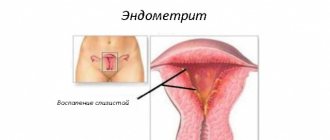
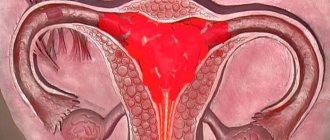
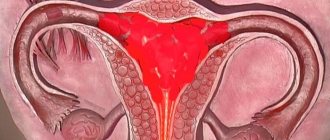
Indications for laparoscopic surgery
Laparoscopy is performed both for diagnostic purposes (during examination of organs) and for the treatment of detected inflammations. It is prescribed when it is impossible to determine the disease using ultrasound, computed tomography, magnetic resonance therapy, etc.
Indications for laparoscopy:
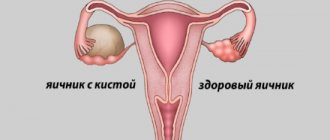
- Gynecology. Used to determine infertility, if a tumor is suspected in the uterus and its appendages. In emergency cases of damage to the internal genital organs of a woman; threat of tubal pregnancy; inflammation.
- Surgical diseases. Acute diseases in the abdominal cavity that have unclear symptoms (pancreatitis, appendicitis).
- Jaundice. To determine the type of disease (hepatic or subhepatic form). Investigation of the cause of disruption of the normal flow of bile.
- Complex or closed injuries to the abdomen, head and limbs. In particular, laparoscopy is performed on persons with alcohol and drug intoxication, coma and traumatic shock. The procedure is prescribed to eliminate the risk of internal bleeding, limb injury and peritonitis.
- Various wounds in the abdominal cavity, ascites with unclear symptoms. The degree of organ damage, the presence of bleeding and inflammatory processes are diagnosed.
- Peritonitis after surgery with vague clinical symptoms.
- Tumors. Clarifying the diagnosis, establishing the boundaries of the tumor, determining metastases to other organs.
Diagnostics using laparoscopy allows you to clarify the patient’s diagnosis.
Choice of anesthesia for laparoscopy
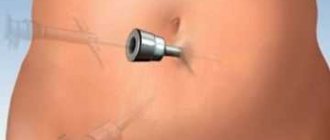
Laparoscopy is a modern method of surgical interventions in which access to the abdominal and pelvic organs is achieved through small punctures, excluding an incision in the abdominal wall, as is done with laparotomy.
Using a special trocar, punctures are made; their diameter does not exceed one centimeter. An optical device and manipulators are inserted into the resulting holes to allow the operation to be carried out.
This method can be used for diagnostic purposes, as it makes it possible to conduct a visual examination of the organs of the abdominal and pelvic region. And also for therapeutic purposes, because it makes it possible to remove detected pathologically altered areas.
Literally, “laparoscopy” means examination of organs located in the abdominal cavity. This range of surgical interventions is widely used in modern surgery and can be used:
- for removal of tumors of various natures of abdominal organs,
- for the treatment of nodular fibroids,
- during surgical interventions for ectopic pregnancy and restoration of patency of the fallopian tubes,
- for surgical removal of ovarian and uterine cysts,
- for surgical treatment of adhesive disease.
Advantages and disadvantages of the laparoscopic method
The choice of surgical intervention is often made in favor of laparoscopy due to the fact that:
- it makes it possible to shorten the postoperative period as much as possible,
- it allows you to perform a surgical intervention of the same volume, but with minimal trauma, which significantly reduces healing time and the intensity of postoperative pain,
- it makes it possible to obtain on the monitor a many times enlarged image of the internal organs in good quality, which helps to perform the operation more efficiently and accurately,
- eliminates the possibility of postoperative scars.
Despite all its advantages, the laparoscopic method of surgery also has its disadvantages. Among them:
- requires the surgeon to have a lot of experience and practice,
- eliminates the possibility of tactile contact with pathological tissues, which in the case of tumors can serve as a diagnostic tool.
Types of anesthesia used to perform laparoscopic operations
Its essence is to perform a puncture of the epidural space, with the introduction of a medicinal substance into it that blocks sensitivity in the lower parts of the body.
Recommended for use in patients with severe concomitant diseases of the cardiovascular and respiratory systems. Allows you to monitor the patient’s condition and quickly learn about the development of possible complications during surgery.
If the technique is followed correctly, this method of pain relief provides a minimum of complications.
May occur in case of short-term diagnostic interventions. For this purpose, a solution of lidocaine or novocaine is most often used, which is used to inject the insertion site of the instrument. When choosing this method of pain relief, the doctor must take into account the characteristics of the action of a particular drug, its consumption, and duration of action.
Achieved by injecting an anesthetic into the area located around a large nerve trunk. Due to this, the transmission of the nerve impulse signaling pain is blocked. A distinctive feature of this method is that the absence of pain sensitivity is achieved only in a specific area of the body, while maintaining consciousness.
Achieved by administering a drug or a mixture of drugs through intravenous injection. This type of general anesthesia can only be performed by an anesthesiologist. It is used in cases where a short-term surgical intervention or diagnostic procedure is expected.
It involves the introduction of a narcotic substance into the patient’s body through the respiratory system, through a special mask and tube. Intubation is performed after the patient, having received a small dose of anesthetic through a mask, falls asleep.
To ensure uninterrupted breathing, the patient is connected to a machine that provides artificial ventilation. The breathing apparatus has such a structure that it allows you to change the concentration of anesthetic in the respiratory mixture, controlling the depth of anesthesia.
When the surgical part of the intervention is completed, the anesthesiologist reduces the amount of anesthetic, and then begins to gradually remove it from the body, increasing the concentration of oxygen in the gas mixture.
Possible complications of anesthesia
- The presence of gas bubbles in the bloodstream and blockage of blood vessels by them (air embolism).
- Impaired patency (thrombosis) of the deep veins or pulmonary artery.
- The presence of air in one part of the pleural cavity (pneumothorax).
- Malfunctions of the cardiovascular system.
- Rejection of gastric contents into the esophagus.
- Violation of the integrity of the dura mater.
- Pain in the back and head varies in duration after surgery.
The choice of anesthesia method is the responsibility of the anesthesiologist.
The choice is made based on the purpose of surgery, age criteria and the general condition of the patient.
Under what anesthesia is laparoscopy performed and its types?
The doctor decides under what anesthesia the patient will undergo laparoscopy after analyzing the general condition of the patient, as well as the presence of concomitant pathologies. General anesthesia is used in most cases. Laparoscopy is rarely performed under local anesthesia, since this is an ineffective method that is used only as additional pain relief. The following types of anesthesia can be distinguished:
- Intubation endotracheal anesthesia. This type involves tracheal intubation and the introduction of medications into the patient’s respiratory system through a special mask with a tube.
- Inhalation. The patient inhales narcotic drugs that cause anesthesia in the form of vapor or gas.
- Intravenous. This type is used for short interventions, by administering the drug intravenously.
- Spinal. An anesthetic substance is injected into the subarachnoid space.
Local anesthesia is preferred for simple therapeutic or diagnostic procedures. Often during laparoscopy, the epidural (injection of an anesthetic into the spine) or conduction (injection of a drug into the area of the nerve trunk) method is used. Epidural anesthesia is used when it is necessary to perform laparoscopy on people with pathologies of the respiratory system, heart or blood vessels.
The period of rehabilitation of a patient after laparoscopic intervention depends on the age category of the patient, the area of surgical intervention, the presence of somatic diseases and general health. A person must definitely take into account what can be eaten after general anesthesia or other important nuances.
Anesthesia for laparoscopy - which one is used: local, general
Laparoscopy has become a widespread method in surgery and gynecology.
The operation involves the surgeon making small holes in the person's body instead of the traditional large incisions that leave noticeable scars. The idea that a doctor will cut the body is terrifying, but if laparoscopy is prescribed, anesthesia will “switch off” the person from consciousness or create the effect of complete anesthesia. The article describes in detail what anesthesia is used to perform laparoscopy, how local anesthesia differs from general anesthesia, and what types exist.
Remember! Anesthesia for laparoscopy is selected only by an anesthesiologist on an individual basis.
Features of anesthesia
Anesthesia for laparoscopy is selected taking into account the individual characteristics of the body. Before deciding which type will be used, the anesthesiologist studies the medical history and evaluates the patient’s body according to the following parameters:
- urgency of the operation;
- the severity of the upcoming intervention;
- indicators of analyzes and research;
- presence of chronic diseases;
- arterial pressure.
The most commonly used surgical interventions are performed under general anesthesia (artificial disconnection from consciousness, immersion in sleep). If the situation is quite mild, the surgeon may decide to use local anesthesia (operating with the patient awake).
Despite the fact that many patients are afraid of the intervention due to the fact that they will have to observe the progress of the operation, local anesthesia is safe for the body, since the risks of complications are reduced, the body recovers earlier, and patients go through the recovery period more easily. Don't worry, be afraid, or panic.
Types of general anesthesia
The main distinguishing feature of general anesthesia during laparoscopy is the disconnection of the person being operated on from consciousness, immersion in sleep due to the effect of medications on the central nervous system and brain. General anesthesia allows you to completely relax, immobilize the person being operated on, and protect him from observing the progress of the operation. The following types of anesthesia exist:
- Endotracheal (tracheal intubation). The patient is put on a mask with a tube through which medications enter the respiratory system. During the operation, the patient's lungs are artificially ventilated. The tube is inserted only after a small amount of medication has been administered, i.e. after the patient falls asleep.
- Inhalation. The patient inhales vapor or gas narcotic anesthetics. Nitrous oxide is almost always used. During laparoscopy, anesthesia of this type is undesirable; it is used much less frequently compared to intubation.
- Intravenous. The sleeping drug is injected into a vein with a syringe. This type of anesthesia is used for short-term operations.
- Spinal. The drugs are injected into the subarachnoid space. The method is used in emergency situations, during pregnancy, the administered drugs do not have a negative effect on the fetus.
Types of local anesthesia
A distinctive feature of the use of local anesthesia is that the operated patient observes what is happening without falling asleep.
The medications used act on nerve endings, immobilize specific areas of the patient’s body, thereby allowing him not to feel pain.
By anesthetizing and immobilizing, anesthetics cause the patient’s muscles to successfully relax, making it easier for the surgeon during the intervention.
Local anesthesia is used for simple operations or diagnostics. The following types of pain relief are most popular during laparoscopy:
- Epidural. An anesthetic is injected into the spine with a syringe to block sensation. This type of pain relief is used by people with weak respiratory and cardiovascular systems to monitor changes in condition, minimize the risks of complications, and also when there is a need to talk with the patient.
- Conductor. An anesthetic solution is injected into the area of the nerve trunk. Impulse transmission is blocked in a certain area.
For children, emotional people and those who are afraid to watch the progress of a surgical procedure, the operation is performed under general anesthesia.
Painkillers used
Among the anesthetics used for laparoscopy are drugs that enter the body through inhalation:
- Nitrous oxide;
- Isoflurane;
- Desflurane;
- Ftorotan;
- Halothane.
Drugs delivered without inhalation:
- Propofol;
- Ketamine;
- Calypsol;
- Relanium;
- Droperidol;
- Midazolam.
The choice of anesthetic is made by the anesthesiologist after studying the medical history, individual characteristics, and complexity of the operation.
Preparing for pain relief
In order for the patient to recover from laparoscopy without consequences, the following rules must be followed:
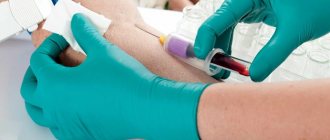
- A preliminary examination of the functioning of internal organs, especially the heart, is carried out, blood and urine tests are taken.
- Inform the doctor about the medications used, because some groups are incompatible with anesthetic (painkiller) medications.
- The body is cleansed using laxatives and enemas the day before surgery according to a scheme discussed with the doctor.
- On the eve of the operation, eating after 18 pm is excluded (exclude food 17-24 hours before the appointed date) and drinking water after 22 pm.
- You must follow a diet for the entire week before surgery.
- Laparoscopy is performed on an empty stomach; it is strictly forbidden to eat or drink drinks directly on the day of surgery.
As a rule, a patient who follows all the recommendations recovers from anesthesia painlessly, quickly and does not experience any unpleasant consequences.
Possible complications after anesthesia
The likelihood of complications is minimal, but possible if the recommendations are ignored. After anesthesia, the following unpleasant consequences may occur:
- disturbance of heart contractions;
- headache and back pain;
- ingestion of stomach contents (food remains) into the esophagus;
- accumulation of air in the pleural cavity;
- thrombosis of the pulmonary artery or deep veins;
- blockage of blood vessels;
- allergic reactions;
- damage to the central nervous system;
- accumulation of pus due to improper injection;
- vomiting, nausea;
- breathing disorder.
In conclusion, we can say that laparoscopy is an absolutely safe, easy operation, because anesthetics intended to put a patient under anesthesia have been repeatedly tested by specialists and patients and almost never cause any unpleasant consequences.
Source: https://oyaichnikah.ru/operatsii/narkoz-pri-laparoskopii.html
EXIT AND SLEEP AND MAIN POINTS OF REHABILITATION
Any anesthesia (local, mask, with or without intubation) requires careful monitoring by an anesthesiologist. Typically, the less invasive the laparoscopy, the easier the patient recovers from the state of anesthesia, and also the faster the recovery in the early postoperative period.
Time spent in hospital is 24 hours. The early postoperative period does not last longer than 3 days. For a month, the patient is recommended to avoid physical activity and stress, eat well, but not abuse heavy or unhealthy foods.
SOURCES: https://oyaichnikah.ru/operatsii/narkoz-pri-laparoskopii.html https://proskopiyu.ru/laparoskopiya/narkoz-pri-laparoskopii.html https://diagnozpro.ru/skopiya/laparoscopy/narkoz- pri-laparoskopii
Possible complications after surgery
Laparoscopy to eliminate adhesions and obstruction of the fallopian tubes is considered a low-traumatic operation. The risk of complications is minimized. But since this is a surgical intervention, there are still side effects after surgery:
- pain at puncture sites;
- discomfort in the abdomen and sternum due to the introduction of gas;
- vomiting and diarrhea as consequences of anesthesia;
- intestinal paresis - manifested by increased gas formation, bloating, constipation;
- general weakness;
- low-grade fever – up to 37.5°C;
- vaginal bleeding.
Pathological complications develop extremely rarely:
- internal bleeding if the surgeon damaged neighboring organs and tissues;
- suture divergence if the patient does not comply with the doctor’s instructions;
- the risk of inflammation that occurs during the development of an infectious process;
- repeated ectopic pregnancy;
- secondary formation of adhesions;
- heart attack or stroke;
- pneumonia;
- development of postoperative hydrosalpinx, endometriosis or pyosalpinx, when the infection has not been completely eliminated.
Also, after tubal surgery, blood clots often form in the veins of the legs. To prevent them, elastic leg bandaging is indicated before laparoscopy.
Preparing for surgery
Planned laparoscopy requires two-stage preparation. The patient will need to undergo tests and consult with specialized doctors. This could be a cardiologist, endocrinologist, nephrologist, etc. If they do not find any contraindications to surgery, the gynecologist gives the woman a referral to the hospital. If infectious or other diseases are detected, it is necessary to treat them and only then proceed to the second stage of preparation for surgery.
Preparation for tubal laparoscopy will include taking the necessary tests and undergoing several examinations.
Tests that will need to be taken before surgery:
- General and biochemical blood test.
- Blood donation for Rh factor and group determination.
- General urine analysis.
- Undergoing fluorography and ECG.
- Taking a vaginal smear.
If the need arises, the doctor prescribes additional examinations for the patient. It all depends on the characteristics of her health. There are tests that need to be taken immediately before surgery.
A few days before the upcoming intervention, the woman needs to start following a diet. It is necessary to avoid foods that increase the formation of gases in the intestines. Alcoholic drinks are absolutely prohibited. You will need to shave your pubic hair 24 hours before surgery. In the evening before the upcoming procedure, heavy food is excluded. Dishes should be light. On the day of laparoscopy, do not eat or drink. Most often, the procedure is prescribed in the morning, so the woman will not experience severe hunger. She is given an enema 2-3 hours before the operation. After this you need to wash.
While in the operating room, a woman should not wear jewelry. Remove dentures and contact lenses. If the patient is allergic to any drugs, then the doctor must be informed about this.
Contraindications to the use of analgesic components
Whatever the patient’s diagnosis, there are contraindications that do not allow the pain relief procedure to be carried out properly:
- Complex respiratory diseases (bronchitis, pneumonia, acute infectious processes and inflammatory reactions of the respiratory tract);
- Any acute infections and inflammations;
- Tissue hypotrophy;
- Ulcers on the dermal tissue;
- Serious damage to the nervous system;
- Psychiatric illnesses;
- Uncontrolled surges in blood pressure;
- Angina;
- Arrhythmia;
- Blockade (second and third).
Spinal anesthesia is not performed for the following pathologies or deviations from the norm:
- Allergic reactions to anesthesia components;
- Lesions of the skin in the place where the anesthetic injection should be given;
- Problems with blood clotting;
- Increased intracranial pressure.
There is only one contraindication for local anesthesia - intolerance to the drug, manifested by local allergic reactions. As you can see, there are many contraindications.
The attending physician will tell you in more detail what kind of anesthesia is used during laparoscopy in each specific case. It is extremely important to take a responsible approach to the process of preparing for the upcoming procedure.
Types of anesthesia
Anesthesia can be of the following types:
- General anesthesia is used most often. The patient is as relaxed as possible, in deep sleep. The body does not experience pain or discomfort. Total anesthesia is important when carrying out large-scale surgical interventions, where surgeons need a lot of time to carry out all manipulations, as well as complete immobilization of the patient;
- Epidural anesthesia is an anesthesia used for surgical interventions on the pelvic organs when there is a need to be in touch with the patient. The use of this type of pain relief is required by patients suffering from disorders of the nervous, respiratory or cardiac systems. Anesthesia acts directly on the lumbar region and lower extremities, without affecting other parts of the body;
- Local anesthesia is used for minimally invasive interventions. The doctor decides to administer this type of anesthesia if a small area needs to be numbed and the procedure itself takes little time. This option is used relatively rarely. Due to the fact that the patient is nervous, muscle spasms occur. Because of this physiological reaction, the surgeon is not always able to perform some therapeutic or diagnostic procedures well;
- Conduction anesthesia is done by blocking bundles of main nerve fibers with a solution of lidocaine (1%). It has the shortest impact and requires constant updating.
Special cases
Sometimes doctors decide to use multicomponent anesthesia, which is accompanied by artificial ventilation. This method is valued because of its ability to minimize blood loss during surgery.
Minimally invasive interventions are performed under controlled anesthesia. Another name is multi-anesthesia. The doctor selects a range of infusion and injection drugs, which are combined in a special way.
Basically, the most modern means are used, the right combination of which minimizes the risk of any complications. Patients feel much better after this anesthesia.
Contraindications
This procedure is considered one of the least traumatic. However, the operation has a number of contraindications, including:
- blood clotting disorder;
- severe cardiac diseases;
- bronchopulmonary pathologies;
- mental disorders;
- state of shock;
- diseases of an infectious nature, inflammation in the pelvis, exacerbation of any chronic diseases, high body temperature, bleeding - all these disorders are temporary contraindications for laparoscopy.
After eliminating the time constraints, the operation is carried out as planned. If a woman is diagnosed with a cancerous tumor in the pelvic area, she is indicated for open surgery. If the patient's life is in danger, emergency laparoscopy may be performed. Although in practice, in such situations, doctors resort to laparotomy.