Chromohydrotubation is a study whose purpose is to check the fallopian tubes for patency. A contrast agent is used for this. It is introduced into the cavity of the pipes, after which its movement is observed. The procedure is performed during laparoscopic surgery.
You can perform chromohydrotubation during laparoscopy in Moscow at affordable prices at the infertility treatment center “Center for Gynecology and Reproductive Medicine”. The clinic has modern equipment that allows you to painlessly and effectively undergo all the necessary tests. The procedure is performed by highly qualified doctors. From our administrators you can get all the information about the cost of services.
Indications
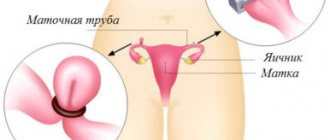
The fallopian tubes play an important role in conception. It is along them that the mature egg moves from the ovary to the uterus, and male gametes move towards the egg. The fusion of germ cells itself also occurs in the tube.
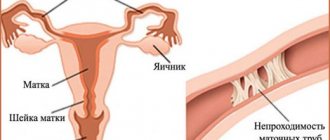
If the patency of the oviducts is disrupted, the woman has serious problems with conception. In especially severe cases, this becomes the cause of infertility.
Pipe obstruction can develop for various reasons. The most common among them are abortions and operations on the pelvic organs. Somewhat less frequently, obstruction occurs due to previous infectious diseases and endocrine disorders.
Indications for hydrotubation may include:
- fusion of the fallopian tubes (complete or partial);
- the need to clarify the patency of the tube after unilateral tubectomy;
- the presence of adhesions in the area of the appendages and infertility as a result;
- period of observation of the condition of the oviduct after surgery.
Stages of chromohydrotubation using laparoscopy
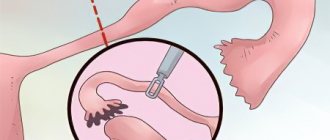
- Puncture of the abdominal cavity using a special needle. Next, a trocar and laparoscope are inserted into the hole.
- Laparoscopic chromohydrotubation is accompanied by dissection of the tunica albuginea of the ovary.
- Treatment of the external genitalia with a disinfectant solution.
- Insertion of a uterine cannula into the cervical area. A syringe is attached to its free end, through which the contrast agent is administered.
The patency of the fallopian tubes is assessed by the degree of penetration of the contrast agent into their cavity.
Preparation
Fallopian tube obstruction is not a pathology that requires emergency medical intervention, so the patient must be carefully prepared before the procedure.
Hydrotubation should be performed during the absence of menstrual bleeding. Ideally, the check should be carried out on days 7-24 of the cycle.
Hydrotubation is allowed if:
- A blood test does not indicate the presence of inflammatory processes in the body; the number of red blood cells and hemoglobin is normal.
- A urine test confirms the absence of inflammation.
- The gynecological smear meets the required level of purity. If during this study it is discovered that a woman has a violation of the microflora of the genital organs, then she will be prescribed appropriate treatment.
Usually, the gynecologist who prescribes this procedure tells about hydrotubation of the fallopian tubes, what it is and how to prepare for it.
Immediately before the start of the study, the woman must empty her bladder and bowels.
Hydrotubation is not a complicated procedure. It does not require hospitalization of the patient. All actions are performed in a hospital setting on a gynecological chair.
Scope of ART
Since the birth of the first American child using ART in 1981, the number of ART clinics and procedures has increased significantly. An estimated 456 ART clinics in the United States performed 157,635 ART cycles in 2012, resulting in 51,261 deliveries and 65,151 infants. In general, ART includes in vitro fertilization (IVF), gamete intrafallopian tube transfer (GIFT), and zygote intrafallopian tube transfer (ZIFT), with IVF accounting for approximately 99% of all ART procedures. However, ART does not include intrauterine insemination, which processes only sperm, or ovulation induction, which involves stimulating oocyte growth with oral or injectable drugs.
Contraindications
Like any other medical procedure, tubal hydrotubation also has some contraindications.
In this case, these can be listed:
- the presence of inflammation in the pelvis;
- autoimmune diseases of a generalized nature;
- damage to the internal or external reproductive organs by tumors;
- bleeding from the genital tract of unknown origin;
- suspicion of pregnancy;
- decompensated pathologies of the cardiovascular system.
Contraindications to fallopian tube laparoscopy
Identifying contraindications is an important step before undergoing tubal surgery. Absolute contraindications include:
- malignant tumors of the appendages and uterus, when surgery will only worsen the situation;
- severe pathologies of important internal organs: acute failure of the liver, kidneys, heart and lungs;
- hiatal hernia, which creates a risk when gas is injected during a laparoscopy procedure;
- poor blood clotting;
- coma or severe exhaustion of the patient.
Relative obstacles are:
- severe obesity;
- diabetes;
- menstrual period;
- high blood pressure;
- feeling unwell: flu, colds, etc.
It should be noted that in some situations doctors have to ignore even absolute contraindications, since sometimes surgery is the only way to save the patient’s life.
Progress of the procedure
Doctors use a special apparatus to ventilate the oviducts. It has a vessel designed for isotonic sodium chloride solution, as well as a uterine probe, which is connected to a control cuff.
To diagnose pathological conditions, an isotonic solution is poured into the oviducts, after which the specialist monitors the level of pressure in the uterine cavity, as well as the general well-being of the patient.
If the pipes are passable, the solution flows in easily. It does not spill out, and the recorder tape shows a decrease in pressure to a level of approximately 60 mm Hg.
If the pipes are partially obstructed, the pressure also decreases, but to about 110 mm Hg. Art.
In case of absolute obstruction of the oviducts, the pressure does not decrease. At a certain stage, the liquid stops pouring in and pours back out. In this case, the woman experiences pain. This becomes a good reason to stop the procedure.
If you wish, you can watch a video about how hydrotubation of the fallopian tubes occurs. This will give you a clear idea of the procedure.
Therapeutic hydrotubation
Hydrotubation can be carried out not only for diagnostic, but also for therapeutic purposes. To achieve a good result, the procedure must be performed about 5 times over several monthly cycles. In advanced cases, the number of procedures can be increased to 15.
During therapeutic hydrotubation, specially selected medications mixed with an isotonic solution of sodium chloride or Novocaine are injected into the fallopian tubes.
In most cases, the following medications are used for therapeutic hydrotubation:
- antibiotics (destroy pathogenic microorganisms);
- corticosteroids (eliminate the inflammatory process in the shortest possible time, relieve allergy symptoms);
- lidase (promotes the resorption of adhesions in the oviducts);
- proteolytic enzymes – (have an antimicrobial effect).
By carrying out therapeutic hydrotubation, it is possible to provoke the resorption of adhesions and improve the general condition of the pipes.
To obtain the maximum therapeutic effect, hydrotubation is recommended to be performed in combination with other procedures. For example, electrophoresis, gynecological massage, etc.
The result will largely depend on the regularity of the procedures, the general health of the patient, as well as the degree of neglect of the pathological process.
Quite often, therapeutic hydrotubation is performed after surgery to remove a cyst. In this case, the procedure is prescribed during the recovery period after laparoscopy. By introducing medicinal substances into the oviducts, it is possible to prevent the formation of adhesions.
The best result in this case can be achieved if you use chymotrypsin and combine hydrotubation with physiotherapeutic treatment.
Chromohydrotubation
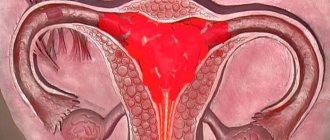
Chromohydrotubation is a diagnostic procedure. Its essence is that a colored liquid (contrast) is injected into the woman’s uterus. The oviducts are considered passable if the solution enters the pelvis through them.
Chromohydrotubation of the fallopian tubes, if necessary, can be combined with laparoscopy. This is the most modern and most informative diagnostic method at the moment.
Carrying out laparoscopic chromohydrotubation of the fallopian tubes at the Garvis Clinic
Chromotubation of the fallopian tubes is performed simultaneously with laparoscopic examination. Anesthesia is not used for this procedure—local anesthesia is sufficient. It is possible to perform chromohydrotubation both laparoscopically and vaginally. During the procedure, the contrast liquid that is injected into the uterus should be poured into the abdominal cavity. If this does not happen, the doctor concludes that the tube is obstructed. During a laparoscopic examination, the doctor can also assess the condition of the mucous membrane, the disruption of which is often the cause of many problems of the female reproductive system. This procedure is not traumatic for the patient, but it gives a clear picture of the situation, which will subsequently allow prescribing treatment, determining the cause of infertility, etc.
Laparoscopy for endometriosis
Endometriosis is a disease associated with the development of lesions that consist of endometrial tissue located outside the uterine cavity. In the area of endometriosis foci located in the pelvis, an inflammatory reaction occurs and an adhesive process is formed, which can lead to infertility. With the development of endometriosis, an endometrioid cyst forms in the ovaries, interfering with normal ovarian function. In case of severe symptoms - pain and large ovarian cysts - surgical intervention is required. Removal of foci of endometriosis and endometrioid cysts is carried out using laparoscopic surgery.
Laparoscopy for ovarian cysts and uterine fibroids
Ovarian cyst. A cyst is a benign formation that occurs in the ovary. The type of cyst depends on the type of cells from which it is formed. Follicular cysts and corpus luteum cysts appear when the follicle grows excessively, usually disappear on their own and do not require surgical treatment. Serous and mucinous (epithelial) tumors form from cells located in the upper layer of the ovary. An endometrioid cyst develops from a focus of endometriosis that affects the ovary. Dermoid cysts (teratomas) originate from the remains of embryonic tissue located in the ovary. All these formations can reach significant sizes, causing pain and disrupting ovarian function. When the cyst reaches a large size (more than 4–5 cm), it must be removed using laparoscopic surgery, during which the cyst is carefully separated from healthy ovarian tissue, preserving ovarian function.
Uterine fibroids. Fibroids are a benign tumor that arises in the muscle layer of the uterine wall. Myomatous nodes can be located deep in the muscular layer (intramural node), on the surface of the uterus (subserous node) and under the mucous membrane of the uterine cavity (submucosal node). If there are indications - pain, heavy bleeding and significant tumor size - surgical treatment is required. Using laparoscopic surgery, subserous and intramural fibroids can be carefully removed (myomectomy) without disturbing the structure and function of the uterus, which is very important during the reproductive period. Already 6 months after the operation, a woman can plan a pregnancy. Submucosal nodes are removed using another endoscopic procedure, hysteroscopic resection. At the end of the reproductive period, if there are multiple fibroids and indications for their removal, laparoscopic removal of the uterus along with fibroids (hysterectomy) is performed.
Laparoscopy for prolapse of the uterus and vagina
Prolapse of the uterus and vagina occurs as a result of weakening of the pelvic floor muscles and ligaments of the uterus, which maintain the normal position of the pelvic organs. With the help of laparoscopic surgery using a special synthetic material, the uterosacral ligaments are strengthened, returning the normal location of the pelvic organs and completely preserving their functions. In cases where prolapse is accompanied by urination problems, an additional procedure is performed to fix the urethra in the area of its sphincter through a minimally invasive sling operation.
Complications
It is important to be prepared for the fact that tubal hydrotubation can have the following consequences:
- A sharp increase in body temperature.
- Spasms of the oviducts (accompanied by pain).
- Pipe ruptures (this happens when an excessive amount of liquid is administered, which is extremely rare).
- Allergy to the drugs used. It can manifest itself in the form of cough, redness, as well as swelling of the genitals and skin, and breathing problems.
- Negative changes in the cervix.
- Exacerbation of inflammatory diseases in the pelvic organs (the symptom appears several days after the procedure and is accompanied by mild pain in the lower abdomen, weakness, and increased body temperature). To eliminate these symptoms, doctors may prescribe broad-spectrum antibiotics.
The most common complication among the above is pain. It may be accompanied by a decrease in heart rate, paleness of the skin and mucous membranes, and breathing problems.
The occurrence of sharp pain during the procedure indicates the presence of problems with the woman’s endometrium, the presence of adhesions or polyps. Reducing the pressure in the device and reducing the volume of fluid used will make it possible to prevent this complication.
Recovery period
The postoperative period after tubal surgery is usually easy, since trauma is minimal, the incisions are small and the risk of complications is also low. After the operation, the woman will be taken to the ward, where she will finally come to her senses after anesthesia. After a few hours you are allowed to get up.
Long-term hospitalization is not required; patients spend no more than 3-4 days in the clinic, and sometimes no more than a day. The entire recovery process usually takes a week, and the same amount of time must be spent with stitches. You should know that pain often persists for several hours after the intervention. In addition, there may be a slight increase in temperature and vaginal discharge mixed with blood.
External sutures take several weeks to heal completely, but it should be noted that internal incisions take longer, so it is important to limit physical activity and heavy lifting for 3-6 months after laparoscopy. In addition, sometimes there are problems with the intestines. Follow a diet and eat often, but in small portions. Intimacy is undesirable for the first month. Check with your doctor about when you can become pregnant.
Pregnancy
During the treatment period, the patient must refuse to conceive and use reliable methods of contraception. Pregnancy after hydrotubation can occur in the first month, but there is a high probability that it will be ectopic.
Typically, gynecologists in such cases recommend that patients use OCs for 2-3 cycles. You can start planning a pregnancy after completing the rehabilitation period. Conception in this case occurs in approximately 1/3 of women.
In many patients, after the procedure, libido is restored, the monthly cycle and the course of menstruation itself are normalized.
If, after completion of hydrotubation, a woman has regular sex life without using contraception and does not become pregnant within 1 year, then she is recommended to resort to IVF.
The essence of this procedure is that conception occurs outside the woman’s body, after which the resulting embryo is implanted in her uterus.
Garvis Medical Center
In our clinic, specialists use modern technologies, which makes the procedure safe and painless. Depending on the situation, after laparoscopic chromohydrotubation of the fallopian tubes has been performed, further treatment tactics are developed. The results of the study will determine the need for conservative (medicinal) treatment or surgical intervention. Our clinic’s specialists have many years of experience, which allows them to minimize possible risks, reduce your time and money, and, most importantly, restore a woman’s reproductive health.
MC “Surgical Clinic “Garvis””:
- 21 years of successful work;
- more than 30,000 operations performed;
- experienced and attentive staff;
- transparent pricing policy;
- We are recommended to loved ones!
To be happy with the happiness of others is the real happiness and the earthly ideal of life for anyone who devotes himself to medical science.
N.I. PIROGOV Chromotubation, what is it?
Advantages
The main advantages of hydrotubation include the following:
- The patient's body is not exposed to ionizing radiation. This allows a woman to begin planning a pregnancy (provided she is absolutely healthy) immediately after diagnosis.
- Hydrotubation does not have a damaging effect on the abdominal tissue.
- The study does not require the use of anesthesia.
- Combination of diagnostics and therapeutic effect.
- It has a low cost, so every woman who wants to conceive a child can afford it.
- The procedure does not take much time. After just a few hours, the woman can go home and start doing her business.
- Hydrotubation of the fallopian tubes has mostly positive reviews. Side effects after the procedure occur extremely rarely (no more than 5% of women).
- High information content and veracity of the research. The diagnostic accuracy is 90%.
The fallopian tubes are an organ that has bends.
Hydrotubation allows you to see their three-dimensional image. This is an important advantage of this procedure over ultrasound, which makes it possible to obtain only a two-dimensional image. Share:
Rehabilitation after chromohydrotubation
Laparoscopic testing of the patency of the fallopian tubes is a low-traumatic and painless procedure for the patient. After it is carried out, on the same day, the woman can go home - hospitalization is not required. However, recovery after the procedure will require compliance with a number of surgeon’s instructions. So, in the first period after the study: you should not lift heavy objects, you should avoid increasing intra-abdominal pressure, and also follow a sleep and diet regimen. Most prescriptions are drawn up individually, depending on the results of the study and the specifics of the procedure.