Although it is believed that the body is a complex self-regulating system, sometimes surgery cannot be avoided. In the animal world, the rule of natural selection operates - those who are stronger, more resilient, and healthier survive. Human life is expensive to carry out such experiments. Therefore, people with serious malfunctions in the body decide to undergo surgical intervention in order to correct the painful condition. Before operations are performed, the pros and cons are weighed, taking into account the chances of improvement and the risks of negative consequences.
Surgery to remove prostate adenoma: time and rehabilitation
How long the operation to remove prostate adenoma lasts depends on the condition of the patient and his age, the size of the hyperplasia, and the capabilities of the medical institution. One of the factors determining the time of its implementation is the method of intervention: transurethral resection (TUR), laser treatment, laparoscopy, open surgery.
Transurethral resection
TUR is a minimally invasive method, performed for mild forms of the disease, if urination is not completely impaired, the kidneys and urethra are not damaged by pathology. The benign tumor is removed using an endoscopic device (resectoscope) using high-frequency electric currents. Excision is prescribed if the size of the adenoma is no more than 80 mm.
The patient is in a supine position: legs apart and bent at the knees. A resectoscope is inserted through the urethra, the prostate gland is reached and part of the overgrown tissue is removed. At the same time, the urethra expands and the blood vessels are cauterized (coagulated).
The duration of the procedure is 30 minutes. Upon completion, the endoscopic device is carefully removed, and a rubber tube is inserted into the urethra to drain urine after the operation. The biopsy material is sent to a histology laboratory to differentiate cancer (carcinoma). The catheter is removed after 7 days. General or epidural anesthesia is used.
The most minimally invasive removal of a benign tumor ensures a rapid rehabilitation period:
- two-day hospitalization;
- the catheter is placed for no more than 24 hours;
- full recovery occurs within two weeks.
Laser treatment
Using a laser, adenoma can be removed in two ways:
- ablation (prescribed to young patients when the gland enlarges to 140 ml. The essence is burning or evaporating the area of pathological growth).
- enucleation (all benign formations are removed).
- Contact vaporization: with the help of endoscopic equipment and visual control, small hyperplasia (adenoma) is evaporated.
- Contact resection: cutting out the adenoma, requires the skill of the surgeon.
- Interstitial coagulation: The laser is inserted through punctures in the bladder. The energy of the laser beam atrophies tumor tissue and reduces its growth.
- Green laser: the beam penetrates into the deepest layers of the organ, the gland is evaporated, in many cases it is not even necessary to insert a catheter.
Depending on the method, size and condition of the prostate, the duration of the procedure ranges from 20 to 110 minutes.
Radical prostatectomy
Surgical excision of the tumor is performed through open surgery, laparoscopy, and robotic laparoscopy. The goal of surgery is to remove the entire tumor, sometimes with cutting out adjacent tissue and nerves, which can lead to erectile dysfunction. To get to the tumor, an incision is made in the perineum (between the scrotum and anus). If indicated, the lower abdomen may be incised. After adenomectomy, a rubber tube is inserted into the bladder for 1-3 weeks. Open adenomectomy lasts 2-3 hours and is performed under general anesthesia. Today this method is used extremely rarely.
Manual laparoscopy
Several incisions are made in the abdomen: a laparoscope with a video camera is inserted into one hole to monitor the progress of the operation; surgical instruments are inserted through other holes to remove hyperplasia. The operation lasts from 2.5 to 3 hours.
Robotic prostatectomy
A less traumatic, more modern procedure with fewer complications. Robotic manipulators perform more subtle and precise movements and hold surgical instruments. This type of surgery is becoming increasingly popular. The duration of surgical laparoscopy is 2.5-3 hours.
The final choice of method depends on the patient’s physical condition and the doctor’s recommendations.
Diagnostics
Ideally, each patient should undergo a detailed medical examination to understand whether surgery can be performed for the given indications. In general cases, a standard commission examination is carried out. At the appointment, the patient declares the presence or absence of complaints about health.
If there are existing health problems, additional examinations are prescribed. In some cases, a complete blood test and x-ray will be sufficient. In others, you may need the results of additional tests, electrocardiography data, ultrasound diagnostics, MRI, and specific tests.
Regardless of the quality of preoperative preparation, the patient is examined by an anesthesiologist before surgery using general anesthesia. Additionally, the absence of contraindications related to the respiratory system, cardiovascular system, and mental disorders is checked.
Laser vaporization of prostate adenoma
Laser vaporization of prostate adenoma is considered the most gentle and popular operation in the world.
It is performed through the urethra, without incisions, under eye control, under spinal (epidural) anesthesia, the patient does not feel pain.
After laser evaporation, a channel of 3–3.5 cm is obtained, which guarantees the patient quality urination for many years of life.
The evaporated prostate adenoma is removed along with the washing liquid. Laser surgery on prostate adenoma lasts about an hour, the next day after the operation the patient has the catheter removed, he urinates on his own and goes home.
Operation duration
Depending on the type of manipulation, removal of the affected areas and reconstruction of the organ can take from 30 minutes to several hours. The scale of the intervention, the severity of the disease and the qualifications of the doctor also determine how long the operation will take. Removing the cervix through the vagina usually takes up to 60 minutes, using the laparoscopic method – up to 2 hours. In case of malignant tumors, amputation of the uterine cervix can take more than 2.5 hours. If it is necessary to collect tissue for histological analysis and in case of complications, the duration of the operation increases. The simplest manipulation of the cervix is conization, during which the surgeon removes a cone-shaped area of the affected tissue. Such an intervention does not involve cutting off the entire neck, but only part of it, and lasts 15-40 minutes.
A more complex type of surgical procedure is hysterectomy, in which the cervix is removed along with the body of the uterus, but the fallopian tubes and ovaries remain. The operation is performed for cancer, rapid growth of benign tumors, complicated endometriosis, and polyposis. A hysterectomy can last from 40 minutes to 4 hours (in later stages of cancer).
Laser enucleation of prostate adenoma
Laser enucleation of prostate adenoma is a laser technique in which adenomatous nodes are enucleated using a holmium laser. This operation is used mainly for large prostate adenomas. Its effectiveness is comparable to open adenomectomy.
The negative side is:
- A very high percentage (almost 90%) of retrograde ejaculation
(when sperm enters the bladder during orgasm). - Enucleation is not suitable for small prostate adenoma, since the adenomatous node is cut off at the base, and there is close to the wall of the bladder or the abdominal cavity.
- And also due to the fact that this technique uses a direct radiation fiber, therefore quite often there are perforations of the prostate capsule with damage to the vascular bundle.
The operation is difficult to master and perform, so in Europe laser enucleation accounts for only 5-7% of the total number of laser operations. It is recommended to use this technique for prostate volumes greater than 60 cm3.
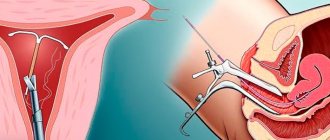
How long does it take to remove the fallopian tube?
In terms of the frequency of ectomies in gynecology, the uterine appendages lead, and removal of the fallopian tube (tubectomy or salpingectomy) is in second place after removal of the ovaries.
The first such radical surgical intervention, which saved the life of a patient with bleeding during an ectopic pregnancy, was performed in 1883 by Scottish surgeon Robert Lawson Tate.
[1], [2], [3], [4], [5]
Indications
The main indications for removal of the fallopian tube include removal of the tube during an ectopic pregnancy: when bleeding occurs after salpingotomy (surgery to remove a tubal pregnancy while preserving the tube); in case of perforation of the fallopian tube due to a violation of pathological pregnancy (tubal abortion); when the size of the fertilized egg in the tube is more than 3.5-4 cm; in cases of repeated ectopic pregnancy in the same tube.
If conservative therapy does not give positive results, the fallopian tubes can be removed in case of inflammation of their tissues - salpingitis, and in cases of purulent salpingitis, the fallopian tube, where purulent exudate has accumulated, is removed in most patients, as in pyosalpinx and tubo-ovarian abscess.
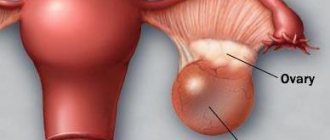
Salpingitis can provoke an inflammatory process in the ovary, and then gynecologists diagnose inflammation of the appendages - adnexitis or salpingoophoritis, which threatens either an ectopic pregnancy or irreversible dysfunction of the appendages leading to infertility. And the way out may be laparotomic or laparoscopic removal of the ovary and fallopian tube.
When there are adhesions between the ovary and the tube, quite often the tube stretches, and in this place the fluid secreted by the mucous membrane accumulates with the development of a chronic pathology - hydrosalpinx. The fluid often contains pus, and if this cavity ruptures, the woman is in real danger of peritonitis.
In addition, as a result of hydrosalpinx, obstruction of the fallopian tubes develops, which is one of the most common causes of female infertility. Removal of the tube during hydrosalpinx, undertaken in such situations, increases the incidence of pregnancy after in vitro fertilization and reduces the risk of developing pregnancy outside the uterine cavity.
Therefore, a protocol for conducting IVF after removal of tubes (both) has been developed.
By the way, the removal of adhesions in the fallopian tubes, which make women infertile, can be carried out by tubectomy - provided that all other methods of separating the overgrown fibrous cords have been unsuccessful.
Among the indications for performing this operation laparotomically, tuberculosis of the appendages, uterine fibroids, ovarian cancer and intraepithelial cancer of the fallopian tubes should be noted.
Removal of the hydatid fallopian tube - subserous cyst - is carried out in cases of twisting of its stem, and removal of the entire tube may be necessary only if these cysts are significant in size and there are multiple adhesions localized around them.
In recent years, evidence has been obtained that the development of most ovarian serous carcinomas is associated with the fallopian tubes.
As a result, recommendations have emerged for the use of prophylactic salpingectomy (opportunistic salpingectomy) for patients with hereditary mutations of the BRCA1 and BRCA2 genes in order to prevent the development of ovarian cancer.
According to the International Journal of Obstetrics & Gynaecolog, unilateral tubal removal reduces the risk of ovarian cancer in this category of women by 29%, and removal of both fallopian tubes by 65%.
[6], [7], [8], [9], [10], [11], [12] The fallopian tubes provide the connection between the uterus and the ovaries. In them, fertilization of the egg occurs and its further movement into the uterus for consolidation there.
But in some cases there is no chance to save female organs. In this case, a special operation is performed - tubectomy - removal of the fallopian tubes.
The consequences for the body after such an intervention may be different, but they do not always occur.
Why are fallopian tubes removed?
Surgery to remove the fallopian tubes is performed urgently or planned. Surgery on the fallopian tubes is necessary for health or life-threatening disorders of their functions, as well as anatomical anomalies.
Most often, such intervention is necessary when:
- A ruptured tube as a result of an ectopic pregnancy. This is accompanied by profuse internal bleeding and can be life-threatening. Therefore, removal of the fallopian tube during an ectopic pregnancy is a necessary measure.
- Undisturbed ectopic pregnancy, when the situation cannot be corrected with conservative surgical therapy.
- Unbroken, but repeated tubal pregnancy on the same side.
- Inflammatory processes of a chronic nature - purulent salpingitis, salpingo-oophoritis, hydrosalpinx on the left or right. Such pathologies are not uncommon lately; their number is only growing from year to year. Early onset of sexual activity, sexually transmitted infections, and abortions cause the development of inflammatory pathologies of the female genital organs, which lead to infertility.
- Pyosalpinx (accumulation of pus in the lumen of one or both fallopian tubes).
- Planning pregnancy with the help of reproductive technologies, if infertility is diagnosed that is not amenable to conservative therapy, caused by hydrosalpinx or chronic salpingitis. For example, with hydrosalpinx, fluid collects in the fallopian tube, which has a toxic effect on the endometrium and the fertilized egg, and may even interfere with implantation, especially if the pathology worsens. Removal of the tube in this case is necessary to increase the effectiveness of the IVF procedure. In addition, tubectomy prevents the onset of a possible tubal pregnancy. But at the same time, intervention can lead to deterioration in egg maturation and suppression of ovulation, so it is usually recommended for large tubes and if hydrosalpinx on the left or right was discovered more than 6 months ago.
- Rupture of an ovarian cyst or twisting of its legs.
- A pronounced adhesive process in which the appendages are also involved.
- Tuboovarian formations, large or multiple fibroids, malignant tumors, external endometriosis, colon oncology. Often, with such pathologies, the tube is removed along with the rest of the female organs.
- Gangrenous perforated appendicitis or Crohn's disease, which are accompanied by peritonitis, as a result of which the appendages were involved in the pathological process.
The operation to remove the fallopian tubes is performed laparotomy or laparoscopically.
Intervention by laparotomy
This is an abdominal operation. The patient is given a longitudinal or transverse incision in the abdominal cavity. The first method is simpler; it is used in emergency cases, when it is necessary to immediately stop heavy bleeding, as well as for adhesions in the pelvis, large tumors of various nature.
The second method is considered less traumatic; during the operation it is possible to apply a cosmetic skin suture, and the recovery period after the intervention is shorter. The indications for using this method are the same, but do not require emergency measures. The operation is also performed in this way if laparoscopy is not possible.
The operation on the fallopian tubes itself is carried out as follows:
- apply clamps to the uterine tube and mesentery, which helps stop bleeding (if any);
- cut adhesions if necessary;
- Having separated the pipe above the clamps, remove it.
If there are no adhesions and the abdominal cavity is not heavily filled with blood, then the operation lasts about forty minutes.
In some cases, instead of completely removing the tubes, partial excision is performed. This procedure is possible if the patient:
- the adhesive process covers small areas;
- an ectopic pregnancy develops, but the tube has not yet ruptured;
- there is a small benign tumor in one of the segments of the uterus.
Laparoscopic intervention
It is carried out by introducing instruments into the abdominal cavity through three small incisions. During the intervention, a laparoscope is used, which looks like a flexible tube with a camera at the end. An image is displayed on the monitor, which allows the gynecologist to assess the condition of the reproductive organs, detect abnormalities and perform surgery.
Intervention performed using laparoscopy is less traumatic. The recovery period after treatment does not last long and is easy.
- The abdominal cavity is prepared. For this purpose, an incision is made in the area near the navel, through which a Veress needle is inserted, through which the abdominal cavity is filled with carbon dioxide. Such manipulations allow you to raise the abdominal wall, which helps to better view the internal space.
- The needle is removed and replaced with a laparoscope.
- Two more incisions are made into which the gynecologist inserts instruments.
- After assessing the condition of the abdominal cavity and identifying the problematic organ, clamps are placed and the vessels are ligated.
- The fallopian tube is removed.
- The instruments are removed. Cosmetic sutures are applied to the puncture area using self-absorbing threads.
Source: https://ginekologiya-urologiya.ru/operacii/skolko-po-vremeni-dlitsya-operatsiya-po-udaleniyu-matochnoj-truby
TOUR of prostate adenoma
Endoscopic types of operations include primarily TUR – transurethral resection of the prostate. During a TUR of the prostate, the resectoscope is inserted through the urethra (transurethral) and the adenomatous nodes are cut off layer by layer from the inside. The operation is performed using a steel loop at the tip of the resectoscope through which an electric current
.
A glucose solution is used as a washing liquid for TUR. The use of glucose solution during surgery can lead to a very serious and life-threatening complication for the patient.
, which is called TUR syndrome. Through the cut and bleeding veins of the prostate, the glucose solution is reabsorbed, which enters all internal organs and they gradually begin to fail. The so-called water intoxication of the body occurs, which can lead to death.
Complications after TOUR include:
- long-term blood in the urine
- urinary incontinence
- retrograde ejaculation (when sperm enters the bladder), which, according to statistics, occurs with this operation from 50 to 100% of cases
- urinary tract infections and inflammations
- urethral strictures (scar narrowing of the urethra), requiring repeated surgery
What to expect after cervical removal?
A consequence of trachelectomy is brown discharge, which is normal and can last up to 6 weeks. If you experience bloody or purulent discharge with an unpleasant odor, as well as a high temperature, you should immediately consult a doctor.
Rarely, complications may occur in the form of suture infection, vein thrombosis, bleeding, lack of menstruation, and bladder damage. If the vagina is shortened during surgery, sexual intercourse may be accompanied by pain.
Sometimes, after surgery, scars remain on the organ. This can pose a health risk to the woman if she gives birth, as there is an increased risk of rupture and bleeding. Scar tissue is easily removed using radio wave surgery. The procedure is painless, does not leave wounds or burns, and is performed with the Surgitron device.
Pregnancy after trachelectomy is possible, but in some cases there may be problems. Narrowing or closure of the cervical canal and decreased mucous production can interfere with conception. Sometimes difficulties arise with pregnancy due to the loss of the optimal position of the uterus. The installation of pessaries - special supporting devices - will help to avoid this.
Partial or complete amputation of the cervix makes natural childbirth impossible. After manipulation, a stump remains in place of the neck, unable to mature, i.e. shorten and expand to accommodate the passage of the child. A woman can only give birth through a caesarean section.
Cervical diseases are increasingly diagnosed in patients of reproductive age. But gynecology does not stand still and new treatment methods are emerging that preserve a woman’s ability to give birth to a child. Regular monitoring of the health of the reproductive system and timely detection of diseases are important. After all, the sooner you start treating the disease, the greater the chances of preserving the organ and not losing the opportunity to become a mother.
Video: trachelectomy - treatment of cervical cancer while preserving reproductive function
Trachelectomy - treatment of cervical cancer while preserving reproductive function
Video: radical trachelectomy: 10 years of experience of the Moscow Scientific Research Institute
Radical trachelectomy: 10 years of experience at the Moscow Oncology Research Institute named after P.A. Herzen
Open prostate adenomectomy
Open adenomectomy is an abdominal operation on the prostate gland. Access to which is made through an incision in the wall of the abdomen and bladder. This operation is used for large nodular prostate hyperplasia in combination with bladder stones.
Quite serious complications are very common with open adenomectomy.
- During the operation, there is severe bleeding as the surgeon blindly pulls out the adenomatous nodes with his fingers. In this case, damage to surrounding organs and tissues is possible, leading to postoperative complications.
- In the postoperative period, prolonged blood in the urine
- total urinary incontinence
- erectile disfunction
- retrograde ejaculation (dry orgasm)
- Sclerosis of the prostatic urethra (scar narrowing of the canal at the site of surgery)
There have been cases when, during open adenomectomy, the sphincter was damaged in patients and cicatricial narrowings occurred in the area of the removed prostate adenoma. And it turned out that the patient urinated drop by drop, and was also constantly wet due to urinary incontinence. Both of these complications required surgical correction. Due to the large number of complications, this type of operation is of only historical interest.
There are contraindications, consult a specialist.
How long does it take to do the surgery?
Surgery may last minutes or extend to hours. It all depends on the type, purpose, complexity of the procedure. When operating for several hours at a time, surgical teams work in shifts so that doctors have the opportunity to rest. In special cases, additional specialists from related fields may be involved if highly specialized consultation is required during the main procedure.
Some operations are performed under general anesthesia, others under local anesthesia. If the effect is minor and fleeting (pulling out a loose tooth), you can avoid the anesthetic altogether. The total duration of the intervention also depends on the time of the preparatory and final procedures. There are cases when the main effect takes a minute, but access to the source requires much more time.
How the surgery is done can also affect the duration. The fundamental principle is that the incision is made as minimal as possible, but so that it provides operational space. If everything goes according to schedule, that’s one thing, but there are often unforeseen situations and complications (bleeding, shock). There is a need to prolong the effect of anesthesia or anesthesia to remove the patient from a critical condition, stop the wound, and complete the operation.
Operation
Good afternoon Please answer my questions. What anesthesia is used for laparoscopic surgery for left varicocele? Approximately how long does it last? How long does the postoperative period last? Is a catheter installed in the bladder after surgery and for how long? Thanks in advance for your answers!
Dear Alexey. During laparoscopic surgery for varicocele, general anesthesia (endotracheal) is given. The operation lasts about 30 minutes. The postoperative period is 1 day. A catheter is not inserted into the bladder.
Good afternoon. My grandmother is 65 years old. She had surgery to remove a tumor on her bladder in March. After the operation, she underwent one chemotherapy in May. And in August they did an ultrasound and found a tumor again. The doctor says that the urine needs to be removed, but it is very expensive. Why did it appear so quickly and what do you recommend doing? We live in the Dnepropetrovsk region. Thank you in advance.
Hysterectomy
The operation to remove the uterus, hysterectomy, is one of the most extensive gynecological operations. It is carried out only in cases where other methods of treatment or surgery do not make it possible to completely eliminate the pathology.
Indications for such surgical intervention include:
- Malignant tumors of the uterus
- Rapidly growing benign tumors (signs of malignancy)
- Uterine ruptures (most often found during childbirth or major trauma)
- Endometriosis (uterine mole)
- Advanced forms of uterine prolapse and prolapse
Hysterectomy is a fairly extensive operation, which requires special preparation and the creation of a rehabilitation course. The most common complication during a hysterectomy is bleeding. It is worth noting that such a complication can develop with any surgical intervention.
A hysterectomy leads to irreversible changes in a woman’s body - she will no longer be able to have children. At the same time, due to the preservation of the ovaries, premature menopause may not occur, which allows maintaining normal hormonal levels for a long time.
The operation to remove the uterus takes varying amounts of time. The duration of the operation depends on several factors, such as the level of qualifications of the doctor, the indication for the operation, as well as the individual characteristics of the body (the presence of adhesions in the abdominal cavity, etc.).
The shortest duration is the operation to remove the uterus, which is performed for such indications as endometriosis, early stages of cancerous tumors without germination into surrounding tissues, benign tumors, and total polyposis. In such a situation, with the proper level of skill of the doctor, the operation can last within 40 minutes, but rarely exceeds 1 hour.
IMPORTANT! The most severe cases are considered to be surgical interventions that are performed in the later stages of uterine cancer. In such a situation, a large amount of time is required to mobilize (separate from surrounding tissues) the uterus and tumor.
At the same time, the duration of the operation can exceed 3-4 hours, as long as it takes the doctor to completely remove the affected tissue.
Hysterectomy is performed under endotracheal and epidural anesthesia.
Complete recovery takes at least six months, since complete healing of the tissues of the anterior abdominal wall is a long process.
Laser vaporization of prostate adenoma
Laser vaporization of prostate adenoma is considered the most gentle and popular operation in the world.
It is performed through the urethra, without incisions, under eye control, under spinal (epidural) anesthesia, the patient does not feel pain.
After laser evaporation, a channel of 3–3.5 cm is obtained, which guarantees the patient quality urination for many years of life.
The evaporated prostate adenoma is removed along with the washing liquid. Laser surgery on prostate adenoma lasts about an hour, the next day after the operation the patient has the catheter removed, he urinates on his own and goes home.
Positive factors of laser surgery on adenoma:
- bloodlessness
- absence of retrograde ejaculation
- no urinary incontinence
- short recovery period
- applicable for all prostate sizes
There are no negative factors for laser vaporization!
Laser enucleation of prostate adenoma
Laser enucleation of prostate adenoma is a laser technique in which adenomatous nodes are enucleated using a holmium laser. This operation is used mainly for large prostate adenomas. Its effectiveness is comparable to open adenomectomy.
The negative side is:
- A very high percentage (almost 90%) of retrograde ejaculation
(when sperm enters the bladder during orgasm). - Enucleation is not suitable for small prostate adenoma, since the adenomatous node is cut off at the base, and there is close to the wall of the bladder or the abdominal cavity.
- And also due to the fact that this technique uses a direct radiation fiber, therefore quite often there are perforations of the prostate capsule with damage to the vascular bundle.
The operation is difficult to master and perform, so in Europe laser enucleation accounts for only 5-7% of the total number of laser operations. It is recommended to use this technique for prostate volumes greater than 60 cm3.
TOUR of prostate adenoma
Endoscopic types of operations include primarily TUR – transurethral resection of the prostate. During a TUR of the prostate, the resectoscope is inserted through the urethra (transurethral) and the adenomatous nodes are cut off layer by layer from the inside. The operation is performed using a steel loop at the tip of the resectoscope through which an electric current
.
A glucose solution is used as a washing liquid for TUR. The use of glucose solution during surgery can lead to a very serious and life-threatening complication for the patient.
, which is called TUR syndrome. Through the cut and bleeding veins of the prostate, the glucose solution is reabsorbed, which enters all internal organs and they gradually begin to fail. The so-called water intoxication of the body occurs, which can lead to death.
Complications after TOUR include:
- long-term blood in the urine
- urinary incontinence
- retrograde ejaculation (when sperm enters the bladder), which, according to statistics, occurs with this operation from 50 to 100% of cases
- urinary tract infections and inflammations
- urethral strictures (scar narrowing of the urethra), requiring repeated surgery