SocLgoty.ru - all about social assistance in Russia
8 Hotline in the Russian Federation
+7 Moscow and Moscow. region
+7 St. Petersburg and Len. region
- home
- Social benefits
- Benefits for disabled people
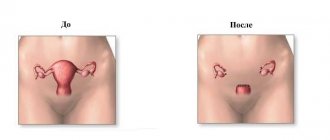
The same disease progresses differently in different people. Despite the great achievements of modern medicine, radical operations to remove internal organs have been performed before and continue to be performed to this day. Today, a certain percentage of women suffer from uterine diseases. In some cases, when treatment fails, this important reproductive organ is removed. Those representatives of the fairer sex who have undergone this operation are often interested in whether they give a disability after removing the uterus? The material below will answer this question.
Are you entitled to disability after hysterectomy?
Important: In these cases, chemotherapy should be included in the complex of postoperative treatment. Combined treatment (surgery + external beam radiation therapy) is used in the absence of extragenital contraindications to it, as well as when it is possible to radically remove the primary lesion during surgery. Combined radiation therapy includes external beam radiation therapy and intracavitary gamma therapy, which simultaneously affects the primary focus and metastasis pathways (both lymphogenous and implantation).
Combined radiation therapy is used when there are contraindications to combined treatment, as well as when the process has significantly spread. Complications and consequences. Given the variety of treatment methods used for uterine cancer, complications and consequences described in the section: “MSE and disability in cervical cancer” may occur. Metastasis of uterine body cancer occurs in three ways: lymphogenous - to the iliac and para-aortic lymph nodes, hematogenous - to the liver and bones, implantation into the fallopian tubes, ovaries and vagina. Histological structure of the tumor. Endometrial cancer in its histological structure is adenocarcinoma, which, depending on the degree of differentiation, is divided into well-differentiated, moderately differentiated, glandular-solid and solid (poorly differentiated). In tumors of varying degrees of differentiation, so-called pseudocellular areas, which are benign structures, can be observed and do not determine the biological properties of the tumor. Such tumors are usually called adenoacanthomas. A rare variant of uterine body cancer are clear cell (mesonephroid) adenocarcinomas, which can be of varying degrees of differentiation.
Stages of the disease
The following stages of oncology are distinguished, which are taken into account when conducting a work ability examination:
0
– atypical endometrial hyperplasia, or adenomatosis (preinvasive adenocarcinoma);
I
– the tumor is limited to the body of the uterus without identifying regional metastases;
IA
– the tumor is limited to the endometrium;
IB
– penetration of cancer cells into the myometrium up to 1 cm;
IB
– penetration of cancer cells into the myometrium more than 1 cm without damage to the serous membrane;
II
– the body and cervix are affected without identifying regional metastases;
III
– spread of cancer outside the uterus, but within the pelvic organs;
IIIA
– the tumor penetrates the serous membrane of the uterus, metastases are detected in the uterine appendages and pelvic lymph nodes;
IIIB
– cancer penetrates into the pelvic tissue, metastases are determined in the vagina;
IV
– cancer cells spread beyond the pelvis and grow into the bladder and rectum;
IVA
– the tumor spreads to the bladder or rectum;
IVB
– cancer of any degree of spread with distant metastases is observed.
Disability is due after removal of the uterus and appendages
Standards of examination when referred for medical examination: - clinical blood and urine tests; - biochemical blood parameters; - x-ray of the lungs, if necessary - tomogram; - ultrasound of the liver; - gynecological examinations with rectovaginal examination. Criteria for disability groups. Moderate limitation of life activity during radical treatment of malignant neoplasms of the ovaries is determined at stages Ia, Ib, Ic and IIa, provided that the macrostructure of organ (i) is preserved, effective completed treatment (full course of chemotherapy) and the absence of pronounced complications and consequences, which allows return the patient to non-contraindicated types and working conditions. If rational employment is necessary with a reduction in qualifications or volume of work, as well as in connection with a significant limitation in the possibility of employment, patients are recognized as disabled people of group III.
The patient must tell each specialist in detail not only about the illness or injury that caused the disability, but also about how he received it, as well as about the working conditions at work. Doctors are required to enter this information into the medical record.
Note: When a person undergoes a medical examination, he tries to defend his rights, and for this it is important for him not only to obtain a certificate of disability, but also to establish a cause-and-effect relationship. The circumstances of receipt of disability are no less important than the assignment of the status itself.
The result of the work of the medical commission will be the resulting certificate-conclusion, which is made on the basis of clinical, functional, social, everyday, professional, labor and psychological data using the classification and criteria approved by the Ministry of Health and Social Development of the Russian Federation. Together with the other consequences of hysterectomy, this negatively affects the postoperative condition of the woman. Even in the absence of the above complications, the body undergoes a number of changes after the operation, and there is a need for some restrictions and a different approach to lifestyle. You may need to adjust your diet, take medications prescribed by your doctor, avoid lifting heavy objects, and see your doctor regularly.
The latter requirement is dictated not only by the need to monitor the restoration of the patient’s health as a result of removal of the uterus, but also to monitor other changes in body functions. An example of negative consequences could be:
- heart problems, vaginal prolapse;
- premature menopause;
- osteoporosis and more.
If any complication occurs, additional treatment will be required.
What affects the duration of sick leave?
A woman cannot independently influence the duration of sick leave. The decision on the need for opening is made only by the doctor based on examination and examination data.
In an attempt to get a ballot, some people resort to tricks and invent symptoms that actually do not exist. With the help of ultrasound, MRI, tests and other diagnostic procedures, the doctor can reliably determine the presence of symptoms and make a decision on whether to open sick leave or deny it.
The duration of sick leave is determined:
- the need for hospitalization;
- the presence of complications and the risk of their development;
- complexity of the operation;
- volume of intervention.
Grounds for extending a certificate of incapacity for work
Complications of surgery may include:
- bleeding;
- the addition of a secondary infection, with the subsequent development of inflammation;
- temperature increase;
- severe pain syndrome;
- failure of the postoperative scar (its divergence or suppuration).
What is life like after a hysterectomy?
After amputation of the female reproductive organ and ovaries, disability is not given. But it can be assigned when a hysterectomy has undermined a woman’s health to such an extent that it is not possible to restore her previous level of ability to work.
If the uterus has been removed, it is worth looking at a number of nuances. A woman’s condition requires attention when:
- After the operation, she fell into depression, feels irritation and anxiety, which become the reason for the development of a panic attack;
- She began to rapidly gain weight and dietary meals, moderate physical activity did not help to lose extra pounds.
Although after operations to remove the uterus there are no problems with sexual life, since it is not the uterus that is responsible for sensitivity, but the vaginal receptors, in some cases a decrease in libido is possible. But this issue can be easily resolved with properly selected hormonal therapy.
What happens to hormonal levels? If, in addition to the uterus, the ovaries were also removed, a woman of reproductive age should pay a lot of attention to hormone replacement. If you ignore this point, a woman may experience hot flashes and other signs of menopause. Since the ovaries produced estrogen, which is responsible for reproductive function and libido, doctors prescribe various estrogen-containing drugs to women after uterine amputation.
Mandatory list of documents
To obtain disability after hysterectomy, patients must provide a referral or (if the doctor refused to issue a referral) a certificate. You will also need the following documents:
- application for examination;
- original passport along with a copy;
- extracts and copies from the hospital;
- outpatient card.
ITU specialists should receive all this from you. Based on the results of the commission meeting, a final decision will be made. The disability group after removal of the uterus is divided into first, second and third. Disability can be obtained for different periods: from 1 year to indefinitely. In case of assignment of disability for a certain period after its completion, the procedure for obtaining disability must be repeated. After removal of the uterus, as a rule, the 3rd group is provided for 1 year.
Surgery to remove the uterus is performed frequently, so there are many patients who suffer from the adverse effects of this procedure. In this regard, both doctors and the commission are reluctant to make a positive decision on granting a disability group. Moreover, after a certain time, many women return to their usual lifestyle and their well-being improves significantly. However, this does not mean that you should not try to obtain disability if you feel that your case requires it.
What is meant by preventive examination?
In the first 12 months after amputation of the uterus, you should be observed by a gynecologist. An extraordinary inspection may be necessary if:
- there are painful sensations of unknown etiology;
- inflammation of the suture has occurred and there is an elevated temperature;
- there is severe pain during sex;
- discharge from the genital tract of a pathological nature has arisen (for the reason that when the ovaries are removed, the cycle is interrupted, then there should be no discharge characteristic of the ovulation period). For any other discharge, the woman should visit a doctor.
Many people are concerned about the question: does this operation affect life expectancy? Doctors answer this question in the negative.
Some women raise the issue of disability due to the difficult postoperative period. In the early postoperative period, a woman should pay a lot of attention to her peace. She should not subject her body to physical activity and must follow a special diet. The late postoperative period involves regular support of the pelvic floor with Kegel exercises. During the first two months you will need daily pads and a support bandage.
Question answer
- Question No. 1. In what cases can a woman be given disability after removal of the uterus? Answer. Disability is possible when a woman: cannot care for herself;
- cannot move;
- cannot study or work;
- I lost control of myself and became a victim of constant panic attacks.
Author of the article: Irina Alekseeva Hello! My name is Belova Olga Borisovna. I have been working in the field of jurisprudence since 2013. I specialize mainly in civil law. Studied at the Northern (Arctic) Federal University named after M.V. Lomonosov. Faculty: Jurisprudence (Lawyer).
Surgeries on internal organs can cause serious complications, which can leave women disabled after removal of the uterus and ovaries. Patients acquire this status if the surgical intervention provokes a partial or complete loss of ability to work.
Application procedure. Step-by-step instruction.
Disability is granted based on a fully stated problem; the patient must first collect all the necessary documents.
If you want to prove that you are right, you need to know the procedure.
- Initially, contact your doctor. He will give you a referral or a certificate about the pathology present.
- At the reception you take your outpatient card.
- Make copies of all statements (from each clinic where you were treated for this pathology or the complications it caused).
- Then you go to work/study and take a reference, a certificate of income and make a copy of the work book.
- Have the copy certified by a notary.
- Make a copy of your passport.
- Write an application in which you contact the medical and social examination with a request to issue a disability.
After receiving all the documents, the ITU sets a date for the medical commission. The woman will receive a notification in a registered letter when the meeting will take place. If it is not possible to come on the specified date, then it is enough to inform the commission members by telephone. Come at the specified time, you will find out the ITU decision.
What to do if you are sure that you should be given a disability, but are refused?
If the commission's decision is not in your favor, you can appeal it. To do this, you need to come with a complaint to the chairman of the regional ITU. If the complaint is accepted, honey is prescribed again. commission, but in a different center.
Here again the same documents are needed. The only thing that can be changed is the nature of your own statements. Perhaps last time they sounded unconvincing or did not fully reveal the essence of the problem.
When is disability granted?
Disability is granted in cases where, due to surgery for pathologies of the uterus and ovaries, a woman has lost the ability to:
- move normally;
- take care of yourself;
- perform work duties or study;
- communicate;
- navigate in space.
The final decision regarding the assignment of status is made based on the decision of the members of the medical and social examination.
It is important to note that in the first few weeks, for objective reasons, a woman becomes unable to work. This fact is not the reason for the assignment of disability. A decrease in working capacity in such circumstances is explained by a temporary disruption of the functionality of internal organs caused by surgery (tissue damage). For this period, the woman is issued a sick leave certificate, which retains her job.
On average, it takes up to 30-40 days to fully restore the body after removal of the uterus and ovaries. If the work does not involve physical activity, the doctor may allow you to return to work duties earlier than the specified period. In cases where complications arise during the rehabilitation period, the validity of the sick leave is extended.
What types of post-operative recovery period are there?
The postoperative period in practice is considered to be a time period lasting from the date of the operation until complete recovery. After removal of the body of the uterine organ, the patient undergoes a recovery period in two stages:
- Early;
- Late.
For patients who are about to have such a surgical intervention, an urgent question immediately arises: how many days does the early postoperative stage last? The duration of the early regeneration period is influenced by the nature of the operation performed, the diagnosis and physiological characteristics of the patient. Immediately after surgery, the woman remains under the total control of the treating specialist. Staying in an inpatient department lasts from five to ten days. The first postoperative days are considered especially difficult in terms of physical condition and pain. After undergoing surgery to remove the body of the uterine organ, pain and discomfort are inevitable for approximately 10 days.
The late postoperative stage continues throughout the entire period of incapacity, as evidenced by a special hospital document. During this recovery period, the patient must strictly follow the instructions of the leading treating specialist.
How to apply for disability?
Disability is issued if the removal of the uterus and ovaries caused a violation of basic life functions. The final decision regarding the assignment of this status is made within the framework of a medical and social examination, the referral for which is given by the attending physician.
If the latter considers it inappropriate to carry out this procedure, the patient has the right to undergo it independently in order to register a disability. The following documents will be required for ITU:
- application (referral) for examination;
- passport with its copy;
- outpatient card;
- extract from the hospital and a copy thereof.
During a medical and social examination, specialists assess the woman’s current condition and complaints. Based on the results of the examination, a decision is made on the need for a change or refusal to grant a new status. If the application is approved, doctors determine the validity period (1-2 years or indefinitely) and the disability group (first, second or third).
If the commission refuses to register a disability, the patient has the right to challenge this decision in the main ITU bureau. This must be done within one month. Change of status may be refused for various reasons. The results of a medical and social examination largely depend on the patient’s behavior and her ability to clearly convey the essence of the problem.
If disability is assigned for a period of 1-2 years, at the end of this period the MSA is repeated, based on the results of which a decision is made to extend or cancel the benefit.
More often, after removal of the uterus, a third disability group is assigned. Moreover, a woman usually acquires a new status for a period of one year.
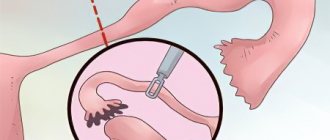
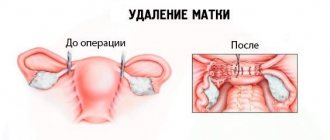
“Do you get disability after surgery to remove the uterus and ovaries?” - one of the main questions of patients who had to undergo surgery on the reproductive organs. Removal of the uterus (hysterectomy) is a last resort measure for a number of gynecological diseases, when other treatment methods no longer give the desired result. Sometimes, along with removal of the uterus, an oophorectomy is performed - the removal of one or both ovaries. Next, we will consider the reasons for such operations, the stages of rehabilitation and a number of measures that should be taken during the rehabilitation period after removal of the uterus and ovaries.
What documents are needed to obtain disability?
If a representative of the fairer sex has encountered severe post-operative consequences that have limited her previous performance or reduced it to “no”, it is worth telling the doctor at the clinic about her desire to receive a disability. Whether to give it or not is up to ITU members to decide. To obtain disability, a woman will have to prepare:
- statement of desire to conduct an examination;
- passport and its copy;
- outpatient card;
- special extracts from medical institutions.
Important!
If the issue of registration of disability is handled by a representative of a woman who has undergone uterine amputation, then it will be necessary to provide a notarized power of attorney.
This material told everything about the causes and consequences of hysterectomy. He also explained in what cases a woman can count on disability.
applications for passing ITU
Why is surgery needed?
Amputation of female reproductive organs is performed for several reasons. The most common of them:
- Oncological diseases of both the uterus or ovaries itself, and other organs, provided that the cancer has metastasized to the female genital area. This is the most common reason for such a last resort as removal of the uterus and ovaries. This type of disease involves donating blood to determine the tumor marker CA 125, the indicators of which are determined based on the following values:
- the norm is considered to be CA 125 no more than 35 U/ml;
- CA 125 can exceed its value not only in the presence of cancer, but also in endometriosis, ovarian cysts, uterine fibroids, autoimmune diseases, pregnancy, menstruation, and even after taking certain foods. Therefore, for the most accurate indicators of CA 125 and to avoid erroneous results, it is necessary to take the test in the morning on an empty stomach and at the beginning of the monthly cycle (after the end of menstruation, on days 5-7).
- Bleeding due to various injuries, as well as during childbirth, localized directly in the uterus or abdominal cavity. In this case, the operation is performed only when the bleeding threatens the patient’s life.
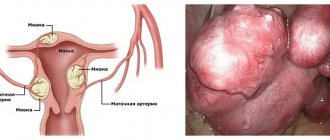
- Myomas, fibrosis and cysts, the drug treatment of which does not give the desired result, is completely impossible, or there is a risk of developing into a malignant formation.
- Prolapse of the uterine body. Complete removal of the organ is performed only when manual reduction is impossible, that is, in later stages of the disease. The uterine body prolapses mainly in women over 45 years of age or in those who have had multiple difficult births in the past, and also have genetic abnormalities in the formation of the pelvic floor.
- Infection during childbirth or birth pathology.
Women of different ages may be at risk. The operation is sometimes performed on patients at a young age.
After undergoing a series of examinations, the doctor decides whether only the uterus will be removed or the ovaries as well.
What is taken into account when assigning a disability group
In addition to the reasons described above, in the presence of which we can talk about temporary loss of ability to work, the following points are taken into account when making a decision:
- the patient’s ability to continue working under the same conditions;
- the presence of metastases and the chances of relapse of the disease;
- the severity of the health condition and the patient’s ability to care for himself;
- multiplicity of metastasis and size of the cancer tumor;
- duration and frequency of chemotherapy;
- the effect of a cancer tumor on adjacent organs, etc.
Life after removal of ovaries and uterus
Disability after surgery to remove the uterus and (or) ovaries is not given, since after it the woman can return to her normal life. Disability can only be obtained if radiation or chemotherapy was simultaneously used, which significantly undermined the state of health and restoration of the previous working capacity is impossible.
However, after excision of the ovaries and uterus has been performed, there are a number of nuances of everyday life that should be paid attention to.
Psychological problems
Often the patient is depressed after surgery, especially if she is still young. After all, the uterus and ovaries are the main reproductive organs that define her as a woman. Hormones that may be out of balance, as well as pain symptoms that sometimes persist for several months, also have a negative impact on mood. If both the uterus and ovaries have been removed, a woman may feel overly tired, irritated, and anxious.
If measures are not taken in time to eliminate these conditions, panic attacks may appear and neurosis may develop.
External support will play a decisive role in the treatment of psychological problems. Relatives and friends should not allow a woman to fall into a depressed state. Sometimes consultation and assistance from a psychotherapist and medications (sedatives or, conversely, stimulants) are necessary.
Weight after removal of the uterus and ovaries
Since physical activity is prohibited in the first months after the operation, and also due to serious hormonal changes, a woman may begin to gain weight sharply. To prevent this from happening, and to prevent thoughts of how to lose weight, you must adhere to the rules of a healthy diet. Sweet foods, baked goods, processed foods and fast food should be excluded from the menu or minimized. It is not advisable to eat too fatty and fried foods. Preference should be given to lean meat and fish, vegetables, fruits, cereals, and low-fat dairy products. Dishes should be boiled or baked. It is advisable to eat food in small portions 5-6 times a day. Dinner should not be later than 3 hours before bedtime.
As for sports after removal of the ovaries, it is prohibited in the first 2-3 months. But doctors recommend taking leisurely walks. They have a beneficial effect not only on the patient’s weight, but are also able to maintain her psychological state at a positive level. In the future, playing sports is possible, it is recommended to lead an active lifestyle, but consultation with a doctor is necessary.
Sex life
Another burning question after a hysterectomy is what sex life will be like and whether it is possible to have sex at all after removal of the uterus and ovaries. The operation is not a reason to terminate sexual relations; moreover, their quality does not change. This is due to the fact that the epicenters of arousal in women are not in the uterus and ovaries themselves, but in the vagina or on the external genitalia. Therefore, the general psychological mood of the woman, as well as the experience of her partner, is of greater importance here.
The only caveat is that you should not have sex in the first month or two after the operation; you need to let the stitches close completely.
In rare cases, problems in sexual life may occur with decreased libido. This situation is associated with an imbalance of hormones if the ovaries were removed along with the uterus. But this situation can be corrected – it is enough to choose hormonal therapy wisely.
Hormones
Hormonal imbalance after removal of the uterus and ovaries is a fairly common and unpleasant consequence of the operation.
If hormone replacement is not started on time, a woman may experience menopause prematurely. Hot flashes and all other symptoms of menopause begin. Moreover, the younger the woman, the more obvious symptoms she experiences. If a woman at the time of the operation was already in the preclimactic period or it had already occurred, then the symptoms are not very pronounced and she does not feel any dramatic changes in her condition.
When the uterus and ovaries are removed, the “female” hormones estrogens, which are responsible for reproductive function and libido, cease to be produced; their level must be maintained, so a hormonal agent containing estrogen is selected.
Motherhood
After the operation, motherhood in the traditional sense is impossible. Moreover, when both ovaries are removed along with the uterus, it will not be possible to conceive a child in any case, since it is the ovaries that are responsible for the formation of the egg; Menstruation stops and ovulation does not occur. If the ovaries are preserved and working properly, then a woman can become a mother using surrogacy. This is possible even after the removal of one ovary, if the second one is healthy.
Preventive examination
In the first year after removal of the uterus and ovaries, you need to conduct an examination of the body once every 1-2 months. If the operation was performed in the presence of cancer, then you should visit not only a gynecologist, but also an oncologist. An extraordinary inspection may be carried out in the following cases:
- the presence of pain of unknown etiology;
- inflammation of the suture or fever in the absence of signs of a cold;
- severe pain during sexual intercourse;
- pathological discharge from the genital tract. Since the cycle stops when the uterus and ovaries are removed, there should be no ovulatory discharge (a sign of normality). If there is any other discharge, you should consult a doctor.
In addition to the above, another possible question among women is how long do they live after removal of the uterus and ovaries and what is the further prognosis? The answer is very encouraging: this operation certainly does not shorten life. But it can increase its duration, since it solves issues of an oncological nature, endometriosis and many other pathologies of the female genital area.
List of documents for registration
If an operation to remove the fallopian tubes or the uterus as a whole is accompanied by a violation of the patient’s basic vital functions, the process of registering a disability group begins. To do this, a referral to the ITU is taken by the attending physician. If he believes that this procedure is inappropriate in a particular case, the legislation makes it possible to carry out the procedure independently.
The ITU assesses the condition of the body based on the written diagnosis and the patient’s complaint, after which it can give permission to obtain disability. Then you should prepare the following documents for submission:
- Original and copy of passport;
- Outpatient medical record;
- Original and copy of hospital extract;
- Application for appointment of an examination.
The procedure for registering a group and the corresponding standards are prescribed in Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation No. 95 of February 20, 2006. When protecting the interests of the patient, the representative must provide a notarized power of attorney. To increase the effectiveness of the defense, you should fully describe the circumstances that led to the filing of the relevant application.
The experts' decision is influenced by the objectivity of the presentation of the problem encountered by the patient himself or his authorized representative. The verdict may be refusal or permission to register disability. If the outcome is positive, the validity period and group are determined. If a woman receives a refusal, she has the right to appeal it no later than a month later at the ITU main bureau.
The commission, at its discretion, assigns disability of groups I, II or III. The period is determined for 1–2 years or indefinitely; upon its completion, an examination is carried out with a second decision to extend or cancel the benefit. Often, removal of the uterus results in group III disability lasting 1 year.
Rehabilitation after hysterectomy
Almost every patient does not know how to live after hysterectomy. This applies not only to the recovery period after a hysterectomy, but also to psychological aspects.
Early postoperative period
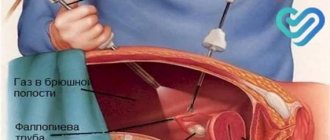
There are several methods of performing the operation: abdominal, vaginal and laparoscopic. Whatever method is chosen by the doctor, the patient must remain in a hospital setting for some time under the strict supervision of the attending physician.
During the first surgical period, which lasts from 5 days to two weeks (depending on the type of operation, possible complications and speed of recovery), it is necessary to undergo a series of tests to monitor the possible occurrence of infection. The patient is also advised to wear special compression socks to prevent thrombophlebitis. In some cases, taking blood thinning medications is indicated.
You can get out of bed on the first day, walking is also possible and even necessary to restore blood flow. Active physical activity should be avoided during this period.
You should also follow a special diet. This is especially important during abdominal surgery, as it can affect bowel function. Fatty and fried foods containing large amounts of salt and spices are strictly prohibited. You should eat simple dishes, steamed or boiled. This could be chicken broth, mashed potatoes, stewed vegetables, porridge, and so on.
In the early postoperative period, the woman feels pain of medium and high intensity, so painkillers are used.
During abdominal surgery, there is a high risk of infection. Therefore, antibacterial therapy is used for a week (most often in the form of intramuscular injections).
Other complications may occur:
- inflammation is not in the abdominal cavity, but outside, of the scar itself. Manifests itself in the form of redness, swelling, the appearance of purulent foci, excessive pain;
- cystitis and urethritis, which manifest themselves in the form of pain when urinating and frequent urge. These diseases can appear if the urethra is injured during surgery and gets infected;
- internal bleeding;
- peritonitis and subsequent blood poisoning (sepsis). Occurs in the event of an emergency operation when preparation was not carried out properly. Manifested by high temperature, heat, fever;
- extensive blood loss that must be compensated with transfusion;
- swelling and hematomas at the location of the sutures.
Late postoperative period
After the patient completes her hospital stay, she needs to apply a number of restorative measures at home. These include:
- Kegel exercises after hysterectomy. Such training is necessary in order to avoid atrophy of the vaginal muscles, restore their tone, prevent prolapse of its walls, prolapse of the cervix and possible urinary incontinence;
- a support bandage that should be worn to tone the abdominal muscles. This is not a mandatory item, but desirable, especially if the woman has had numerous births in the past (i.e., the abdominal muscles have already lost their tone), and also if she is over 40 years old;
- wearing panty liners, as in the first month after surgery, bloody and other discharge from the genital tract may be observed. The use of tampons during this period is prohibited.
All of these measures are necessary to prevent the negative consequences that occur in most cases after removal of the uterus.
In any case, it is up to the patient to decide whether to have surgery or not. The doctor can only justify its necessity.