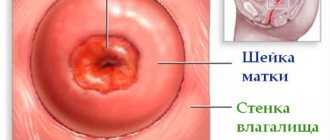
Cervical erosion is a violation of the integrity of the epithelial layer of the vaginal segment of the organ. The disease is diagnosed during a gynecological examination. If we talk about what the damaged area looks like, these are bright red areas.
The disease is one of the most common pathologies of the female genital organs. According to statistics, the condition is detected in 50% of all sexually mature representatives of the fairer sex.
What is cervical erosion?
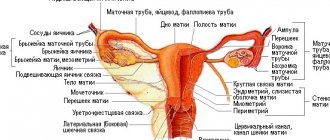
Cervical erosion (ECE) is a gynecological disease accompanied by damage to the mucous membrane of the vaginal part of the cervix (Fig. 1), namely, a violation of the integrity of the squamous epithelium (ulceration, desquamation). This is one of the most common pathological conditions in gynecology, affecting about 10-15% of all women. However, it very often does not manifest itself with any symptoms, which is why many are not even aware of the disease.
Figure 1. Cervix. Source: Rosa Elemil Martínez/Pixabay
Cervical ectopia is often mistakenly equated with erosion. This is a condition in which the area at the junction of the columnar and squamous epithelium (transformation area, Fig. 2) is shifted to the vaginal part of the uterus. Normally, columnar epithelium covers the area of the cervical canal without extending beyond it.
Minor areas of ectopia can be caused by cyclic hormonal fluctuations and over time are independently replaced by squamous epithelium. According to statistics, the prevalence of this condition ranges from 17% to 50% of the female population of childbearing age.
Figure 2. The transformation zone is the junction of two types of uterine epithelium. Source: Dr. Afanasyev M. S.
Types of pseudo-erosions
Pseudo-erosion is not characterized by damage to the epithelium. With this pathology, there is a proliferation of cylindrical cells, which normally should be located in the cervical canal and not extend beyond its limits.
Pseudo-erosion of the cervix can be complicated or uncomplicated. In the first case, a woman needs to constantly visit a gynecologist and get tested. Symptomatic treatment and medications to enhance defenses are possible.
The course of the disease is complicated by the penetration of infection into the genital tract or into the body, hormonal imbalance, for example during pregnancy, or inflammatory processes of a non-infectious nature (during hypothermia). In such a situation, antibacterial or antiviral drugs, anti-inflammatory drugs and vitamins are prescribed.
The reaction of the cervix to infection or inflammation can vary.
Glandular papillary erosion
As the columnar epithelium grows, the number of glands simultaneously increases. Upon vaginal examination, the surface is bright red, there are dilated glandular formations. Glandular pseudo-erosion of the cervix is difficult to treat; it is a so-called chronic form, in which malignant tissue degeneration often occurs.
With the papillary (papillary) form of erosion, there are visible formations on the surface with signs of an inflammatory process.
In addition, there are mixed forms in which both papillary and glandular growths are present.
Cystic epidermal pseudoerosion
Cystic pseudo-erosion of the cervix is the most severe form of erosion. It is accompanied by an inflammatory process and is characterized by the presence of cysts in which mucus collects. At the same time, it should be taken into account that the cervix during this period is susceptible to various infections, since local immunity is significantly reduced.
Epidermization (regression of erosion) complicates treatment, since the cylindrical epithelium is replaced by flat stratified epithelium, but the blockage of the glands persists, and recovery does not occur. Cure is possible with complete rejection of the columnar epithelium along with the resulting glandular neoplasms.
Viral
When the human papillomavirus enters the body, the first symptoms may appear on the cervix - menstrual irregularities, mucus discharge more than usual. In cases of low immunity, the virus is capable of damaging squamous epithelial cells by penetrating into them and exposing them to toxins.
To understand the connection between HPV and erosion, it is necessary to conduct a series of studies to determine the presence of the virus in the body, the degree of protection of the immune system, that is, to approach the diagnosis of the disease individually.
Treatment of viral erosion begins with cell histology and polymerase chain reaction (PCR) analysis. For histological analysis, tissue measuring 3x5 mm is taken from the suspicious area and examined for the presence of atypical cells. The papilloma virus changes the cell nucleus, the number of such nuclei varies from 2 to 5.
The polymerase chain reaction method is based on searching for viral DNA molecules. This is a highly informative test that allows you to determine the presence of the virus at the very beginning of the disease.
Erosion, which is caused by a virus, can be accompanied by keratinization of the upper layer of the cervix and other related diseases - cervicitis, inflammation of the appendages and endometritis.
Why is cervical erosion dangerous?
The transformation zone (the place where squamous epithelium transitions to columnar epithelium) is the most important place on the cervix. Here cell differentiation occurs, that is, the formation of immature cells into full-fledged ones. The presence of erosion in this area can provoke disruptions in the normal course of this process, which will become a trigger point for malignancy (malignant degeneration) and the development of cancer. It is from the transformation zone that a cytological smear is taken for early diagnosis of cancer.
Possible complications
The most serious complication of cervical erosion is the development of dysplasia (the appearance of atypical, mutated cells). Dysplasia, in turn, is a so-called precancerous condition - a lesion that is highly likely to lead to a malignant tumor (Fig. 3).
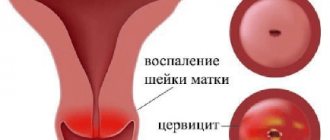
Defects in the mucous membrane during ESM are also “entry gates” for infection, which can cause inflammation of the cervix (cervicitis), vagina (colpitis), inner lining of the uterus (endometritis), etc.
During pregnancy, ESM significantly increases the likelihood of spontaneous abortion and premature birth.
Also, cervical erosion is the cause of about 25% of all postcoital bleeding (bleeding that occurs after sexual intercourse).
Figure 3. CIN-1 cervical dysplasia. Source: cleanmedjournals org
Traditional methods of treating ectopia
Before using folk remedies, you should consult a gynecologist to avoid unforeseen complications:
- Therapeutic tampons - dissolve two mummy tablets in a small amount of warm water, adding sea buckthorn oil. Insert a tampon soaked in the solution overnight.
- Infusion of bergenia root – 4 tbsp. spoons of root pour 200 gr. boiling water and cook over low heat for 25 minutes. Drink 3 times a day an hour before meals.
- Calendula infusion is a prophylactic agent, used for congenital pathology or mechanical damage to the mucous membrane for vaginal douching.
- Honey tampons - wrap one tsp. honey in a bandage, make a tampon and insert it overnight.
- Levomekol ointment - insert tampons soaked in ointment at night.
- Aloe juice – daily for 30 minutes. in the vagina.
- Douching – 5 tbsp. l. St. John's wort pour two liters of boiling water, boil for 20 minutes. over low heat and leave for forty minutes.
Folk remedies are used mainly for prevention, but it is impossible to cure true erosion on your own at home.
Causes
Clinically significant ESM occurs as a result of the following diseases and pathological effects:
- Inflammatory processes - colpitis, cervicitis, etc. Against the background of inflammation, maceration and rejection of part of the normal epithelium of the mucous membrane occurs. Cervical erosion is often associated with chlamydial infection, HPV (human papillomavirus) types 2, 16 and 18, as well as syphilis and tuberculosis.
- Traumatic injuries, including during rough sexual intercourse, early onset of sexual activity, gynecological examination with vaginal speculum, use of intrauterine contraceptives (spiral), pessaries, etc. This also includes burns of the mucous membrane of the cervix that occur after treatment of other gynecological diseases (for example, endometrial polyps) using cryo-, electrocoagulation.
- Cancers of the female genital organs, their treatment (primarily radiation therapy) and accompanying trophic disorders, also observed with uterine prolapse, venous congestion in the pelvis and with age-related degenerative changes.
There is evidence indicating a significant relationship between HPV types 16 and 18 and malignant tumors of the cervix. It has been established that these virus strains are responsible for 54% of cancer cases in this localization. In turn, HPV 18 is recognized as one of the causes of 17% of squamous cell carcinoma of the cervix. Progression towards dysplasia is detected in 80% of women with asymptomatic HPV 16 infection.
What to do to stay healthy
To prevent ectopia from interfering with your life and from growing into something dangerous, follow a few rules:
- Do not change sexual partners frequently.
- Go to the gynecologist for a preventive examination 2 times a year.
- Make sure you don't have chronic inflammation.
- Include fermented milk products in your diet.
- Do not take antibiotics without medical supervision. This disrupts the natural microflora of the vagina.
- Take care of your health and that of your partner.
- Be sure to undergo a colposcopy once a year. Especially if you already have erosion or pseudo-erosion.
- During the period when there is erosion, it is especially important that no infection gets into the genitals.
Remember! Monitoring the condition of the female genital organs is especially important! With ectopia, a woman feels so healthy that she completely forgets about the existence of doctors.
A good gynecologist always warns about this. For example, when ectopia is detected after childbirth. The doctor must say that he has discovered erosion, and warn that under no circumstances should inflammatory processes or infections be allowed to occur for the next 2 years. In addition, the woman is asked to warn her husband or sexual partner about this. The gynecologist warns that you will need to undergo examinations 1–2 times a year to keep the situation under control. There have always been such attentive doctors.
Some women eliminate erosion using folk methods. For example, tampons moistened with alcohol tincture of celandine diluted with distilled water. Insert at night for 10 days. But remember that allergy sufferers need to check their body’s reaction to plants.
To prevent ectopia from creating problems, try not to catch an infection or inflammation of the female organs, maintain normal immunity and hormonal levels.
Try not to injure the vagina and cervix, treat inflammatory processes in a timely manner. If the cervix ruptures during childbirth, insist on timely surgical care. Your female organs must be intact.
Classification
Depending on the histological characteristics of changes in the mucous membrane of the cervix, true and pseudo-erosion are distinguished.
True erosion
Accompanied by damage and subsequent desquamation (exfoliation) of the squamous epithelium, which leads to the formation of a wound defect and inflammation. Needs medical intervention.
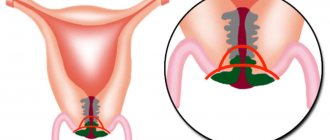
Pseudo-erosion (ectopia)
It is a displacement of the boundaries between flat and cylindrical epithelium beyond the external os to the vaginal area of the cervix. It is not accompanied by inflammatory processes. It can be either congenital (exposure to high levels of sex hormones in the prenatal period) or acquired (discrepancy in the rate of growth and formation of muscle structures of the cervix and its mucous membranes). In most observations, it does not require treatment and is regarded as a normal variant in women under 25 years of age.
Figure 4. Variants of ectopia (ectopion) of the cervix, which are normal. Source: mft. nhs. uk
True and false erosion
In medicine, there are the following types of erosion:
- True – acquired under the influence of unfavorable and damaging factors (inflammatory exudate), which exfoliate the epithelium of the organ and provoke inflammation at the site of damage. This type of erosion is bright red in color and irregular in shape. True pathology is accompanied by bleeding from the inflamed area, dilated blood vessels, traces of purulent and bloody discharge, swelling, wounds have different depths and sizes. After 7-14 days, the lesion defects heal and this stage can turn into pseudo-erosion - the healing phase. With deep damage, a scar can form, making the cervix rigid and preventing it from stretching during childbirth.
- False - the cause of false erosion of the cervix is a shift of the border of the columnar epithelium beyond the border of the external pharynx. The columnar epithelium consists of cells of the internal canal of the cervix. This type occurs in 50% of women and does not cause concern. But when any infection occurs, leucorrhoea appears from the genital tract, pain in the lower abdomen, and bloody discharge after intimate contact. During the healing process, defects in the squamous epithelium are replaced by cylindrical ones, which spread to erosion from the cervical canal. The replacement stage is considered the first stage of healing of true erosion. The cylindrical epithelium has the ability to grow both over the surface of the erosion and in depth, forming branching glandular ducts.
Symptoms
Often, cervical erosions do not have any manifestations, but can occasionally be accompanied by discomfort during sexual intercourse. As a rule, the symptoms that arise are caused by primary diseases, for example, colpitis (inflammation of the vaginal mucosa).
The most typical clinical signs that can be observed with concomitant ESM are:
- Pathological discharge from the vagina, usually of a mucous or purulent nature;
- Pain during sexual intercourse, which is occasionally accompanied by minor bleeding;
- Presence of bleeding during the intermenstrual period;
- Irregularity of the menstrual cycle.
Important! Symptoms of erosion are nonspecific; they can also occur with other diseases, including in the early stages of cancer. If they appear, you should immediately seek help from a specialist. The possible absence of symptoms, in turn, makes annual women's health screenings mandatory.
How is the examination carried out?
Photos 3 and 4 of the colposcope show what healthy cells and damaged cells look like. This method of research with a powerful microscope allows you to see what is happening to the cells. The doctor describes everything in the conclusion. If the surface of the epithelium raises even the slightest doubt about its “purity”, a scraping, smear, biopsy is taken and sent to the laboratory for histology analysis.
Photo 3. Colposcopy of the cervix
Histology will show the structure of the cell and will reveal the presence of dangerous changes. In the treatment of dangerous diseases, including cervical cancer, an early stage of diagnosis allows a complete recovery from the disease.
If you, without a medical or microbiological education, see in photo 4 how different cells are during various pathologies, then the laboratory assistant will even more so give the most correct conclusion on the material examined.
Photo 4.
These procedures are painless. But there are certain rules that must be applied after you have a biopsy. Be careful about your health. These rules are in photo 5:
Photo 5.
Don't hesitate to ask your gynecologist questions. Remember that medicine keeps up with the times and there are already medical centers that use modern equipment. This is a very big breakthrough in diagnostic quality. Everything that was previously examined with a magnifying glass and a simple microscope is now studied with powerful equipment immediately while you are in the gynecological chair. If your antenatal clinic does not have such a technique, get examined at least once a year where it is used.
Read
Also:
- What is cervical erosion
- How does a cervical biopsy occur during erosion: preparation, course of the operation, rehabilitation period
- Why does cervical erosion bleed and what to do?
- Congenital erosion of the cervix in nulliparous women: causes and symptoms
- Endocervicosis – pathology of the cervix
- Why is cervical erosion dangerous?
Questions and answers
After giving birth, my gynecologist found erosion.
She said it was nothing to worry about. She asked me to protect myself from infections and not get too cold. And she also told me to just come and get checked in 3 months, otherwise, they say, she would forget. What does it mean? There is erosion, but should I just live with it? Yes. You will just live like this. Will go for re-examination. And ask your husband not to make “left movements” for the sake of your health. This happens after childbirth. The doctor will observe and nothing more. You don't need to think about ectopia every day. Why are they afraid that if there is erosion, then cancer will start? There are people predisposed to cancer. Submit tumor markers. You will know about the properties of your body and will be able to control all the processes occurring in your body. Do not forget that hormonal contraceptive drugs must be taken under the supervision of a doctor after tumor markers (blood tests). People predisposed to cervical cancer can get sick without any erosion.
Everything is so strange, some doctors say that erosion must be treated, but then they also say that it is absolutely not necessary to touch it. What to believe? No need to touch. If the cells don't look the way they should, you will be referred for additional tests. All over the world, ectopia is not treated.
Diagnostics
The presence of symptoms indicating disorders of the reproductive system requires consultation with a gynecologist. The specialist will conduct a gynecological examination, after which additional tests may be prescribed:
- A smear to check the cleanliness of the vagina, allowing one to judge the severity of the inflammatory process.
- PAP test (Papanicolaou smear, cytological screening). Allows you to evaluate the nature of cell changes in the defect area, thereby providing not only differentiation between erosion and ectopia, but also early diagnosis of malignant degeneration. As a cancer screening, a Pap test, along with an HPV test, is recommended annually.
- Bacteriological examination of vaginal discharge. This technique allows you to accurately identify the causative agent of bacterial lesions of the genital organs, as well as create an antibiogram to determine their sensitivity to the main groups of antibiotics. May be combined with polymerase chain reaction (PCR) and serological tests.
- Extended colposcopy. When it is carried out, it is possible to identify an epithelial defect with clear boundaries and signs of inflammation, surrounded by a slight area of edema and full-blooded blood vessels. When stained with Lugol's solution, the bottom of the defect does not change its color.
- Targeted biopsy. This is a detailed histological and cytological analysis of a tissue sample taken directly from the erosion. It allows you to reliably identify dysplasia and is used as the most accurate method of differentiation between erosion, ectopia and cancer. Its results can be a criterion for choosing treatment.
How can pseudoerosion be treated?
The method of therapeutic intervention varies depending on several factors. First of all, the origin of the pathological process is taken into account, as well as the nature of the course of the disease.
If the patient is diagnosed with an uncomplicated type of ectopia, in which intense symptoms do not appear and the risk of complications is minimal, then narrowly targeted treatment is not carried out. Dynamic observation is established, during which it is necessary to regularly visit a gynecologist. This will allow timely detection of deviations and potential complications. Therapy of a complicated form is carried out taking into account the changes occurring in the structure of the cervix.
Conservative treatment of ectopia
Treatment is aimed at eliminating the factors causing pathological changes. In the overwhelming majority of clinical cases, the causative agents of acquired ectopia are bacterial and viral, less often fungal infections. Having determined the causative agent of inflammation, appropriate medications are prescribed.
These include:
- Antibacterial.
- Antiviral.
- Anti-inflammatory.
- Anti-stress.
- Vitamin complexes.
In addition to medication, women need to follow a number of recommendations during treatment. If necessary, the use of contraceptives is adjusted. If ectopia is detected during pregnancy, comprehensive pregnancy management is necessary.
Related recommendations:
- Compliance with hygiene standards.
- Controlled medication intake.
- Rejection of bad habits.
- Wearing underwear made from natural materials.
- Elimination of traumatic factors (including intense sexual intercourse).
- Control of the menstrual cycle.
- Strengthening the immune system.
Approaches to the treatment of cervical erosion
Treatment tactics for ESM vary depending on the etiology, the presence of concomitant diseases, as well as the results of laboratory and instrumental diagnostic methods (Table 1). Therapy can use pharmacotherapeutic agents and various surgical techniques.
Important! Asymptomatic cervical erosions that are not associated with other diseases and do not have signs of malignant degeneration confirmed by laboratory test results do not require medical intervention.
Table 1. Approaches to the treatment of cervical erosion
| Causes of erosion | Treatment tactics |
| Infectious diseases, inflammatory process | Drug therapy (primarily antibiotic therapy and anti-inflammatory drugs), local treatment with antiseptic solutions. |
| Traumatic injuries, burns | Self-recovery after 3-10 days. If necessary, symptomatic medications (for example, painkillers) and local treatment are used. |
| Malignant diseases | Surgical treatment, if necessary, supplemented with radiation and/or chemotherapy. |
Drug and local treatment
There is no specific drug therapy for cervical erosion. Some medications are used to prevent progression or eliminate symptoms.
For example, in case of inflammatory processes, depending on the infectious agent, antibiotics, antiprotozoal or antifungal agents are used in the form of tablets and/or vaginal suppositories. As a topical treatment, douching is performed - irrigation of the vagina with solutions of drugs.
Also in the form of tablets or vaginal suppositories, in order to suppress the inflammatory process and relieve pain, drugs from the group of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) are used. To restore normal vaginal microflora, biological products are prescribed that promote the growth of lactobacilli.
Surgery
Various surgical treatment techniques can be used to remove cervical erosion. The choice depends on the clinical situation and the capabilities of the medical institution.
All operations are carried out on days 5-9 of the menstrual cycle, since during this period pathological changes are most pronounced, and a general contraindication to their implementation is the presence of an active inflammatory process in the body, not only in the genitals. The rehabilitation period, during which lifting heavy loads, taking warm baths, visiting saunas and sexual intercourse is prohibited, can be quite long.
Diathermocoagulation
The affected area of the mucous membrane is cauterized using a high-voltage electric current. Recovery after surgery takes about 2-3 months.
Laser vaporization
Allows you to remove erosion using a helium-neon or CO2 laser beam of adjustable power. Rehabilitation after surgery can take up to 1 month. The most widely used method because it rarely causes complications and does not affect reproductive function.
Cryocoagulation
It involves the destruction of the affected area of the epithelium using local exposure to low temperatures, usually using liquid nitrogen. Unlike other techniques, it does not require pain relief. The recovery period ranges from 4 to 10 weeks.
Radio wave conization
Removal of an area of erosion, which is performed using a device that generates high-frequency alternating currents. The rehabilitation period is from 4 to 7 weeks.
How can cauterization of ectopia or erosion harm it?
Surgical techniques are used only in the presence of bleeding or signs of malignant degeneration.
Asymptomatic erosions are not subject to such treatment, since the transformation zone, where two types of epithelium meet, can shift into the cervical canal as a result of cauterization, which complicates diagnosis in the future, increasing the risk of developing cancer inside the cervical canal (Fig. 5). Figure 5. The transformation zone may be hidden from the doctor’s eyes, including due to cauterization of the ectopia. Source: Dr. Afanasyev M. S.
Folk remedies
As an auxiliary treatment for cervical erosion, the following can be used:
- douching using solutions with mumiyo, celandine or bee honey,
- daily use of decoctions of medicinal herbs (St. John's wort, bedstraw, celandine).
There are also recipes for preparing vaginal suppositories from honey and aloe vera and moistening a hygienic tampon with sea buckthorn oil.
Treatment with traditional methods should definitely be discussed with your doctor, since certain remedies may distort or neutralize the effects of medications or be completely contraindicated in some conditions.
Treatment of pathology
The decision on the choice of treatment method (conservative or surgical ) for cervical erosion is made by the gynecologist only after laboratory and instrumental examination.
Conservative method
This therapy consists of the following:
- Nonspecific anti-inflammatory therapy;
- Drugs to suppress the development of sexually transmitted viruses;
- Treatment of hormonal disorders;
- Physiotherapeutic techniques - helium-neon laser, tampons containing therapeutic mud, phonotherapy, microcurrent therapy, iontophoresis, ultraviolet therapy;
- Chemicals - in some cases, cervical erosion is removed with chemicals for a chemical burn. One of these drugs is Solkovagin, which contains: zinc citrate, acetic, nitric and oxalic acids. The solution affects only the columnar epithelium of the canal, without involving the stratified, non-keratinized epithelium. Treatment of the mucous membrane has a positive result after just one procedure. Another drug is Polycresulene, which has a cauterizing, antiseptic and astringent effect.
Surgery
The surgical method consists of several procedures depending on the course of the disease:
- Cryodestruction involves freezing organ erosion with liquid nitrogen. Under the influence of low temperature conditions that occur during the evaporation of nitrogen, tissue necrosis occurs. But the procedure has a poorly controlled effect and extends to a tissue depth of up to 5 mm or more, which can cause a narrowing of the external pharynx. Also sometimes requires re-freezing.
- Laser vaporization is laser removal using high-energy radiation devices: ruby, carbon dioxide, argon lasers. The advantage of this method: the ability to control the depth and area of tissue necrosis, the absence of inflammation after the laser. Disadvantages: painful, high cost.
- Radio wave surgery – treatment with the Surgitron device. The method consists of a controlled, limited tissue incision without contact with the tissue. High thermal energy from radio waves affects erosive areas of the mucosa, destroying and evaporating cells. The advantage of this method: a painless procedure with precise effects, absence of pain and bleeding after surgery, bactericidal effect and healing without scars, which increase the risk of rupture during childbirth.
Separate use of conservative or surgical treatment sometimes does not lead to persistence and positive results. Only comprehensive treatment can remove the pathology and prevent the formation of a new disease. With conservative treatment, the mucous layer is restored or a scar is formed. To restore the squamous epithelium after removal of the inflammatory process, cauterization of the affected area is prescribed. Cauterization activates the restoration processes of the epithelium, as leukocytes and other cells appear in the burn area to enhance regeneration.
Forecast
Cervical erosions respond well to treatment with early diagnosis and timely initiation of therapy - all clinical manifestations of the disease are completely eliminated and complete recovery occurs.
What will happen if left untreated?
Most erosions caused by traumatic or drug-induced damage to the mucous membrane can resolve on their own. But even such defects can cause infection.
Infectious forms of the disease always require additional diagnosis and treatment. When they form, a woman experiences previously absent symptoms, such as pain during sexual intercourse, pathological discharge, irregularities in the regularity of menstrual cycles, etc.
Without proper treatment, other, initially healthy tissues will also become involved in the inflammatory process, which can cause inflammation of the vagina, lining of the uterus, etc.
It is also worth noting the connection between cervical erosion and malignant diseases. Quite rare, but these changes can lead to dysplasia, which is the basis for the development of cancer.
Types of false erosion
The false stage is divided into several types, which without appropriate treatment can exist for several months or years, and each of them becomes one of the sources of inflammation due to existing infections in the erosive gland:
- Follicular erosion is determined by pronounced glandular ducts and a cyst.
- Papillary – determined by superficial papillary growths, in which women experience burning, itching in the vagina, massive white and translucent odorless leucorrhoea, and mild pain in the lower abdomen. A change in the color of the leucorrhoea and odor indicates the presence of an infection.
- Cystic - small cystic growths.
- Papillary – papillary growths with inflamed and infiltrated areas, caused by the papilloma virus. This disorder exists on the cervix for a long time, without causing concern, but there is a risk of developing dysplasia - a precancerous condition. As the cervix becomes overgrown, sperm cannot penetrate into its cavity, which leads to the development of infertility.
- Glandular-papillary - combines the symptoms of the previous types.
- Congenital - when the border of the columnar epithelium is displaced during fetal development, such a pathology develops. It is located on the area of the external pharynx, having a bright red tint on a flat surface. It often manifests itself in adolescence and even childhood and heals itself over time. When a girl reaches puberty, it can become infected, inflamed, and change. Sometimes flat condylomas may develop against its background, but malignancy is not observed with this erosion.
When inflammation subsides on its own or due to treatment, the cylindrical epithelium is replaced with flat epithelium, during which the normal integumentary epithelium of the organ is restored, which is considered the second stage of healing. Often, small cysts appear in the area of healed erosion due to blockage of the ducts of the erosive gland.
The long course of false erosion and inflammatory processes ultimately change the epithelial cells, which can lead to atypia and dysplasia.
Pregnancy with cervical erosion
In the absence of proper treatment for clinically significant erosions, reproductive function suffers significantly: the incidence of infertility, miscarriage, intrauterine infection of the fetus, complications during childbirth and the postpartum period increases.
According to statistical data, the frequency of miscarriage with ESM is 38 times higher than the average in the population, spontaneous miscarriage - 14.9 times, premature rupture of membranes - 5.2 times.
The effect of erosion on conception
Cervical erosion does not directly affect conception. The disease may be associated with discomfort during intercourse and post-coital bleeding, but does not reduce the likelihood of becoming pregnant. However, pregnancy with untreated ESM is undesirable due to the above-mentioned complications.
The effect of surgery on conception
The most favorable options for surgical treatment of ESM are laser coagulation with a helium-neon laser and cryodestruction. These techniques make it possible to achieve epithelization in 97% of cases and do not in any way affect the possibility of conceiving and bearing a child.
Complications caused by ectopia
The absence of symptoms during erosion does not indicate that there is no need to treat the disease. Pseudo-erosion that occurs around the organ canal contributes to the appearance of epithelium that does not protect against infections from the vagina into the uterus. In some cases, spontaneous epithelization of erosion develops with the formation of defective epithelia.
The danger of gynecological disease depends on changes in the organ:
- Pseudo-erosion – does not pose a threat to health or consequences;
- True against the background of infectious diseases - the danger of infection in the uterus, appendages, the risk of infertility;
- Dysplasia is the risk of developing cervical cancer over a period of time.
If the pathology is detected in a pregnant woman, it does not affect the pregnancy and the developing fetus and treatment can begin after childbirth.
Prevention
All preventive measures regarding cervical erosions can be divided into two main categories:
- Primary prevention. Involves preventing the occurrence of erosion. This includes: HPV vaccination, proper intimate hygiene, early treatment of gynecological diseases and avoidance of exposure to other risk factors.
- Secondary prevention. Includes active monitoring of identified ectopia and regular screening studies: gynecological examinations, PAP tests, etc.
The most effective protection against HPV is vaccination. Today, in most developed countries of the world, vaccination against HPV is an integral part of the vaccination schedule. First of all, it is relevant for girls under 18 years of age who have not yet begun sexual activity. Since HPV infection often occurs during the first sexual contact, the ideal age for vaccination of girls is 12–14 years. It makes sense for adult women to get the vaccine if they plan to change sexual partners.
Taken from the article: Human papillomavirus
Preventive measures
To prevent the development of the disease, a woman should follow the following recommendations:
- Visit a gynecologist twice a year;
- Maintain personal hygiene, especially during menstruation;
- Use condoms when having sexual intercourse with a casual partner to avoid contracting various infections;
- Live a regular sex life;
- Avoid abortions that cause cervical injury.
The insidiousness of the pathology lies in the absence of manifestations and symptoms of the disease for a long time. The pathology appears at different ages and is considered one of the leading diseases in gynecology. If even one of the signs of the disease appears, a woman should begin timely treatment.