- Indications for hysterectomy
- Types and methods of operations
- Preparation
- Execution techniques
- Rehabilitation period
- Sexual life after hysterectomy
In gynecology, in the treatment of uterine bleeding in recent years, various conservative methods of influencing the uterus have been used, for example, hysteroresectoscopic removal of the myomatous node and endometrial ablation, thermal ablation of the endometrium, hormonal suppression of bleeding.
However, they often turn out to be ineffective. In this regard, surgery to remove the uterus (hysterectomy), performed both planned and emergency, remains one of the most common abdominal interventions and ranks second after appendectomy. The frequency of this operation in the total number of gynecological surgical interventions in the abdominal cavity is 25-38%, with the average age of women operated on for gynecological diseases being 40.5 years and for obstetric complications being 35 years. Unfortunately, instead of trying conservative treatment, among many gynecologists there is a tendency to recommend that a woman with fibroids have her uterus removed after 40 years, citing the fact that her reproductive function has already been realized and the organ no longer performs any function.
What is uterine laparoscopy?
This method causes less harm to the body and has virtually no complications.
There are two types of laparoscopy:
- diagnostic – it is used to confirm or refute a diagnosis.
- surgical – used for the treatment of female genital organs.
If the disease is in its early stages, this method helps to completely remove the tumor. Even at an advanced stage, laparoscopy allows you to save the uterus and remove only the tumor present in it. This method helps maintain the menstrual cycle and also gives a woman the opportunity to become a mother.
Pregnancy
Obviously, pregnancy after such an intervention is impossible for several reasons. Firstly, there are no ovaries, which means that eggs are not formed and the normal hormonal balance necessary for conception is not maintained. In addition, there is no cervix, which means sperm cannot penetrate beyond the vagina. And finally, there is no uterus itself in which fertilization would occur and the embryo would attach. Thus, the only way for a woman to have children after such an intervention is to resort to the services of a surrogate mother.
Features of uterine laparoscopy
This technique has gained great popularity in gynecology, and all because:
- It does not require an incision.
- Prevents the development of adhesions in tissues due to low risk of injury.
- Helps to examine the abdominal cavity in detail.
- It is possible to increase it several times.
- Short rehabilitation period.
- Leaves no marks or scars.
In what cases is laparoscopy performed?
As noted above, laparoscopy has different purposes; some require it to accurately diagnose a disease, while others need it to treat it. It may also be prescribed after surgery to monitor the healing process. But the most common purposes of laparoscopy are:
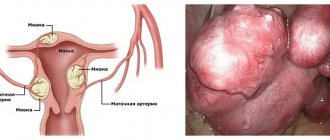
- fibroids and fibroids;
- abnormal development of the uterus, its prolapse;
- oncological diseases;
- violation of the patency of the fallopian tubes;
- cysts, endometriosis;
- ectopic pregnancy;
- lack of effect from taking hormones;
- infertility treatment;
- trachelectomy and hysterectomy.
When is laparoscopy performed?
Preparation for the operation begins with finding out the patient’s menstrual cycle. This question is very important, because the effect of the procedure depends on it. If you do it during menstruation, you can get an infection, because the female body is most susceptible to various types of infections at this time.
According to gynecologists, laparoscopy is best done immediately after menstruation, or in the middle of the cycle. If this method is required to treat infertility, then it is better to do it after ovulation, so you can see what happens to the egg.
Definition
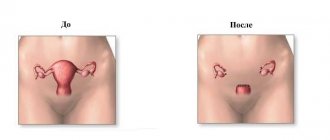
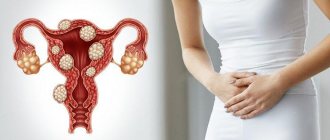
Total hysterectomy or vaginal hysterectomy is, as mentioned above, the most extensive intervention in gynecology, during which almost all components of the reproductive system are removed, with the exception of the genitals. During the intervention, the uterine cavity itself is removed, as well as its cervix, fallopian tubes on both sides and the ovaries, also on both sides.
What is hysterectomy with appendages? This phrase is synonymous with what is described above, since hysterectomy without appendages is a completely different procedure in which only the organ cavity and its cervix are removed. It has a separate name - radical hysterectomy.
Access to the operated system during such an intervention can be carried out in different ways. With laparotomy access, an incision is made in the abdominal wall, and then the entire intervention takes place in the operating pit. During laparoscopic intervention, vascular ligation and sometimes the installation of clamps are performed using a laparoscope, but in the future it is still necessary to dissect the abdominal wall, since it is impossible to remove the severed tissue through the laparoscope. Another method is access through the vagina and cervix. It is not always convenient and not always feasible, therefore most often the intervention is performed laparotomically.
Laparoscopy of ovarian and uterine cysts
A method such as laparoscopy is used to treat ovarian and uterine cysts. To do this, three punctures are made in the abdominal cavity without cutting the abdominal muscles. The main advantages of this method are:
- Minimal risk of developing adhesions.
- There is a low likelihood of a hernia occurring after surgery, which usually occurs due to incompetence of the cut muscles.
- There are no major incisions, which allows for a quick recovery.
- Reducing the risk of intestinal hypotension, as well as the development of other diseases of nearby organs.
This method allows you to return to normal life much faster and forget about the disease. To be completely confident in a favorable outcome of the operation, I advise you to consider the option of treatment in a Swiss clinic.
Polypectomy
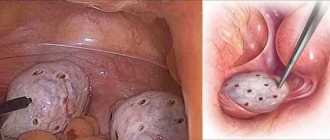
Another benign tumor disease of the uterus is polyposis. Polyps are small formations that grow in the uterine cavity. Most often, these formations are multiple, they can cover the entire surface of the endometrium.
Removal of polyps is carried out transvaginally, and can take place in a gynecological office. This is due to the fact that polyp removal is a minor gynecological operation. It does not require special preparation or special management of the postoperative period. In most cases, women are advised to remain in the hospital for a day under observation, as there is a risk of bleeding.
Topical agents can be used as anesthesia.
The operation itself is performed using a laser, diathermocoagulator or cryodestruction apparatus. Such equipment can significantly reduce injuries and reduce the risk of damage to blood vessels to a minimum.
Depending on the severity of the polypous process, surgery to remove a uterine polyp lasts from 20 to 45 minutes. After the manipulation, women are advised to refrain from sexual intercourse, physical activity and visiting the bathhouse for 2-3 weeks so that the wound surface has time to recover.
What complications can there be?
After ovarian laparoscopy, most often you experience severe pain not only in the place where the operation was performed, but also in the area of the right side and shoulder. The reason for this is the accumulation of carbon dioxide residues in the liver, which acts on the nerve as an irritant. Muscle pain and swelling of the limbs may also occur.
In the first days after the procedure, gases may accumulate in the upper fat layer. This is not life-threatening and goes away within a few days.
Adhesions may also appear, but after laparoscopy this occurs very rarely.
Complications such as:
- Damage to internal organs, which can occur both during the penetration of the instrument and during the process of filling the abdominal cavity with carbon dioxide.
- Damage to blood vessels during the puncture process. This can lead to severe bleeding and blood transfusions.
- Infection that can penetrate the wound. It is to prevent such consequences that after surgery it is necessary to take a course of antibiotics.
In any case, after the operation, an individual rehabilitation course is selected for the woman and her nutrition is regulated (refusal of fatty, sweet, starchy, spicy, etc.).
How long does the operation take?
No doctor can give an exact answer to the question about the duration of this method. Everything here is individual and depends on many factors. On average, the operation takes from half an hour to 3 hours. During this time, the surgeon carries out a number of activities:
- Introduction of anesthesia.
- Performing punctures, usually 3 or 4.
- Filling the abdominal cavity with carbon dioxide. This is necessary to protect internal organs from injury and create space for the surgeon to work.
- The insertion of the laparoscope is a small tube with a mini camera. This helps the doctor monitor what is happening inside.
- If necessary, additional tools can be used. For example, during ovarian laparoscopy you will also need scissors, forceps and a coagulator.
- Removing the laparoscope and removing gas.
- Stitching.
Important! On average, after 2 hours the patient will be able to move independently. This point is mandatory; it helps prevent the development of adhesions.
How is laparoscopy performed to remove the uterus?
Laparoscopy to remove the uterus is an excellent alternative to hysterectomy, which is performed in the case of a malignant tumor. First, a woman must undergo a full course of examination. Only after this can a laparoscopy to remove the uterus be prescribed. The examination consists of:
- Ultrasound of the pelvis.
- General blood test, biochemical, glucose test, syphilis, hepatitis, etc.
- Urine tests.
- Vaginal smears.
- ECG.
- Fluorography.
- Colposcopy.
Based on the patient’s condition, other types of examination may be prescribed.
Indications
In what cases is extirpation of the uterus and appendages indicated? Since this is a fairly serious operation, doctors try to avoid it until the last minute, especially in women of reproductive age who have not yet given birth. Therefore, such intervention is prescribed only in the presence of very serious, and sometimes life-threatening, indications. The operation is performed in the following cases:
- Cancer of the uterus or other organ of the reproductive system in a sufficiently developed state;
- A precancerous process, but not amenable to conservative treatment, actively spreading and aggressive;
- Dysplasia, leukoplakia, which are difficult to treat or do not respond to it at all, often recur (since horses pose a danger from the point of view of transformation into an oncological process);
- Adenomyosis, endometriosis, which are difficult to respond to or do not respond to conservative treatment at all, recur and cause very severe symptoms;
- The presence of multiple cysts, polyps, papillomas that cannot be removed accurately;
- A serious hormonal imbalance that cannot be corrected by conservative means, as a result of which benign neoplasms constantly recur.
Laparoscopy to remove the uterus
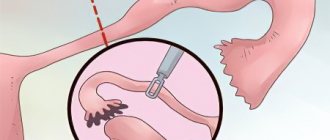
Typically, uterine laparoscopy is performed for existing fibroids, which grow very quickly and are accompanied by pain. In this case, the doctor, based on the examination, decides whether to remove the tumor itself or the uterus itself. If you have to resort to the second option, then the procedure is as follows:
- Four punctures are made and trocars with a special chamber are inserted. This allows you to see and control what is happening inside. This device also has a light installation.
- After the examination, the surgeon alloys (i.e. places ligatures on them to prevent bleeding) the vessels and cuts off the uterus from the vaginal walls.
- The uterus is then removed through the vagina and the incisions are sutured.
Important! This operation also makes it possible to remove lymph nodes.
- If a large amount of blood has accumulated during laparoscopy, it is also removed.
- The surgeon examines the abdominal cavity.
- Sutures are applied to the puncture sites.
Anesthesia is an integral part of the laparoscopic method. This issue is resolved individually by the doctor and anesthesiologist. At the same time, the patient’s condition is assessed, the examination results are reviewed, and, based on this, the issue of anesthesia is decided. Endotracheal anesthesia is most often prescribed; it eliminates headaches after surgery. After the procedure, the woman wakes up within 15 minutes.
Sports activities
Especially active patients who love sports and cannot imagine life without it are concerned with the following question: “is it possible to play sports after removal of the uterus.”
Sport is life, and no one will argue otherwise.
After the operation, when 2-3 months have passed, you can try yourself in light types of fitness. This could be regular walking in the evenings, yoga, breathing exercises, Pilates, bodyflex.
It has long been proven that women who do not neglect fitness or even regular gymnastics can protect themselves from such unpleasant postoperative consequences as:
- haemorrhoids;
- pain during sexual intercourse;
- adhesions and blood clots;
- depression;
- urinary incontinence;
- frequent constipation;
Doing Kegel exercises is very helpful. Many women have long heard about them. Just a few minutes a day, by squeezing and relaxing the muscles of the vaginal walls, you can protect yourself from the above unpleasant consequences, as well as increase sexual sensations.
Riding a bicycle is a completely acceptable and enjoyable activity. The main thing is not to do this if 3 months have not passed after the operation, and not to raise the seat high in order to avoid heavy stress.
Carrying out laparoscopy to remove an ovarian cyst for endometriosis
Endometriosis is a disease in which cells of the walls of the uterus grow outside of it (on the fallopian tubes, peritoneum, appendages, etc.), including on cysts. This disease requires mandatory removal of the tumor, as it very quickly becomes large. In this case, laparoscopy is the most optimal and safe option, thanks to which you can completely recover from this disease.
Before starting the operation, you need to decide on anesthesia. This is decided by the anesthesiologist and the anesthesia is different for each case. After that:
- The patient is given a sleeping pill and a sedative.
- A puncture is made in the abdominal cavity and carbon dioxide is injected inside.
- Then two more punctures are made and a laparoscope with a video camera is inserted.
- The surgeon examines the abdominal cavity and clarifies the diagnosis. After this, the question of the method of surgical intervention is decided. If the tumor is malignant, then you will have to resort to more radical methods.
- Next, the cyst is enucleated and part of the ovary is removed.
- After this, the doctor examines the abdominal cavity again and removes the devices.
- The operation is completed, stitches are placed on the puncture sites.
Recovery process
For several days after the procedure, the woman may experience pain in the abdominal area. This is a normal phenomenon that goes away after a couple of days. If you experience severe nausea during the recovery period, it is better to consult a doctor .
The first days after laparoscopy you need to drink water, and, preferably, do this in a supine position. Already on the second day, you can start eating light snacks so as not to put too much strain on your stomach. These can be broths, cottage cheese, oatmeal. Usually sick leave is given for a month, but physical work is prohibited for two months.
Two weeks after the operation, the patient already feels normal, but there is no need to overload the abdominal muscles. Sometimes women develop adhesions, this happens due to a genetic predisposition or endometriosis. Disturbing discharge is a normal process, which means the ovaries produce hormones.
Various types of inflammation occur very rarely, since antibiotics are indicated after surgery. All medications recommended by a doctor should be taken in the prescribed manner, otherwise it will lead to adverse consequences (inflammation, infections, etc.).
Any disease of the female genital organs requires a complete examination and treatment. If pathologies requiring surgical intervention are identified, it is best to resort to laparoscopy. Thanks to it, it is possible to perform the operation without severe damage to the abdominal area.
Video: what is laparoscopy?
What is laparoscopy?
Video: second day after surgery. GHA. Laparoscopy
Second day after surgery. HSG. Laparoscopy.
Video: diagnostic laparoscopy
Diagnostic laparoscopy