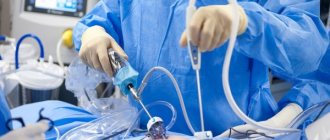
The technology of laparoscopic surgery in modern surgery of tumors on human tissues is positioned as one of the highest quality methods for eliminating tumors. This is the only type of operation that allows all abnormal formations to be cut out with the slightest damage to the body, and the patient to recover in the shortest possible time. In a short time, if certain conditions are met, menstruation returns after laparoscopy of an ovarian cyst.
About the method
Since the method of diagnosis and treatment involves minimal dissection of the skin, laparoscopy is commonly called a minimally invasive surgical method. Laparoscopy is often performed to diagnose uterine fibroids, tubal obstruction, endometriosis, as well as ectopic pregnancy and ovarian cysts. After this type of intervention, recovery is faster and more effective. The patient’s condition must be monitored by a doctor, since the procedure can provoke irregularities in the menstrual cycle and changes in hormonal balance.
It is especially important to monitor the restoration of the menstrual cycle and the general condition of the body’s reproductive system if the patient plans a successful pregnancy and the birth of a healthy child in the future.
Pregnancy and laparoscopic intervention
The innovative technique of manipulation allows laparoscopic interventions to be performed during pregnancy. Such procedures should only be done in specialized clinics under the supervision of professional doctors.
The operation can be performed at any period of pregnancy, but the second trimester is the most favorable. It must be taken into account that as a result of the intervention after laparoscopy, discharge will begin, similar to scanty menstruation. The use of a minimally invasive procedure minimizes the possibility of premature birth.
If surgery was performed to achieve pregnancy, the timing of probable conception varies depending on the initial disease. In case of manipulation of the fallopian tubes or polycystic disease, it is necessary to become pregnant as soon as possible. In other cases, pregnancy occurs in the first postoperative year.
Modern minimally invasive interventions not only contribute to high-quality diagnostics, but will always come to the rescue in difficult cases. Endoscopic intervention is an ideal solution to many gynecological problems. To avoid complications, it is necessary to choose professional doctors.
Source
Is it possible to do laparoscopy during menstruation?
It is almost impossible to answer unequivocally the question of whether laparoscopy is performed during menstruation. If for some specialists the possibility of successful surgical intervention is associated with increased immunity and the general activity of the body’s reproductive system, others are ready to argue their refusal with an insufficient level of hemoglobin in the blood and a decrease in blood clotting, which is dangerous due to possible additional bleeding during laparoscopic operations.
Among the possible serious complications after laparoscopy, it is worth highlighting the risk of developing varicose veins, the occurrence of disturbances in the functioning of the cardiovascular system, as well as the appearance of pathological bleeding. Thus, performing an operation during menstruation is possible only if it is urgently and immediately necessary.
The optimal period for surgical interventions using a laparoscope is days 5–7 of the cycle (approximately a week after the end of menstruation, so that the body has time to recover).
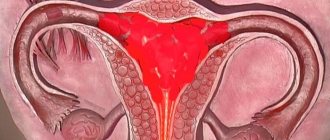
Menstruation after removal of formations
When tumors appear on the ovaries and female pathologies, laparoscopy is prescribed in most cases to reduce the risk of infertility or increase the chances of pregnancy. Thanks to this operation it is possible to treat:
- cystic formation;
- ovarian endometriosis;
- polycystic disease;
- adhesions and other pathological formations.
Treatment of endometriosis
Endometriosis is a disease that is diagnosed and treated by laparoscopy. After treating this pathology with this particular method, a feeling of pain and bleeding may appear, which women mistake for menstruation. If such symptoms are detected, the specialist will prescribe conservative treatment that will restore hormonal levels.
Treatment of other types of formations
Menstruation after surgery to remove an ovarian cyst or treatment of polycystic disease, with prescribed hormonal therapy, is restored and comes on time. If their appearance does not occur in the near future, the woman is recommended to conceive a child. This recommendation is used to prevent the formation of new cystic formations and to reduce the risk of relapse of adhesions.
The effect of laparoscopy on the menstrual cycle
The surgical intervention may precede characteristic changes in the patient’s body, which relate to a delay in the onset of menstruation with the onset of the next cycle. In addition to the timeliness of the start of a new cycle, the nature of the discharge itself, as well as the presence of characteristic painful sensations, is subject to mandatory observation. Studying all the details together allows the attending physician to prescribe the necessary further treatment. This also applies to symptomatic relief of the patient’s condition.
Rehabilitation period
After laparoscopy, it is important to follow all the surgeon’s recommendations. This will shorten the recovery period. For rapid rehabilitation, early activation of patients is necessary. The faster a woman begins to move, the less likely it is that adhesions will form.
During the rehabilitation period, you must adhere to a diet. It is advisable to avoid salty, spicy foods, alcohol, and reduce the consumption of fatty and fried foods. It is advisable to eat often, but in small portions.
In the first 2 weeks after laparoscopy, sexual contact should be completely avoided. This is necessary to reduce the risk of developing infectious and inflammatory diseases. In the first month after laparoscopy, it is necessary to use protection. It is better to start planning a pregnancy after your period ends.
Cycle changes after laparoscopy
Disturbances in the functioning of the reproductive system of the body, as a rule, appear if the surgical intervention involved the treatment or partial removal of organs, for example, uterine fibroids or endometriosis. At the same time, the problem of no menstruation after laparoscopy is temporary. If laparoscopy was performed, for example, to remove appendicitis, then it does not affect the menstrual cycle in any way. Any delay in the onset of discharge may be associated with stress or excessive anxiety. The menstrual cycle also depends on the individual reaction of the body to the anesthesia used. As a rule, the body needs about 2 – 3 weeks to fully recover.
Bloody discharge is typical for the first 2–3 days of the postoperative period. They are moderately abundant and are caused by disturbances in the integrity of the organs of the reproductive system, for example, the uterus, ovaries or fallopian tubes. After a few days, the discharge may turn yellow. The onset of the first postoperative menstruation with heavy discharge is not considered a pathology. A shift in the onset of menstruation by several days is also normal. Especially if the discharge is not accompanied by any painful sensations.
Menstrual cycle shift
The first day of the new menstrual cycle after laparoscopy is considered the day of the operation itself. In the absence of any complications, menstruation should pass without any special changes and with mucous discharge. Bleeding may begin immediately after surgery and last about 2 to 3 weeks. This is a normal reaction of the body and does not require any treatment. Normal full periods will occur in the next cycle.
The patient should be alerted to discharge that begins to acquire a brown or greenish tint with a very unpleasant odor. As a rule, this indicates an infectious infection or inflammation of the organs, but a more accurate diagnosis can only be made by the attending gynecologist.
Long delay
If your first period is delayed by more than three weeks, you should consult a doctor. The situation is not pathological if the existing disorders are associated with the body’s reaction to the stress suffered or are the result of the effects of anesthesia. A long delay in menstruation after laparoscopy is also considered normal if the operation was performed on the ovaries. An operation performed in the fallopian tubes may also be a precursor to the fact that menstruation does not come on time.
Serious reasons for delays can be the combination of surgery with a hormonal treatment procedure. If normal periods do not begin, but there is uncharacteristic discharge with painful sensations in the lower abdomen, it is important to immediately consult a doctor and undergo additional examination. Only a specialist can explain the absence of menstruation, how normal the situation is and why they do not start at a certain time.
Heavy periods
Extremely heavy menstruation after laparoscopy may be due to the fact that internal organs take much longer to heal and recover. The situation is considered normal even with an increase in the volume of bleeding in the second cycle. The reason to consult a doctor in such a situation is the manifestation of any painful sensations in the abdominal area, which may indicate an inflammatory process in the organs or their infection.
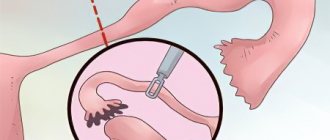
Principles of cyst excision during laparoscopy
It is worth saying that laparoscopy is performed after a complete examination of the patient’s body. The effectiveness and quality of the operation performed is directly influenced by the skill and professionalism of the doctor.
The main essence of laparoscopy is that this type of operation eliminates major tissue damage.
The operation is aimed at eliminating abnormal tissues and appendages as painlessly as possible without compromising the integrity of healthy organ tissues. The less damage and shock to the body during surgery, the faster the patient can return to a normal and healthy life. Due to the low invasiveness, the patient experiences only minor pain after laparoscopy of an ovarian cyst. IT IS IMPORTANT TO KNOW!
It is worth remembering that in some cases laparoscopy saves from a fatal outcome of the disease. This happens when the cyst is on the verge of rupture and can burst at any moment. Rupture of a cyst is dangerous due to infection of healthy organs and tissues and intoxication of the abdominal cavity. Surgical intervention in the event of a threat of rupture is carried out under the constant vigilant supervision of an ultrasound scanner and camera.
The slightest incorrect cuts and manipulations can damage the capsule tissue. In this case, discharge after laparoscopy may be caused by ovarian cysts, spreading of fluid into the area of the problematic ovary or genitourinary system. To prevent such consequences and pain after laparoscopy, ovarian cysts a month later, most problematic benign tumors are recommended to be cut out immediately after diagnosis.
Why does my stomach hurt after laparoscopy of an ovarian cyst? The pain is explained by a small, but still impact on organ tissue. As a rule, there is no need to worry about this. Soon the pain goes away.
Cycle recovery process
The result of a successful operation provides for complete normalization of the cycle within 2 to 3 months. Painful periods are a disorder if they were uncharacteristic before surgery. Often, pain during laparoscopy is considered normal if the intervention involved removing organ particles, making incisions, or taking tissue scrapings for further research.
Full restoration of the menstrual cycle after laparoscopy depends on the following important factors:
- presence of hormonal imbalances;
- physiological characteristics of the body (including those related to the patient’s age);
- quality of operational work performed;
- the general level of health of the patient before the operation begins.
If the doctor’s work is performed at the highest level, then a delay in menstruation is usually provoked by stress and the cycle is restored on its own.
Discharge after surgery
Immediately after laparoscopy, bloody vaginal discharge may begin, but this cannot be considered a full period. After the intervention and damage to the integrity of the tissues, residual blood and endometrial particles come out. Such bleeding is usually minor, lasts several days and is moderately heavy. As such discharge is completed, the shade may change from scarlet to yellowish, which is caused by increased activity of the glands of the genital organs (this is how they react to intervention).
During extensive operations, for example, those performed to remove an ovary, fibroids, or part of a pathologically overgrown endometrium (with endometriosis), bleeding may be delayed and last one or two weeks. But it should not be excessively abundant.
Vaginal bleeding that occurs after laparoscopy may be accompanied by aching or mild cramping pain in the lower abdominal cavity, mild weakness, and malaise.
Such symptoms are again caused by impaired tissue integrity, increased activity of the myometrium (the uterus strives to get rid of everything unnecessary due to contractions), as well as blood loss.