A woman’s life is completely determined by hormonal changes - only thanks to the production of hormones can she perform the functions assigned to her by nature - the reproduction of the human race.
Inflammatory diseases of the reproductive system and hormonal disorders can cause serious complications that deprive women of the joy of motherhood. In case of serious pathological changes in the gynecological organs, surgery to remove the appendages may be required.
Diagnostics
Before surgery, you must undergo a medical examination, which includes:
- Taking a biochemical and general blood test.
- Checking the speed of blood clotting.
- Search for antibodies to infections and viruses.
- Detection of hepatitis B and C.
- Cardiogram.
- Fluorogram.
After undergoing a comprehensive examination, the feasibility of the operation and the method of surgical intervention are determined.
For which malignant ovarian tumors is resection possible?
Definitely, with a widespread process involving cancer of the ovarian tissue, the question of partial excision is not raised. A young woman's "clean" ovary can be preserved if she wishes to give birth after cancer treatment. With a simultaneous process in both glands, it is not procreation that is important, but the preservation of the woman’s life.
To complete the reproduction program, complete removal of one gonad altered by a malignant process and partial excision of tissue from a visually healthy ovary is possible in a menstruating woman only at stage 1:
- Ovarian cancer;
- Germ cell tumor;
- Granulosa cell tumor.
For all other volumes of damage to the gonads, this option of surgical intervention is certainly non-radical, and therefore dangerous.
Wedge resection
Recommended for large cyst growth due to inflammatory processes and hormonal imbalance. The surgeon removes the affected tissue in the shape of a triangle (the base is located in the ovarian capsule). This is done so that new follicles with eggs can easily penetrate the uterus. This allows you to normalize ovulation in severe pathologies. In this case, a positive result is achieved in 85% of cases and lasts for six months or a year, depending on the severity of the pathology.
A more modern and safer method is to use a laser or electricity to create numerous incisions, making it easier for the eggs to be released. Despite high safety, excellent results are achieved only in 70% of cases.
This operation is recommended both for eliminating numerous cysts and for performing a biopsy. The tissue is removed in a triangle shape and sent to the laboratory for in-depth diagnosis and identification of cancer cells.
What are the consequences of removing the ovaries in women?
Immediately after oophorectomy, a woman’s body experiences a sharp decrease in the level of sex hormones. Despite the fact that hormones continue to be produced by other organs and tissues, they are not enough for normal life. Regardless of the presence of a uterus, after removal of both ovaries, menstruation stops completely. Ovulation disappears, after which the mucous membranes of the uterus atrophy.
A sharp decrease in estrogen provokes menopausal syndrome. This means that regardless of age, a woman will begin to feel all the characteristic symptoms of menopause. It happens that such artificial menopause manifests itself very weakly, but, as a rule, women who have undergone surgery to remove the ovaries are faced with a number of endocrine, nervous and cardiovascular pathologies.
The course of menopausal syndrome often depends on the woman’s age at the time of surgery. If the patient’s body is experiencing menopause, then the ovaries have already stopped functioning due to natural causes. The operation of excision of the genital organ will be simply invisible for women over 50 years of age. Often at this age, removal may be indicated if multiple ovarian cysts are observed or if there is a dangerous inflammatory process even in one of them. Also, the operation can speed up the approach of menopause at the appropriate age.
For young women of childbearing age, deprivation of both ovaries is extremely undesirable. That is why doctors are trying to take all measures to preserve at least one of their paired organs. Often, thanks to timely detection of a gynecological problem and proper therapy, surgery can be avoided. This is why regular visits to the gynecologist and ultrasound examination of the pelvic organs are important.
However, the rapid development of a malignant tumor even in one of the organs means the need to excise both.
Ovarian cancer often affects women approaching menopause, but a similar situation can occur at an earlier age. In addition, removal of the ovaries is indicated for hormone-dependent breast cancer of the fourth stage. This type of malignant formation is associated with the activity of estrogen and progesterone, which means that the development of the disease cannot be stopped with normal functioning of the ovaries. First, the girl will lose her period, and then menopausal syndrome will occur.
In addition to the inability to become a mother, after the operation a young girl may face a huge number of other problems affecting all systems of the body, namely:
- hot flashes;
- increased sweating;
- frequent dizziness;
- migraine;
- blood pressure surges;
- lethargy and fatigue;
- increased heart rate;
- decreased sex drive;
- irritability;
- sleep disorders;
- decreased appetite;
- unpleasant sensation in the vaginal area, dryness;
- frequent urination;
- disruptions in the functioning of the digestive system are possible.
All of these symptoms, as a rule, accompany a woman in the first 2-3 years after the operation. After 3-5 years, disturbances in metabolic processes and the activity of the endocrine system become more noticeable.
Ovariectomy also significantly increases the risk of developing many diseases.
- Atherosclerosis. Estrogens tend to protect blood vessels, and its sharp decrease leads to the accumulation of cholesterol plaques.
- Coronary heart disease and myocardial infarction.
- Hypertension and stroke.
- Osteoporosis. Bones begin to quickly lose calcium, and bone tissue is renewed much more slowly. This causes bone fragility and, as a result, the risk of injury.
- Deterioration of skin and hair condition. It occurs according to the scenario of age-related changes: wrinkles appear, nails become brittle, hair thins.
- Obesity.
- Glaucoma.
- Blood clotting disorder.
- Conjunctivitis.
- Periodontal disease.
Of course, the set and degree of severity of certain manifestations depends on the individual characteristics of the patient’s body. Special therapy aimed at eliminating the deficiency of sex hormones helps to ease the course of the menopausal period as much as possible.
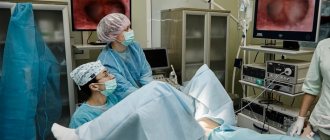
How is ovarian resection performed in CELT?
- Painless The operation is performed under endotracheal anesthesia.
- Low-traumatic The operation is performed laparoscopically, through three punctures of the abdominal wall with a diameter of 5 and 10 mm under visual control using a video camera.
- Effective During the operation, the cyst is removed while preserving normal ovarian tissue to the maximum possible extent, or (for polycystic disease) - wedge-shaped excision of part of the ovarian tissue or multiple cauterization (electroperforation) of the surface of the ovaries.
Consequences of removing an ovary
After surgery to excise the ovaries, women experience not only physiological changes, but also pathological disorders of the nervous system.
Physiologically, the following disorders may occur after oophorectomy:
- the rapid onset of menopause if the woman was of reproductive age, with all its characteristic symptoms - hot flashes, headaches, a feeling of dryness in the vagina;
- problems with urination;
- the occurrence of arterial hypertension;
- cardiac ischemia;
- periodontal disease;
- glaucoma;
- osteoporosis;
- atrophy of the vaginal walls.
Sometimes, after removal of the ovaries, ventrofixation of the uterus is required - securing it in the pelvis.
If the position of the uterus in the small pelvis was disturbed - it was bent or deviated from its axis towards one of the appendages - sometimes, with the development of an adhesive process, cords form between the uterus and the ovaries. In this case, during oophorectomy, another surgical intervention is required - ventrofixation - which results in 2 operations at a time.
Ventrosification is a surgical intervention in which the uterus is fixed in the pelvis, attaching it to the abdominal wall to avoid future prolapse.
It is possible to correct physiological disorders by taking hormonal medications, but hormone replacement therapy does not help get rid of moral suffering. Women often develop neuroses, depression occurs - they cease to feel like women, sexual intimacy - which can be returned to 2-3 months after the operation - ceases to bring joy. Libido decreases, and psychological problems appear when communicating with the opposite sex.
In this case, sometimes the help of a psychologist and normalization of the nervous system with the help of medications are necessary.
Nervous system disorders are also caused by an increase in external changes - signs of aging appear.
Reviews of doctors providing the service - Ovarian resection
Many thanks to Inna Vasilievna Kardava for her sensitivity, professionalism, and high level of medical care.
Low bow to you. With great respect, your patient, Olga Anatolyevna Z. Read full review Olga Anatolyevna Z
26.11.2020
I would like to express my gratitude to the gynecologist KARDAVA INNA VASILIEVNA. I had an appointment with a gynecologist on November 26, 2020. Thanks to the Doctor for his professionalism, participation, and excellent attitude towards the patient. Low bow to you. Read full review
Olga Anatolyevna Z
26.11.2020
What happens to hormones after oophorectomy?
Although the ovaries are small reproductive organs, their importance cannot be overestimated. These organs not only store eggs, but are also responsible for the production of female and male hormones. Life with one ovary changes significantly due to hormonal changes. Ovariectomy leads to changes in the condition of the entire organism. The fact is that reproductive hormones affect all organs of a woman, including the state of the nervous system. They support healthy hair, skin and nails, and are also responsible for reproductive function. After surgery, the concentration of hormones in the patient’s blood sharply decreases. Of course, their production does not stop, however, other organs are involved in this and are unable to maintain the number of hormones at the required level.
Similar article - White vaginal discharge without odor
Postoperative consequences directly depend on the woman’s age. So, if the patient is in the menopause, we can say that the resource of eggs has already been exhausted. Therefore, if one of the organs is removed, the consequences in this case will not be particularly noticeable.
For patients who are of childbearing age, doctors are in no hurry to prescribe surgery, so they first try to carry out drug treatment. If surgical intervention cannot be avoided, specialists perform organ-preserving surgery. There are good reasons for this, because it is important to preserve a woman’s ability to conceive and give birth to a child, and also not to disrupt hormonal levels. Of course, any operation is a severe stress for the female body, however, if doctors manage to preserve the organs as much as possible, life will not be so difficult for the patient.
General information
Hysterectomy is an operation to remove the uterus, which is performed due to the occurrence of various pathologies of this organ or the reproductive system as a whole. The most common cause is the discovery of tumors in the uterine cavity. If pathological problems arise during pregnancy or during birth complications, surgery may be the only way to prevent serious negative consequences for the patient. Also, indications for hysterectomy include severe cases of advanced endometriosis, severe bleeding, and uterine prolapse.
Ovariectomy is an operation to remove the ovaries. A common reason for this procedure is the appearance of malignant neoplasms. In the presence of hormone-dependent cancer, the ovaries are removed to prevent the development of cancer. Only surgery can stop the development of an existing tumor. Adnexitis is also considered an indication for the procedure, but is prescribed only in case of accumulation of pus and serous fluid (acute stage). In case of apoplexy, oophorectomy is performed urgently to avoid death, since it threatens peritonitis. Moreover, such a pathology is dangerous due to its suddenness and bleeding into the abdominal cavity. In case of an ectopic pregnancy, when the fertilized egg develops in one of the ovaries, an urgent operation is required - resection of the uterus. With further development of the fetus, rupture of the fallopian tube, ovaries and appendages may occur, and this condition leads to extensive bleeding and infection of internal organs.
It must be remembered that the operation to remove the uterus and/or ovaries is performed to save lives!
Living without ovaries or without a uterus leads to a change in a woman's daily existence. Often the most severe problems are of a psychological nature. One of the women interviewed said that after the operation her life had just begun. This is due to the fact that her condition before the operation was much worse and more bleak than after. Constant, prolonged bleeding exhausted her body and lowered her hemoglobin to a critical level. Because of this condition, sex with my husband became impossible. It was only after the operation that her life returned to normal.