Symptoms, causes and methods for eliminating adhesions on the ovaries
Every woman dreams of becoming a mother.
However, it happens that the presence of adhesive formations in the ovaries becomes an obstacle to her happiness. Often, adhesions form between the ovaries and the uterus, its ligaments, fallopian tubes and intestinal loops. With adhesive formations, conception, ovulation and the movement of a fertilized egg through the fallopian tubes is almost impossible. This is how infertility appears, which becomes a big problem for many couples. That is why you should know all the factors, symptoms of ovarian adhesions and treat them immediately.
Symptoms of adhesions
The main symptom of adhesions in the pelvis is chronic pain. Women feel a dull aching pain in the groin, lumbar region, perineum, sacrum, above the pubis. The pain can intensify with hypothermia, exercise, heavy lifting, as well as during menstruation and ovulation. Infertility is also one of the manifestations of adhesive disease that affects the ovaries and fallopian tubes.
If adhesive formations involve the lower parts of the intestine, then symptoms of an intestinal disorder are added to the pain: flatulence, pain in the rectum and ileal areas, periodic diarrhea, constipation.
Causes of adhesive disease in the ovaries
Ovarian adhesions can form for numerous reasons, but the main factor in their occurrence in the pelvic organs is a long-term process of inflammation. If inflammation of the ovaries and nearby organs is not treated for a long time, the adhesions begin to actively grow and lose their elasticity. Other causes of the disease include:
- Erosion on the cervix, non-compliance with hygiene rules when cauterizing it.
- Rapid labor with numerous deep lacerations;
- External endometriosis subsequently, blood from the endometrium enters the abdominal cavity;
- Surgical interventions in the pelvic organs:
- Appendectomy;
- Myomectomy performed via laparotomy;
- Ovarian resection;
This is important to know! The risk of inflammation and adhesions after surgery directly depends on the individual characteristics of the abdominal cavity of a particular patient, as well as on poor hygiene during surgery.
- Incorrect installation of the intrauterine device;
- The presence of inflammation of the intestines and genital organs;
- Abortion;
- Abdominal injuries;
- Long-term use of antibiotics, sulfonamides;
- Diseases of the pelvic organs:
- Endometritis;
- Oophoritis;
- Salpingitis;
- Sexually transmitted infections;
- Appendix;
- Ectopic pregnancy;
- Hysteroscopy, its illiterate implementation and the introduction of pathogenic bacteria;
- Hypothermia;
- Inflammatory process in the fallopian tubes.
Symptoms of the presence of adhesions in a woman’s body
Adhesions on the ovaries have their own characteristic symptoms. Very often, a woman cannot even imagine the presence of adhesions, and takes a simple nagging pain in the lower abdomen as the beginning of her period.
The symptoms of the disease are similar to other gynecological diseases, so a woman only learns about the presence of adhesions when problems with conception arise. Therefore, it is important to know the most common signs of adhesions.
So, most often the patient experiences the following symptoms:
- Irregular menstrual cycle;
- Pain during menstruation;
- Infertility or inability to conceive a child for a year;
- Drawing, periodic or stabbing pain in the lower abdomen, sometimes in the lower back;
- Pain during intercourse;
Attention! If you find even minor symptoms of adhesive disease and suspect that you have it, be sure to consult a specialist!
Pain during intercourse
The adhesive process often interferes with normal sexual life. Women complain of aching, nagging pain in the lower abdomen, more often on one side. Unpleasant sensations accompany the entire sexual intercourse from beginning to end, but may decrease slightly with changes in body position. In some cases, pain during sexual intercourse is accompanied by bloody discharge from the vagina (while the inflammatory process persists).
This is what an ovarian commissure looks like
Diagnosis of adhesions in the ovaries
Only a qualified gynecologist can determine the presence of adhesions through a routine gynecological examination. However, it often happens that it is difficult to confirm or refute this disease. That is why the specialist prescribes a number of other examinations, including:
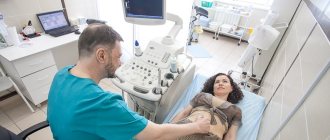
- Ultrasound of the ovaries and uterus;
- Hysterosalpingography;
This is important to know! The examination is carried out between 5 and 11 days of the menstrual cycle on an empty stomach and after an enema. Before carrying out this diagnosis, it is imperative to cure all sexually transmitted diseases!
- Smear for polymerase chain reaction and flora;
- Blood analysis;
- Magnetic resonance imaging.
Only after a comprehensive examination and study of its results, excluding other causes of pain in the lower abdomen, the diagnosis is confirmed and appropriate treatment is prescribed. The effectiveness and speed of treatment depends on correctly performed diagnostics and competent interpretation of tests.
Possible complications
One of the main risks of having ovarian adhesions is the inability to get pregnant, resulting in infertility. Adhesions can grow rapidly, displace neighboring organs, and disrupt contact between the uterus, fallopian tubes and ovaries. Reduce peristalsis and patency of the fallopian tubes.
Adhesive junctions worsen the ovulation process, prevent the fertilized egg from penetrating into the uterine cavity, and compress nerves and blood vessels. Increases the possibility of ectopic pregnancy.
Treatment of synechia
Despite the continuous increase in the number of women diagnosed with infertility as a result of the formation of adhesions in the fallopian tubes, medicine can offer newer methods of treating this disease. One effective method is treatment by laparoscopy. This method is a type of surgical intervention. During the procedure, an action occurs that has the medical name adhesiolysis. This method involves making an incision into the fallopian tube and then removing malignant tumors from it. Treatment of fallopian tube adhesions - video below.
Adhesions after laparoscopy of an ovarian cyst - after surgery on the ovary
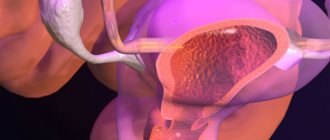
Adhesions on the ovaries cause the development of pelvic adhesive disease (synonym: plastic peritonitis). The pathology is accompanied by the formation of strands (adhesions) of connective tissue that connect internal organs located in close proximity to each other.
The cause of development may be surgical abortions, surgical intervention on the organs of the reproductive system. The condition manifests itself as constant pain in the lower abdomen and menstrual irregularities. If left untreated, it can cause infertility.
What are ovarian adhesions and how do they form?
Adhesions are cords (fibers) that connect the pelvic organs and are formed by connective tissue.
They arise against the background of an inflammatory process that accompanies both surgical interventions on the pelvic organs and inflammation occurring in this area. When tissues are damaged, the body initiates self-regeneration processes. The damaged areas and adjacent areas are covered with a layer of fibrin. The resulting threads “glue” together, forming thick, coarse fibers.
Adhesions after laparoscopy or laparotomy of the ovary for cysts and tumors
Pathology often develops against the background of surgical manipulations on the pelvic organs.
Provoking factors are:
- impact of surgical instruments on tissues, which causes their traumatization - the most severe damage accompanies abdominal surgery;
- drying of the serous membranes due to penetrating air;
- tissue burns caused by exposure to a medical laser beam, radio wave knife and other instruments of this type;
- penetration of blood into the abdominal cavity;
- reaction response to the presence of foreign objects in the peritoneum;
- use of non-absorbable suturing material;
- tissue hypoxia during surgery;
- postoperative infection.
The likelihood of the formation of adhesions increases after surgical manipulations on open cavities. Laparoscopy reduces the risk of strands.
Adhesions after removal of the uterus and fallopian tubes
After resection of only the female glands or appendages completely, numerous adhesions are formed in the organ bed. As a rule, they connect its edges, attaching in parallel to the walls of the bladder or rectum. Sometimes the strands can entwine them in a dense mesh.
Adhesions in inflammatory diseases of the pelvic organs
Strands on the ovaries form not only after surgery. The initiators may be:
- inflammation of the layer lining the uterine cavity;
- combined inflammatory process of the fallopian tubes and gonads;
- suppuration of a cystic formation located on the surface of the female reproductive gland.
During the inflammatory process, damaged tissues are covered with a layer of fibrin. Since there are a lot of such fibers, they “stick together.” As a result, rough adhesions are formed that connect the organs to each other. This leads to the development of a characteristic clinical picture of the disease.
Adhesions after abortion and caesarean section
Any medical manipulations on the pelvic organs - even those not associated with surgery - become traumatic. After mechanical damage is caused to tissues, an inflammatory reaction is formed, triggering the formation of fibrin fibers. The result is the formation of strands.
Diagnostic tests
There are two professional medical methods for detecting the presence of adhesions in the fallopian tubes and establishing the cause of female illness, which are called salpingography and sonosalpingoscopy:
- The salpingography method is based on the detection of adhesions by X-ray scanning of tubes into which a special solution was prematurely injected. During salpingography, all the resulting growths and matter are clearly visible against the background of the solution, so the specialist is able to make the correct diagnosis. A prerequisite for this procedure is that the process itself is carried out before ovulation, since the negative effects of X-rays on the female body can lead to miscarriage.
Salpingography method
- The sanosalpingoscopy method involves studying the results of an ultrasound scan, which was performed after injecting saline solution directly into the fallopian tubes.
Tubal neoplasms are a serious problem that leads to female infertility and related physical and psychological diseases. Every woman, regardless of age, should have a clear understanding of this disease. Regular examination by a gynecologist is a mandatory measure for the early detection and treatment of various female diseases.
An experienced gynecologist recommends that a woman undergo an ultrasound of the body, which can identify the disease at an early stage, including the presence of adhesions in the tubes, after which it will be possible to begin treatment. It must be borne in mind that there are folk remedies that, according to healers, can have an effective therapeutic effect.
However, truly effective treatment can only be prescribed by an experienced specialist, providing an individual approach to each woman. For example, one effective way to get rid of adhesions is an operation called laparoscopy.
Treatment methods for adhesions on the ovaries
Elimination of ovarian adhesions is carried out in different ways. At the beginning of the development of the disease, a conservative technique is implemented. If the practiced methods do not produce results, then surgery is used.
Medicines
The choice of remedy depends on the reasons that caused the development of the condition:
- antifungal and antibacterial - indicated for inflammatory processes;
- hormonal - used for adhesive disease caused by endometriosis;
- anti-inflammatory – relieve pain, prevent worsening of symptoms;
- enzymes - promote the resorption of existing cords.
Drugs are selected individually.
Physiotherapy
Good results are obtained by using techniques that improve local blood circulation. These are electrophoresis with enzymes/anti-inflammatory drugs, magnetic therapy.
Vitamins
Vitamin complexes are prescribed for the appointment. They are necessary to increase overall tone.
Operation
Surgical intervention is practiced if previously used techniques did not bring the expected result. Laparoscopic surgery is most often performed. To cut adhesions, an electric knife, a medical laser, or a stream of water is used.
Folk
Traditional recipes against adhesive disease do not help. Decoctions and infusions of herbs act as auxiliary symptomatic therapy. They help relieve pain and reduce the severity of the inflammatory process.
Adhesions on the ovaries: symptoms and treatment
Adhesive disease is a very common problem in gynecology, the etiology of which is quite difficult to identify.
In fact, any disease of the female reproductive system can cause the development of adhesions - an infectious agent, surgery, untreated inflammatory diseases of the pelvic and abdominal organs, ectopic pregnancy.
In all these cases, a kind of “memory” of the trials experienced remains in the body - connective tissue cords.
But the formed ovarian adhesions make themselves felt very soon - problems with conception, ovulation and patency of the fallopian tubes appear. IN
Infertility caused by this factor becomes a serious problem for women of reproductive age and requires a more attentive attitude on the part of a married couple wishing to conceive a child.
In such situations, it is necessary not only to consult an obstetrician-gynecologist, but also to carefully diagnose and treat adhesive disease to eliminate obstacles to the long-awaited pregnancy.
Diagnostics
Diagnostics is based on ultrasound and laparoscopy. On ultrasound, dense, fibrous cords can be detected, but membranous, single, slightly pronounced adhesions are often not visualized. Diagnostic laparoscopy is also a treatment method.
Laparoscopic intervention is performed if a disease is suspected (infertility, pain).
If the intestine is involved in the process, irrigoscopy is performed - filling the intestine with a radiopaque substance and taking a picture in which filling defects are detected.
If not only the ovaries, but also the fallopian tubes are enveloped in adhesions, then hysterosalpingography and ultrasound hysterosalpingoscopy can detect defects.
Blood tests do not show any abnormalities.
Causes of adhesions
Pelvic peritoneal adhesions in women - this is exactly what this diagnosis sounds like according to the international classification of diseases - are the primary cause of secondary infertility.
The appearance of adhesions due to ectopic pregnancy
The most common reasons that leave behind an “adhesive mark” are:
- Inflammatory diseases of the pelvic organs (PID). Against the background of a number of predisposing factors - undiagnosed and untreated sexually transmitted infections, a history of abortion and curettage, prolonged wearing of an intrauterine device, background diseases of the cervix, frequent hypothermia - ideal conditions are created for the development of the inflammatory process, exudate is formed from edematous organs, and fibrin plaque. Fibrin promotes gluing and fusion of tissues with each other, from which adhesions are subsequently formed. Due to this mechanism, the body limits the process of inflammation in one area, preventing generalized forms from developing.
- Inflammatory diseases of the abdominal organs (appendicitis, peritonitis, mesenteric intestinal thrombosis, intestinal obstruction).
- Trauma and surgery. In emergency situations, for example, with ovarian apoplexy, the patient urgently requires hospitalization with further surgical intervention, which is inevitably associated with tissue trauma and the development of adhesive disease.
- Hemorrhage into the abdominal cavity is a very common finding in ectopic pregnancy. Tubal abortion contributes to the development of adhesions due to bleeding and its infection.
- Endometriosis is a disease characterized by spontaneous growth of the endometrium outside the uterine cavity. To date, the etiology of this disease is unknown and difficult to treat; the process is prone to relapsing.
- Rapid labor with ruptures.
- Long-term use of antibacterial therapy and sulfonamides.
The likelihood of developing adhesive processes is purely individual for each woman’s body and her immune defenses.
Symptoms of adhesions on the ovaries
This disease is characterized by a latent course and an asymptomatic clinical picture.
Symptoms of adhesive disease
There is a classification in which there are 3 forms of the clinic of adhesive disease:
- Acute form. The woman complains of pain in the lower abdomen, attacks of nausea and vomiting, increased sweating, rapid heartbeat, decreased blood pressure, and low-grade fever. Upon examination and palpation of the abdomen, tenderness of the anterior abdominal wall is revealed. Subsequently, the process worsens until a state of shock develops - diuresis decreases (anuria may occur), blood pressure drops critically, the skin becomes pale, and loss of consciousness occurs.
- Alternating form. The pain syndrome occurs spontaneously and periodically, does not last long and also passes quickly, combined with diarrhea or, conversely, intestinal constipation. Characterized by dyspareunia - pain that occurs during sexual intercourse. The patient may complain of menstrual irregularities.
- Chronic form. Asymptomatic, the diagnosis is most often made during a medical examination by a gynecologist. There may be complaints about pregnancy not occurring for a long time. In such cases, obstruction of the fallopian tubes is detected, which prevents the movement of the egg from the ovary into the uterine cavity.