The most common diseases of the reproductive system are endometriosis and fibroids. Often they occur simultaneously. Both diseases affect the uterus and can lead to undesirable consequences. As diseases develop, lesions can spread and affect other organs. Pathologies require immediate treatment.
Clinical picture
Uterine fibroids and internal endometriosis are very similar; they are both associated with hyperplasia of uterine cells, their increased development under the influence of various factors. With adenomyosis, these are endometrial cells that, for various reasons, enter the myometrium, multiply there and cause the development of adenomoyous nodes. And with fibroids, these are smooth muscle cells of the myometrium, the proliferation of which also causes the development of nodes, but myomatous ones.
Their combined detection significantly complicates the course of the disease, since changes in the uterus occur faster than with a separate pathology. Therefore, it is important to detect them in time and begin treatment. It is very difficult to identify the symptoms or causes of the development of such a pathology, since the causes of development and symptoms of diseases are similar both in the early stages and in later stages.
The disease often occurs latently, which often makes diagnosis difficult, but visiting a doctor, examination and additional research can quickly detect both diseases.
Clinical manifestations: how to recognize the disease
Uterine endometriosis and fibroids are very similar, and in the initial stages these diseases can be confused. The first symptoms appear predominantly at 25-35 years of age, although manifestation at an earlier age or, conversely, closer to menopause is not excluded. Often, fibroids are combined with adenomyosis, and an accurate diagnosis can only be made after an instrumental examination.
Leading symptoms of pathology:
Menstrual irregularities
Menometrorrhagia is the main symptom of submucous fibroids and adenomyosis. In this condition the following is observed:
- Increased volume of menstrual flow;
- Prolongation of bleeding time (up to 6-7 days or more).
- The appearance of spotting and spotting 1-2 days before and after menstruation (more common with adenomyosis).
With submucous myoma and adenomyosis during menstruation, blood loss is pathological in nature: copious bleeding is observed and the duration of bleeding increases.
With interstitial myoma, cycle disturbances are not so pronounced and are observed against the background of large nodes. What kind of discharge can be observed with a tumor is written in detail in a separate article.
On a note
Many gynecologists recommend their patients to lose weight, and this is not surprising. Adipose tissue reserves contribute to increased estrogen synthesis, which disrupts hormonal balance and increases the risk of developing hyperplastic processes. The first symptom of problems is usually a disruption of the menstrual cycle.
It is also useful to read: Use of ASD-2 fraction for uterine fibroids
Pelvic pain
Chronic pain syndrome is more typical for uterine fibroids and external endometriosis, in which lesions are located in the ovaries, fallopian tubes, and peritoneum. The pain is localized in the lower abdomen, radiating to the lumbar region, perineum, sacrum, and rectum. The intensity of pain can vary and largely depends on the individual sensitivity threshold. We wrote in more detail about the nature of pain with fibroids in another article.
Pain in the lower abdomen is one of the characteristic signs of uterine fibroids and external endometriosis.
Constant pain is not typical for adenomyosis. Unpleasant pulling sensations in the lower abdomen and lower back are noted a few days before menstruation and directly in the first days of the cycle. After the end of menstruation, the pain subsides. By this sign you can distinguish one disease from another, but you should not trust it too much. Detection of adenomyosis does not exclude the presence of uterine fibroids. Often pathological processes are combined, changing the clinical picture and complicating diagnosis.
Causes
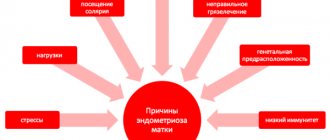
The reasons for the development of uterine fibroids against the background of internal endometriosis are often the same for both diseases. Thus, factors contributing to the development of fibroids are:
- heredity;
- hormonal disorders;
- endocrine diseases;
- inflammatory infectious processes;
- surgical and diagnostic interventions;
- decreased general immunity;
- incorrect lifestyle and bad habits.
The factors contributing to the development of internal endometriosis are almost the same, but inflammatory diseases, multiple or difficult births and surgical interventions, curettage lead to it more often. A decrease in general immunity, when the immune system responsible for destroying improperly developing cells of the body cannot protect the body, causes the occurrence of both adenomyosis and fibroids.
Endometriosis is more common in young women 20-30 years old, and fibroids are more common after 30, so combined lesions of the genital organs occur in patients 25-40 years old.
Fibroids and endometriosis: what are the differences?
Fibroids and endometriosis are not the same thing. Yes, diseases have common causes, similar clinical symptoms, and even diagnostic methods are the same, but treatment approaches are significantly different. It is impossible to say for sure which is worse: fibroids or endometriosis. Both pathologies can significantly disrupt the normal course of life, cause infertility and other equally serious complications.
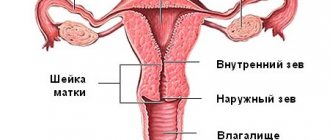
Uterine fibroids are a hormone-sensitive benign tumor of the myometrium (muscle layer). Another name is leiomyoma or fibromyoma. Pathology is detected in 80% of all women (according to autopsy data).
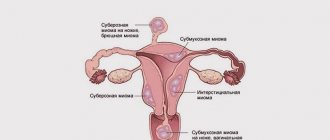
The following types of endometrioid uterine fibroids are distinguished:
- Submucosal – growing into the submucosal layer;
- Interstitial – localized only in the muscle layer;
- Subserous – reaching the outer membrane;
- Intraligamentary – located between the ligaments of the uterus.
Submucous fibroids form under the lining of the uterus. Interstitial - localized in the anterior or posterior wall, and subserous - on the outside of the uterine body.
Endometriosis is a genetically determined disease in which areas of the endometrium are located outside the lining of the uterus. According to statistics, pathology is detected in 10% of women.
The following types of endometriosis are distinguished:
- Genital – lesions are localized only in the genitals;
- Extragenital - endometriotic heterotopias are found outside the pelvis.
Genital endometriosis is divided into two forms:
- External - lesions in the appendages, in the vagina, on the cervix;
- Internal (adenomyosis) - the proliferation of pathological foci in the uterus.
Adenomyosis is also called endometriosis of the uterine body and the clinical picture is very similar to fibroids.
The distinctive features of the diseases are presented in the table:
| Characteristic | Uterine fibroids | Adenomyosis |
| Affected tissues | Myometrium with germination to the subserous and submucosal layer | All layers of the uterus, starting with the endometrium |
| Woman's age | More common after 35 years | Detected at any age, including young women |
| Menstrual irregularities | Mainly for submucous fibroids | One of the leading symptoms |
| Chronic pelvic pain | For large fibroids | Possible |
| Uterine bleeding | Yes | Yes |
With adenomyosis, the endometrium grows too much and begins to be outside the area of the uterine mucosa.
Symptoms
Symptoms of uterine fibroids with internal endometriosis do not appear immediately. Since pronounced symptoms appear after the nodes enlarge, it is difficult to detect the disease at an early stage. Its signs are:
- menstrual irregularities;
- heavy menstruation with dark brown discharge;
- pain before and during menstruation;
- long periods;
- pain during sex;
- frequent urination;
- constipation;
- infertility;
- miscarriages.
Prolonged heavy bleeding leads to extensive blood loss; the body does not have time to restore hemoglobin levels on its own, so such women experience weakness, dizziness, pale skin, and fatigue. All this can lead to the development of severe anemia.
Signs of the disease
Small fibroids and a thin layer of endometriosis at the initial stage of formation are asymptomatic - symptoms are usually absent or appear in a mild form. The following signs will help identify a disturbed gynecological process:
- heavy discharge during the menstrual cycle;
- the period of menstruation increases;
- before the start of the cycle there is spotting mixed with blood;
- excess body weight;
- pain in the pelvic area;
- pain during sexual intercourse;
- the reproductive process is disrupted;
- frequent urge to urinate;
- pain during bowel movements;
- large fibroids are accompanied by severe vaginal bleeding.
Endometrioid disease on the background of uterine fibroids occurs with similar symptoms. To determine an accurate diagnosis, it is necessary to undergo an instrumental examination of the woman, which allows us to identify the structure of the disorders.
Complications
Complications with uterine fibroids against the background of internal endometriosis can occur both due to adenomyosis and due to an increase in myomatous nodes, these can be:
- bleeding, anemia;
- necrosis of the node due to torsion of the leg or disruption of its nutrition, possible development of abscesses and endometritis;
- diseases of the genitourinary system (pyelonephritis, hydronephrosis);
- diseases of the digestive tract;
- acute conditions requiring immediate surgical intervention (peritonitis, acute intestinal failure);
- problems with conception and pregnancy (miscarriages).
It is interesting that if with adenomyosis pregnancy can cause reverse development of lesions, then with combined lesions there is a deterioration in the condition of the uterus, since myomatous nodes grow faster under the influence of estrogens, which leads to rapid deformation of the uterus.
Endometriosis: symptoms, causes, features
Endometriosis in general is the growth of the endometrium of the ovaries, intestines, and cervix. If we talk about internal endometriosis of the uterine body, then it is usually called adenomyosis. In a normal state, the endometrium, which lines the inner surface of the uterus, grows into the cavity during a woman’s menstrual cycle. There is an explanation for this: the loose layer is designed to absorb the fertilized egg and help it attach. If conception does not occur, this layer is torn off and comes out along with menstrual flow.
The causes of internal endometriosis have not yet been fully identified. It is generally accepted that it is caused by injuries to the uterus:
- childbirth, especially through caesarean section;
- multiple abortions;
- surgical intervention in the uterine cavity;
- inflammatory processes;
- removal of fibroids.
However, uterine adenomyosis occurs even in girls who have barely reached puberty and are not sexually active. In this case, the pathology is explained by the peculiarities of the individual structure, as well as disorders of the girl’s intrauterine development.
The main symptoms of the disease are pain in the lower abdomen, which intensifies during menstruation and sexual intercourse. The menstrual cycle gets confused, in the middle of it there is a brownish discharge from the vagina. Endometriosis of the uterus can be localized, in which case it is called focal. Diffuse adenomyosis is localized randomly, affecting the entire uterus. There is also a nodular one, whose characteristics are similar to fibroids. The difference from the latter is that the myomatous node is formed from muscle and connective tissue, and the adenomyosis node is formed from connective and glandular tissue. There are also mixed forms of the disease.
This process itself does not lead to infertility, however, when endometriosis and uterine fibroids are combined, the consequences can be serious.
Diagnostics
Diagnosis of uterine fibroids against the background of internal endometriosis is carried out on the basis of examination, medical history and additional studies. During a gynecological examination, changes in the shape and size of the uterus can be detected. But to clarify the diagnosis, the following is prescribed:
- hysteroscopy, hysterography;
- ultrasonography;
- laparoscopy;
- CT scan;
- Magnetic resonance imaging.
Hysteroscopy can detect signs of adenomyosis and myomatous submucosal nodes, the same can be seen in ultrasound images. Pronounced changes cause deformation of the uterus and its enlargement.
Causes of adenomyosis
Scientists have still not been able to determine the exact causes of the disease, perhaps due to the complex mechanism of its development. Since adenomyosis is a hormone-dependent pathology, its appearance can be caused by many factors, including the woman’s hormonal background. A major role of hereditary predisposition to adenomyosis cannot be ruled out. Among the factors that can provoke, if not adenomyosis itself, then its rapid growth, doctors name:
- Injuries to the uterus, including surgical ones - abortions, curettage, removal of polyps, caesarean section.
- The presence of concomitant gynecological diseases - pelvic inflammation, fibroids and other pathologies.
- Excessive physical and emotional stress.
Treatment
Treatment of uterine fibroids against the background of internal endometriosis is complex. In the first stages, when the nodes are small and there are no noticeable complications, conservative treatment includes:
- hormonal therapy;
- immunomodulators;
- symptomatic therapy (painkillers, sedatives);
- physiotherapy;
- hirudotherapy;
- ozone treatment;
- ultraviolet irradiation of blood;
- laser therapy;
- plasmapheresis.
For hormonal treatment, gonadotropin-releasing hormone inhibitors are used, but individual treatment is selected in each case.
Surgical treatment is used if at least one node exceeds 10 mm in size or there are complications:
- bleeding between periods or heavy blood loss during them;
- rapid growth of nodes;
- anemia;
- suspicion of malignancy;
- node necrosis;
- violations by other organs.
Surgery for uterine fibroids against the background of internal endometriosis in young nulliparous women involves removing nodes and is called myomectomy. This is an organ-preserving operation, after which long-term conservative treatment is required. In the later stages, it is very difficult to restore the reproductive function of the uterus, so if a woman does not plan to give birth, then removal of the uterus (hysterectomy or extirpation) is recommended.
Treatment of pathology
Treatment depends on the form of the disease, general health, age and area of the lesion. Also, when choosing a therapy method, it is important for the doctor to know whether the patient is planning a pregnancy in the future or not. When infertility is diagnosed, the treatment process is aimed at preserving reproductive health using gentle methods of therapy.
Conservative therapy
The drug treatment for endometriosis with fibroids is aimed at reducing estrogen production and increasing progesterone levels. This method allows a woman to preserve her ability to bear children. The doctor prescribes the following medications:
- Qlaira is an oral contraceptive, available in tablet form. The composition includes estradiol with dienogest. The package contains 28 tablets, designed for a full menstrual cycle. The medicine blocks the process of ovulation, fertilization and the release of the egg from the uterine cavity, hormonal balance is restored to normal. The tablets are recommended for use in the early stages of pathologies. Cannot be prescribed to women over 35 years of age.
- Buserelin is a drug containing a synthetic gonadotropin-releasing hormone. Available in the form of drops, injections, implants and spray. The substance affects the functioning of the pituitary gland, which is responsible for the production of sex hormones. In a woman’s body, there is a decrease in the production of estradiol and luteinizing hormones, which resembles the process of menopause. The drug blocks the growth of tumors and causes their resorption. Hormone levels return to normal after taking the medicine in 2-4 months. Often prescribed before surgery and after tumor removal.
- The Mirena hormonal device is intended to prevent pregnancy. But during use, doctors noticed a beneficial effect of the drug on the endometrium of the uterus. The spiral contains levonorgestrel in a special container, which is released daily in small doses into the uterine cavity. The substance maintains normal hormonal balance, which has a resolving effect on pathology. After some time, the woman stops feeling pain in the pelvic area, and the menstrual cycle normalizes. The spiral is designed for 5 years. No side effects or manifestations of allergies were observed in medical practice.
In the treatment of the disease, gynecologists often prefer special suppositories. The most popular drugs are:
- Suppositories with propolis relieve pain symptoms with the presence of an inflammatory process. Propolis has antiseptic properties, which prevents the development of infection. Prescribed after surgery to speed up the regeneration of damaged tissues.
- Ichthyol suppositories are characterized by analgesic properties. When a suppository is administered, the pain is blocked within 5-10 minutes. Allowed to be used in the later stages of the disease.
- Indomethacin NSAID blocks painful spasms and lowers high body temperature. Helps improve the patient's overall well-being.
- Viferon helps prevent the development of possible complications related to disruption of the functioning of the reproductive system.
- Longidaza is used in the presence of adhesions or if there is a risk of their occurrence. Mainly prescribed after surgery. The substance promotes rapid regeneration of diseased tissues.
- Galavit refers to a drug that is used to treat chronic endometriosis. It stimulates active healing of affected cells, relieves pain, eliminates signs of intoxication, and restores the menstrual cycle.
- Terzhinan relieves the inflammatory process in the genitourinary system, blocks pain with the presence of other unpleasant symptoms.
- Antican with Endometrin are indicated in the diagnosis of heavy bleeding. The medicine restores hormonal balance with improved reproductive function and promotes rapid resorption of atypical tumors.
The choice of drug depends on the woman’s condition and the degree of damage to the body. The doctor takes into account the medical indicators and physical well-being of the patient.
Surgical treatment of pathology
Urgent surgery on a woman with fibroids is recommended if the following indications exist:
- Infertility was diagnosed due to the presence of a tumor in the uterine cavity.
- Myoma exceeds 30 mm.
- Active growth of the tumor is observed.
- The tumor grows during menopause.
- There is a risk of degeneration into a malignant form.
Indications for surgery for internal endometriosis are:
- the disease is at stage 3-4;
- there are signs of oncological degeneration of atypical cells;
- Nodular type of endometriosis was diagnosed.
The presence of heavy uterine bleeding in the absence of a positive effect from drug therapy is a prerequisite for prescribing surgical intervention. The area of operation depends on the type of disease and the degree of damage to the body. Closed fibroids can be removed using uterine artery embolization or traditional myomectomy. Nodular adenomyosis is usually excised laparoscopically.
Radical resection is indicated for the following symptoms:
- the uterus measures more than 12 weeks of pregnancy;
- multiple clusters of fibroids with diffuse adenomyosis grade 3-4 were diagnosed;
- the process of cell degeneration into a malignant form has been confirmed;
- there is an active growth of pathology during menopause;
- diseases occur against the background of endometrial hyperplasia;
- A woman experiences heavy bleeding during drug treatment.
Hysterectomy is prescribed for women who do not plan to become pregnant in the future, or other methods are ineffective in treatment. It is possible to perform endometrial ablation - the mucous layer of the uterus is eliminated with the cessation of uterine bleeding. Also used in women with children.
Treatment with traditional medicine
The conservative treatment method is often supplemented with recipes from traditional medicine. For this purpose, decoctions and infusions of medicinal herbs are used. The following are considered popular and effective means:
- Propolis suppositories help stop the growth of atypical tissue. Propolis (100 g) needs to be grated and poured with alcohol (150 l). Leave the mixture for 12 days in a cool, dark place. You need to stir the mixture daily. Then heat the finished tincture until the alcohol evaporates. After obtaining the consistency of honey, you need to add cocoa (80 g) and tea tree extract (25 g). Mix everything thoroughly, cool and form candles. Place the finished suppositories in the refrigerator to freeze. Use every day for 10 days. Afterwards you need to take a break of 5 days and repeat the course again.
- Take propolis and honey in equal proportions and mix. It is recommended to apply the resulting mass onto a tampon and insert it into the vaginal cavity at night. Repeat the procedure for 10 days. Then a break is required for the same period. Repeat the course 3-4 times.
- Dissolve mumiyo (2 g) in 1 glass of water. Insert a tampon soaked in the resulting solution into the vagina.
- Prepare 2 mixtures - butter with camphor, 1 tbsp each. and butter with birch tar in the same proportion. Use the resulting mixtures in turn every day for a month. Then a break of 10 days is taken and the course is repeated again.
- 2 tbsp. pour 1 cup of boiling water over the shepherd's purse and keep in a water bath for 15 minutes. After this, remove and cool. Bring the strained broth to 200 ml using boiled water. Take 1 tbsp every day. before eating.
- Mix yarrow, bird knotweed, horsetail, stinging nettle and rose hips - 1 tbsp. pour hot water (1 cup). Place in a water bath, keep for 15 minutes. Then remove and leave for 1 hour, drink 1/3 cup in the morning and evening.
- Mix freshly squeezed celery juice with honey in a 1:1 ratio. Consume orally before meals.
- Take 3 tablespoons of flaxseed oil daily. on its own or by adding it to prepared dishes.
Before using alternative medicine, you should consult with your doctor to exclude possible complications and unpleasant consequences.
Prevention
Prevention of uterine fibroids against the background of internal endometriosis consists of early detection of the disease; only in this case, timely treatment can preserve a woman’s reproductive function. Since the causes of the disease have not yet been sufficiently studied, the following is recommended as prevention:
- lead a healthy lifestyle;
- avoid heavy loads and stress;
- monitor your health and promptly treat infectious sexual diseases and somatic diseases;
- maintain general immunity at a high level;
- plan a pregnancy, use contraceptive methods to avoid curettage during an unplanned pregnancy.
To maintain health, women of childbearing age need to visit a gynecologist for preventive examinations.
Endometriosis and uterine fibroids
Uterine fibroids and endometriosis are the result of impaired hormone secretion.
Fibroids are malignant neoplasms both inside and outside the organ, and endometriosis is the spread of altered cells through the tissue of the uterus to places that are not typical for them.
As a result, characteristic pain appears, and pathologies develop rapidly. The abundance of blood discharge increases sharply.
The regularity of the appearance of nodular uterine fibroids in combination with endometriosis has recently increased sharply. This is due to poor ecology, weak immunity and an unhealthy lifestyle.
The main cause of pathologies is hormonal imbalance. An excess of female sex hormones, estrogens, leads to the development of pathogenic cells.
As a result, malignant formations and the proliferation of differentiated epithelial cells form in the uterus. Cysts may also form on the ovaries or cervix.
But there are other risk factors:
- Weak immunity and vitamin deficiency are risk factors. In this case, endometriosis rapidly develops in the myometrium of the organ, and the lobes connect with tumor cells and grow together as fibroids.
- Frequent abortions, curettage and infection during childbirth also cause inflammation of the uterine organ with the further development of pathology.
- Genetic factors and heredity especially increase the risk of malignant tumors.
- Constant long-term stress, fatigue and malaise reduce immunity and increase the chance of inflammation.
- Environmental degradation, toxic factors, unhealthy lifestyle, bad habits. All these factors also affect immunity and the general condition of the body.
- Abuse of mud baths and insolation.
Uterine fibroids, together with internal endometriosis, most often occur due to excess estrogen, as well as in conjunction with inflammatory processes in the organ.
Due to these risk factors, the chance of getting sick becomes even higher, so you need to lead a healthy lifestyle, give up bad habits and increase your immunity.
Most often, the signs of pathologies - uterine fibroids in combination with endometriosis - are disguised as other diseases, but there are a number of symptoms that are most likely with this particular disease, namely:
- Severe pain in the lower abdomen, in the pelvic area. Most often, they intensify before menstruation and decrease after menstruation.
- Bloody vaginal discharge outside of menstruation.
- Disrupted menstrual cycle due to fibroids and endometriosis – long periods, too much discharge.
- Lethargy, constant fatigue.
- Pain when urinating and defecating.
- Disorders of the gastrointestinal tract.
- The main signs are severe pain during sexual intercourse, menstruation and gynecological examination.
Most often, if these signs are present, girls do not immediately seek help, but take painkillers. But this is where the danger lies.
After all, the sooner the disease is diagnosed and treatment is started, the faster the recovery will be, and the fewer the consequences will be.
Therefore, if you detect at least a few signs, you should urgently consult a doctor for help.
What is the disease?
Internal endometriosis is a pathology in which the cellular structures of the endometrium grow beyond the boundaries of this layer.
As a result, functional connections between the ovaries and the uterus are destroyed, follicular maturation and ovulatory processes are disrupted.
Such disorders provoke disruption of hormonal status, weakening of the immune system and lead to the appearance of tumor formations.
Reasons for development
The etiology of endometriosis has not been fully elucidated, however, experts have been able to identify a range of factors that can influence its occurrence:
- Abuse of mud therapy in the form of mud baths;
- Frequent stress overload;
- Pathological childbirth or a history of abortion, accompanied by inflammatory complications, uterine perforation, etc.;
- A sharp change in climatic living conditions;
- A large number of diagnostic scrapings and other intrauterine manipulations such as the installation of an IUD or surgical operations;
- Exposure to ultraviolet rays (insolation).
Treatment of adenomyosis and endometriosis
Uterine fibroids adenomyosis and endometriosis can be easily stabilized with hormonal drugs, but their use is justified only in the first stages of the disease. In more complex forms, surgical intervention is often unavoidable.
There are several ways to stabilize and partially reduce the manifestations of adenomyosis and endometriosis. At the first stage of the disease, taking oral contraceptives can achieve significant improvement and “preservation” of the patient’s condition. With more pronounced symptoms, when the disease has begun to progress, the method of introducing the patient into artificial menopause is often justified. Since endometriosis and adenomyosis regress during menopause, this method helps to significantly reduce the manifestation of the disease and stop its further development.
In most cases, endometriosis requires more radical treatment; depending on the location of the lesion, laparoscopic or abdominal surgery may be necessary. In the future, such women must still undergo a course of hormone therapy to avoid relapses.
In addition to treating the pathology itself, treatment can be aimed at relieving inflammatory processes and generally strengthening the body. In general, the treatment of endometriosis and adenomyosis is a complex and challenging task, and the doctor’s goal is not only to reduce their manifestations, but also to preserve the basic functions of the organs.
Diagnosis methods
Typically, such diseases are detected during gynecological examinations; some patients develop any of the listed signs, which forces them to consult a gynecologist.
To confirm the diagnosis, it is necessary to undergo an ultrasound examination, hysteroscopy, etc. These diagnostic procedures make it possible to detect characteristic signs of both diseases.
In addition, the patient is sent for hysterosalpingography diagnostics and laparoscopic examination. These procedures involve the use of a special drug administered through abdominal punctures.
Typically, therapy for uterine fibroids with endometriosis is based on surgical measures. The specific technique is selected in accordance with the form of the fibroid tumor, the patient’s condition, age characteristics and the degree of neglect of the pathological processes.
Surgical intervention
The main indications for surgical removal of pathologies are:
- Large fibroid nodes;
- Bleeding of intrauterine localization;
- Noticeable decrease in performance;
- Rapid growth of formations;
- Necrosis of nodal tissues;
- The presence of malignant processes;
- Unbearable pain;
- Spread of endometriosis to adjacent tissues.
In most cases, specialists carry out organ-preserving surgical measures such as laparoscopy, hysteroresectoscopy, etc. Modern operations are carried out even without punctures in the abdomen, all manipulations are carried out transvaginally.
Treatment after surgery
After undergoing surgical treatment, the patient is usually prescribed long-term hormonal therapy with drugs like ARGG (hypothalamic rizlin hormone agonists).
With the help of these drugs, menopause is artificially induced in the patient. When the body gradually recovers and the hormones are canceled, menstrual functions resume again.
If the case is pathologically serious and there is a real danger to the patient’s life, then the uterine body is removed.
Fortunately, such an operation is used quite rarely and in especially advanced cases of pathology.
After a uterineectomy, complications such as:
- Sexual dysfunction;
- Memory disorders;
- Sudden changes in emotional and mental state;
- Completeness;
- Pain during sex;
- Frigidity;
- Anorgasmia;
- Oncological pathologies, etc.
Endometriosis and adenomyosis of the uterus - similarities and differences
Despite the common mechanism of occurrence and manifestation of endometriosis and adenomyosis, these two diseases have some differences. Firstly, endometriosis is a more complex form of pathology because Many organs can be involved in the process; with adenomyosis, only the uterus is affected. Secondly, the symptoms of endometriosis are more extensive, which can lead to difficulties in making a diagnosis. Thirdly, adenomyosis itself rarely causes infertility, while endometriosis, on the contrary, often leads to infertility and other disorders.
Causes of endometriosis
The causes of endometriosis, like adenomyosis, are completely unknown. It is assumed that in addition to the hormonal component, there is also an immune component. During normal functioning of the immune system, the body does not allow endometrial particles to take root outside the uterine cavity. There are several theories about how the endometrium enters the body - one theory suggests that it is through menstrual blood, the second allows particles to enter through the lymphatic flow. Both of these theories have not yet been confirmed. However, supporters of both theories agree with the influence of hormones on the development of the disease, so hormonal imbalance is still one of the main components of this pathology.
What is endometriosis
The endometrium is a mucous layer on the inner surface of the uterus containing a large number of blood vessels. The composition of the endometrium is very complex, its epithelial component has ciliated and secretory, argyrophilic, fibroblast-like cells, macrophages, mast cells, T-lymphocytes and single B-lymphocytes. In the endometrium, conditions are created for pregnancy; its vessels grow and then become part of the placenta, which delivers nutrients to the fetus. The endometrium is a hormone-sensitive tissue; it changes depending on the menstrual cycle - it thickens, begins to be abundantly supplied with blood, and the number of glands increases. If pregnancy does not occur, menstruation begins and the functional part of the endometrium is rejected.
Since the endometrium is sensitive to hormones, an imbalance of sex hormones leads to the development of the disease, endometrial hyperplasia. The endometrial layer becomes thicker, which is associated with the effects of excess estrogen and lack of progesterone. As a result of hormonal imbalance, decreased immunity, and stress, excessive growth of tissue cells identical to the endometrium is triggered. Tissue identical to the endometrium begins to grow beyond the normal layer of the uterine mucosa - endometriosis develops. The disease is characterized by heavy and prolonged menstruation, before and after which spotting, brownish discharge may appear. The onset of menstruation is painful, and the disease is often accompanied by anemia, which develops due to large blood loss during prolonged menstruation. The patient constantly experiences fatigue, weakness, dizziness, and is bothered by pain in the pelvic area.
Endometriosis can be internal and external genital, extragenital. With genital lesions, the lesions spread to the woman’s genital organs - the uterus (adenomyosis), cervix, ovaries. Extragenital endometriosis spreads beyond the uterus, affects the abdominal organs, lungs, other tissues and organs, leading to regular bleeding in all organs affected by the overgrown endometrium. The trigger is the onset of menstruation. With endometriosis, the maturation of the egg in the ovary often does not occur, the tissue around the lesion becomes inflamed, the patency of the fallopian tubes is disrupted, and the properties of the mucous layer of the uterus change.
Features of diagnosis of adenomyosis and endometriosis
Diagnosis of the early stages of both adenomyosis and endometriosis can be extremely difficult due to the lack of symptoms and complaints. However, it is early diagnosis that provides the most significant results for preventing further development of the disease and treatment. With late diagnosis, treatment will be longer and more radical. In most cases, especially with endometriosis, surgery cannot be avoided. Therefore, in addition to the professionalism of the doctor, women also need to be attentive to their health and undergo timely preventive examinations with a gynecologist and other specialists.
To diagnose adenomyosis, both ultrasound examination and MRI and laparoscopic examination are used. At later stages, a diagnosis can be made by palpation and based on anamnesis. The situation is much more complicated with endometriosis. Depending on the location of the pathology, the diagnosis can be very difficult to establish. Usually, if symptoms are present, the diagnosis is made based on research and the exclusion of other diseases.
Endometriosis
Endometriosis is a more complex and severe pathology. The mechanism of its development is also not well understood, but it is assumed that during menstrual bleeding through the fallopian tubes, pieces of the endometrium enter the abdominal cavity along with blood. The location of the endometrium can be very diverse - most often it is implanted in the pelvic area: on the ovaries, on the outside of the uterus in the tubes, on the intestines, bladder, etc. However, cases of endometriosis appearing in other organs - lungs, liver, muscle tissues and even in the eyes.
Uterine fibroids in combination with endometriosis
Since fibroids are a disease whose main cause is hormonal imbalance, it often develops simultaneously with endometriosis, a pathology of the inner uterine layer. The endometrium is also sensitive to changes in the level of reproductive hormones in a woman’s body. Moreover, endometriosis is a disease that contributes to the formation of fibroids. Normally, the endometrium cyclically grows and thins, but an imbalance of hormones produced by the ovaries causes the endometrial tissue to acquire aggressive properties towards the body of the uterus. With this pathology, the endometrium is able to multiply uncontrollably and penetrate inside the uterine walls, disrupting the anatomy of the myometrium and even forming through channels in it.
Other factors influencing the development of endometriosis with the formation of myomatous nodes:
- hereditary predisposition;
- excess body weight;
- irregular cycle (too long or too short);
- multiple abortions;
- absence of childbirth;
- refusal of lactation;
- therapeutic and diagnostic gynecological manipulations on the uterus (primarily curettage);
- prolonged stress;
- weakened immune system;
- addiction to cigarettes.
Signs of trouble
The combination of fibroids and endometriosis is quite common in the practice of a gynecologist and is easily diagnosed by ultrasound, which is prescribed after collecting anamnesis and complaints, as well as a standard examination in a chair. Often a woman is not aware of a health problem, but the illness can manifest itself with one or more symptoms, including:
- periodic nagging or cramping pain in the lower abdomen, intensifying after intimacy, under the influence of provoking factors (visiting a solarium or excessive sun exposure, physical strain, hot baths), before the onset of menstruation, with constipation;
- changes in the menstrual cycle;
- a long period of menstrual bleeding and/or its significant volume, non-cyclic bleeding;
- genitourinary disorders associated with frequent urge or discomfort when urinating.
Treatment of fibroids and endometriosis
Therapy for myoma-endometriosis pathology is primarily aimed at suppressing the production of hormones that stimulate atypical hyperplasia of endometrial tissue. Hormone-containing drugs cause reversible atrophy of the endometrium, as during menopause, which helps reduce fibroids in size, and in some cases, its resorption. In addition, it is necessary to take measures to strengthen the immune system, as well as eliminate sources of stress (in the best case, consult a psychotherapist). In addition, it is necessary to exclude the influence of negative factors by refusing to visit the solarium, mud and sunbathing, or sauna: any overheating of the body stimulates the growth of fibroids.
As for uterine fibroids themselves, the main strategy adopted in modern gynecology when identifying small nodes is observation, i.e. systematic control over their size and quantity. Myomatous neoplasms of significant size, multiple nodes or fibroids that create obstacles to a planned pregnancy may require surgical treatment.
Since the disease is associated with excess estrogen, it affects girls over 16 years of age and all women of fertile age, but is more common in patients over 30 years of age. Moreover, during menopause, when ovarian function declines and, as a result, the level of estrogen in the body decreases to zero, previously diagnosed fibroids may well disappear on their own.
The main recommendations for women with this disease are to protect themselves from heat exposure, excessive physical and emotional stress, follow a diet and rest regimen, and regularly - 1-2 times a year - undergo ultrasound diagnostics (ultrasound of the uterus and appendages).
Timely contact with a specialist about uterine fibroids in combination with endometriosis gives a chance for cure without radical surgery. Make an appointment with a gynecologist at the AllergyFree clinic to learn more about gentle and effective methods of restoring women's health!
Forms and stages of development of endometriosis
It is customary to divide endometriosis according to location:
- Genital form – when endometriosis affects only the female reproductive system.
- Extragenital form - in this case, the endometrium is found in any other organs except the reproductive system.
- Combined form - foci of endometriosis are common both in the uterus and other genital organs, and in other tissues and organs.
According to the degree of spread and penetration of endometriosis, it is divided into four stages:
- The first stage is a small number of small lesions and endometriosis. Usually it has no significant manifestations and does not affect the quality of life of a woman.
- The second stage - the lesions are multiple in nature and have penetrated quite deeply into tissues and organs.
- The third stage is characterized by a large number of foci of endometriosis or several deeply embedded foci. At the third stage, the clinical picture begins to appear in the form of inflammatory processes, tumors and cysts.
- The fourth stage - endometrial foci, deeply embedded in tissues and organs, are widespread and often lead to the appearance of benign and malignant tumors.
Contraindications
If uterine fibroids and endometriosis are treated conservatively or the doctor simply monitors the tumor, then the patient needs to slightly adjust her life, eliminating contraindications such as:
- Self-medication or complete refusal of medical intervention in the therapeutic process;
- The use of progesterone drugs that can accelerate formation;
- Pregnancy. In this state, a woman must avoid unwanted conception and abortion;
- Many hours of sunbathing. Patients with fibroids need to be exposed to less ultraviolet radiation;
- It is prohibited to visit massage treatments, saunas or steam baths, body wraps, solariums, etc.;
- You will also have to give up unhealthy habits such as cigarettes, gluttony, alcohol, etc.;
- Avoid physical overload such as cycling, running, gym classes, jump rope or barbells.
If pathology is detected in a timely manner, the prognosis is positive.
Video about laparoscopic uterine surgery for symptomatic fibroids in combination with retrocervical endometriosis:
Possible complications of endometriosis and adenomyosis
Despite the fact that both of these pathologies can be asymptomatic, as the disease progresses, endometriosis can cause infertility and other disorders. Therefore, if a woman is unable to get pregnant, a good doctor must conduct an examination for the presence of endometriosis or adenomyosis. Often this pathology is accompanied by other disorders and diseases, the most common of which are ovarian cysts, obstruction of the fallopian tubes, adhesions in the pelvic organs, fibroids, etc.