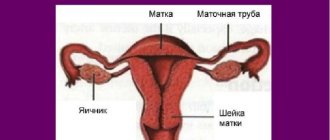
Cervical erosion is a pathology that occurs in half of all representatives of the fair sex. The disease can be asymptomatic for a long time, and pathology is often discovered by chance during a routine medical examination. And only in a quarter of all patients with erosion does it make itself felt by the appearance of bloody discharge from the genital tract. Is this normal and why do such symptoms occur?
Before talking about the problem, one point should be clarified. Erosion is a defect in the epithelium that occurs for a variety of reasons. It is not surprising that a thin layer of mucous membrane can be damaged and bleed for the slightest reason. It is not the fact of bleeding itself that is alarming, but its frequency, intensity and cause. Knowing what discharge may occur during cervical erosion, you can recognize the disease in time and take the necessary measures to eliminate it.
Does bleeding erosion of the cervix happen? Do you need to see a doctor in this case?
The diagnosis of “cervical erosion” has long firmly taken a leading position in the statistics of gynecological diseases.
For many women, the doctor’s conclusion was news, because they simply came for a routine examination. In other cases, there was a pathological clinical picture in the form of irregular bleeding.
What is this? Erosion? But can it bleed? Let's figure out whether cervical erosion can bleed, including during examination, why it bleeds and what to do about it.
Mandatory diagnostic methods
When examined on the mirrors, the doctor will see pathological cervical changes and will notice that the cervix bleeds when taking regular smears. Even a slight touch of a cytobrush or spatula during a standard examination causes slight bleeding from the eroded surface.
If cervical erosion bleeds, this indicates a serious situation in which the following studies must be performed:
- smears for common infections;
- oncocytology (taking smears from the cervical canal for cancer cells);
- bacterial culture to identify microbes;
- conducting a special examination for human papillomavirus (HPV), genital herpes and chlamydia;
- Ultrasound with a transvaginal sensor;
- colposcopy with special studies;
- biopsy to exclude a malignant tumor.
When cervical erosion bleeds, it is imperative to do PCR (polymerase chain reaction) for HPV: only this laboratory test can reliably confirm or reject the presence of a dangerous viral infection. The PCR test is carried out painlessly and quickly: this procedure is similar to taking a regular smear from the cervical canal.
If it bleeds, is this normal or not?
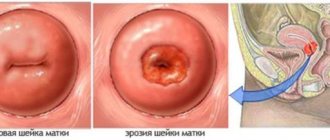
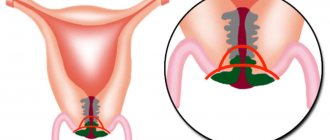
Cervical erosion is a small damaged area of the mucous membrane of the uterine pharynx. Visually it looks like a red spot at the external opening of the cervix.
Ectopia of the reproductive organ looks approximately the same . With this diagnosis we are talking about partial replacement of squamous epithelium with cylindrical epithelium, which manifests itself in redness of the vaginal area.
Does this condition have symptoms? Can cervical erosion bleed? Yes.
The last point adds anxiety, since the abundance of the “daub” varies:
- rare spotting (often a few days before menstruation);
- profuse bleeding;
- severe bleeding due to cervical erosion.
The symptom also appears under different circumstances:
- with increased physical activity;
- during or after sexual intercourse;
- during gynecological examination with mirrors;
- during douching;
- when trying to use a gynecological tampon.
The peculiarity of all types of discharge is independence from the menstrual cycle.
The cause of the pathology is erosion/ectopia of the cervix.
A specialist will make a more accurate diagnosis based on the results of the patient’s examination.
In terms of the frequency of manifestation of this variant of the clinical picture of the disease, it is a leader in medical practice.
Thanks to such a symptom as bleeding erosion of the cervix, every second woman still reaches the doctor’s office and learns about the erosive ulceration in time.
Erosion (ectopia) of the cervix and accompanying discharge:
Period
There are several signs by which erosion can be timely tracked before the first dangerous symptoms appear. First of all, they relate to the course of the menstrual cycle.
Usually, a few days before bleeding, a woman experiences brown discharge with an unpleasant odor. The brown color of the discharge should alert you and serve as a reason for a timely visit to a gynecologist and further diagnosis.
Delay
Important! Menstruation itself comes without delay, sometimes even before the due date. Problems begin after the disease is diagnosed and treated. Sometimes, after cauterization, the menstrual cycle is seriously delayed.
In this case, it is necessary, just in case, to rule out pregnancy, and consult with your doctor.
There are a huge number of methods for treating the disease , ranging from banal cauterization to removal of affected tissue. But if you detect the disease in a timely manner, monitoring the condition of your body and the nature of the discharge, you can easily get rid of erosion without receiving any negative consequences for the body.
Modern diagnostics and regular examinations twice a year by a gynecologist will help prevent and cure the disease in the early stages of its development.
Why does blood start to come out?
The main cause of bleeding is injury/damage to the mucous membrane, which was already not intact, having a defective area.
The following factors contribute to this:
- examination on a gynecological chair;
- active/rough sexual intercourse;
- use of vaginal contraceptives/hygienic tampons;
- installation/removal of an intrauterine device;
- ultrasound examination using a vaginal probe;
- surgical intervention (medical abortion, curettage).
If the bleeding was a one-time occurrence and stopped soon after the above reasons, this is considered normal and does not apply to gynecological pathologies.
Otherwise, specialists prescribe a comprehensive examination of the patient’s genitourinary system. What do the results indicate:
- a woman suffers from progressive erosion of the uterine os. The activation of pathology was facilitated by sexually transmitted diseases, human papillomavirus, pathogenic infections/viruses/microorganisms;
- the patient has a history of cervicitis;
- Polyps were discovered in the cervical canal, which, due to hormonal imbalance, changes in microflora, and severe stress, began to enlarge and bleed.
Treatment Options
Erosion of the cervix will bleed with exacerbation of inflammation and with serious pathology, so in this situation treatment cannot be delayed. After a complete examination, the doctor will prescribe therapy depending on the identified problems:
Detection of HPV or genital herpes
Identification of active human papillomavirus is the basis for a long course of antiviral therapy. Considering that HPV is transmitted sexually, both men and women will need a course of treatment. Only after completing all treatment procedures and a control examination for viruses can the erosion on the neck be cauterized.
Detection of other types of infections
For colpitis and cervicitis, the doctor will prescribe standard treatment to eliminate the inflammatory process. If control smears and colposcopy show that there is no infection, then cauterization can be performed using radio wave therapy or laser.
Common erosion
In the absence of inflammation and oncopathology, the cervical problem can be removed in the near future using conventional methods (using liquid nitrogen, a laser or the Surgitron device).
Cervical dysplasia
Detection of precancerous changes during colposcopy and biopsy is the main factor for surgical intervention. According to indications, diathermocoagulation and cauterization with radio waves should be performed. If there is a high risk of cancer, the doctor may suggest surgery.
Any intermenstrual bleeding is a reason to consult a doctor. One of the reasons for bleeding may be cervical erosion. It is necessary to identify the problem in time and get rid of the disease.
How to recognize whether true or pseudo-erosion is bleeding
To accurately diagnose an erosive lesion, a number of known factors are used:
- bleeding erosion does not depend on the menstrual cycle. The discharge is chaotic;
- the discharge is most often brown in color, sometimes with an admixture of ichor;
- With mechanical irritation of the mucous membrane, heavy bleeding may occur, which does not last long and stops on its own.
If the clinical picture of the pathology differs from the indicated points (bleeding does not stop for a long time, is accompanied by pain/discomfort, has an unpleasant odor), this may mean either uterine bleeding or the manifestation of other gynecological diseases (even oncology).
To clarify the situation, colposcopy is prescribed , which will describe in detail the condition of the mucous membrane of the uterine pharynx and help establish the correct diagnosis.
What to do
At the first signs of bleeding or suspicious spotting, a woman should seek medical help.
Firstly, the gynecologist needs to see them , because often the color/consistency/heaviness of bleeding says a lot about a potential diagnosis. An ultrasound should show the source of the pathology.
Secondly, the discharge may not stop . The woman will lose a lot of blood, her life will be in danger.
Thirdly, if the problem is only embarrassment in front of the doctor , then you can use a sanitary tampon or pad for convenience.
The slightest delay can cost a woman’s health. It is possible for the disease to progress, which could have been eliminated at the initial stage. This includes oncology, which has already taken many lives.
Is this condition dangerous?
How to assess the risk of erosion? Normally it shouldn't bleed .
During surgical interventions, the doctor himself will warn you how the rehabilitation period will go and how long the bleeding will last.
There are a number of dangers:
- excessive bleeding that is ignored can be fatal;
- scarlet/brown discharge with an unpleasant odor and an admixture of mucus/pus indicates an inflammatory process or a progressive disease of the genitourinary system;
- chronic discharge can result from tumor growth and its acquisition of oncogenic status;
- bloody “smears” are accompanied by HPV, polyps in the cervical canal.
Bleeding during pregnancy is especially It can be provoked either by erosion with concomitant pathogenic infection, or by placental abruption, which will lead to fetal death and premature birth.
A doctor's examination is required. Only he will make the correct diagnosis and draw up a competent treatment regimen for the woman. Perhaps this will save a woman’s life or preserve her health and reproductive function.
What is the disease
In essence, cervical erosion is an abrasion that can often become inflamed. Inflammatory processes lead to the rejection of epithelial cells, which in turn leads to exposure of the mucosa.
Exposed mucous membranes can bleed and cause a woman a lot of discomfort - pain, increased volume of discharge, infection, etc.
Erosion can occur in a woman of any age; causes are different:
- hormonal imbalances;
- mechanical damage as a result of rough sexual intercourse, unqualified medical examination, abortion;
- early sexual activity, interrupted pregnancy at a young age;
- the presence of a spiral;
- allergic reactions to sperm;
- sexually transmitted infectious diseases;
- inflammatory processes in the pelvic organs;
- lack of proper hygiene and so on.
Erosion can be:
- congenital. Such erosion is not considered a disease by many doctors; it is rather an anatomical feature of the body. This type of pathology is capable of self-healing, so it is almost never treated;
- true erosion lasts only two weeks, after which it moves to the next stage;
- pseudo-erosion is an attempt by the body to get rid of the disease on its own. In this case, the stratified squamous epithelium is replaced by a cylindrical one. Treatment in this case is necessary, especially for women who have oncogenic strains of papillomavirus in their blood.
Why might it bleed?
The manifestations of such a symptom are completely justified. In fact, erosion is the appearance of certain ulcers on the uterus , which gradually damage the connective tissue of this organ. If you do not bother with treatment in a timely manner, the disease enters the active stage, which is accompanied by the appearance of bloody discharge.
The reason for their appearance is quite simple and banal. When ulcers worsen, the mucous membranes begin to gradually peel off, thus leaving the body. In addition, the organ itself becomes inflamed, which leads to frightening consequences.
Symptomatic manifestations
In the early stages of the disease, symptoms do not appear in most cases. In some cases, erosion can cause some discomfort, but most often a woman attributes it to other reasons.
A woman may experience discomfort during sexual intercourse , as well as the presence of uncharacteristic discharge.
In rare cases, such minor symptoms can encourage a woman to make an appointment with a doctor. Most often, she simply ignores them, while the disease moves into the next stage.
In later stages, symptoms may become more characteristic. If an inflammatory process occurs, the discharge can be very copious and have an unpleasant odor.
Naturally, the clinical picture of different forms of erosion is slightly different:
- congenital erosion does not bother the patient at all;
- with true erosion, the volume of leucorrhoea increases, it can change color and have bloody impurities. After intimacy, slight bleeding may occur, which goes away on its own after a couple of hours. With true erosion, a woman most often does not feel pain, but in rare cases, discomfort may be observed during sexual intercourse. In some cases, spotting may not be related to sexual contact;
- pseudo-erosion is most often accompanied by infections and inflammation, so in this case the clinical picture becomes brighter.
After sexual intercourse, their intensity, as a rule, increases, in addition, blood may appear during sexual intercourse. Most often, sexual intercourse causes severe pain to a woman.
It is no longer possible to ignore such manifestations of the disease, and the woman consults a doctor. Therefore, the diagnosis of “erosion” is most often made in the later stages of the disease.
Bleeding from cervical cancer
Some forms of deep epithelial damage (dysplasia II and III) can degenerate into a malignant tumor. This process is long and gradual, and at home it is impossible to notice the transition of simple erosion into cancer. The only symptom of carcinoma may be bloody discharge from the vagina. Blood remains on underwear and pads, occurs outside of the menstrual cycle and indicates the beginning of tumor disintegration. Treatment in this situation is only surgical, and it is no longer just about eliminating unpleasant symptoms, but about saving a woman’s life.
It is important to know
Cervical cancer is often reported in menopausal women. The appearance of any strange discharge during menopause should not go unnoticed. It is imperative to undergo an examination by a gynecologist and find out the exact cause of these unpleasant symptoms.
Malignant tumors of the cervix may be accompanied by the appearance of copious watery discharge without a specific odor and signs of inflammation (itching, burning). Pain occurs in the later stages, when the tumor grows into neighboring organs. There is causeless weight loss and general weakness. Against the background of bleeding erosion, these symptoms should alert the woman. Do not delay treatment - the consequences can be very serious.
Why does bleeding occur?
As is already clear from the above, erosion can bleed, and this is one of the very first and most common clinical signs of the disease.
Erosion can bleed in the following cases:
- during or immediately after sexual intercourse;
- during severe physical exertion;
- when examined by a gynecologist using mirrors;
- when using tampons;
- during douching.
It is thanks to bleeding, which is the leader among all signs of erosion, that a woman finally reaches the gynecologist’s office, learns about her diagnosis and begins treatment.
The main reason why cervical erosion bleeds is trauma to the mucous membrane, which already has a defective area.
Emergency assistance for bleeding
What to do if the bleeding is very heavy? In this case, you cannot hesitate - you need to call an ambulance or urgently consult a doctor.
Before the ambulance arrives, you need to do the following:
- lie on the bed with a cushion under your feet;
- apply cold to the lower abdomen - ice or a heating pad with cold water. The ice pack must be wrapped in cloth to prevent frostbite. Cold is applied for 10 minutes, then a 5-minute break is taken;
- drink more fluids.
It is not recommended to take hemostatic agents before the ambulance arrives , but if bleeding occurs in a situation where medical help is unavailable, you can take Dicynone 0.25 g or Vikasol 0.015 g three times a day 4 times a day.
What not to do:
- apply a warm heating pad to your stomach;
- douche;
- to take a bath;
- take the pills before consulting your doctor.
If the bleeding is not very severe, you need to insert a tampon and immediately go to see a gynecologist. You should not wait until the bleeding stops. Firstly, the bleeding may increase, and secondly, the gynecologist must see the color, consistency and intensity of the bleeding. After all, most often it is these parameters of bleeding that can indicate to the doctor the cause of the pathology.
Treatment methods
Treatment of erosion can be medicinal and surgical.
Most often, as a drug therapy, patients with erosion are prescribed Solkovagin for a month.
For severe bleeding, the following medications are prescribed:
As for traditional medicine , it can only be used as a complement to drug treatment - these remedies cannot eliminate bleeding, and even more so they cannot eliminate their cause.
Folk remedies for erosion help get rid of itching and can have an effect on inflammatory processes.
Most often used to treat erosion:
- tampons with aloe, sea buckthorn oil or thuja oil;
- mumiyo;
- douching with decoctions and infusions of medicinal herbs.
In case of bleeding, douching is prohibited.
Unfortunately, drug therapy cannot always cope with bleeding erosion, so doctors prescribe surgical treatment:
- laser cauterization. This is an effective and less traumatic method of eliminating pathology. Erosion is burned out using a laser beam, while healthy tissue remains undamaged. Complete healing occurs within a month. Recommended for women who are planning pregnancy in the future;
- cryodestruction. This procedure involves the use of liquid nitrogen. The erosion is frozen, and the pathological areas are destroyed. Full recovery occurs no earlier than two months;
- diathermocoagulation. Prescribed for bleeding. This is a rather painful procedure, during which high-frequency current is used. It is not recommended for nulliparous patients, since after the procedure scars may remain, complicating pregnancy and childbirth;
- chemical coagulation . In this case, erosion is treated with special preparations. There are no scars left after the procedure, complete rehabilitation period is two months;
- radio waves. A painless and quick procedure that does not leave wounds or scars. The integrity of the mucous membrane is not compromised; complete recovery occurs within a month;
- in the case of a precancerous condition, the affected area is amputated .
What to do if cervical erosion is bleeding
Not all women know what to do if cervical erosion bleeds. To treat this symptom, immediate action must be taken.
Discomfort and minor bleeding with cervical ectopia are among the most common complaints when examined by a gynecologist. The cervix can bleed for various reasons. According to statistics, this problem has no age restrictions, so it can occur in young and mature women. Many girls do not know what to do if cervical erosion begins to bleed.
Conditions in which bleeding occurs due to pathology
Bloody discharge against the background of erosion can appear in a variety of situations:
- After sexual intercourse,
- When inserting tampons,
- When using barrier contraception (diaphragm),
- After examination by a gynecologist (bimanual, in speculum),
- When taking a smear or performing other medical procedures,
- After transvaginal ultrasound,
- When douching,
- When administering suppositories and vaginal tablets.
In all these situations, mechanical damage to the mucous membrane occurs and bleeding of varying intensity occurs. Can we say that such bleeding is normal? It would be more correct to say that with erosion this is a common symptom, and often it is suspicious discharge that becomes the reason for examination by a gynecologist. A photo of the bleeding erosion can be seen below.
View of the cervix. Against the background of acute cervicitis, bleeding vessels stand out.
The development of bleeding in the following situations deserves special attention:
- During pregnancy,
- With exacerbation of the inflammatory process in the cervix.
Here we are no longer talking about mechanical damage to tissue, but about disruption of the vaginal biocenosis and/or hormonal changes. In these situations, a comprehensive examination is required to exclude concomitant pathology and select the optimal treatment regimen.
It is important to know
Any bleeding from the genital tract that is not associated with menstruation is a reason to visit a doctor.
Symptoms
The nature of erosion varies, so usually the cause becomes known after a series of diagnostic studies. If cervical erosion bleeds intensely, this will be accompanied by the presence of streaks of fresh blood in the mucous discharge, spotting or brown discharge.
Ectopia is quite easy to detect at the first gynecological examination. If a hyperemic defect is detected, which begins to bleed upon slight contact with the mirror, the doctor can diagnose true erosion. Pseudo-erosion may be present, which is characterized by the replacement of squamous epithelium with cylindrical epithelium. But externally the lesions look the same. Columnar epithelium, located in an uncharacteristic location, is perfect for the development of bacterial infections in the cervix. There are several types of erosion:
- True erosion. This is a wound that is a reaction to any damaging factor. The circumference of the cervical canal becomes bright red and begins to bleed at the slightest contact or after sexual intercourse.
- Pseudo-erosion. The result of improper healing of the true form. This type is characterized by the absence of specific symptoms, and when an infection occurs, the lesion becomes inflamed and may bleed upon contact.
- Congenital erosion of the cervix. This type of pathology does not bleed. The congenital form has the most favorable course and most often regresses before the age of 20.
In addition, diseases may occur on the cervix that accompany or are a consequence of ectopia and can bleed:
- Leukoplakia is diagnosed during a gynecological examination and has the appearance of a whitish spot that can bleed on contact. Appears as a result of long-term human papillomavirus infection (the most dangerous form) or as a consequence of injuries and ectopia.
- Ectropion appears after trauma to the mucous membrane, childbirth or surgery. The appearance is an inverted mucous membrane of the cervical canal. Bleeding is not typical.
- Erythroplakia. It has the appearance of a stagnant red spot; it occurs when the epithelial cells atrophy, and its basal layer, on the contrary, hyperplasias. Most often it is the result of persistence of HPV. It is considered a precancerous pathology. The area may bleed.
- Dysplasia. Atypical changes in the structures of epithelial cells with damage to the nucleus and cytoplasm. It is the result of a human papillomavirus infection and can bleed.
You should know that any acyclic bleeding, even of low intensity, requires immediate consultation with a doctor. Bleeding first requires the exclusion of cervical cancer.
What danger is there?
Only true erosion and dysplasia are considered dangerous. It carries a hidden but very dangerous threat.
Gradually, both can develop into cervical cancer. This cancer leads to the need for organ removal or complete infertility.
In addition, erosion leads to a complete or temporary cessation of sexual activity (at least for the duration of treatment). Advanced stages require constant monitoring and medical supervision.