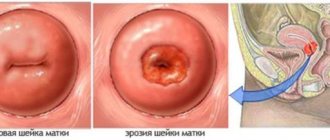
What is leukoplakia?
Leukoplakia of the cervix is considered a pathological change in the cervix, during which pathological thickening and keratinization of the integumentary epithelium lining the area of the cervix is noted. Externally, it manifests itself in the form of whitening of areas of epithelial tissue, which visually differ from the normal structure of the mucous layer.
Note! Leukoplakia is not considered a disease; this condition is used to visually describe the appearance of the mucous membrane. This pathological process may be the main sign of the presence of various gynecological diseases, which may require additional study and examination.
The danger of cervical leukoplakia is that it cannot be detected on its own. It can only be detected during a routine examination by a gynecologist.
What kind of disease is this?
When a woman is examined by a gynecologist and diagnosed with leukoplakia, she does not immediately understand what kind of illness it is. Translated from Greek, the word “leucos plax” means white plaque. During a gynecological examination, leukoplakia and cervical dysplasia are similar in symptoms to each other.
But if you compare these two diseases, you can find distinctive features. Dysplasia is considered a precancerous condition in which pathological changes are observed in the structure of the endometrium. And with leukoplakia, keratinization and thickening of the integumentary endometrium is observed. Moreover, these changes are benign in nature.
Note! Leukoplakia of the cervix is quite rare. According to scientific data, only 5% of women who have gynecological problems have it. It usually manifests itself in women of reproductive age, but it does not occur in girls and adolescents under 15 years of age and in women after 45 years of age.
In fact, cervical leukoplakia is not considered cancer. But if this process is started and not detected in time, then the resulting white plaques can degenerate and turn into oncology. But this only happens in cases where timely treatment was not carried out. In almost 30% of patients, the lesion degenerated into a malignant tumor. It is for this reason that it is important to carry out timely treatment.
Causes
Leukoplakia is not an independent disease, but an accompanying symptom, which may be the main sign that there are disorders in the female reproductive system. The development of leukoplakia can occur with erosive lesions of the cervix, with inflammatory and infectious pathologies of the uterus and cervix, and with various injuries.
Typically, leukoplakia occurs with a history of the following diseases:
- Ureplasmosis;
- Chlamydia;
- Endometriosis;
- Cystitis;
- Gonorrhea;
- Mycoplasmosis;
- Trichomoniasis;
- Vaginosis with a bacterial nature;
- Thrush;
- Pathological processes with an inflammatory and infectious nature - adnexitis, endometritis;
- Rarely, leukoplakia can be caused by conditions such as dysplasia and cervical cancer.
There are also other reasons that can cause the development of cervical leukoplakia:
- various mechanical injuries - abortions, curettage;
- this condition can cause erosive damage to the cervix and its improper treatment;
- the influence of hormonal imbalances that may occur during pregnancy or at the onset of menopause;
- regular menstrual irregularities;
- promiscuous sexual intercourse.
It is worth noting! Sometimes white spots on the epithelium can be observed in girls from birth. But there is no reason to worry, because these symptoms are only a congenital feature.
Cervical dysplasia, degrees and types of pathologies
- histological,
- cytological,
- clinical and morphological,
- colposcopic.
There are three main groups of cervical diseases: background, precancerous and cancer.
Background or benign processes
– conditions in which there are no changes in the cells, i.e., the so-called normoplasia of the epithelium is preserved. Cells reproduce, grow, and differentiate correctly. These diseases include: cervical ectopia, ectropion, polyp, endometriosis, leukoplakia, papilloma, cervicitis, true erosion.
Ectopia of the cervix or ectopia of the columnar epithelium.
This is a special diagnosis and requires special emphasis. The condition of ectopia is detected in approximately half of gynecological patients.
It represents a displacement of the boundaries of the epithelium, that is, the inner part of the cells seems to slide down. This is not a disease, but rather a violation of cellular boundaries. Usually the junction of the internal and external cells of the neck (transformation zone) is located in the inner part of the canal and is not visible.
But if the border shifts to the vaginal part of the cervix, then this is visualized during examination.
Congenital uncomplicated form of ectopia
is not included in the nomenclature of pathologies, is not a disease and is a physiological condition. Just a few years ago, any red spot on the neck was called “erosion” and was mercilessly healed.
That is why a huge number of Soviet and Russian women suffered from erosion, and this was the leading diagnosis! Today, the correct definition of displaced columnar epithelium is “ectopic columnar epithelium.”
Physiological ectopia of the cervix is a normal variant in young women under 25 years of age; in older women it requires regular examination, cytological and colposcopic monitoring. The risk of developing cancer against the background of ectopia occurs when combined with another pathology - inflammation, leukoplakia, flat condylomas.
The complicated form of ectopia is combined with inflammatory and precancerous processes and requires a careful approach to examination and treatment.
Ectropion
– eversion of the mucous membrane of the canal. It occurs after rupture and/or improper suturing of the cervix. This is a consequence of postpartum trauma or abortion. That is, acquired ectropion always has a traumatic origin; congenital is extremely rare and is usually combined with menstrual irregularities.
Cervical polyp
– growth of the mucous membrane of a round shape, with a smooth surface. When the polyp is located inside the cervical canal, there are no symptoms, but if it grows and protrudes from the cervical canal, it can manifest itself with bloody discharge outside menstruation and/or during sexual intercourse.
Cervical endometriosis
characterized by the appearance of foci of endometriosis on the cervix. Usually it is asymptomatic and is detected only upon examination in the form of red dots, the so-called “eyes”. Rarely manifests itself with bloody discharge or a feeling of discomfort.
Cervical endometriosis occurs after surgical interventions using sharp instruments - endometrial cells penetrate into the puncture or incision site and take root there, as with any extragenital endometriosis.
Cervical endometriosis, as a rule, does not pose any danger and requires routine monitoring and cytological examination.
Leukoplakia
– this is keratinization (thickening) of the surface layer of cells of the cervix. By the way, this is the oldest diagnosis and the name leukoplakia - “white plaque” - has not changed since 1887.
Leukoplakia does not manifest itself in any way and is detected only during examination; colposcopy and Pap test confirm the diagnosis.
If leukoplakia is simple, that is, it does not have any altered cells and is not combined with another pathology, it requires the usual screening examination method, and nothing more.
Cervical erosion.
We are talking about true erosion, that is, a defect in the mucosa with exposure of the underlying tissues (stroma). Synonym: cervical ulcer. A rather rare disease, detected in no more than 2% of women. True erosions are divided into trophic, traumatic, burn, cancer, syphilitic, tuberculosis.
Condylomas and papillomas - HPV (HPV)
– are called associated pathologies. They manifest themselves as epithelial growths, resulting from infection with the human papillomavirus.
Genital condylomas (papillomas) are individual transparent papillae, have folds, outgrowths and villi. Flat condyloma looks like an irregular contour, slightly rising above the mucosa.
These formations can be located both on the cervix and in the folds of the vagina, on the perineum and in the perianal area.
Processes are called precancerous
, in which changes occur in the structure and growth of cells with impaired differentiation. These processes include: CIN, leukoplakia with atypia, erythroplakia, adenomatosis. This is a group of pathological changes that occupy an intermediate position between normal cervical epithelium and cancer.
Attention! CIN – cervical intraepithelial neoplasia, synonym – cervical dysplasia.
According to the International Classification of Diseases, the following types of dysplasia are distinguished:
- CIN I – mild dysplasia
- CIN II – moderate
- CIN III - severe, as well as carcinoma in situ
The prevalence of dysplasia in the world is extremely high. This diagnosis has been made to millions of women around the world. CIN II is the most commonly reported, with approximately 10 million cases annually. But not every dysplasia turns into cancer and it is important to know about this! Screening, timely diagnosis and treatment significantly (!) reduce the likelihood of dysplasia turning into cancer.
Mild and moderate dysplasias are often combined with an inflammatory process. High-quality treatment of inflammation allows not only to prevent the transition of dysplasia to the next phase, but also to restore the normal structure of tissues and get rid of dysplasia itself.
It is important to pay attention to your well-being, regularly undergo gynecological smears for microflora and sexually transmitted infections, and timely detection of problems and treatment will keep the vaginal flora in a stable state and reduce the likelihood of dysplasia.
Cervical cancer never occurs “suddenly”; this disease must necessarily go through all stages of its development. And at every stage, correct diagnosis and treatment can interrupt the process of cancer development. This is why it is so important to treat the diagnosis carefully - cytology, colposcopy, and timely (!) biopsy can quickly detect precancerous processes.
Source: https://oxy-center.ru/uslugi/operativnoe-otdelenie/operativnaya-ginekologiya/biopsiya/eroziya-sheyki-matki/
Leukoplakia of the cervix psychosomatics
The psychosomatics of cervical leukoplakia in every woman may lie in internal factors of an emotional nature. This pathology can be caused by the following reasons:
- grievances against men, loved ones;
- stressful situations;
- constant fatigue;
- depression;
- bad attitude towards yourself, not love.
The main reason for the development of this disease is a strong resentment towards a man. This feeling can corrode a woman from the inside and cause serious problems with the organs of the reproductive system. Self-dislike can also have a strong influence.
Note! The only solution in these situations is to change your worldview. Working with beliefs and accepting your own body. You also need to let go of all grievances and forgive offenders.
Main differences
Both diseases do not have pronounced external symptoms, so the differences between them are not so obvious to patients. Often, gynecological abnormalities are detected only during a routine examination by a doctor. In rare cases, women complain of pain and slight discharge of ichor.
Leukoplakia differs from erosion in that it involves structural changes. Ectopia implies a violation of integrity and is often a background symptom rather than an independent disease. Against the background of erosion, the soft tissues of the vagina become inflamed, but against the background of leukoplakia - not.
Symptoms
Leukoplakia is usually not accompanied by symptoms. It can develop for a long time, but without showing itself in any way. For this reason, the patient does not complain and does not consult a doctor in a timely manner. Often, the detection of a pathological process occurs by chance. This is facilitated by various concomitant diseases, in which leukoplakia often develops.
In addition, the following general symptoms may sometimes appear with leukoplakia:
- There is abundant discharge and leucorrhoea, which is accompanied by an unpleasant odor;
- The occurrence of contact discharge with blood impurities;
- There may be a feeling of itching in the vagina;
- During sexual intercourse there may be severe pain;
- Cracks with blood may form on the surface of the skin and mucous membrane of the vagina.
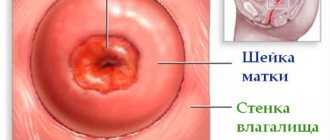
What is erosion?
Erosion (or ectopia) is understood as a defect in the mucous membrane of the lower segment of the cervix. Such changes often occur in young girls and women under 45 years of age. Ectopic epithelium looks like a reddened spot near the wound, localized on the surface of the uterus.
Erosion is often regarded as a normal physiologically variable condition of a woman. Multiple ulcerations with ectopia do not indicate a precancerous stage. But without treatment, the pathology can transform into dysplasia, which easily progresses to cancer.
Forms
Cervical leukoplakia usually occurs in several forms. There are three types of this pathological process:
- simple leukoplakia. During this form of pathological condition of the cervix, white spots appear that do not rise above the epithelial tissue. Usually this form is not accompanied by any unpleasant symptoms. For this reason, the disease only manifests itself during a gynecological examination, which may be performed for a completely different reason. However, if leukoplakia has just begun to develop, then the doctor may not notice it;
- erosive form. With this form, the doctor identifies white spots on the surface of the cervix. Around the white formations there are cracks and areas with erosive lesions;
- warty form. During this form, the affected areas on the surface of the epithelial tissue are clearly visible. They have a dense structure. In most cases, lesions are layered on top of each other. If treatment is not started in time, this form can quickly develop into an oncological process. For this reason, a biopsy is prescribed during it, which helps to identify atypical cells.
Cytological examination (PAP smear)
Particular importance in diagnosing pathological conditions of the cervix is given to the cytological method of research. First proposed by E. Pachet in 1847 and improved to the point of clinical application by S. Stockard and G.N. Papanicolaou in 1917, this method is currently represented by various modifications. Cytological diagnosis is a morphological research method based on a microscopic study of the nature of cellular changes in normal and pathological conditions.
A sample of the analysis result in the CIR laboratory (the conclusion is issued according to the Bethesda international system)
An oncocytological study is a study of scarified smears from the vaginal portion of the cervix and cervical canal. Diagnosis is based on dividing smears into 5 classes (Papanicolaou) or issuing a conclusion according to the international Bethesda system. Papanicolaou classification:
- Absence of atypical cells.
- Cells with signs of atypia are in small quantities.
- Cells with pronounced signs of atypia.
- Suspicion of a malignant process.
- Convincing signs of malignancy.
The main goal of a cytological study is to identify the morphological features of cells that characterize a specific process. There are up to 80 signs of an atypical cell, with about 10 of them being the most constant.
Diagnostic features
Diagnosis of leukoplakia often occurs by chance, usually during a routine examination or during an examination due to a completely different disease. This pathological process can be revealed during a visual examination - the doctor, using a special gynecological mirror, can notice small white spots with an oval shape on the surface of the cervix, and they may have clear boundaries or plaques that can rise above healthy areas of epithelial tissue.
After the first symptoms of leukoplakia are identified, the following diagnostic tests may be prescribed:
- Carrying out a cytological examination allows you to determine the number and level of accumulation of cells with a parakeratotic and hyperkeratotic structure;
- Performing colposcopy allows us to identify the extent and nature of the lesion. This procedure is performed using a colposcope. This instrument is similar to a microscope; it has the ability to magnify the affected area several times;
- sometimes colposcopy is combined with a Schiller test (a special test during which epithelial tissue is stained with a solution of Lugol's drug). When stained, healthy tissue usually turns dark brown, but tissue with lesions does not change color. This procedure is quite easy and is not accompanied by unpleasant sensations;
- biopsy. During this examination, examination of the superficial layers of epithelial tissue is performed. With the help of a biopsy, it is possible to identify the level of development of the pathological process, possible tissue degeneration, and the transition of the disease to a malignant form. This study must be performed in conjunction with histological and cytological examination. During the biopsy, local anesthesia and electrocoagulation systems are used.
It is imperative to differentiate the diagnosis for such pathological processes as erosive lesions of the cervix and dysplasia. But first it is worth considering the features of the course of these diseases:
- With erosive lesions of the cervix, concomitant symptoms may occur, namely bleeding, especially after sexual intercourse. Typically, this pathology develops when the cervix is exposed to chemicals, as well as as a result of mechanical damage;
- Dysplasia is similar to leukoplakia. This pathological process can also occur without signs; during it, pain or discomfort does not appear. Often these diseases can occur at the same time, for this reason they require prompt treatment. Dysplasia is dangerous because it can develop into a malignant tumor.
Important! In order to timely detect the presence of dysplasia, leukopenia, and erosive lesions of the cervix, a consultation and visual examination of several doctors is required, namely a gynecological oncologist, a gynecologist, and an endocrinologist.
Colposcopy
Colposcopic examination, first proposed in 1924 by H. Hinselmann, consists of examining the cervical mucosa using a binocular magnifier equipped with a lighting system and color filters. The improvement and development of devices and colposcopic technology has led to the emergence of many of its varieties:
- Simple colposcopy - examination of the vaginal part of the cervix using a colposcope;
- Extended colposcopy associated with the use of a 3% solution of acetic acid (when treated with it, spasm of the subepithelial vessels occurs and swelling of the mucosa, which promotes better visibility), as well as Lugol's solution (pathological areas, the epithelium of which is deprived of glycogen, do not turn brown, which allows you to determine the boundaries of the lesion).
Colposcopic images of the vaginal part of the cervix are very diverse. To understand the essence of the pathological process, they are divided into two large groups: benign (most often found in background processes) and atypical (characteristic of precancer and cancer).
Features of treatment
It is imperative to remember that leukoplakia is a dangerous pathological condition that is classified as a precancerous disease. For this reason, when it is identified, it is worth starting treatment immediately. But it is worth paying attention to the important features of therapeutic therapy:
- if a simple form of leukoplakia is detected, then in these cases conservative treatment therapy can be used. If this pathology is provoked by an infectious-inflammatory process, then antibacterial drugs with a wide spectrum of action can be used;
- often therapeutic therapy is carried out using cauterization and chemical coagulation using Solkovagin. This drug contains acids of organic and inorganic origin. The influence of acids causes the process of destruction of areas with lesions, but the components of the drug do not affect healthy tissue. This method is not accompanied by unpleasant sensations, but at the same time exhibits increased effectiveness;
- for complicated forms of leukoplakia (erosive and warty), radical treatment procedures can be used. For example, the conization procedure, during which tumors are removed, is highly effective. In the subsequent period, plastic surgery may be performed to restore the organ;
- Radio wave healing therapy is usually performed for patients who have not given birth.
Pay attention! Many specialists in the field of gynecology believe that for complicated forms of leukoplakia, which can be accompanied by dysplasia, erosion and other serious complications, the most effective treatment methods will be laser treatment and cryotherapy.
Features of laser treatment
Laser treatment for cervical leukoplakia is considered a modern method of therapeutic therapy, which is highly effective.
Laser treatment has a number of advantages:
- this surgical intervention is not accompanied by unpleasant sensations or discomfort;
- All antiseptic measures are observed during the procedure;
- promotes rapid coagulation of damaged tissues, prevents bleeding;
- After surgery using a laser, high protection is created through which bacteria and infections cannot penetrate.
Cryotherapy
During cryotherapy, the area of affected epithelial tissue is exposed to low temperatures. During this procedure, a process of tissue necrosis is observed. To achieve a positive effect, cauterization should last 5 minutes.
This method of treatment is not accompanied by pain or discomfort. Cryotherapy is highly effective, it is above 94%. But patients who experience menstrual irregularities may experience a relapse.
Treatment of cervical leukoplakia with Surgitron
For this therapeutic therapy, a special device “Surgitron” is used. Main features of radio wave treatment:
- during the operation, an electrode is inserted into the area of the cervical canal;
- at the tip of the electrode, electrical waves are converted into radio waves;
- further heating of cells with a pathological structure is observed;
- The fluid in the cells evaporates, and the destruction of the leukoplakia lesion occurs.
Excision of the cervix for leukoplakia
If a woman has serious damage to the cervix, and dysplasia or a precancerous condition is additionally detected, then she may be subject to serious surgical intervention, including complete excision of the cervix.
Features of the surgical operation:
- this procedure uses a scalpel;
- everything is carried out under general anesthesia;
- Additionally, modern hardware technologies can be used;
- surgical intervention is considered dangerous, after which serious complications may develop;
- long rehabilitation period.
Leukoplakia of the cervix section with a loop
A cauterization procedure is often used using a device with a wire loop at the tip. This method allows you to obtain a high-quality sample for subsequent histological examination with minimal trauma.
The main advantage of loop excision is that there is no scarring and the tissue heals quickly. But reviews from many patients indicate that after the operation there may be abdominal pain, as well as bloody-brown discharge, which can be observed for two weeks.
Cervical proliferation treatment
Proliferation is a pathological process during which an increase in the number of glandular structures is observed in the epithelial tissue of the cervix. This process is not considered an independent nosology, but only an isolated cytological sign, which may not always indicate the presence of a serious pathology.
It is worth noting! Epithelial tissue proliferation is not usually treated in isolation from the underlying disease. Therapeutic therapy can be the same as for ectopia, infectious inflammation, hormonal disorders, hyperplastic processes in the uterus.
When proliferation develops against the background of leukoplakia or pseudoerysia, the following treatment methods can be used:
- diathermocoagulation;
- cryodestruction;
- destruction of an area of epithelium with glandular proliferation with a laser;
- radio wave destruction.
In accessible language - what is the difference between cervical ectopia and cervical erosion?
It is widely known that the percentage of cancer diseases is growing every year. Cervical cancer is of particular relevance for women. Sometimes the rhythm of life does not allow you to undergo a routine examination with a gynecologist, as required, twice a year.
And finally, when she gets to him and hears the unfamiliar word “ectopia,” the woman gets scared, mistakenly assuming that this diagnosis will inevitably lead to cancer.
That is why, you need to figure out what it is, and how, in fact, erosion differs from ectopia of the cervix.
The vaginal part of the cervix is lined with stratified squamous epithelium. The diagnosis of ectopia, or, as it is otherwise called, pseudo-erosion, implies its replacement with a cylindrical one, which normally should line the inside of the cervix. There is no damage to the epithelium.
It looks like a scarlet spot, round in shape, located on the surface of the pale pink mucous membrane of the vaginal part of the cervix. As a rule, ectopia is an accidental finding; it does not cause any inconvenience to the woman.
In rare cases, it can make itself felt by bloody discharge or pain during sexual intercourse.
There are many theories about the occurrence of ectopia:
- increased levels of estrogen (most typical during puberty and the early reproductive period);
- pregnancy and the postpartum period, since during these periods there is a powerful change in hormonal levels;
- taking oral contraceptives;
- recurrent inflammatory diseases;
- mechanical injuries of the cervix
Pseudo-erosion mainly occurs in young women. In 11.5%, it is actually a congenital defect. If it is detected, a thorough differential diagnosis should be carried out:
- colposcopy is a method of examining the vagina and cervix, during which an image is displayed on the screen under high magnification;
- Schiller's test was performed - the mucous membrane of the uterine pharynx is stained with Lugol's solution.
Healthy areas acquire a dark brown color. The difference between the changed areas is that they are weakly stained; - biopsy;
- smears were taken for flora and oncocytology;
- A PCR test for HPV was performed.
This is done because visually, ectopia of the cervix is not much different from erosion. If the studies confirm that there is indeed ectopia on the cervix, in most cases, not treatment, but regular observation will be required. Pseudo-erosions of small sizes tend to disappear spontaneously with age or when hormonal levels normalize.
For the reasons that caused it:
- Congenital
- Traumatic
- Dishormonal
According to the dynamics of development:
- Healing
- Stationary
- Progressive
Erosion of the cervix, also called true, is a more serious condition that requires constant monitoring and treatment. The difference is that during erosion, damage to the stratified squamous epithelium is observed.
It happens that erosion is confused with cervical dysplasia. Although the symptoms of these pathologies are similar, their essence is different. Erosion occurs primarily due to injury to the mucous membrane of the cervical canal, and the cause of dysplasia is a disruption of the normal cellular structure of the tissue.
Reasons that can cause erosion:
- trauma to the cervix (complicated childbirth, abortion or diagnostic curettage, rough sexual intercourse);
- frequent douching with chemicals (for example, manganese solution);
- the use of certain traditional methods for treatment or when attempting to carry out criminal abortions;
- frequent inflammatory diseases of the genital area.
Chronic infections and HPV, early onset of sexual activity, frequent changes of sexual partners, a general decrease in the body's resistance, and burdened heredity can aggravate the course of erosion, contribute to the fact that the pathological process will spread and, possibly, transform into cervical cancer. With this disease, the patient often complains of spotting contact bleeding, pain during sexual intercourse, long and painful menstruation, weak, nagging pain in the lower abdomen, and rarely pain may occur after urination.
When examined in a mirror, the cervical canal has a defect in the form of a round bright scarlet spot. Upon contact with the instrument, the damaged epithelium may begin to bleed. Colposcopy and biopsy will help establish an accurate diagnosis.
Erosion is a background disease of the cervix. As with other similar processes (polyps, ectropion, leukoplakia), the successful outcome of the disease will depend on how quickly the correct diagnosis is established and treatment begins.
Treatment of true erosion
It should be noted that this disease is highly treatable, especially if it was caught at the very beginning.
Depending on the reasons that caused it, treatment can be different and is prescribed individually for each woman:
- Drug treatment includes the prescription of anti-inflammatory drugs, drugs aimed at speedy regeneration of damaged epithelium, and, if required, antibiotics.
- Surgical treatment is prescribed for large defects, in the absence of effect from medications, in case of individual intolerance to medications:
- diathermocoagulation or its variety - diathermoconization - the disadvantage of this procedure is that after treatment a scar forms on the cervix;
- cryotherapy is a modern, painless method of treatment, there is no scar after it;
- agonoplasma coagulation is a very effective method, but, according to some experts, it is not recommended for use in nulliparous women;
- the use of radio wave surgery – a scar does not form after treatment, but bleeding is possible for a month;
- chemical coagulation - used only for small defects, 3 to 5 or more procedures may be required, in some cases it may be ineffective.
Full recovery after erosion treatment usually takes up to 2 months. During this period, it is important to follow the following recommendations:
- do not engage in strength sports;
- do not lift heavy objects;
- hygiene procedures should be carried out in the shower;
- towards the end of the recovery period it is allowed to take a non-hot bath;
- sexual intercourse should be carried out only with a condom;
- do not use tampons.
To summarize, it must be emphasized once again that only a specialist with the appropriate qualifications and equipment can distinguish cervical ectopia from its erosion. It is strictly forbidden to engage in diagnosis and treatment on your own, as this can have the most dire consequences!
How to cure cervical leukoplakia with folk remedies
Leukoplakia of the cervix can be treated using traditional methods. But they should be used during the initial development of the pathological process, as well as in addition to the main treatment therapy.
The most effective folk remedies include:
- decoction of St. John's wort and calendula. St. John's wort quickly restores damage to the mucous membrane, and calendula eliminates the inflammatory process. When preparing, the herbs are mixed in equal quantities to make 3 tablespoons. Pour in 500 ml of hot water. Leave in a thermos for 20 minutes. Next, filter, cool and use for douching;
- a decoction of yarrow, chamomile, horsetail, knotweed, eucalyptus. Herbs should be taken in an amount of 25-300 grams and pour 500 ml of boiling water. Leave for 45 minutes and strain. Use the cooled broth for douching;
- At night, you can place a tampon in the vagina, which is pre-moistened in sea buckthorn, olive, unrefined sunflower, and eucalyptus oil.
Prevention
Reviews from many patients claim that following preventive measures will help protect yourself from the manifestation of leukoplakia. Prevention should be aimed at preventing inflammation, menstrual irregularities, and hormonal disorders.
The following recommendations must be followed:
- if cryotherapy and diathermocoagulation were performed, then in these cases the woman should regularly come to see her gynecologist, who, in turn, will perform a visual examination;
- If an erosive lesion of the cervix is detected, it is worth immediately starting to eliminate it. The same applies to inflammatory and infectious diseases that can affect the organs of the reproductive system;
- regular sex life;
- a complete diet containing natural and healthy foods.
By following all the important preventive advice and doctor’s instructions, the appearance of leukoplakia can be prevented. But if, nevertheless, it was not possible to avoid this pathological process, then it is better to immediately begin to eliminate it. It is imperative that you first conduct a full examination, which will help identify the cause and form of leukoplakia, and based on the data obtained, the doctor will be able to prescribe effective treatment therapy.
Video: I have leukoplakia. I do the installations myself!
Episode 13. I have leukoplakia! I do the instillations myself! There are changes in sensations!
Video: cervical leukoplakia associated with PVI
Cervical leukoplakia associated with PVI
Condylomas
Condylomas. They are benign formations that look like growths with a whitish tint. Most often they are a symptom of HPV infection.
Interpretation of colposcopic examination indicators
Colposcopic examination is an important stage of the diagnostic search in gynecological practice.
It is important to follow the doctor’s recommendations for preparing for the procedure and conduct additional examinations if required by the doctor’s conclusion obtained during colposcopy. This is important if colposcopy is unsatisfactory - there is no visualization of the boundaries of the epithelium, atrophic and inflammatory changes are observed.
Deciphering the colposcopy result and describing the examination picture are carried out only by a specialist, but it is necessary to understand the terminology in order to understand what certain data indicate and avoid erroneous interpretation.
After the examination, the gynecologist may prescribe additional diagnostic procedures.
Identified pathology of the cervix, regardless of its cause, requires immediate therapeutic measures to prevent complications. A poor colposcopy is a reason for additional diagnostic procedures and a course of therapy. This will ensure that the next study will show a good picture, and therapeutic and preventive measures will consolidate the results of correcting the condition.
The importance of conducting the examination is described in the video at the link:
Get tested at a discount in the online store
Despite certain advances achieved in the field of diagnosis and treatment, cervical cancer continues to occupy one of the leading positions in the structure of cancer incidence in the female genital area. The main and most promising direction in the fight against this disease is its prevention, which consists of timely detection and adequate treatment of background, precancerous processes, as well as initial forms of cervical cancer.
Background processes include erosion, pseudo-erosion of the cervix, leukoplakia, and precancerous (pre-oncological) processes include epithelial dysplasia of three degrees of severity.