- In the fight against leukoplakia, you need to reconsider your diet. It must include fish oil, butter, cottage cheese, egg yolks, and cheese. And also: offal, greens, pumpkin, carrots, black currants, rose hips, sea buckthorn.
Localization of leukoplakia on the laryngeal mucosa requires microlaryngosurgical surgery. Coagulation of the affected areas of the bladder mucosa is possible during cystoscopy. In the treatment of bladder leukoplakia, the introduction of ozonated oil or liquid, as well as ozone gas, into the bladder has been successfully used. However, in case of persistent disease, resection of the bladder is required.
Hyperkeratosis is a disease that occurs without pronounced symptoms and does not cause pain or discomfort in a woman. Symptoms appear most often in the clitoris and labia minora area.
Complications
Detection of horny leukoplakia during extended colposcopy is usually carried out against the background of stratified squamous epithelium, which is thinned unevenly. It is impossible to recognize the basis of leukoplakia with the naked eye. Colposcopic picture: a whitish-pinkish area with dark red dots; if you apply a 3% acetic acid solution,
clear boundaries and relief can be detected; the lesion is iodine-negative. There are both single and multiple foci of the base of leukoplakia, in the transformation zone and against the background of an unchanged cervix.
Reasons for the development of the pathological process
Leukoplakia is a reaction of the mucous membrane to irritants. The following factors lead to its appearance:
- neuroendocrine diseases (disorders of the endocrine glands: hypothyroidism, polycystic ovary syndrome, diabetes mellitus, obesity, etc.);
- chronic inflammatory processes of the internal and external genital organs (herpes, HPV);
- cervical dysplasia;
- damage to the external genitalia;
- neglect of personal hygiene rules;
- stress and psycho-emotional overload;
- decreased immunity;
- vitamin deficiency (especially vitamin A deficiency);
- insolation;
- bad habits.
Causes of leukoplakia
If a patient is diagnosed with leukoplakia, the specialist can offer several treatment options depending on the woman’s situation and the nature of the altered lesions. What treatment is used for cervical leukoplakia:
Psychiatrists suggest that this disease is psychosomatic. The formation of hyperkeratosis of the genital organs is caused by a number of mental and emotional disorders.
Birch tar can be used for indoor and outdoor use. You should start taking it from 1 drop and gradually increase it to 18. Before using this product, consult your doctor. Because birch tar can lead to gastrointestinal or liver disease.
located at the level of squamous epithelium,
In addition, the causes of this pathology are:
Soft leukoplakia . described under this name by B. M. Pashkov and E. F. Belyaeva, or white spongy nevus, is a nevoid benign disease of the oral mucosa, sometimes combined with damage to the mucous membrane of the genital organs. Soft leukoplakia is characterized by extensive lesions in which the mucous membrane becomes spongy and cloudy; after some time, it seems to loosen and become covered with many grayish-white scales, resulting in the impression of peeling. When scraped with a spatula, some of the grayish-white scales are removed without the formation of erosions; no inflammatory reaction occurs. Patients usually bite off the rejected areas of the epithelium. Unlike leukoplakia, the disease can begin in childhood, affects large areas of the mucous membrane, and its symptoms periodically change until the pathological changes temporarily disappear.
Each subsequent form of the disease develops against the background of the previous one and is one of the stages of the ongoing pathological process.
Description of the disease
Leukoplakia in women develops during menopause, i.e. when menstruation stopped. At this time, age-related involution occurs in the body - this is a natural aging process.
The level of sex hormones decreases, because the glands and tissues atrophy, the skin and mucous membranes become drier, elasticity is lost, and trauma increases.
Lately, doctors have noticed that this disease is “getting younger,” i.e. Women under 40 years of age present with pathological symptoms.
Leukoplakia of the labia is a chronic, relapsing process. The disease develops slowly, and at first the symptoms are not always noticeable to the woman.
Types of leukoplakia:
- flat - the lesion has clear boundaries, practically does not protrude above the surface, looks like a film that cannot be removed with a spatula. Color – white-gray. The surface of the formation is dry and rough;
- verrucous - white-yellow or gray plaques that rise above the mucosa. Or lumpy growths, similar to warts, up to 3 mm in height. This form can develop on flat leukoplakia;
- erosive - varied in severity and amount of erosion, developing in place of the two previous forms. Cracks often appear. This form of the disease brings pain and discomfort.
Photo of leukoplakia of the external genitalia in a woman
»Attention,
the development of leukoplakia can be stopped if treatment is prescribed or the effect of provoking factors is eliminated. In this case, the disease regresses. If the disease is left unattended, the forms of leukoplakia gradually replace each other, and the process develops into cancer.
Symptoms of the disease
Leukoplakia is initially asymptomatic. In the area of the clitoris or labia minora, small multiple white spots appear, similar to plaque.
Gradually, the spots become keratinized, their color changes to gray with a pearlescent tint. The lesion area increases (labia majora, vagina, etc.). The plaques merge with each other and become thicker.
The more the mucous membrane changes, the more difficult the disease progresses. All this leads to the appearance of pathological symptoms:
- unbearable itching in the external genital area, which increases at night and after urination;
- burning sensation;
- numbness and tingling of the vulva and clitoris;
- pain during intercourse.
Gradually, erosions and cracks appear, which become easily infected. When a bacterial infection accumulates, foci of inflammation form.
Symptoms of the disease change a woman’s life: insomnia, decreased performance, depression and irritability.
Leukoplakia of the oral cavity: photos, signs, treatment
The flat (simple) degree of leukoplakia is characterized by the appearance of flat, smooth white spots on the surface of the genitals without an inflammatory process, which are not washed off, and after they are removed they appear again. Flat hyperkeratosis may appear in limited areas, and subsequently, as a generalized process, the disease affects large surfaces of the genital organs.
Kraurosis is considered a protective reaction to damaging factors that appear in the proliferation of the epithelium. Hyperkeratosis develops simultaneously with chronic inflammation of the mucous membrane, with the development of immune neuroendocrine and metabolic disorders. The occurrence of this disease in a child is a very rare case.
Upon examination, you can detect a whitish, and in some cases cloudy, rounded formation, the appearance of which, as the process progresses, resembles mother-of-pearl, slightly protruding above the surface of the mucosa. The lesions can be single or multiple. In most cases, this form of the disease is discovered accidentally during a dental examination. This can lead to the development of mental and neurological disorders.
Cytological examination is mandatory in the diagnosis of leukoplakia. It allows you to identify cellular atypia characteristic of precancerous diseases. During a cytological examination of smears from the affected area of the mucosa, a large number of multilayered epithelial cells with signs of keratinization are detected. However, the smear usually does not contain cells from the underlying layers of the mucosa, where atypical cells may be located. Therefore, in case of leukoplakia, it is important to conduct a cytological examination not of a smear, but of a biopsy material.
To diagnose hyperkeratosis, the Schiller test is used. To do this, the genital areas are stained with Lugol's solution. Foci of the disease are not pigmented and become clearly visible.
Symptoms of hyperkeratosis are constant severe itching and burning. Symptoms intensify after urination, at night and during sexual intercourse. Numbness and tingling may occur. Often, kraurosis is detected only during examination by a doctor.
To relieve symptoms, patients are advised to comply with the following requirements:
For research there are a number of methods that need to be carried out:
Patients with hyperkeratosis are under dynamic supervision of a gynecologist or oncologist. They are prescribed colposcopic and cytological control with a repeat course of treatment.
Diagnosis of the disease
Colpo- and vulvoscopy
Pathological manifestations force the patient to consult a gynecologist. The doctor conducts an external examination and prescribes additional diagnostic methods:
- Colpo- and vulvoscopy – examination of the mucous membranes of the vagina and cervix under a microscope. This method allows us to exclude malignant neoplasms;
- Schiller test - staining the lesion with iodine solution; areas of leukoplakia are not painted over and are clearly visible;
- smear for microflora and oncocytology;
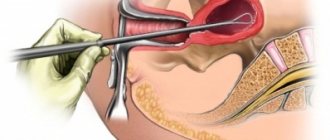
- biopsy - taking a sample of affected tissue and examining it under a microscope. The most accurate method for diagnosing leukoplakia.
Differential diagnosis is carried out with syphilis, condylomas, papillomas, vitiligo, neurodermatitis, genital itching, diabetes mellitus, etc.
Classification of leukoplakia
areas of keratinization have sharp outlines, often they overlap with foci of flat leukoplakia; lumpy surface. ?
1. External:
Diathermosurgical operations,
Despite their high efficiency, they have complications in the form of high bleeding during the procedure, bleeding during scab rejection, failure of reproductive function due to stenosis of the cervical canal, progression of cervical endometriosis and “coagulated cervix syndrome.”
Diagnosis of kraurosis is based on the patient’s complaints, the results of laboratory tests and gynecological examination. Due to the fact that similar signs also appear in dermatoses of various types (psoriasis, lichen planus, neurodermatitis, eczema), diabetes, syphilis, lupus, etc., it is necessary to carry out a differential diagnosis with these diseases.
To treat vulvar leukoplakia, the doctor prescribes anti-inflammatory antiseptics, creams, vaginal balls with hormones, and ointments. The following drugs are used for treatment: unconjugated estrogens, prednisolone, androgen. Vitamins, microelements, antihistamines are also prescribed, and in case of severe itching, novocaine blockades are performed.
Leukoplakia is a term that refers to a dystrophic change in the mucous membrane, accompanied by excessive keratinization of the surface layer of the epithelium. The disease occurs on the mucous membranes of the mouth, respiratory tract, larynx, vulva and cervix, bladder and anus. The main predisposing factors in the development of this pathology are the local irritant effect of negative factors on the oral mucosa, for example, smoking and alcohol. Vitamin deficiency, in particular vitamin A deficiency, trauma from metal crowns, the thermal effects of the cigarette itself, concomitant neurodystrophic diseases of the mucous membrane, and congenital hyperkeratosis can also be provoking factors. In the case of leukoplakia of the mucous membrane of the labia and cervix, dishormonal changes are of decisive importance. Under certain conditions, a lesion of leukoplakia can undergo malignant transformation.
Therefore, pathogenetic treatment begins with correction of the way of thinking.
All about squamous cell non-keratinizing cervical cancer can be found in this article.
Treatment of pathology
Treatment of the disease is complex. It includes medication, physical therapy, diet, and consultation with a psychotherapist upon request. The choice of technique is made based on the patient’s age, degree of damage and medical history.
- Hormonal ointments with hydrocortisone or prednisolone are applied to the affected areas twice a day for 1-2 weeks.
- Oral hormonal drugs: estrogen-progestogen (COC) or estrogens and androgens. Such medications are selected strictly individually. Some of them: Janine, Norkolut, Logest, Tri-Mercy.
- Antipruritic ointments are applied topically for no more than a week: Akriderm, Beloderm, Triderm.
- Antihistamines can also be taken orally: Suprastin, Claritin, Fenkarol.
- If all of the above does not relieve itching and burning, a novocaine blockade is prescribed (in a clinic or hospital setting).
- Ointments or suppositories with antibiotics and antiseptics relieve inflammation; they are prescribed if there is an accompanying pathological microflora: Baneocin, Polygynax, Elzhina, Pimafukort.
- On the recommendation of a psychotherapist, it is possible to use sedatives and tranquilizers to treat insomnia and irritability.
- Complex vitamins and microelements for 2-3 months.
Physiotherapy includes ultraphonophoresis with drugs, balneotherapy and oxygen therapy.
If all of the above treatment does not help, surgical treatment is resorted to. For isolated areas of leukoplakia the following is used:
- cryodestruction – destruction of lesions with liquid nitrogen;
- laser therapy - evaporating them using a laser;
- radio knife or scalpel - radical excision of the affected areas.
If the damage to the external genitalia is extensive, extirpation of the vulva is resorted to. This operation is performed using a regular scalpel and a radio knife.
General rules of conduct for women with leukoplakia:
- You need to wash yourself with warm water without soap, you can use decoctions of soothing herbs (chamomile, calendula);
- underwear should be made from natural fabrics;
- When sleeping, it is better to cover yourself with a light blanket;
- do not take hot baths;
- engage in physical therapy;
- take walks in the fresh air;
- During treatment, avoid saunas, swimming pools, etc.
The diet for leukoplakia includes lean meats and fish, dairy products, vegetables and cereals. It is necessary to completely exclude fried, salty, spicy, as well as alcohol. Drink enough fluid (at least 2 liters per day).
Patients with leukoplakia are seen not only by a gynecologist, but also by an oncologist. You definitely need to be examined by a doctor at least 2 times a year, take tests and cytology.
Forecast
The prognosis for the initial form of leukoplakia is considered favorable. This type of disease often undergoes regression. But with the verrucous and erosive form, everything is much more complicated.
They very often become malignant (lead to cancer). Therefore, it is very important to detect pathological symptoms as early as possible and begin treatment of the disease.
Leukoplakia is a rare disease in which chronic destructive processes occur in tissues. It is difficult to treat and over time leads to mucosal atrophy.
What is vulvar leukoplakia?
Leukoplakia is a degenerative process of the vulvar mucosa that occurs in a chronic form. With leukoplakia, tissue proliferation is pronounced, and excessive keratinization of the epithelium occurs, which will subsequently lead to structural changes and sclerosis
Leukoplakia is noticeable both visually and is detected after instrumental and laboratory tests. This condition is considered precancerous and often has a poor prognosis. Treatments that could restore tissue health have not yet been developed, so therapy is more supportive in nature (if surgical intervention is not used).
The stratified epithelium of the vulva can be affected for various reasons, but an exact relationship with any factor has not yet been discovered. Dystrophic changes over time lead to the formation of the stratum corneum and hyperkeratosis.
This disease primarily affects women who are entering menopause or are already experiencing hormonal changes. Leukoplakia is often observed simultaneously with kraurosis of the vulva - its atrophic changes. Dystrophic processes that occur in the organ several times increase the risk of developing cancer, so timely diagnosis is very important to maintain the patient’s health.
Stages of the disease
Changes in leukoplakia occur slowly. Without adequate treatment, the manifestations of the disease worsen and the prognosis worsens. Depending on the stage of the clinical picture, three forms of leukoplakia are distinguished:
- Flat. White plaques appear on the vulva, which can be removed with a cotton swab, but then they appear again. Apart from this, there are no visible changes in the affected area. The area of the lesion can vary - from a limited area to covering the entire vulva.
- Hypertrophic. The spots take on a gray-white hue. The tissues of the vulva become bulging in some places, and the inflamed lesions merge into a larger affected area. At this stage, it is impossible to remove stains from the surface of the mucosa.
- Warty. At this stage, leukoplakia is regarded as a precancerous condition. The spots turn into white warts and protrude noticeably above the surface. Due to the convex structure, the formations can be damaged, which leads to abrasions, cracks, increased inflammation or infection.
Establishing diagnosis
The examination begins with an examination on a gynecological chair. Leukoplakia of the vulva is detected when examined on the speculum, and a round white formation is visible on the vulvar mucosa. Depending on the form of leukoplakia, the formation may be covered with villi or ulcerated. When examined under a magnifying glass (colposcopy or vulvoscopy), you can more clearly see the surface of the formation and perform a Schiller test. The test is based on the absence of staining of the pathological area of the vulva when the vaginal mucosa is treated with Lugol's solution. Normal mucous membrane will turn brown during treatment, while the leukoplakia area will remain the same color.
A vaginal smear must be taken for flora, oncocytology, and bacteriological examination. In a general smear from the vagina and cervix, the number of leukocytes is assessed, pathogenic microorganisms are identified, which are visible under a microscope and do not require additional culture of the medium (Trichomonas, gonococcus, yeast).
Leukoplakia of the cervix is not cancer. A smear for oncocytology allows us to exclude a tumor process.
Leukoplakia of the vulva requires the exclusion of a malignant process in the vagina. Suspicious areas of leukoplakia are examined for the presence of atypical cells by biopsy and histological examination. Culture of the vaginal environment will help identify possible pathogens and determine their sensitivity to antibiotic therapy. Additionally, the doctor may prescribe PCR diagnostics for the herpes virus and cytomegalovirus. An ultrasound examination of the ovaries and uterus is performed to exclude other pathologies.
Blood tests usually do not reveal any changes. With inflammation, there may be slight leukocytosis and an increase in ESR. If the menstrual cycle is disrupted, it may be necessary to donate blood for female sex hormones, thyroid hormones, and have it undergo an ultrasound examination. If diabetes is suspected, blood is tested for sugar and glycated hemoglobin. A thorough medical history is taken to determine whether there have been any previous injuries or medications taken.
The first signs of vulvar leukoplakia
The pathology does not develop acutely, so in the initial stages the woman may not be bothered by anything. There are no characteristic first signs. Sometimes discomfort or burning may occur in the area of the clitoris and labia minora, since these places are the first to undergo dystrophic changes. Some patients note tingling and numbness in some areas of the vulva in the absence of external visible changes. After this, white spots begin to form, which indicate the height of the disease.
Symptoms of vulvar leukoplakia
Dystrophic changes begin with uncharacteristic symptoms (tingling, burning), which many women explain by other, incorrect reasons (synthetic underwear, thrush). After some time, white spots appear on the mucous membrane. They are easily removed from the surface of the vulva, which is why patients may confuse them with discharge or leucorrhoea due to candidiasis.
However, leukoplakia spots do not disappear over time, but, on the contrary, form chains or occupy a certain area of the vulva. From this moment on, the symptom should alert the patient and prompt him to urgently consult a doctor.
In the area where spots appear, changes occur in the tissues themselves, which is manifested by their keratinization and thickening. The white areas increase in size - they now protrude above the surface of the mucosa and can be felt with a finger. Some areas of the vulva are characterized by increased dryness and flaking.
Simultaneously with these visible manifestations, the patient experiences increased itching and discomfort, which gradually become permanent. Exacerbations usually occur at night, and may be accompanied by problems with urination and pain during sexual intercourse.
Itching also does not go away after hygiene procedures, use of feminine hygiene products, as well as after treatment if it was prescribed incorrectly at this stage. By scratching the skin and mucous membranes, a woman creates areas of erosion and wounds that become infected. The inflammatory and destructive process only worsens - the labia minora and majora swell greatly, the mucous membrane secretes less secretion, and the woman notices vaginal dryness.
At the last stage, raised warts appear. Inside them, a focus of inflammation is actively developing, and around there is a whitened zone of degenerated mucosal cells. The formations are constantly injured and heal very poorly. Due to associated infection, the cracks can fester and hurt. Constant itching, sleep disturbances, lack of intimacy and ongoing hormonal changes have a negative impact on the state of the nervous system. The patient notices general symptoms - irritability, increased emotionality, tension, apathy.
Symptoms and signs of the disease
Signs of vulvar leukoplakia also include whitish spots (foci of depigmentation) located asymmetrically. Such spots are usually located on the labia majora, on the mucous surface of the labia majora, on the clitoris, and then spread to the inguinal folds and perineum.
Leukoplakia of the vulva is also often accompanied by symptoms such as itching (usually occurring at night), a feeling of numbness, crawling, burning, tingling. Unpleasant sensations and pain during sexual intercourse often lead to the development of psychoneurotic disorders.
Leukoplakia of the vulva is often accompanied by itching, which gets worse at night.
Causes and prevention of vulvar leukoplakia
The exact relationship between any provoking factor and the development of leukoplakia has not been established. However, doctors attach great importance in this pathological process to general malfunctions in the body, in particular, in the endocrine and immune systems. Chronic inflammation, which can occur for various reasons, leads to poor tissue metabolism and, over time, to destructive changes.
The most likely causes of depletion of the vulvar mucosa and its subsequent degeneration may be:
- Hormonal changes that occur in a woman during menopause.
- Mechanical damage to the vaginal mucosa.
- Failure to comply with the rules of hygiene for the genitals.
- Endocrine disorders (diabetes mellitus, obesity, thyroid problems).
- Chronic inflammation in gynecology (papillomavirus or herpetic infection).
An important role in the development of such a disease is assigned to the psycho-emotional state of a woman. Chronic experiences and prolonged stress significantly affect well-being and also lead to changes in hormonal levels. Before leukoplakia is detected, the patient can contact doctors with complaints of ovarian diseases, menstrual irregularities, and increased irritability.
Thus, leukoplakia more often occurs as a response to the action of various provoking factors. Failures in the functioning of various organ systems, especially those that last for a long time, negatively affect metabolic processes. This leads to poor tissue trophism, lack of nutrients and destructive changes.
It is impossible to predict the development of leukoplakia. To avoid the disease, the patient needs to undergo regular examinations with a gynecologist, as well as take care of her general health. Doctors' recommendations for the prevention of leukoplakia:
- Maintain personal hygiene every day and avoid synthetic underwear.
- Have annual gynecological examinations.
- Try to minimize stress and worries. To do this, you can change your job, sign up for yoga, or take a course of sedative medications.
- Treat other diseases to the end so that they do not become chronic.
- Get rid of sudden hormonal changes. A proper regime that balances work and rest can help with this. In addition, endocrine correction is possible with the help of medications.
- Exercise daily. Even regular exercise will improve metabolic processes and blood circulation.
- To prevent metabolic disorders, it is necessary to maintain your weight within normal limits, as well as switch to a healthy diet that will provide the body with the necessary substances with minimal stress on the digestive tract.
In addition, general strengthening procedures can be included in recommendations for prevention and treatment:
- taking vitamin supplements;
- physiotherapy;
- drinking oxygen cocktails;
- hygiene procedures with herbal baths.
Leukoplakia and pregnancy
Sometimes vulvar pathology is detected only during pregnancy. Vaginal leukoplakia during pregnancy does not have a negative effect on the fetus, however, when a woman’s hormonal levels change, the risk of malignant degeneration of the pathological formation increases. That is why doctors recommend preparing for pregnancy in advance and undergoing the necessary examination.
Modern gynecology offers many ways to treat vulvar leukoplakia. Treatment begins with medicinal methods, and only in case of extensive damage, ineffectiveness of conservative therapy and the threat of cell degeneration into malignant ones, surgical methods are used.
Read
Also:
- Kraurosis of the vulva: what is it and how to treat. Why does it develop and what are the symptoms?
- What is cervical erosion
- Glandular hyperplasia of the endometrium - what is it?
- What is hysteroscopy of the uterus
- What is metroendometritis: causes, symptoms, treatment and prevention
- Removal of a cyst: a lump or lump inside the vagina
Diagnostics
Diagnosis of the vulva to identify leukoplakia includes the following measures:
- Examination by a gynecologist. The doctor listens to the patient’s complaints, studies the medical history and concomitant diseases. In addition, the doctor conducts a visual examination of the vulva and palpation, which may reveal raised areas of tissue and keratinized white spots.
- Colposcopy. The study is carried out with a special apparatus, which increases the area of study many times and makes it possible to photograph the resulting image. The method is used to clarify the nature of tumors and refute oncology.
- Smear. The resulting biomaterial is examined in laboratory conditions and the strain and amount of microflora are identified. Based on the results of the analysis, the doctor assesses the presence of pathogenic microorganisms.
- Schiller's test - a reagent is applied to areas of inflammation, after which the affected area does not stain and remains white.
- Biopsy - a small sample of the affected tissue is subjected to detailed examination, after which leukoplakia and the malignancy of the formations are accurately determined.
If, according to the results of the examination, atypical cells are detected in the patient, the condition is considered precancerous.
Treatment of vulvar leukoplakia
The disease develops slowly and is rarely detected in the initial stages. Treatment also involves a comprehensive approach over a long period of time.
To draw up the correct treatment regimen, the doctor collects a complete medical history, taking into account the patient’s age, her lifestyle, concomitant diseases and the stage of development of leukoplakia. The main therapy is carried out under the guidance of an oncologist and a gynecologist, but a psychotherapist, endocrinologist and other specialists can also participate.
Therapeutic measures recommended for leukoplakia:
- Drug treatment. The regimen includes local and systemic therapy. Drugs with antipruritic, anti-inflammatory, antiseptic, and regenerating effects are prescribed locally. To normalize hormonal levels, suppositories containing estrogen or a combination thereof are used. Hormonal drugs can also be taken systemically in 2-3 monthly courses. Antihistamines will help relieve itching and swelling; in severe cases, with severe discomfort, novocaine blockades are used.
- Dieting. Preference is given to dairy products and plant fiber, which vegetables are rich in. The main principles of a healthy diet remain - unfried food, lean meat, exclusion of smoked foods, dyes, and alcohol.
- Physiotherapy. They help enhance the effectiveness of the main treatment and have many positive effects. With the help of physiotherapy, it is possible to obtain anti-inflammatory, desensitizing effects, activate metabolic processes in the pathological area, strengthen the immune system, and saturate tissues with oxygen.
- Working with a psychotherapist. Hormonal changes in the body and the unpleasant symptoms experienced by a woman lead to a disturbance in the psycho-emotional state. Even if neurological disorders are not the main cause of leukoplakia, they require medical correction. In addition to communicating with a psychotherapist, it is necessary to undergo a course of treatment with sedatives.
- Physical exercise. It is recommended to do physical therapy, which strengthens the pelvic floor muscles and increases blood circulation in the genital area. Patients are advised to spend as much time as possible in the fresh air so that the tissues are enriched with oxygen.
- Hygiene procedures. They must be carried out daily at least once a day. It is recommended to avoid soap and all products that contain fragrances. It will be enough to wash with boiled water or herbal infusion. The use of douches and antiseptics disrupts the balance of microflora, reduces the protective properties of the mucous membrane and contributes to the progression of leukoplakia. You need to take care not only of the health of the mucous membrane, but also of the skin - patients should wear white underwear made from natural materials, avoid synthetic pads and tampons. Prolonged sunbathing and hot baths are considered harmful for leukoplakia.
When a comprehensive treatment regimen does not produce the desired results, the doctor suggests surgery. Keratosis lesions are surgically removed and then treated to prevent changes in adjacent areas.
Among precancerous dermatological diseases, leukoplakia occupies one of the leading places. The pathology belongs to the group of dyskeratosis. Its pathogenesis is based on cell proliferation followed by keratinization.
At first, the disease may occur without pronounced clinical symptoms. However, as it progresses, specific symptoms appear, which depend on the form and location of the pathological process.
Causes
The etiology of the disease is still unclear. However, it has been established that it occurs as a result of constant irritating effects of a number of external factors that provoke chronic inflammation of the mucous membrane. They can be:
- mechanical (injuries);
- chemical (alcohol, smoking, occupational hazards);
- temperature (consumption of hot drinks and food, excessive insolation).
The disease often begins to develop with concomitant neurodystrophic changes. They aggravate the situation and contribute to the progression of the pathology:
- diseases of the digestive system;
- immunodeficiencies;
- hormonal imbalances;
- vitamin deficiencies.
Hereditary predisposition to the disease plays an important role in etiology.
Forms of leukoplakia
There are several clinical forms of pathology.
- Flat (simple) shape. The mucous membrane is covered with a thin whitish film that cannot be scraped off or removed with a spatula.
- Verrucous (warty) form. It looks like smooth white plaques or bumpy growths that resemble small warts.
- Erosive leukoplakia. In most cases, it occurs against the background of the two previous types of pathology. Shallow wounds appear on the surface, causing quite painful sensations.
- Leukoplakia of smokers (Tappeiner's leukoplakia). The process of keratinization affects the area of mucous membrane covering the palate. The entire surface of the lesion on top of the plaque is dotted with nodules with reddish dots in the center.
A separate type is hairy (hairy) leukoplakia, which develops against the background of some immunodeficiency condition. It is caused by the Epstein-Barr virus. The affected area has the appearance of a whitish or gray coating that forms folds or plaques.
How do leukoplakia lesions appear?
The formation of foci occurs as follows. Due to constant traumatic irritation of the mucous membrane, an inflammatory process occurs. Gradually, keratinization begins in this area as a protective reaction. As a result, a zone of flat leukoplakia appears, which looks like a thin film.
If the traumatic factor is not eliminated, the pathology progresses. Against the background of flat leukoplakia, foci of the verrucous form of the disease arise. They thicken and grow, causing damage as a result of exposure to a traumatic factor to only worsen. Wounds and their complications appear - deeper cracks, characteristic of the erosive type of leukoplakia.
If the negative influence of provoking factors is not excluded at this stage, malignancy of the pathological process is subsequently possible - the appearance of atypical cells and malignant degeneration of leukoplakia foci.
Symptoms of the disease
In the context of adequate therapeutic measures, leukoplakia can be treated successfully. Leukoplakia itself is rarely fatal, but there is a risk of developing cancer. The warty and erosive forms are especially at risk. They can be regarded as precancerous conditions.
The appearance of cancer is noted only in cases where verrucous and erosive-ulcerative forms of leukoplakia take a long chronic course, during which persistent erosions appear, prone to bleeding and rapid increase in size.
Herpes, papilloma viruses, cytomegalovirus infection and others also provoke the occurrence of disorders in the epithelium.
Over time, against the background of flat leukoplakia, verrucous leukoplakia develops. In this case, the lesion becomes denser and rises slightly above the surface of the mucosa. A whitish, lumpy plaque with warty growths 2-3 mm high is formed. Against the background of foci of keratinization, erosions and painful cracks may occur, characteristic of the erosive form of leukoplakia.
It should be remembered that simple leukoplakia (i.e. without atypia) is a benign disease, but leukoplakia with atypia is a precancerous condition. Based on this, the doctor should draw up a treatment plan.
Leukoplakia
is called a lesion of the mucous membranes, in which keratinization of the integumentary epithelium develops to varying degrees.
Included in the group of precancerous diseases.
It is located on the mucous membrane of the corner of the mouth, the lower lip, the bottom of the cheek cavity and tongue (in these cases, as a rule, it is localized along the line of closure of the teeth), mouth, on the clitoris, vulva, in the cervix, in the vagina, in more rare cases - in the circumference of the anal opening, in the area of the head of the penis and the preputial sac.
Typically, the disease affects people around 30
years of age.
At the third stage of the disease, lesions grow. The warty form is complicated if the keratinization of the mucous membrane grows, erosions and painful cracks appear that heal poorly. These signs are also accompanied by the development of inflammation due to microbial infection, swelling and hyperemia. During sexual intercourse, painful sensations interfere with the woman.
For preventive purposes, it is recommended to carry out regular sanitation of the oral cavity and pay increased attention to personal hygiene.
The main danger of leukoplakia is the possibility of its malignant transformation. The period of time after which malignant degeneration begins is very individual and depends on the form of the disease. Leukoplakia can exist for decades without developing into a malignant neoplasm. The verrucous and ulcerative forms are most prone to developing into cancer, and the highest percentage of malignancy is observed with leukoplakia of the tongue.
Video: What is cervical leukoplakia
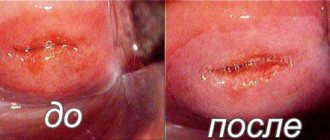
The appearance of leukoplakia is fairly typical, but if your doctor is unsure, he may recommend a biopsy. This allows you to examine the area of the changed mucosa under a microscope and confirm the diagnosis.
Main symptoms of the disease
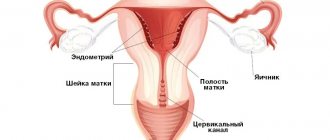
Leukoplakia of the cervix
Leukoplakia of the cervix photo
Leukoplakia of the cervix is characterized by the appearance of zones of proliferation of cells of the stratified epithelium of the exocervix with their subsequent keratinization. Visually, during colposcopy, whitish plaques are visible, which are slightly elevated compared to healthy areas of the mucosa. Sometimes they can be located inside the cervical canal. In a third of patients, the pathology undergoes malignant degeneration.
The main reason for the development of cervical leukoplakia is a hormonal imbalance and, in particular, a failure of the functional connection in the chain hypothalamus - pituitary gland - ovaries - uterus. This leads to a lack of progesterone and an excess of estrogens, and as a result – hyperplastic processes.
The disease often occurs after inflammatory processes or with menstrual irregularities. Traumatic factors (abortion and other aggressive interventions affecting the cervix) significantly increase the risk of developing pathology.
There are two forms of cervical disease - simple and proliferative. Simple leukoplakia affects only the superficial layer, proliferative leukoplakia spreads to all levels of epithelial tissue, causing increased cell division in them, resulting in the appearance of atypical elements.
The pathology occurs without a clear clinical picture. In most cases, it is discovered during a preventive examination by a gynecologist. Only sometimes a woman may be bothered by leucorrhoea with an unpleasant odor and spotting after sexual intercourse.
Treatment
The method of radically influencing the pathologically altered epithelium of the cervix (cryosurgical, laser vaporization, electrosurgical), like any other monotherapy, will not bring much effect. Complex treatment required
including: antibacterial (depending on the infectious pathology of the lower genital organs), hormonal, immunostimulating treatment, laser or cryodestruction of the lesion, correction of microbiocenosis.
Removal of affected areas of the mucosa can be carried out using a laser or radio wave method. by diathermocoagulation and electroexcision (excision with an electric knife). The use of cryodestruction is undesirable. since after exposure to liquid nitrogen, rough scars remain on the mucous membrane. In some cases, surgical excision of not only the mucous membrane, but also the area of the affected organ (urethra, vagina, bladder) is required, which entails reconstructive plastic surgery. Signs of malignant transformation of leukoplakia are an indication for radical surgery followed by x-ray therapy.
With leukoplakia of the cervix, virtually no symptoms are observed. As a rule, it is discovered accidentally during a gynecological examination.
Symptoms of uterine cancer can be found here.
When leukoplakia is localized in accessible places (oral cavity, glans penis, clitoris), the diagnosis usually does not cause difficulties. The final diagnosis is established on the basis of cytology and histological examination of the material obtained during a biopsy of the area of the altered mucous membrane.
The cause of all female diseases are parasites! Find out what Elena Malysheva recommends.” Read more >>>
Important!
Important! According to statistics, warty leukoplakia in 50% of cases becomes malignant and causes the development of cancer.