseases or acute inflammatory processes are detected in the genitals. If emergency curettage is required, the operation is carried out according to vital indications.
Also, cleaning is not carried out if it is necessary to remove a malignant tumor from the uterine cavity.
There are a number of contraindications to this surgical intervention, which include:
- diseases of the genital tract that are infectious in nature: colpitis, inflammation in the appendages, vaginitis;
- vascular pathologies and those that are in acute form, hematopoietic diseases, heart diseases, diabetes mellitus;
- acute infections caused by viruses and bacteria.
Recurrence of endometrial polyp after hysteroscopy
The polyp tends to form again in the same place if it was not completely removed. Often, due to imperfect technology or the anatomical features of the female genital organs, it is impossible to completely remove it. A small leg or piece of a blood vessel remains. After some time, a polyp grows from it.
The risk of a recurrent polyp is minimal with hysteroresectoscopy and maximum with curettage and open operations. You can avoid relapse if you undergo high-quality postoperative treatment.
Source
A few words about the endometrium
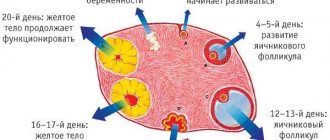
This mucous membrane is hormonally sensitive, as it undergoes changes in accordance with the phase of the menstrual cycle. For example, immediately after critical days, the thickness of the endometrium can vary within two millimeters, while by the end of the cycle this figure can exceed two centimeters.
Before we figure out what diagnostic curettage of the uterine cavity is, let's find out what the endometrium consists of:
- Functional layer. It is the outer layer that is shed with each monthly cycle. The thickness of this layer and its structure are individual, as they depend on the hormonal background of each woman.
- The basal layer is the lower layer of the endometrium, which is adjacent to the muscular layer. It practically does not react to hormonal changes in the body associated with critical days, and performs a restorative function of the mucous membrane after childbirth, menstruation and curettage.
- The stroma is considered the basis of the endometrium, as it consists of cells and fibers of connective tissue. This layer is a dense mesh.
- The uterine glands are tubular glands that secrete a mucous secretion, which ensures the normal functioning of an organ such as the uterus.
So, we have understood a little about the structure of the female reproductive organ. Now let's find out what curettage of the uterine cavity is. According to reviews from both doctors and patients, this procedure is considered a fairly common manipulation, so you should not be afraid of it.
Ovarian cyst on ultrasound
During the examination, an ovarian cyst is visualized as a round-shaped formation filled with fluid, several centimeters in diameter. Using an ultrasound, the gynecologist determines not only the size of the tumor, but also its type, since cysts can be not only functional, but also represent a benign neoplasm that is not associated with the consequences of curettage and hormonal imbalance.
Using an ultrasound, the doctor can also see the presence of polycystic ovary syndrome. With the disease, the size of the ovary also increases - up to 10-13 cm3, with normal values 7-8 cm3. Another sign of polycystic disease, which is noticeable on ultrasound, includes thickening of the ovarian membrane and the presence of a large number of follicles in it.
To avoid complications after curettage of the uterus, it is important not only to undergo timely examinations prescribed by the doctor, but also to follow the recommendations of a specialist after the curettage procedure.
Carrying out the procedure
Before carrying out cleansing during a frozen pregnancy, it is mandatory to undergo a general clinical examination, including tests and research:
- determination of blood group;
- diagnosis of syphilitic infection;
- general and biochemical blood and urine tests;
- Rh factor diagnosis;
- examination of the cervix, smear;
- urethral smear.
An electrocardiogram is also performed as part of the examination. Such a diagnosis is necessary to eliminate the risk of genital diseases and other contraindications to surgical intervention. Then the woman removes all hair from the intimate area and washes thoroughly.
Before performing curettage of the uterine cavity when the development of the fetus has stopped, it is necessary to avoid eating foods that contribute to the active formation of gases in the gastrointestinal tract. Also, the final consumption of food should be no later than 6 hours before surgery, since it is carried out on an empty stomach. If urgent curettage is indicated, gastric lavage is performed before the procedure.
Before surgery to remove the remaining fertilized egg, it is necessary to prepare the cervix. This is mandatory, especially for nulliparous women, and is necessary to dilate the cervix and reduce the likelihood of damage to it.
Preparation is carried out by introducing kelp into the cervical canal. Algae gradually absorb vaginal secretions, swell, and expand the canal. This is done on the eve of the operation. Also, before the procedure, you should consult an anesthesiologist or obstetrician-gynecologist.
After the preparatory stage is completed, an operation is scheduled, which is performed under general anesthesia. The woman sits on a gynecological chair. Before the procedure, the gynecologist must conduct an examination. It's necessary:
- to determine the location of the uterus;
- assessment of the size characteristics of the uterus;
- disinfection of genital organs.
Then anesthesia is administered and the cervical canal is expanded using an expander. Curettage is performed using a curette. The gynecologist removes the contents of the reproductive organ, capturing the upper layer of the endometrium. During the operation, the doctor uses substances that cause contractions of the uterus.
The duration of the described procedure is 15 minutes.
Vacuum aspiration for a frozen pregnancy is considered a more modern method of curettage, so we recommend studying the information about its implementation in more detail.
How is it carried out?
Before prescribing a cleaning procedure, the doctor reviews the results of laboratory and instrumental examinations:
p, blockquote 10,0,0,0,0 —>
- Blood analysis.
- Coagulogram (checking the rate of clotting).
- Smear for microflora and oncocytology.
- ECG.
- Ultrasound of the pelvic organs.
- Fluorography.
At the same time, the attending physician consults with an anesthesiologist and therapist. On the day of surgery you should not drink or eat. The use of vaginal products is prohibited for 24 hours. Before the procedure, the bladder is emptied. The operation is performed in a gynecological chair under general anesthesia, most often intravenous. In case of individual contraindications, local anesthesia is possible.
p, blockquote 11,0,0,0,0 —>
Separate diagnostic curettage (SDC) lasts from 10 to 15 minutes. First, the external genitalia are treated with an antiseptic composition. Then the uterine canal is expanded. Using a curette, a special tool in the form of a spoon with a long handle, a scraping is taken. These biomaterials are sent to the laboratory separately to distinguish between pathologies. During a frozen pregnancy, the contents are sucked out using a vacuum aspirator. The operation ends with repeated treatment of the vagina with an antiseptic, and ice is placed on the abdominal area for 15 minutes.
In case of prolonged reddish or brown discharge, if there is no pregnancy, the bleeding is stopped with medication. You will learn about this possibility from your attending physician. When re-evaluating the condition after the next menstruation, it often turns out that cleaning would be unnecessary. Curettage for endometrial hyperplasia or polyposis may not be necessary if a drug that can solve this problem is prescribed already in this cycle. When, a month later, the diagnosis is confirmed, cleaning with a hysteroscope is inevitable.
p, blockquote 13,0,0,0,0 —>
A gynecologist offering curettage as a diagnostic method may begin with an aspiration biopsy, a simple informative analysis performed in an outpatient setting and not requiring anesthesia. Its essence is to absorb a small area of tissue for further histological examination.
p, blockquote 14,0,0,0,0 —>
Concept and classification of the procedure
In gynecology, there are two types of uterine cavity curettage:
- Diagnostic. This type of procedure involves removing (scraping) the inner layer of the endometrium for further examination. In this way, biomaterial is collected to determine the presence of cancer cells.
- Separate diagnostic curettage of the uterine cavity. The manipulation is carried out in two stages. First, the inner layer of the cervical canal is removed, and then the upper layer of the uterine cavity. Therefore, very often this procedure is also called curettage of the uterine cavity and cervical canal. Most often, this mini-operation is performed not for diagnostic, but for therapeutic purposes. For example, this method is actively used to remove neoplasms in the form of polyps, pathologically dangerous lesions, or overgrown endometrium. The biomaterial obtained after separate curettage of the uterine cavity is sent for the necessary research.
Recently, when carrying out manipulations, the attending physician uses a device such as a hysteroscope, thanks to which the organ is illuminated from the inside. Moreover, the image of the surface is optically enlarged, thereby improving visibility. This affects the operation, since the specialist can see the situation more accurately and act according to the circumstances.
Next, we will discuss each of the methods described above in more detail.
Consequences of removal of endometrial polyps: discharge, pain, temperature
All iLive content is reviewed by medical experts to ensure it is as accurate and factual as possible.
We have strict sourcing guidelines and only link to reputable sites, academic research institutions and, where possible, proven medical studies. Please note that the numbers in parentheses ([1], [2], etc.) are clickable links to such studies.
If you believe that any of our content is inaccurate, out of date, or otherwise questionable, please select it and press Ctrl + Enter.
In some cases, removal of an endometrial polyp may be accompanied by endometritis - inflammation of the endometrium, which can develop for various reasons, including: infection, intensive recovery. With multiple polyps, aseptic (non-microbial inflammation) often develops.
How you feel depending on the trimester
In general, recovery after cleansing the uterus is quick, without any health-threatening complications. But after curettage of the embryo, unpredictable consequences may appear for the general condition of the woman and her reproductive system.
Most often they do not pose any danger, but are physiological in nature. Such consequences include the appearance of pain and bloody discharge from the vagina after curettage.
First trimester
When cleansing is carried out by an experienced doctor in the early stages, any complications rarely arise. In this case, the following side effects may occur:
- bleeding;
- the appearance of an inflammatory process;
- the occurrence of hormonal imbalance;
- isthmic-cervical insufficiency;
- damage to the uterus;
- formation of scars on the internal uterine surface.
Also, as a result of removing an embryo that has stopped developing, an increase in temperature and painful sensations in the lower abdomen may occur. After surgery, therapy may be required to restore the cycle, but in most cases it normalizes on its own.
Second trimester
If the pregnancy is frozen and curettage is required in the second trimester, the risk of complications increases. Among them are:
- the occurrence of bleeding;
- damage to the inside of the uterus or its puncture by an instrument or fetal bone during the procedure;
- the appearance of bloody discharge without an unpleasant odor or a different color shade;
- formation of hormonal disorders;
- spread of abdominal pain after curettage;
- increase in body temperature.
If you start the prescribed therapy in a timely manner, the body will quickly recover and prepare for the next conception. In this case, planning a pregnancy after curettage is possible within six months.
Third trimester
Curettage during pregnancy fading in the third trimester requires the longest recovery period. In almost all cases, a woman needs long-term rehabilitation.
Before the operation, the doctor must evaluate the condition of the fetus. When it becomes dead, an abortion is performed. After such a procedure in the third month of pregnancy, a woman will have to stay in the hospital for at least 1 week.
Cervicitis
The reason for the increase in temperature - sometimes to very significant levels - after cleaning (curettage) of the uterine cavity is inflammation of the vaginal segment of the cervical canal.
In addition to high fever, the disease is characterized by the appearance of vaginal discharge. They can be either mucous or contain purulent impurities. In addition, the pathology is accompanied by pain in the lower abdomen, as well as significant discomfort accompanying the process of urination.
There are two forms of cervicitis. The gradation depends on which tissues of the cervical canal were involved in the pathological process.
The main cause of the disease is tissue damage during uterine curettage, which is subsequently joined by nonspecific infectious agents. The development of inflammation after cleansing and the accompanying rise in body temperature can be provoked by:
After cleaning (scraping) the uterine cavity, the female body becomes more vulnerable to various types of infections as a result of decreased immune defense.
In addition to its own opportunistic flora, inflammation and fever are caused by pathogenic microorganisms. Pathogens such as chlamydia, mycoplasma and ureaplasma, viruses can provoke cervicitis when open sexual activity begins after cleansing earlier than recommended by the doctor. The disease also becomes more active if the infection has progressed before the cleansing. Failure to comply with the principles of rational antibiotic therapy leads to cervicitis and a rise in temperature after cleaning.
Symptoms
As a rule, after injury to the cervix during curettage and the addition of a secondary infection, a woman develops acute cervicitis. In addition to the increase in temperature, the following symptoms appear:
During a gynecological examination - a few days after curettage - swelling and redness of the cervix are noted.
If an increase in temperature is typical for all types of cervicitis, then the accompanying symptoms depend on the pathogen and the current state of immune defense.
In the absence of adequate therapy, the disease becomes chronic, which is fraught with the development of serious consequences. An ascending infection can penetrate the tubes and ovaries, leading to an inflammatory reaction, which is quite difficult to treat and causes infertility.
Why is diagnostic curettage necessary?
This procedure can be used as an independent manipulation or as an auxiliary one (before surgery).
Most often, indications for diagnostic curettage are the following factors:
- Endometrial hyperplasia. Most often, anomalies are detected on ultrasound, when thickening of the mucous membrane of the uterine cavity is visible. To identify an objective picture, curettage of the uterine cavity may be prescribed. With endometrial hyperplasia, various neoplasms can be detected. The cleaning procedure will reveal their nature and etiology.
- Endometriosis. This condition is characterized by the spread of the mucosal layer beyond the organ.
- Polyps.
- Various menstrual cycle disorders.
- Uterine fibroids.
- Cervical dysplasia.
According to patient reviews, the procedure is most often performed when there is bleeding. Curettage of the uterine cavity helps not only to eliminate it, but also to determine the true cause.
Endometriosis on ultrasound
The pathological condition is characterized by the growth of the inner layer of the uterus into the muscular layers of the organ. On ultrasound in case of disease, the gynecologist detects a heterogeneous structure of the myometrium with heterogeneous inclusions.
The condition means that in the muscle layer of the organ there are areas of the endometrium that look like small cysts on ultrasound. ECHO signs on ultrasound include an enlarged uterus, heterogeneous endometrium that does not correspond to the phase of the cycle. Endometriosis after curettage can develop if it is performed poorly, when the basal layer is removed with a curette and the myometrium is affected.
Rehabilitation after curettage
This is also an important issue. Since women do not always take cleansing seriously, they may behave incorrectly after it is done. However, it is very important to follow the doctor’s recommendations, and then the postoperative period will pass without complications.
So, after cleansing, a woman may experience painful, aching sensations that can be localized not only in the pelvic area, but also radiate to the lower back. To reduce pain, you can apply a cold heating pad to the lower abdomen.
Does a woman worry about discharge after curettage of the uterine cavity? Certainly. According to reviews from many patients, the discharge is profuse, with large bloody clots, as during normal menstruation. This phenomenon is considered normal when cleaning the uterus, and you should be prepared for it. Therefore, a woman needs to stock up on pads. Remember, using tampons during the postoperative period is strictly prohibited!
How long will a woman be bothered by discharge after curettage of the uterine cavity? Heavy bleeding is possible in the first days after the procedure. Then the strong discharge will smoothly turn into spotting. They can be released for another week, or even ten days after the procedure.
What to do if a woman does not have such discharge? Curettage of the uterine cavity is a kind of operation. It should be accompanied by bloody discharge. If they are not there, or they end very quickly, and the patient is worried about the high temperature, then such symptoms may indicate blood stagnation or an inflammatory process. In this case, you need to consult a doctor. Perhaps he will decide to stimulate the uterus by prescribing a course of oxytocin.
Is it possible to wash after scraping? Of course, but you can't take a bath. Hygienic procedures should be carried out twice a day and after each bowel movement.
Don't forget about rest! It's best to spend a day or two in bed. Avoid sitting in a sitting position to avoid putting pressure on the uterus.
The period when everything is behind, that is, the recovery period can be either the closest or the furthest. The closest one includes the following recommendations:
- avoid taking a hot bath;
- avoid tanning;
- sex life is also put under lock and key;
- taking certain medications.
The goal of this period is to restore normal reproductive function in a woman. Therefore, for a good result you will need:
- examination and exclusion of the cause of frozen pregnancy;
- taking hormonal contraceptives in order to restore the sensitivity of the uterine receptors for subsequent perception of the fertilized egg. The recovery period lasts up to half a year. Only after this time has passed can pregnancy be planned. If pregnancy suddenly occurs earlier, there is again a high probability of its termination.
So, curettage can be performed in such cases when it is necessary to terminate the pregnancy or it is necessary to clean it in case of an incomplete miscarriage.
Curettage is an outpatient medical procedure performed under intravenous anesthesia, during which the uterine mucosa is removed (scraped) using a special curette. The procedure is called therapeutic and diagnostic, since it removes disease-modified tissue (if any), which can be examined under a microscope and an accurate diagnosis made.
So far everything is clear, logical and obvious. However, there is another side to this manipulation. The procedure is performed with a sharp iron curette, with the help of which the mucous layer of the uterus is actually “torn off”, and inevitable injury to the uterus itself occurs. As a result, there is a risk of several serious complications: damage to the growth layer of the endometrium (impairing its growth in the future), the appearance of adhesions in the uterine cavity, and the development of inflammation.
In addition, this procedure contributes to the development of a disease such as adenomyosis (uterine endometriosis) - due to the violation of the boundary between the layers of the uterus, which contributes to the growth of the endometrium into the uterine muscle. As a result, curettage may lead to problems with conception or trigger the development of adenomyosis.
It is quite obvious that such a procedure must be done strictly according to indications and the benefit-risk ratio must be seriously assessed. But this is possible anywhere, but not here, and this is very sad.
After the operation, discharge appears, since curettage causes severe damage to the uterine mucosa.
Immediately after cleansing, spotting is observed, which is similar to menstruation. They can have different durations depending on the individual characteristics of the organism. Basically, bleeding is observed for 6 days, and then its intensity subsides, and a brown ichorous secretion appears. Gradually it becomes white, and then disappears completely.
The maximum duration of bleeding should not exceed 9 days. If they are observed after this period, it is necessary to urgently contact a gynecologist.
In some cases, pathological discharge may occur. The development of a disease in the vaginal area can be recognized by the appearance of the following symptoms:
- discharge continues for more than 10 days - this often happens against the background of hormonal imbalance;
- the secretion is accompanied by an unpleasant odor - this indicates an infection;
- all sorts of discharge suddenly stop - a phenomenon indicating that clots have formed in the uterus, preventing the flow of blood.
The development of pathology can also be indicated by severe pain and increased temperature after surgery. Normally, the temperature increases only on the first day after the procedure.
Temperature after endometrial polyp removal
After any surgical intervention, an elevated temperature persists for some time. This occurs as a result of intensive recovery processes occurring in the body. But the temperature should not exceed 37.2-37.3. If the temperature rises above these indicators, this may indicate the development of complications. Often this is how an infection manifests itself, the accession of which occurred against the background of a weakened immune system. There can be many other causes besides infection, so you need to see a doctor for diagnosis.
Why is separate curettage necessary?
This method is also actively used in gynecology for various types of bleeding. For example, emergency cleansing during heavy bleeding can help prevent severe blood loss. Another reason for prescribing this procedure may be infertility, but only if no obvious hormonal pathologies that provoke such a condition are detected.
According to reviews from women, most often the operation is performed a couple of days before the start of menstruation. This is necessary so that cleaning at least approximately coincides with the physiological rejection of the mucous membrane. However, there are exceptions. For example, for polyps, the procedure can be scheduled in the first two days after the end of the critical days. This is due to the fact that the neoplasm is well visualized against the background of a thin endometrium.
What can be said about when manipulation cannot be carried out? It's best not to cleanse mid-cycle. Why? The hormones that the ovaries secrete during this period will prevent the mucous membrane from growing again, which can cause heavy bleeding.
During menstruation, they also try not to cleanse. This is explained by the fact that during this period the mucous membrane dies and becomes uninformative as a biomaterial for further research.
Many women worry about curettage, and this is not surprising, because cleaning is a kind of mini-operation. However, you shouldn't worry too much. The procedure is common and uncomplicated.
All manipulations are carried out on a special table equipped with leg holders (like in a gynecological chair). What does a doctor do?
At the very beginning, using palpation, he examines the uterus, its position and size. Then he moves on to the internal inspection. To do this, the specialist treats the external genitalia with a solution of iodine and alcohol, after which he expands the vaginal walls using gynecological speculum. Then the cervix is fixed with special bullet forceps.
Then a metal probe with a rounded end is inserted inside, thanks to which the uterus is examined in more detail. In order to carry out curettage, it is necessary to expand the cervical canal. To do this, the gynecologist uses small metal cylinders called Hegar dilators. The passage must be enlarged so that surgical spoons (curettes) can be inserted.
After this, they begin cleaning. The curette is inserted very carefully, then it is pressed against the wall of the mucous membrane of the cervical canal and the epithelium is scraped out. This action must be performed several times until all the walls are completely cleaned. The resulting material is placed in a special container, pre-filled with a ten percent formaldehyde solution.
After this, the gynecologist proceeds to curettage of the uterus. It is necessary to clean the mucous membrane with careful but energetic movements, starting from the front wall. As cleaning progresses, smaller curettes are used until all mucous is removed. The biomaterial is also placed in a container with a formaldehyde solution.
Then comes the final stage - the vagina and cervix are treated with a special anesthetic. To stop bleeding, ice is placed on the woman's stomach. You can keep it cold for half an hour.
The patient is then transferred to a ward, where she recovers from anesthesia and rests for another six hours. Many women are interested in the question of how long the procedure takes and how long to stay in the hospital. Curettage of the uterine cavity cannot be called a complex operation, therefore, if it was successful and without complications, and if the patient feels satisfactory, then she is discharged on the same day that the procedure was performed. A woman’s sick leave can be closed the next day.
As you can see, this is a fairly simple operation - curettage of the uterine cavity. How long a woman will stay in the hospital depends on how well the manipulation went and how well the patient herself feels. According to reviews from many women, within a few hours after cleaning they were able to get home on their own.
Temperature after cleaning the uterus
The temperature after diagnostic or therapeutic curettage of the uterus rises for only one reason - the development of inflammation. The provoking factor may be the introduction of infection into the organ cavity during cleaning during medical procedures, the penetration of pathological microflora from the vagina, as well as the activation of the infectious process that took place before curettage of the uterus.
Normally, the next day after the procedure, the body temperature returns to normal. A temperature that rises to high or low-grade levels after curettage may indicate the development of the following infections:
Recovery
Basically, the duration of recovery after a frozen pregnancy is calculated taking into account the normalization of the menstrual cycle. It is also necessary to rehabilitate the body from the effects of general anesthesia. To speed up this process, you must adhere to a healthy lifestyle and follow all the recommendations of your doctor.
It is believed that you can plan your next pregnancy immediately after the menstrual cycle is restored. But it is advisable to create conditions for the body to fully recover.
In this case, oral contraception is prescribed for six months. After stopping the drug, the woman will again be able to bear and give birth to a healthy child.
Menstruation after a frozen pregnancy is restored in 30–40 days. But due to hormonal imbalance, this period may increase. You can also speed up the rehabilitation period and quickly restore the vaginal microflora by carefully observing personal hygiene and refusing physical activity. In addition, during the period of bleeding after curettage, it is necessary to exclude sexual activity.
Endometritis
Endometritis is the next reason why the temperature may rise after curettage of the uterine cavity. The inflammation that develops in this case covers the inner surface of the organ - the endometrial layer.
Endometritis that forms after cleansing the uterus can be caused by various factors. The cause of illness and fever can be:
Pathology with an increase in temperature can be caused by various pathogens, which are usually divided into specific and nonspecific. The first category of endometritis includes infectious inflammation of the uterine cavity initiated by STIs. With nonspecific formats, pathogenic microflora is not detected. The cause of endometritis can be bacterial vaginosis, vaginal dysbiosis, but an increase in body temperature occurs in any case.
Symptoms
The acute form of endometritis develops approximately on the third or fourth day after completion of curettage of the uterine cavity.
Its typical signs are: In addition to high temperature, the patient during a gynecological examination reveals typical signs of endometritis:
The acute form of the disease lasts approximately 10 days, during which elevated body temperature may persist. Then, in the absence of treatment, endometritis becomes chronic, and with low body resistance it can lead to inflammation of the entire uterus, peritonitis and sepsis.
Treatment
Since the acute form of endometritis, which develops after curettage (cleaning) of the uterus, is accompanied by an increase in body temperature, the woman will be recommended bed rest.
Drug therapy for acute forms of endometritis is carried out with drugs from the antibiotic category. The choice of drug depends on the sensitivity of the pathogen. This may be Amoxicillin, Clindamycin, Lycomycin. Gentamicin and other drugs.
When diagnosing a mixed microbial form, treatment is carried out with several drugs at once. In almost every case, in addition to antibiotics, Metronidazole is prescribed. Temperature - sometimes very high - is accompanied by intoxication of the body. To alleviate the condition, intravenous infusion of saline and protein solutions is indicated.
Treatment
Recovery after a frozen pregnancy also involves taking certain medications. They are prescribed exclusively by the attending physician. The list includes medications that relieve pain and antibiotics to reduce the likelihood of inflammation. To increase the muscle tone of the uterus and enhance its contractility, oxytocin is prescribed. Physiotherapy may also be prescribed to speed up the rehabilitation period.
Basically, the freezing of the development process occurs due to random genetic disorders in the fetus, so the risk of recurrence of a similar situation is low. But to confirm a woman’s ability to bear and give birth to a child after a frozen pregnancy and prescribed therapy, it is necessary to undergo an examination, including:
- Ultrasound;
- analysis for the presence of various infections;
- blood and urine tests.
But there is a risk of repeated death of the embryo in the mother’s womb. When a woman experiences a repeat miscarriage, the above list is expanded with the following points:
- hormonal balance study;
- conducting a spermogram of the partner;
- examination of the fetus for pathologies of histology and genetics;
- carrying out bacterioscopy;
- preparation of an immunogram, coagulogram;
- carrying out analysis for hidden infections.
Karyotyping of partners is also carried out. The listed studies will allow us to diagnose the causes of fetal development arrest and identify ways to eliminate them. With proper and timely treatment, a woman will be able to carry and give birth to a baby.
It is worth considering that such a complication as infertility occurs only in rare cases: when the operation is performed incorrectly, or the woman refuses to follow the doctor’s prescription.
With normal rehabilitation, pregnancy after cleaning can occur within 1 month. If a woman does not plan to become a mother in the near future, she should consult her doctor to select the optimal means of contraception.
Methods
Depending on the purpose, the uterus is cleaned in two different ways: curettage (scraping with a curette) and vacuum (using a special vacuum apparatus) cleaning.
The vacuum method is considered less traumatic and safer. Unfortunately, the obtained material cannot be studied in the laboratory, so this method is used for therapeutic purposes:
- Medical abortion can be performed according to indications (fetal pathology, frozen pregnancy, threat to the woman’s life, etc.) and at the request of the woman.
- Accumulation of blood in the uterine cavity (hematometra).
- Repeated or additional cleaning to remove residue from previous cleaning.
- After spontaneous termination of pregnancy (miscarriage).
- To remove remnants of the placenta and membranes after childbirth (sometimes the baby’s place in the uterus is retained).
- Endometriosis is an indication for cleaning the uterine cavity.
- In some cases, vacuum cleaning may be prescribed according to some individual criteria.
Curettage is often a diagnostic procedure, but can also be prescribed for the indications listed above. In addition, this procedure is prescribed in the following situations:
- For problems with conception, female infertility.
- Preparation for in vitro fertilization (IVF).
- Long and heavy periods.
- When neoplasms are detected for the purpose of establishing a diagnosis (benign or malignant, fibroids, polyps, etc.)
- Irregular menstrual cycle, scanty menstruation.
- If you suspect endometriosis, hyperplasia and other pathologies accompanied by changes in the endometrium.
- Adhesive process in the uterine cavity.
- Dysfunctional bleeding.
The range of indications is quite wide, but curettage is sometimes the only way to help a woman or establish an accurate diagnosis.
Do you need pain relief?
Since cleaning is a painful and quite lengthy procedure, it is carried out under local or general anesthesia.
Most often, as patients say, the second type of pain relief is used. The woman is given intravenous anesthesia (sodium iopental or Propofol is used for this). The anesthesia lasts only twenty to thirty minutes, during which the woman sleeps and does not feel anything. This type of anesthesia is also convenient for doctors, since it is easier for them to perform the operation when the patient is completely motionless.
Very rarely, local anesthesia can be used, when the tissues around the cervix and the organ itself are impregnated with a certain anesthetic. At the time of the operation, the woman is conscious and experiences discomfort.
Recommendations
To quickly restore the body, you must follow simple rules.
What not to do after cleaning the uterus:
- Have sex. Sexual relations (sexual contact) should be avoided for 4 weeks after cleansing.
- Drink alcoholic beverages while taking medications.
- Use tampons after cleaning the uterus.
- Take baths, visit baths, saunas.
- Carry out douching (exceptions only in case of medical prescriptions).
- Play sports and exercise, lift weights.
What you can do:
- Use pads that need to be changed every 4 hours. This minimizes the risk of developing inflammation after cleaning the uterus.
- Maintain personal hygiene. Since taking a bath is prohibited, you should use a shower. The water temperature may be quite high, but you should limit your time in the shower to 10-15 minutes. Do not wash the abdomen and genital area with very hot water.
- You can return to light physical activity approximately 2-3 weeks after cleansing. However, before this, it is necessary to consult with a specialist, since the recovery of the body depends on individual criteria.
- After the period of abstinence ends, use contraceptives (preferably condoms) for 4-6 months to protect against pregnancy. This measure is necessary for the complete restoration of the body.
- Go to the toilet at the first urge. Overfilling of the intestines and/or bladder can provoke kinking of the uterus, which will provoke a deterioration in the contraction of the organ.
- Maintain proper nutrition.
- After cleaning the uterus, it is recommended to sleep at least 8 hours a day. In cases where the work involves heavy physical activity, it makes sense to issue a sick leave for at least 3-4 days.
You can plan a pregnancy no earlier than 6 months after cleansing, although ovulation will occur in the next menstrual cycle. However, a pregnancy that occurs in the first months after curettage will be terminated with a 99% probability. You need to give the body time to recover and then pregnancy will not bring problems and complications.
What is required from the woman herself
Despite the fact that cleaning is a simple and common procedure, it is a mini-operation and requires the necessary preparation not only on the part of the gynecologist, but also on the part of the patient herself. What should a woman do to ensure that the manipulation goes well? Of course, your doctor will tell you in more detail about preparing for the procedure, but it would be useful to familiarize yourself with the information presented below.
According to reviews of many specialists, additional examinations should be carried out before performing the operation. For example, take the necessary blood tests (this includes a general analysis, biochemistry, analysis for HIV, hepatitis, coagulogram). A urine test and a bacteriological smear from the vagina will also be required.
A woman should also warn her doctor about what medications she takes on a regular basis and tell her about her concomitant chronic diseases.
Three days before the procedure, it is best for the patient to refuse sex, stop douching and use vaginal suppositories. It is recommended to perform the operation on an empty stomach (most often, doctors ask women not to drink or eat for twelve hours). Before the procedure, it is best to perform a cleansing enema and take a shower. It would be a good idea to remove hair around the labia.
Scraping (cleaning). I'm getting ready. Damn how scary.
Most women in their lives are faced with a situation where the gynecologist, after an examination, prescribes curettage. “cleaning”
among themselves Not all patients are told in an accessible form what this operation is, and this ignorance gives rise to unfounded worries.
- What is scraped out (a little anatomy)?
- Explanation of names
- Why is curettage performed?
- What preparation for curettage
- How does scraping happen?
- Complications of curettage
- What's next?
Possible pathologies
Manifestations of anomalies after the procedure can be identified by the following symptoms:
- the color of the discharge is not bloody, but rather, it may resemble meat slop;
- blood after curettage takes too long (more than 10 days) and there is a lot of it;
- the presence of a repulsive odor in the discharge, which signals an infection;
- stopping bleeding, which indicates the formation of blood clots in the uterus.
In addition to the indicative discharge that accompanies uterine infections in the fair sex, body temperature may increase, and pain in the lower abdomen is also likely.
A similar picture is observed with an abrupt cessation of uterine bleeding - hematometra, since blood clots formed in the organ can provoke inflammation in it. In such circumstances, an additional course of antibiotic treatment is suggested and curettage is duplicated.
Excessive duration of bleeding indicates an imbalance in the woman’s hormonal levels. Such women need regular monitoring by an endocrinologist and gynecologist. But, in addition, due to prolonged bleeding, anemia may develop. That is why during such a period a woman needs not only to take medications, but also a balanced diet. Particular emphasis should be placed on products that promote hematopoiesis:
- liver;
- buckwheat;
- grenades;
- all types of red meat.
Metroendometritis
Metroendometritis is a combined inflammation of the mucous and muscular layers of the uterus. After cleaning, pathology is formed relatively rarely. The cause of metroendometritis is the penetration of opportunistic microflora into the uterine cavity from the vagina or fallopian tubes, as well as pathogenic microorganisms and the patient’s failure to comply with the antibiotic regimen.
With metroendometritis, both the endometrium and myometrium are involved in the pathological process.
After infection penetrates into the uterine cavity, the endometrium is involved in the pathological process and only later, as a result of the penetration of infectious agents into the deeper layers, does the muscle layer (myometrium) become inflamed. In most cases, metroendometritis is formed precisely after curettage (cleaning), since it is during the procedure that severe damage to the endometrium occurs.
Symptoms
Metroendometritis occurs differently in all women, but certain symptoms still exist. It is worth including these.
- Pain in the projection of the uterus. In acute endometritis, pain is eliminated with the help of painkillers, but after the myometrium is involved in the pathological process, the pain becomes unbearable. They radiate to the lumbar region, groin or rectum.
- Serous-purulent discharge, which is determined during a gynecological examination.
- Vaginal discharge that looks like meat slop.
- Soreness of the uterus on palpation. An attempt to palpate the uterus is accompanied by severe pain.
Symptoms of acute metroendometritis can develop three to four days after completion of uterine cleansing.
In order to prevent inflammation, after cleaning the uterus, a woman must take medications from the category of antibiotics. An increase in temperature after curettage is an unfavorable symptom that requires qualified medical advice.
Inflammation of the uterus can lead to the spread of microorganisms to the ovaries and tubes, which can lead to the development of adhesions and infertility. Serious complications such as peritonitis and sepsis pose a danger to a woman’s life, therefore, if the temperature rises after curettage, it is necessary to urgently seek medical help.
Advantages
Over 58,000 patients per year
Doctors and Candidates of Sciences
Gynecological diseases are one of the most serious illnesses for women. The minimum of problems they can cause is discomfort and poor health. The maximum is the development of other serious diseases.
Gynecology is one of the main areas of the clinic. The department's doctors treat patients with various pathologies in accordance with modern medical standards.
Diagnostics
Modern diagnostic methods make it possible to accurately assess the degree of functional disorders and the nature of developing morphological changes. For this purpose, the clinic offers various diagnostic methods:
- endoscopic methods;
- hormonal examination;
- microbiological methods;
- genetic testing;
- immunological examination;
- breast imaging methods (mammography, ultrasound);
- microscopy of smears for flora;
- infectious screening;
- antibiotic sensitivity test;
- Papanicolaou smear (cytological);
- analysis for tumor markers;
- M.P.T., K.T.
The department performs more than 120 operations per month. Our specialists advise patients with various pathologies and diseases:
- intrauterine pathologies;
- abnormal development of the genital organs;
- premenstrual syndrome;
- polycystic ovary syndrome;
- pelvic organ prolapse;
- urinary disorders;
- menstrual irregularities;
- chronic pelvic diseases;
- reproductive dysfunction;
- benign and malignant tumors of the genitals, external genital endometriosis and adenomyosis;
- benign and malignant diseases of the uterus;
- emergency gynecological pathologies.
Operations of varying levels of complexity are performed by all possible types of access:
- laparotomy,
- vaginal,
- hysteroscopic,
- laparoscopic.
When to contact a gynecologist
- Are you experiencing pain, discomfort, or discharge?
- You need to choose contraception
- Are you planning a pregnancy or are already pregnant?
- You need to undergo preventive
- annual inspection
- Infertility
Recovery period
After curettage, until the integrity of the vessels is completely restored, the uterine cavity will bleed. It is considered normal if spotting after curettage lasts from 3 to 10 days. To relieve pressure in the uterus, during the first three to four days it is better for a woman to stay in bed, avoid physical activity, and not sit for a long time.
During this period, a woman should use only pads. The use of tampons is prohibited.
Discharge
For the first 5 days after the procedure, a woman may feel pain in the vagina and may be bothered by pain in the lower abdomen.
To relieve unpleasant symptoms in the first two days, a woman is recommended to apply an ice pack to her lower abdomen (for half an hour every two hours).
Discharge after curettage in the form of bloody clots should continue until the vessels damaged during the procedure are restored. Red clots normally turn brown after a few days, and by day 10 they turn yellow or whitish. The day of intervention is equal to the first day of the menstrual cycle, which means that normal menstruation should begin in 24-32 days.
In women after a frozen pregnancy or abortion, the onset of menstruation is delayed. If menstruation does not occur for more than 2 months, a woman should urgently consult a doctor.
Maintenance therapy
Relieving pain, preventing infection and possible complications is the task of the next, recovery stage.
During the recovery period, the doctor may prescribe the following drug therapy:
Metronidazole is most often prescribed as monotherapy, but in some cases it is used in combination with other antibiotics.
During the recovery period, decoctions of stinging nettle and oregano are prescribed to contract the uterus.
You should not drink salicylates after curettage.
If by the tenth day the discharge after curettage does not decrease, the number of clots increases, and the pain persists, this is a reason to urgently consult a doctor. The opposite condition, when the discharge after cleansing is very scanty, is also dangerous and indicates the onset of a complication.
General recommendations
After the curettage procedure, a woman should abstain from sexual intercourse, not take a bath, not swim in bodies of water, and not visit the pool or sauna.
What else you can't do:
After two weeks, the woman should visit her doctor. By this time, the results of the histological examination will be known. The doctor may prescribe a control ultrasound. Based on the collected data, repeat curettage may be prescribed.