How is ultrasound done?
The principle of operation of an ultrasound device is one, but there are several ways to examine the ovaries, and the choice of examination method will depend on age characteristics and diagnostic purposes. This or that ovarian ultrasound method is prescribed directly by the attending physician. It is he who will be able to accurately determine which of the following methods is more informative in a particular situation. Methods of ultrasound of the ovaries: 1. The transabdominal ultrasound method is carried out using an external sensor, which is installed in the projection of the ovaries and passed through the wall of the abdominal cavity. This method is suitable for medical examinations and primary diagnosis of gynecological pathologies. This method is not informative for overweight women, since adipose tissue can have a large volume and not transmit ultrasonic waves to the required depth. About 15 years ago, the transabdominal examination method was the main and almost the only method in diagnosing female organs. Now doctors more often prescribe the transvaginal method, whose information content is much higher. 2. Transvaginal ultrasound of the ovaries is done using a probe that is inserted into the woman’s vagina. This method is the most accurate. During it, the visualization of the organ is much better, and with its help, doctors can assess the condition of the uterus and follicles. A transvaginal ultrasound examination will show pathologies such as ovarian cysts, polycystic diseases, and tumors better than transabdominal ones. 3. The transrectal method is an alternative to the transvaginal type of diagnosis. It is usually prescribed to young girls with intact virginity. This study is carried out with a thinner sensor, which is inserted into the patient through the rectum. It also has good information content for the diagnosis of cysts and tumor formations of the ovaries. Previous Next
Restrictions
Ultrasound of the ovaries and uterus is a fairly fast and reliable method of examination. And yet, it is possible to make a diagnosis when it comes to tumor formation only by approaching diagnosis in a versatile and comprehensive manner. Unfortunately, it is impossible to accurately assess the tumor based on ultrasound results and distinguish its nature. To clarify whether this tumor is malignant or has a different nature, it is necessary to resort to histological examination or MRI of the pelvic organs with contrast.
| Ultrasound service of pelvic organs | Price, rub | Promotion Price |
| Ultrasound of the bladder with determination of residual urine | 800 rub. | |
| Ultrasound of the pelvis in women and men with an abdominal sensor | 1200 rub. | |
| Ultrasound of the pelvis in women with a vaginal probe | 1300 rub. | |
| Comprehensive pelvic ultrasound with abdominal and vaginal probe | 1400 rub. | |
| Ultrasound of folliculogenesis | 750 rub. | |
| Ultrasound cervicometry | 1100 rub. | |
| Ultrasound of the prostate gland with a rectal probe | 1500 rub. | |
| Ultrasound of the scrotum (testicles, appendages) | 1000 rub. | |
| Ultrasound of the prostate and bladder with an abdominal probe | 1900 rub. | |
| Comprehensive ultrasound (ultrasound of the abdominal organs + ultrasound of the kidneys + ultrasound of the thyroid gland + ultrasound of the pelvis with an abdominal probe + ultrasound of the mammary glands) | 4200 rub. | 2999 rub. |
| Comprehensive ultrasound (ultrasound of the abdominal organs + ultrasound of the kidneys + ultrasound of the thyroid gland + ultrasound of the prostate gland with an abdominal probe) | 3300 rub. | 2499 rub. |
How is an ovarian ultrasound performed?
Ultrasound of the ovaries is of three types: abdominal, transvaginal and rectal (used to diagnose the ovaries in virgins and in elderly patients with vaginal stenosis). Special preparation for diagnosing this organ is not required, except for cases in which the ovaries are not visualized (bloating). Before performing an abdominal ultrasound, the patient is advised not to empty her bladder until the end of the procedure.
Ultrasound of the ovaries is usually not performed separately; the fallopian tubes, uterus and ectopic space are also subject to diagnosis. No diagnosis is made based solely on ultrasound of the ovaries, since the full pathological picture, in addition to ultrasound signs, is described by the results of blood tests for sex hormones (progesterone, estradiol, testosterone, LH and FSH, cortisol, 17-OH progesterone, etc.) and gynecological examination of the patient on the chair.
Preparing for an ultrasound of the ovaries
Transvaginal, transrectal and transabdominal ultrasound are different from each other, and you need to prepare for each individually. Although there are a few things to consider when preparing for any of these procedures:
- The first thing you will need to do is to give up food that causes flatulence 2-3 days before screening. This includes baked goods, all legumes, lactic acid products, and sauerkraut. It will be useful to introduce boiled vegetables, lean meat (beef or chicken), steamed fish, and water-based porridge into your diet. If there are problems with the intestines and you suffer from increased gas formation, it is recommended to start taking medications: Espumisan, Mezim-Forte or activated carbon. All this must be done a day or two before the study.
- On the day of the procedure, all medications that are taken on an ongoing basis must be discontinued.
- Don't forget about basic hygiene of the groin area.
Transvaginal ultrasound of the ovaries and uterus is performed with a full bladder. Therefore, the patient needs to take about 1 liter of water without gases and not urinate before screening. You won’t be able to drink so much water at one time; you need to drink in small portions. You can drink the first 0.5 liters of water at home if you live near the clinic. If you need to spend time on the road, it would be better to come to the clinic half an hour before the examination and while waiting for the procedure, drink the required amount of liquid in small portions. During transrectal examination (through the rectum) the night before, the last meal should be no later than 18.00. Before going to bed, it is necessary to cleanse the intestines naturally or with the help of an enema and a mild laxative. In the practice of doctors, there are cases when the ovaries cannot be examined on ultrasound. This may occur due to improper preparation and formation of gases in the intestines or due to a congenital anomaly, adhesions due to a tumor or inflammation. Then doctors carry out differential diagnosis using MRI of the pelvic organs. Previous Next
Diagnosis of ovaries
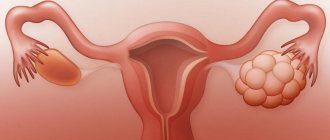
Ultrasound of the ovaries allows you to study the structure of this organ, as well as help the doctor make a diagnosis. This is the most accessible and safe diagnostic method, which is carried out with a special abdominal (through the abdomen) or transvaginal (through the vagina) sensor. The last method of ultrasound diagnostics is the most reliable. Preparation for an ovarian ultrasound is not necessary. Preparation for ultrasound of the ovaries is required only for the transabdominal method of examination.
Ultrasound of the ovaries in women is usually performed when there are problems with pregnancy; the corpus luteum in the ovary is clearly visible on ultrasound. Also, this research method makes it possible to detect ovarian cysts and cancer on ultrasound. The dimensions of the ovary according to ultrasound in reproductive age are 25 mm in width, 15 mm in thickness, 30 mm in length. Ultrasound of the ovaries is normal, the normal size of the ovaries in women according to ultrasound: the volume of one ovary should not exceed 8 cubic centimeters. Ultrasound of the ovaries on the day of the cycle may deviate in size from the norm. At 39-40 years old, the largest sizes according to ultrasound are in women. When to conduct an examination: pain in the lower abdomen; preparation for pregnancy; painful periods; inflammatory processes of the appendages; observation during the dynamics of IVF; pain during sexual intercourse. Preparation for ultrasound of the ovaries: the optimal time for ultrasound is 5-6 days of the menstrual cycle; with transvaginal ultrasound, the bladder should be empty; with external ultrasound, the bladder should be full; A few days before an ovarian ultrasound, you should adhere to a slag-free diet. You can find photos of what an ovarian ultrasound looks like on the Internet.
Ultrasound of the ovaries is indicated for women in the following cases:
- If organ pathology is suspected (ovarian dysfunction, PCOS);
- Preventative annual examination;
- To clarify the diagnosis.
It is very difficult to determine ovarian diseases by palpation on a gynecological chair.
Get a free doctor's consultation
Norm
The concept of normal ovaries depends on the stage of the cycle and the age of the patient.
At the beginning of reproductive age, the ovaries are the same size in all women. By the beginning of natural decline, by the age of 40, the size of the glands decreases. Normally, the ovaries have lumpy outlines due to the follicles. During normal reproductive activity of the body, there should be 9-10 follicles. If there are significantly fewer of them, this makes us think about pathological changes in the reproductive sphere. The diameter of the follicles is about 3-5 mm. During maturation, the dominant follicle increases to 24 mm. It consists of a fully mature egg, which is released from the follicle at the end of ovulation. Author: Telegina Natalya Dmitrievna
Therapist with 25 years of experience
Ultrasound signs indicating ovarian pathologies:
- Compacted stroma and its increased echogenicity. Normally, the capsule should be absent and also contain a moderate number of blood vessels, so the stroma of healthy ovaries is not visualized by ultrasound. A thickened capsule may indicate PCOS (polycystic ovary syndrome) or an inflammatory process occurring in the pelvic organs.
- Increase in the size of the ovaries. The normal dimensions of the ovary in women aged 16-40 years are no more than 38 mm in length, 28 mm in width and 20 mm in diameter. An increase in organ size may also indicate PCOS, an inflammatory process, as well as the presence of single cystic formations.
- Uneven location of the ovaries. Normally, they should be located evenly at the right and left ribs of the uterus. If one ovary is adjacent to the uterus, and the other is located away from it, then this indicates a congenital or acquired (as a result of mechanical trauma) ovarian anomaly.
- Absence of one or both ovaries. Organs may not be visualized by ultrasound as a result of their removal, congenital absence, or premature exhaustion syndrome. Also, the presence of an organ is difficult to determine in case of severe bloating, during menopause, or during adhesions in the pelvic organs. If the ovary was not visualized at diagnosis, provided that it was previously present and was not surgically removed, then the woman will need to undergo special training and repeat the ultrasound. Preparation consists of cleansing the intestines with an enema and eliminating bloating.
- A large number of follicles arranged like a “necklace”. The presence of more than twelve immature follicles measuring less than 1 mm indicates polycystic ovary syndrome. If, on the contrary, the size of the follicles exceeds 25 mm, then this indicates OHS (ovarian hyperstimulation), which occurs as a result of taking hormonal drugs to stimulate ovulation (Clostilbegit, etc.).
- The presence of a cystic (echoic) formation larger than 30 mm. It is not difficult to identify a cyst by ultrasound - it looks like a ball with clear or fuzzy edges. Depending on the structure and form of the neoplasm in medical practice, the following types are distinguished:
- Follicular cyst - formed as a result of persistence (progression of growth) of the follicle. It is a ball filled with liquid - its shell is thin, and the contours can be fuzzy and clear. A follicular (functional) neoplasm appears in the middle of the menstrual cycle and persists until its end - often the cyst remains throughout the next cycle. An ovarian cyst on ultrasound shows an accurate result.
- Corpus luteum cyst - appears after ovulation, as a result of dysfunction of sex hormones. The size of such a neoplasm varies from 10 to 40 mm, often it persists for 2-3 months and even during pregnancy.
- Endometrioid cyst.
Ultrasound diagnostics of the ovaries allows the doctor to make a diagnosis, but cannot give definitive answers to questions regarding prognosis and treatment. Over the course of the menstrual cycle, the structure of the ovaries and the size of the follicles change, for example, at the beginning (on days 5-7) their size is 6-8 mm, and on days 10-12 - 11-18 mm. Before ovulation, on days 10-13 (with a 28-day menstrual cycle), a dominant follicle is normally determined, the size of which is on average 18-22 mm. If such a follicle was identified by ultrasound, this means that the woman will ovulate in 12-24 hours. Dominant follicles are often found in both ovaries, but ovulation in most cases occurs from one.