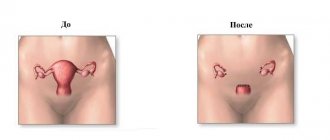
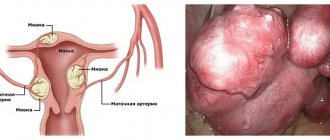
Hysterectomy, or hysterectomy, is a gynecological operation in which the uterus is removed along with the cervix and appendages (ovaries and tubes).
- Indications
- How is hysterectomy performed?
- Extended hysterectomy
- What other types of operations are there?
- What types of operations are most often performed in oncology?
- Which method of hysterectomy is better?
- Possible complications
How is hysterectomy performed?
Hysterectomy can be performed using several methods:
- Laparotomy is an open method through an incision in the anterior abdominal wall.
- Laparoscopic hysterectomy. The intervention is carried out with the help of auxiliary endoscopic equipment through punctures of the anterior abdominal wall, and the direct removal of organs is carried out through an incision in the area of the vaginal vault.
Extirpation of the uterus using the laparotomy method
- A layer-by-layer incision is made in the tissues of the anterior abdominal wall from the navel to the pubic symphysis. The skin, subcutaneous tissue, aponeurosis and peritoneum are cut.
- For better access to the operated tissues, mirrors are inserted into the wound and expanded.
- The uterus is grabbed by the bottom using special instruments and removed from the wound.
- Clamps are applied to the round ligament of the uterus and its intersection is performed.
- To remove the fallopian tubes and ovaries, the infundibulopelvic ligament of the ovary is isolated, clamps are applied to it, crossed and tied.
- Next, the broad ligament of the uterus and the peritoneum of the vesicouterine space are opened. They are separated and lowered down along with the bladder.
- Then the vascular uterine bundles are isolated, clamps are placed on them, they are crossed and ligated.
- Then the walls of the vagina are opened and the uterus is separated from its fornix.
- The wound is sutured in layers and cosmetic sutures are applied to the skin.
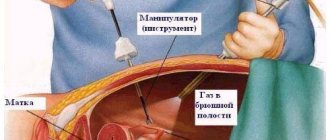
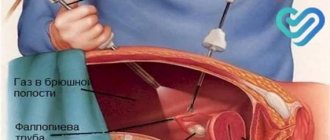
Laparoscopic hysterectomy
During laparoscopic removal of the uterus, manipulations are performed through 4 punctures. The first is located just above the navel; through it, using a Vischer needle, air is supplied into the abdominal cavity to increase its volume and “straighten” the organs. Next, two symmetrical punctures are made in the iliac regions and one under the navel. Trocars are inserted through these punctures. With their help, all manipulations that are performed during the abdominal method of hysterectomy are performed.
The use of a morcellator (shredder of large organs) during oncological operations is prohibited, since contamination with malignant cells and the development of multiple metastases may occur. Therefore, the organs are removed through an incision in the vaginal area. To prevent “depressurization” of the abdominal cavity, an obturator is installed in the vagina. The uterus together with the cervix is cut off from the vaginal vault and the stump is sutured.
Complications
Complications that may arise in the postoperative period include:
- postoperative bleeding;
- suppuration of the surgical wound;
- formation of adhesions in the abdominal cavity.
A special feature of this intervention is changes affecting the reproductive function of women. This could become a psychological trauma for her, but there is no point in worrying and worrying about this. You need to correctly assess the pros and cons of the operation.
So, after surgery to remove the uterus, the following consequences are possible:
- cessation of menstruation – surgical menopause or amenorrhea;
- absolute infertility - it is possible to obtain offspring only through IVF with a surrogacy program;
- reducing the risk of developing ovarian cancer;
- increased risk of pelvic organ prolapse.
The cessation of menstruation does not indicate a loss of femininity. It is important to understand that when the uterus is removed, the ovaries remain in place and continue to function as usual; only the visible sign of their work – menstruation – is absent. Therefore, removal of the uterus or removal of the fallopian tubes is not equivalent to the onset of menopause. Menopause occurs in women with a removed uterus at the age at which it would have occurred if the uterus had not been removed. The inability to give birth is a serious problem, especially for those who do not yet have children. But there is a surrogacy program in which your eggs can be used for fertilization. This will be genetically your child. As a last resort, you can adopt a baby; many children from the orphanage need affection and care.
There is, of course, a risk of pelvic organ prolapse, but there are a number of exercises to strengthen the pelvic floor. Additionally, exercising can also help. You need to monitor your weight, as obesity can be a provoking factor. The big plus is that the unpleasant symptoms of the disease that bother you will disappear. In addition, studies show that when the uterus is removed, the likelihood of developing ovarian cancer decreases.
After the rehabilitation period, the woman can lead a normal life and have sexual intercourse.
Extended hysterectomy
This operation involves removing tissue in the following volume:
- Uterus.
- Cervix.
- Fallopian tubes.
- Ovaries.
- The lateral parametrium is removed to the ureters.
- The ureters themselves do not tunnel.
- The anterior parametrium and posterior parametrium are not deleted.
- Blood vessels are excised as close as possible to the uterus.
- Vaginal resection is not performed or is performed to a minimal extent.
- If necessary, pelvic lymph nodes are removed.
This intervention is also called type 1 hysterectomy and is provided for the surgical treatment of stage 1b and 2a cervical cancer. For other types of cancer, the scope of the operation may be wider.
What is included in the cost of the operation and its features
The cost of any operation, regardless of its type, includes an initial appointment and examination by a gynecologist. The cost of this service averages 1,000 rubles per appointment.
Taking blood and urine tests, undergoing an ultrasound, cardiogram, and chest x-ray will cost 10,000 rubles . Before the operation, the patient must undergo an endometrial biopsy procedure, the cost of which can vary from 3,000 to 9,000 rubles .
The cost of an open operation is 13,000-20,000 rubles . The price for a vaginal hysterectomy will be about 30,000 rubles . The minimum cost of laparoscopic intervention will be 20,000 rubles .
In addition, it is necessary to take into account intimate plastic surgery, which is necessary in special cases. Its cost can reach about 25,000-30,000 rubles . The rehabilitation course, which includes examination and the services of medical staff to care for the patient after the procedure, is 30,000-35,000 rubles .
What other types of operations are there?
In oncological practice, the volume of tissue removed during hysterectomy is determined by the main diagnosis and stage of cancer. The most gentle operation is panhysterectomy of the first type, which we described above.
Hysterectomy II or type B involves working with tissue in the following volume:
- Resection (partial removal) of the sacrouterine and vesicouterine ligaments is performed.
- The ureters are tunneled.
- Resection of the paracervical ligament is performed at the level of the tunneled ureters.
- The upper third of the vagina is removed.
- The pelvic lymph nodes are removed.
Hysterectomy class C:
- Lateral (lateral) parametrial tissues are removed to the iliac vessels.
- The vesicouterine ligament is removed down to the bladder.
- The uterosacral ligament is removed down to the rectum.
- Complete mobilization of the ureters is also performed.
- According to indications, the pelvic nerves can be transected (operation type C 2).
- ¾ of the vagina and pelvic lymph nodes are removed.
Book a consultation 24 hours a day
+7+7+78
Class D hysterectomy
Class D hysterectomy is the most extensive and difficult operation. It is also called partial exenteration, since it involves not only the removal of all internal female genital organs, but also partial removal of the bladder and rectum. It is performed for highly aggressive tumors or locally advanced cancer that has affected neighboring organs:
- All tissue located between the obturator internus muscle and the lumbosacral nerve plexus is removed.
- Partial removal of the iliac blood vessels and, of course, lymph nodes is also carried out.
Indications
Uterine amputation is prescribed in the following cases:
- cancer of any location with metastases to the genital organs;
- benign tumor formation of the uterus and/or appendages, affecting the functioning of neighboring organs;
- fast-growing fibromyoma of gigantic size, which cannot be treated in any other way;
- abnormalities of organ development, including acquired ones (for example, prolapse, prolapse);
- abnormal bleeding that cannot be treated conservatively or with organ-conserving surgery.
There are other indications for removal, but in each specific case, doctors take into account the patient’s age and desire to have children, and in non-life-threatening conditions they try to carry out organ-preserving intervention.
Which method of hysterectomy is better?
It is impossible to say unequivocally which method of extirpation is worse and which is better. Each of them has its own advantages and disadvantages. For example, laparoscopic and vaginal hysterectomy are easier to tolerate by patients, since they do not involve layer-by-layer dissection of the abdominal wall. However, in oncological practice, open intervention is often required, since a thorough examination of the pelvic organs, and in some cases the abdominal cavity, is necessary to search for cancer metastases and radical removal of all interested tissues.
The extent of the operation is determined by the diagnosis and stage of the disease. The most extensive interventions are performed for ovarian cancer, since it is prone to early contact metastasis through the peritoneum. Therefore, during the operation, not only extensive extirpation of the uterus and appendages is performed, but also excision of the greater omentum and peritoneum.
How is a hysterectomy performed?
If drug treatment does not help, in surgical gynecology, patients are prescribed a hysterectomy - an operation to remove the uterus. Before it is carried out, it is necessary to undergo many examinations, as well as prepare the intestines. You will learn more about the operation and post-operative actions below.
Examinations before surgery
The surgical intervention takes place under anesthesia, so the gynecologist must collect all the information about the patient’s health - the presence of chronic diseases, allergies to medications and the possibility of anesthesia. For this purpose, examinations are prescribed:
- Are common
. Lung X-ray and spirography, electrocardiogram and tonometry. A general blood test and biochemistry are also taken, including checking blood clotting, glucose levels, hormones, as well as establishing the group and Rh, identifying the presence or absence of HIV, hepatitis and sexually transmitted diseases. If problems with the respiratory, cardiovascular, endocrine or kidney systems are detected, it is necessary to undergo additional examination by specialists. - Gynecological.
Ultrasound of the pelvis; colpocytology; microflora smears; examination of the vagina and uterus. If there is a suspicion of oncology, magnetic resonance imaging, biopsy and histological examination are prescribed. It is also necessary to exclude infectious diseases of the genitourinary system.
If the patient has a number of pathologies or chronic diseases, she is prescribed drug treatment. Only after completing the course and re-examination can the doctor give permission for surgery under anesthesia.
Preparing for hysterectomy surgery
Before any intracavitary operation, the intestines must be cleansed. The attending physician must give recommendations that must be strictly followed:
- Usually, 3 days before surgery, you follow a diet. Rough foods that contain fiber and dietary fiber are excluded from the diet. Including fresh vegetables and fruits, rye bread and legumes are prohibited.
- The day before surgery, follow diet No.1. The menu contains only pureed liquid food.
- On the day of hysterectomy, you should never eat or drink to avoid vomiting during anesthesia and getting it into the respiratory tract.
You should also pay close attention to the veins, especially with thrombophlebitis. Pelvic surgery affects blood flow. There is a risk of increased venous pressure, blood stagnation, and blood clots. Therefore, be sure to consult with a phlebologist, who can prescribe treatment or recommend compression of the veins using an elastic bandage using certain ointments.
Methods and progress of the operation
Based on the course of the disease and the area affected by the female organs, the doctor chooses the method of hysterectomy and decides how many organs should be removed.
There are three methods of operations according to the technique of execution:
- Open cavity
. To reach the organ, the surgeon makes an incision in the abdomen. Although this method is often used, it has disadvantages - greater trauma for patients, a rather large postoperative scar on the abdomen. - Vaginal
. Removal of the uterus takes place through the vagina, and the woman recovers quickly. Compared to the previous one, this method is used infrequently, as it has many contraindications - it is not suitable for patients who have had a cesarean section, have malignant neoplasms, combined pathologies, inflammatory processes and a large uterus. - Laparoscopic
. The most gentle way. To carry out the operation, equipment and instruments are used. Before a hysterectomy, a special tube is inserted through a small incision and the abdomen is filled with gas so that the wall of the peritoneum rises and the doctor can clearly see the uterus. Tubes are then inserted through small incisions and cameras and instruments are lowered inside.
The duration of the operation depends on the complexity of the disease and complications during its implementation. The abdominal method takes from 40 minutes to 2 hours, laparoscopic – 1.5–3.5 hours, vaginal – 2 hours.
An example of abdominal surgery to remove the uterus is presented in the video:
The cost of the operation depends on the country, region, city, clinic, specialist and surgical method. Thus, in Russia, the cost of a laparoscopy service starts from 20,000 and can reach up to 200,000 rubles.
Postoperative diet
After the operation, you are allowed to drink after 1-2 hours, and eat after 3-4. Then they follow a diet that improves the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract. General recommendations:
- Food should have a liquid or semi-liquid consistency.
- The portion size is small.
- The number of meals per day is 6-7.
- Drink 2 liters of drinking water per day.
The menu includes crumbly porridge, boiled fish, and meat. It is allowed to consume fermented milk products, meat broth, vegetable puree and salads flavored with vegetable oil. For drinks, preference should be given to pomegranate juice and green tea.
The diet should not contain:
- mushrooms;
- smoked meats and semi-finished products;
- fried foods;
- sweets, confectionery, white bread;
- from drinks - soda, black tea, coffee
Postoperative period
Rehabilitation takes different times for each woman. If the operation went without complications, it will be much shorter. If abdominal surgery is successful, the sutures are removed on days 9-12. With laparoscopy, early rehabilitation takes 3-5 days. During this period, bleeding and other symptoms are eliminated. Particular care is taken to ensure that inflammatory processes do not begin and infection does not occur.
Next, the patient undergoes a recovery period at home and must regularly visit a specialist. General recommendations:
- After the operation, lifting weights is prohibited for 2 months.
- Visiting the swimming pool, bathhouse, sauna is allowed after 6 months.
- Sexual activity is allowed after 4–6 weeks after surgery, until the discharge is completely gone.
- The period of incapacity for work is 30–45 calendar days, but in case of complications it is extended.
Consequences of hysterectomy
The consequences also manifest themselves differently for each woman. Among the main ones are:
- Menopause occurs immediately after removal of the organ with all the accompanying symptoms. If the removal occurred at a young age, the woman is prescribed hormonal therapy. You will have to take sex hormones for a long time.
- The risk of developing osteoporosis and heart failure increases, since the uterus is involved in the functioning of the endocrine system.
- Loss of reproductive function. If at a more mature age this is a plus, then for women of childbearing age it is a tragedy. Therefore, the doctor evaluates all factors before recommending this radical method.
- Adhesive processes, which are accompanied by pain, impaired urination and defecation.
- There may be psychological problems that women experience after surgery.