✓ Article checked by doctor
Nagging pain after ovulation in most cases is considered normal, which is explained by the physiological characteristics of the process and the woman’s menstrual cycle. This pain is reminiscent of the sensations before menstruation: a woman’s lower abdomen feels tight, and cramping pain may appear. If discomfort does not disappear within three days after ovulation or is accompanied by abnormal discharge, fever and other warning symptoms, you should go to the hospital. The cause may be gynecological diseases and pathologies of the genitourinary system, as well as the onset of a malignant process.
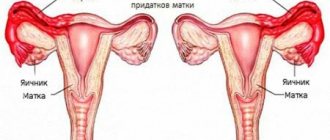
After ovulation, the stomach feels like before menstruation
Causes of pain
Ovulation is always preceded by the process of egg maturation. Each woman of fertile age normally matures 1 follicle every month. The explanation of the pain mechanism consists of several components. The mature egg becomes so large that it is crowded in the follicle and ruptures it.
It releases and releases the mature egg. All these processes occur under the influence of hormones. Every month this happens alternately on each side, which is why the pain appears from below, sometimes on the right, sometimes on the left.
This dominant follicle, i.e. differing from others in its size and rate of maturation, is also called a graph bubble. When ripe, it is clearly visible on ultrasound. Inside the follicle, the pressure of the fluid present here, in which the egg is located, increases, and tension occurs on its walls.
After such maximum tension, the follicle bursts - this happens instantly. When the egg breaks the walls of the follicle and finds itself outside of it, the follicular fluid flows out with it. It comes into contact with the peritoneum, the mucous membrane of the tubes and there is a response irritation of the peritoneum, spasm of the fallopian tube and its contraction in the form of pain in the lower abdomen.
Also, during exit, small vessels around can be damaged and ruptured, microdamage to tissues is observed, which also causes pain. Fluid from the follicle also reaches the endometrium, which does not leave the uterus motionless. This causes its contraction and is also expressed in the appearance of algia. The discharge at this stage may have scanty blood impurities due to partial rejection of the endometrium. In addition, the process of egg maturation leads to stretching of the ovary.
The egg begins its movement through the fallopian tube, which leads to its contraction, which also gives unpleasant sensations. And finally, impressionable girls can become anxious with the expectation of pain, and the pain actually appears. Thus, there are quite a lot of reasons that give rise to algia.
Possible reasons
Absence or skipping of ovulation affects menstruation. Missing two to three times a year is considered normal. From birth, a woman has a certain number of eggs. As reproductive function declines, the number decreases. My periods are coming, but sparingly.
If ovulation is absent during a woman’s fertile age, this indicates that the reproductive system is impaired. The consequence may be infertility or the inability to bear a child. If the release of the egg does not occur for two to three months in a row, you should consult a doctor. After conducting research, the gynecologist will identify the causes of ovulatory dysfunction.
Increased estrogen levels
A tightening of the lower abdomen in the middle of the cycle can be due to low estrogen levels. The activity of the uterus and the sensitivity of a woman directly depend on hormones. The maximum increase in estrogen is observed in women closer to 40 years of age. During this period, menstruation is accompanied by especially severe pain.
Changes in hormonal levels cause PMS and algodismenorrhea (lower back pain, sharp pain in the lower abdomen). Dizziness, nausea, and weakness begin. To alleviate the condition, it is recommended to take analgesics.
Elevated prostaglandin levels
The appearance of pain is the main sign of high levels of prostaglandins. Due to their increase, a hormonal imbalance occurs. Accompanied by pain in the back and lower back during menstruation.
The purpose of prostaglandins is to cause uterine contractions during childbirth. Enzymes are produced in the uterus. When the follicle matures, the pressure increases and it ruptures. Therefore, in the middle of the menstrual cycle, cramping pain occurs.
Gynecologists call the process ovulatory syndrome. Often accompanied by headache, rapid heartbeat, nausea, chills and vomiting.
The cause of the syndrome can be an infectious disease, which causes an inflammatory process in the ovary. Its walls become denser, and the release of the egg is difficult. In order for the egg to be released, a lot of pressure is required on the follicle. This is how vascular injury occurs.
Thyroid enlargement
The thyroid gland is responsible for the work and creation of hormones in the human body. When it increases, hormonal levels are disrupted. During menstruation, a woman experiences pain syndromes and insomnia.
An enlarged thyroid gland disrupts the functioning of the entire body. Pathological inflammatory processes occur in the uterus and vagina. Infectious and bacterial diseases, uterine fibroids, and endometriosis occur.
Use of intrauterine contraceptives
Intrauterine contraceptives can cause pain in the middle of the cycle. Painful sensations are caused by the presence of a foreign body. Also, the syndrome is sometimes triggered by the synthesis of prostaglandins.
If pain occurs frequently, it is better to abandon the intrauterine device. You need to see a doctor if:
- Throughout menstruation there are sharp nagging pains in the abdomen and lower back.
- The pain intensifies and does not go away for more than 2 days.
- The syndrome is accompanied by discomfort, itching, burning of the genitals. Urination is accompanied by sharp pain. Vaginal discharge has a pungent odor.
- Heavy bleeding occurred during menstruation (the pad fills completely within an hour).
- Increased temperature due to an inflammatory process.
When it comes to the norm
When aching pain appears in the lower abdomen during ovulation, this is considered a physiological norm, although it occurs only in every 4-5. The pain is short-lived, lasts in different ways, but no more than 48 hours and is not severe. There may be nagging or cramping pain in the lower abdomen on the right or left - on the side of follicle maturation.
They are so insignificant and inconspicuous that they are often not noticed; sometimes they can cause significant discomfort with loss of performance. But all this goes away without treatment. Sometimes it is possible that the follicle works several times on 1 side for several cycles.
In addition to these minor abdominal pains, there may be back pain, but there should be no other manifestations. In addition, discomfort in the abdomen is always accompanied by special discharge, which must be kept in mind. In general, ovulation, white discharge and pain in the lower abdomen coexist together. Before ovulation, the discharge is mucous, but it is thick enough to close the entrance to the cervix.
The onset of ovulation is also expressed in an increase in mucus; it becomes viscous, mucous, reminiscent of snot. After the egg is released, the mucus thins, this is necessary for easier passage of sperm through the vagina.
During ovulation, pinkish discharge may be observed for 1-2 days; often it is not noticed due to its insignificance. When the follicle directly bursts, brown spots in the discharge are possible, which will be the norm at this time. But if there is bleeding and pain in the lower abdomen for more than 3 days, we are talking about pathology.
The nature of the pain can be stabbing, sharp, dull; pulling, cramping (spasmodic pain), but not severe and the pain is always self-limiting. Also, lower back pain becomes a very common manifestation. If a woman is forced to take analgesics during ovulation, it would not hurt to consult a doctor.
Pathological causes of pain
Pain, cramps and a feeling of heaviness in the lower abdomen in women in the middle of the menstrual cycle can also have a pathological etiology. Such symptoms can primarily be caused by diseases of the female reproductive system. These include endometritis - inflammation of the mucous membrane of the intrauterine cavity, endometriosis - pathological growth of the endometrium, inflammation of the ovaries and fallopian tubes (adnexitis), rupture of the ovarian cyst, torsion of the cystic pedicle, intrauterine adhesions, fibroids and fibroids. In addition to painful sensations, they may be accompanied by brown discharge, sometimes with an unpleasant odor, and even bleeding.
Non-gynecological causes of hypogastric pain syndrome include:
- Sexually transmitted diseases such as chlamydia or gonorrhea.
- Acute or chronic cystitis is an inflammation of the bladder, characterized by frequent urination and a burning sensation in the ureter.
- Proctitis is an inflammatory process of the rectal mucosa.
- Hemorrhoids are inflammation of hemorrhoids located near the anus.
- Cracks in the anus - in this case, the pain worsens at the time of defecation.
- Intestinal obstruction - it can be caused by both a neoplasm in the abdominal cavity and the accumulation of feces caused by constipation.
- Inflammation of the kidneys - pyelonephritis. With this disease, the body temperature rises, pain appears when urinating, and the lower back ache.
- Renal colic - this pathology is characterized by an acute manifestation of abdominal pain syndrome, sometimes leading the patient to a state of shock.
- An attack of kidney stones or urolithiasis, along with pain, causes difficulty in the outflow of urine, which acquires a cloudy reddish tint.
- Appendicitis - the irradiation of pain depends on the location of the vermiform appendix of the cecum, which does not have a clear localization in the abdominal cavity. The appendix can be located either near the stomach or reach the pelvic area, then its inflammation causes pain in the lower abdomen.
If alarming symptoms occur, you should consult a doctor or call an ambulance as soon as possible. Rupture of an ovarian cyst, an attack of appendicitis, kidney stones or urolithiasis, as well as intestinal obstruction require emergency hospitalization for surgical intervention.
Why unpleasant sensations do not always occur
If pain in the lower back and lower abdomen does not appear at the appropriate time, it means that there was no mature follicle and no release of the egg. This is often noted before menopause; for stress, strict diets and illnesses in young women.
Representatives of public and creative professions, such as show business, cinema, etc., are more susceptible to this. These representatives of the elite very often go on diets.
The released egg travels through the fallopian tubes towards the uterus; On the way she may encounter a sperm, then conception occurs. In place of the follicle, a corpus luteum begins to form in it.
I am pregnant?
Keep in mind that sometimes aching pain in the back and lower abdomen can be symptoms of pregnancy.
If there is a possibility of conception, act as if you are pregnant before your period begins. Do not take medications that are contraindicated in the first trimester. Avoid stress, alcohol, get more rest. Start taking folic acid (even if you find out that the “alarm” is false, this vitamin will not hurt). On the first day of your missed period, you can take a pregnancy test.
Types of ovulation
It can be premature, timely and late. With premature ovulation, the egg is released much earlier, long before its due date. This cannot be excluded as a result of rough sexual intercourse, nervous tension, diets and increased physical activity. Pain then occurs in the form of spasms. Late ovulation is associated with hormonal imbalances. In these cases, to find out the cause, you need to undergo an ultrasound.
Ovulation dates for different cycles:
- if the cycle lasts 22 days, the ovulation period is 6-10 days;
- with a 24-day cycle – days 8-12;
- 26 days ovulation on days 10-14;
- 28-day cycle – ovulation on days 12-16;
- 30 days – ovulation period 14-18;
- 36 days – on day 20-24.
Additionally, there are ovulation tests that can be purchased over the counter that are similar to pregnancy tests. This is important for women who want to “catch” ovulation to conceive. There are 10 tests in one package and detailed instructions are attached to them.
Symptoms of ovulation
Women accustomed to the appearance of ovulatory pain describe the moment of ovulation as: sudden and short colic for 5 minutes, which goes away on its own; the pain resembles premenstrual cramps, but is weaker; nagging and aching pain, one-sided, in the lower abdomen. They are also accompanied at this time by increased discharge, reminiscent of snot or egg white. Since the entire process of maturation occurs entirely under the influence of hormones, their target organs are also the uterus and breasts.
Therefore, pain and discomfort may also occur here. They may be accompanied by increased libido, nausea and mood instability. There is increased sensitivity of the mammary gland and aching in the chest.
Bloating – can it occur during ovulation? This is a fairly common symptom. Bloating, accompanied by mild colic, also depends on hormonal effects and fluctuations in estrogen and is accompanied by increased intestinal motility.
This especially depends on eating disorders. When the abdomen is bloated, the lumbar region may also hurt.
Moderate or mild pain may be observed on the ovaries - this is normal during the ovulation process. Also during this period, gastralgia and stomach problems are possible; Algias can be localized in the lower back, anus, or side.
Help with pain
If pain in the abdominal area is severe during ovulation, it is not forbidden to take an over-the-counter analgesic or antispasmodic - No-shpu. Analgesics you can take are Ibuprofen, Naproxen, Paracetamol, and Aspirin. There is no need to be afraid of them, since the intake will not exceed 2 days. True, it is better to take them with the permission of a doctor.
Also, a woman should lie down, relax, drink more fluids, herbal infusions - yarrow, calendula, lemon balm, chamomile. All of them relax the smooth muscle fibers of the organs and relieve pain and spasms.
To make sure there is no infectious process, you can measure your temperature several times throughout the day. Some gynecologists prescribe OK to the patient for such regular pain.
A dull aching pain, if the pain is associated only with ovulation, can be easily relieved with a warm heating pad. It can be applied to the stomach or lower back. You can apply it several times a day, for 15 minutes, but it should not be very hot. The heat will relax tense muscles and relieve pain.
Diagnosis and treatment methods
If the pain in the lower abdomen is severe, then it is better to consult a gynecologist , who will determine whether these sensations are really related to ovulation. A visual examination of the patient is carried out and sometimes additional tests are required.
If the diagnosis is confirmed, the doctor may prescribe oral contraceptives that suppress ovulation and the woman tolerates this period more easily.
If there is any suspicion of a disease, an ultrasound of the peritoneum and a vaginal puncture . If pathologies are detected, treatment is determined.
If your doctor confirms that the discomfort is related to ovulation, pain medications . Folk remedies also combat the problem .
However, self-medication should be done very carefully; it is better to consult a doctor first. A relaxing massage and aromatherapy will help . Warm compresses with herbs are also used: nettle , sorrel , sweet clover , calendula and others.
But you need to be careful with such procedures, since in the presence of inflammatory processes, the effect of heat on the abdomen can only worsen the condition.
You need to take your health seriously, visit a gynecologist once every six months , so that if any diseases arise, they can be identified at an early stage.
Postovulatory syndrome
Postovulatory syndrome or luteinizing phase are those pains that cannot be excluded after ovulation and they are also physiological. After the egg is removed, the remaining follicle forms and produces the corpus luteum, which accumulates yellow pigment and fat.
The corpus luteum is a temporarily functioning endocrine gland; its purpose is to produce progesterone. This is a pregnancy hormone; it is important for the growth of the embryo and helps form the looseness of the endometrium, where the zygote will attach. If fertilization does not occur, after a certain time menstruation arrives and regression of the corpus luteum occurs. Thus, the luteinization phase lasts the entire remaining period from the beginning of ovulation until the end of menstruation and the beginning of a new cycle. Its symptoms are similar to PMS inflammation.
Its manifestations:
- cutting, spasmodic, pulling and stabbing pain in the lower abdomen;
- instability of emotions;
- slight malaise;
- increased sexual desires;
- changes in discharge.
When to worry
In 70% of cases, pain is pathological and can be associated with problems of gastroenterology, abdominal surgery, the endocrine system, and, of course, inflammation of the abdominal cavity.
Nagging and cramping pain in the lower abdomen and lower back may be accompanied by altered discharge. Regarding the discharge, it is worth noting that sometimes it can be present even after ovulation is completed.
If at the same time they acquire an unpleasant fishy smell, and the woman experiences itching of the genitals, or the white discharge turns gray or green; Most likely, this indicates an STI, and you should go to the doctor.
By taking a smear, you can identify the pathogen and undergo a course of treatment. Pain from infections in the abdomen can be severe.
Also, a manifestation of the pathology will be the appearance of cheesy discharge with itching, bad odor, and increased urination. Most likely, we will be talking about candidiasis. But the most dangerous thing is when the discharge becomes bloody and severe abdominal pain appears.
In addition, changes in discharge may be accompanied by fever, nausea, chills, vomiting and diarrhea. Shortness of breath may appear, pain in the head pulsates, movements become more frequent and become painful; Abdominal pain can be unbearable. But even if there is nothing, but signs of inflammation and bleeding after ovulation last more than 3 days, you should urgently consult a doctor.
Abdominal pain in the middle of the cycle: causes and help
Some women experience pain in the lower abdomen in the middle of the cycle, without paying much attention to them. These pains have different causes. More often they are associated with gynecological problems.
Although there is a whole range of diseases and disorders that are sources of pain in the lower abdomen.
Usually these are aching, nagging pains. This pain can radiate to the sacrum, rectum or vagina.
Statistics and practice show: in every sixth woman, these pains are frequent. So why does the lower abdomen hurt in the middle of the cycle?
Pain due to possible pathologies
Ectopic or ectopic pregnancy - in 95% of cases, the embryo attaches to the wall of the fallopian tube. When it bursts, the pain in the lower abdomen increases and is accompanied by bleeding. The pain is cramping and intensifies with movement and defecation.
Ovarian pathologies - among them, torsion of the cyst leg, ovarian tumors or ovarian apoplexy may occur; ovarian neoplasms. In this case, pain can be localized from different sides.
If a cyst bursts, its fluid always causes cutting abdominal pain. There is also a nagging pain in the lower abdomen and spotting after ovulation.
The main symptom is bleeding. When contacting a gynecologist, they will make a puncture of the vagina in its posterior fornix on the spot, in a gynecological chair; Blood volume will be assessed. With a small volume of blood accumulation, the patient immediately feels better and can be discharged home within a day. Otherwise, we are talking about ovarian apoplexy and surgery will be necessary.
Ovarian apoplexy occurs rarely and can be associated with intense physical exertion and heavy lifting. More often the vessel bursts when the follicle ruptures.
Ovarian hyperstimulation – can also be accompanied by pain in the abdomen and lumbar spine if a woman is receiving hormonal treatment for infertility.
The drugs can hypertrophy the ovaries and stimulate the growth of follicles, causing the ovarian stroma to become swollen. Pain in the lower abdomen during treatment is aching, and may be accompanied by bloating, weight gain, cystitis, and shortness of breath.
Inflammatory diseases of the pelvic organs - this includes cervicitis, endometritis, salpingo-oophoritis, adnexitis. In this case, there may be throbbing pain in the lower back and lower abdomen.
Appendicitis - if colic with appendicitis coincides with ovulation, the picture may be similar to gynecology. At first, the pain is not always clearly localized; it can be aching in nature. Gradually, the aching pain in the right side of the lower abdomen intensifies, becomes cutting, and is localized in the iliac region on the right. Additional manifestations include: single vomiting, refusal to eat, nausea, low-grade fever.
Causes of pain
- A follicle breakthrough is a microtrauma inside the body. In which of the ovaries the rupture occurs, nagging, aching pain may appear on that side. Bloody discharge (from bright red to dark brown) may also appear - implantation discharge. Some women don't notice a breakthrough.
- Defective ovulation. Interruption of the process of rupture of the follicle or release of the egg into the tube can be accompanied by severe nagging pain.
- The appearance of pain as the first sign of pregnancy. The implanted egg can affect the female body. Immediately at the moment of attachment, cramping tingling sensations appear in the lower abdomen. A spotting discharge interspersed with blood may appear.
- One of the reasons for the appearance of nagging pain is female gynecological diseases. Polycystic disease, infections, ovarian cysts, inflammation of the genitourinary system and others. Pain occurs due to the weakening of the body as a whole during periods of ovulation. It is worth paying attention to this if there are unusual sensations such as discharge, burning sensation and itching.
After ovulation, before a delay or the onset of menstruation, you can do a test to determine pregnancy with high sensitivity. Tests show the presence of a fertilized egg 7-14 days after expected ovulation.
Pain similar to ovulation
Pain in the lower abdomen, similar to the moment of ovulation, can be observed with:
- peritonitis;
- inflammation of the appendages; ectopic
- pregnancy (bleeding always occurs during pregnancy);
- appendicitis;
- cystitis;
- oncology;
- varicose veins in the pelvic area;
- colitis or OKI; With colitis, pain often appears in the lower abdomen on the left side.
Hormonal imbalances - if your health changes, you should urgently consult a specialist, since only a doctor can diagnose the pathology.
Endometriosis – in this case, pain in the lower abdomen is constantly felt, and by the beginning of menstruation it intensifies. Between periods there is spotting.
Salpingitis is inflammation of the fallopian tubes. The obligatory symptom in this case is pain. Ovulation simply always intensifies it. Despite the fact that the ovaries and tubes are different in location and functioning, they are part of a single MPS and the condition of some parts always affects others. This is a kind of “echo”.
Varicose veins of the pelvis - with an increase in blood supply to the vessels in this area during ovulation, this part of the body becomes hypersensitive and pain in the lower abdomen and lower back almost always occurs.
Adhesions in the pelvis – with adhesions in the pelvic cavity and excessive sensitivity, pain in the lower abdomen and lower back may also occur. They may appear due to chronic inflammation of the MPS in this area. Connective tissue grows between the inflamed areas. These adhesions limit the space for the free release of a mature egg. In addition, when released, the egg touches new tissue - adhesions.
Neoplasms on the internal reproductive organs - malignant formations occur without symptoms for a long time. But ovulation pain is extremely painful, and it could be an early sign.
Mastopathy – during ovulation and the presence of mastopathy, the breasts always hurt. This is the effect of estrogen.
Chronic pathologies of MPS
They often develop from hypothermia: sitting on cold surfaces, unseasonably light clothing, swimming in a mountain stream. In this case, symptoms of cystitis appear with burning, stinging and increased urination; the volume of urine excreted is reduced. There may be pain in the left side of the lower abdomen or on the right and is usually aching in nature.
Inflammations of the appendages include: chronic colpitis, cystitis, pyelonephritis, endometritis, salpingitis or adnexitis. STIs also play a role: mycoplasmosis, chlamydia, ureaplasmosis, trichomoniasis, gonorrhea, etc.