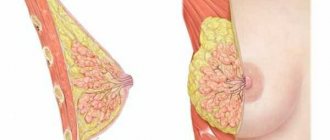
Functions of glandular tissue
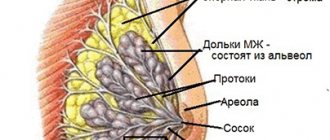
Connective layers extend from the skin of the chest in different directions, dividing the entire gland into small lobules. Between the lobules there is a layer of fatty tissue. It forms a kind of pillow on which the gland is located.
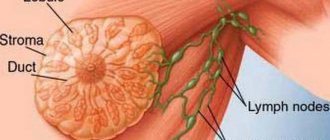
As for glandular tissue, its structure consists of many small glands. They are located in the lobules of the chest. Each section has tubes, at the end of which there are small extensions - alveoli.
A large number of tubes are complex body structures for the production and passage of milk. Throughout life, female glands change - they actively grow during puberty. The mammary gland functions under the influence of certain substances. During hormonal changes such as menstruation and pregnancy, women's breasts become larger and more sensitive.
During menstruation and after it ends, the gland undergoes various changes. In the second phase of the menstrual cycle, under the influence of the hormone progesterone, active growth of the alveoli begins. However, at the end of the cycle, the underdeveloped alveoli disappear.
Long-term production of progesterone after the conception of a child contributes to the maturation of the alveoli. At the end of pregnancy, the female body produces prolactin, which also affects the condition of organic structures. The body is preparing for breastfeeding. The hormone oxytocin regulates the release of milk from the breast. The functions of glandular tissue are directly influenced by the work of the thyroid gland, pituitary gland, adrenal glands and the consistency of hormonal substances. If there is a lack of certain hormones, it is necessary to increase their level in the body.
With age, various changes occur in the components of the gland. The risk of pathology may increase during menopause and postmenopause. The production of certain hormones in a woman’s body stops, and the density of the layers changes.
Prevention
For prevention, it is necessary to regularly visit a specialist and undergo examination. This is especially recommended for those who are at risk. Hyperplasia as a disease is becoming younger and younger. This means that it can appear at almost any age of a woman.
As for men, they are also susceptible to this disease, but to a lesser extent. In appearance, such breasts in men are similar to women's. It is painful and enlarged. Often the disease occurs in obese men whose breasts hang down due to the abundance of fat.
A woman should independently examine her breasts and notice any deviation from the norm.
Prevention includes:
- regular examinations and monitoring by a doctor
- elimination of concomitant chronic diseases
- control of the nervous system
- proper nutrition
- limiting self-administration of medication
Nutrition
If you don’t pay attention to the signals from the chest, very soon he will pull the rest with him. The body is a single system in which everything is interconnected. It is necessary to exercise, spend more time in nature and eat the right foods. If a woman comes into contact with harmful substances at work, they will definitely affect her health. Folk remedies work well if there are no serious pathologies. Both nicotine and alcoholic beverages have a detrimental effect.
The diet should be balanced with the least amount of carcinogens and hazardous substances. Eat more fruits and vegetables, supplement them with herbs, nuts, grains, and dairy products. It is best to purchase products from trusted outlets. If you grow vegetables yourself, try not to use harmful chemicals and fertilizers.
Meat consumption should be steamed or boiled. Any frying of foods adds harmful substances to your body. If you are not sure about the quality of meat, it is better to refrain from purchasing. A large number of meat products contain hormones that can harm the body. Monitor your body and take timely measures - this will help avoid serious consequences.
Diseases of the glandular tissue of the mammary gland
Pathological changes in the layers occur with such ailments as:
- Endometriosis
- Uterine fibroids
- Polycystic ovary syndrome
- Tumors of the uterus or ovaries
- Endocrine disorders
Blast hyperplasia develops with regular stress, breast trauma, and prolonged lactation. The most common pathology is the proliferation of glandular tissue of the mammary gland. Often the mammary glands undergo mastopathy. Cysts, tumors, benign and malignant formations can develop inside the mammary gland.
Hyperplasia of glandular tissue
The pathology is characterized by the proliferation of thoracic structures and imbalance of hormones. The onset of the disease is caused by genetic predisposition and a number of negative factors. The disease can develop after trauma to the mammary gland, nervous exhaustion, stress, or taking hormonal medications. Sometimes pathology is differentiated when a person works with hazardous chemicals. The thickness of dense tissue can increase due to hormonal age-related changes in the body.
Main signs of the disease:
- Breast pain
- Presence of nodes in glandular tissue
- Breast swelling
- Secretion from the nipple
The diffuse form of hyperplasia occurs without pronounced symptoms, so detecting the disease is extremely difficult. The disease is usually diagnosed during a routine examination of a woman. Glandular hyperplasia can affect boys and men, but the incidence rate among males is significantly reduced.
According to ICD-10 code, the disease is classified No. 60.
In pathology, neoplasms are sometimes diagnosed in the form of nodes of varying mobility and size. There is active growth and thickening of the tissue. Pain with hyperplasia can moderately radiate to the armpit or shoulder. There are menstrual irregularities and changes in the structure of the gland.
In medicine, hyperplasia is divided into several types:
- Dishormonal – occurs against the background of hormonal imbalance.
- Epithelial – accompanied by damage to the epithelium.
- Nodular – nodes are present.
- Diffuse – characterized by the presence of granular small tumors.
- Fibrous - dense affected areas of tissue are fused with surrounding tissues.
- Cystic - multiple and single cysts are diagnosed.
- Ductal - tissue growth is observed in the milk ducts.
- Stromal – a benign fibromuscular tumor is present.
- Atypical - proliferation is observed in glandular, as well as adipose and epithelial tissues. Diagnosed as a precancerous condition.
Glandular mastopathy
The disease manifests itself as severe pain inside the mammary gland. Discomfort and heaviness appear in the chest. The pain sometimes radiates to the armpit. There is discharge of secretion or pus from the nipple. Mastopathy is also characterized by the proliferation of glandular layers. Photos show what changes in glandular tissue look like. To the touch, you can detect a lump of various sizes in the thickness of the chest.
In medicine, the following forms of the disease are distinguished:
- Glandular-fibrous – benign seals are diagnosed
- Glandular-cystic – cysts are present in the thickness of the breast
- Fibrous-adenomatous – the tumor is characterized by the proliferation of organic structures
The causes of the disease are genetic predisposition, endocrine disorders, hormonal imbalances, and injuries. Most often, mastopathy develops in women who have crossed the forty-year mark. Irregular sex, psycho-emotional disorders, deficiency or excess of iodine in the body contribute to the appearance of the disease. Often the disease is diagnosed after frequent abortions.
With glandular mastopathy, formations are palpated that are densely localized in the lobules of the mammary gland. Their predominance, as well as increased breast tenderness, indicate a serious pathology. These are benign cystic neoplasms or small tumors. With the adenomatous form, characteristic tuberous formations are found deep in the thickness of the chest. The disease usually does not affect the lymph nodes.
In the diffuse form of mastopathy, the seals are small in size and distributed over the surface of the entire gland. Cystic mastopathy is a pathology with the formation of small capsules filled with liquid. As the cysts grow, they compress the nerve endings and cause pain in the chest. There is also a mixed form of the disease, in which cysts may predominate.
Mixed type mastopathy is a form of diffuse process
Mixed type mastopathy DFCM SF is a form of diffuse process in which areas with different types of cellular components are identified in the breast tissue in areas of pathological degeneration of the tissue structure of the organ. This form of the disease arouses the interest and caution of doctors because it indicates the heterogeneity of changes in the organ. This, in turn, may indicate a different reason for the occurrence of one or another form of tissue restructuring. Such a morphological variety of forms of mastopathy in one patient requires high oncological alertness and a comprehensive examination with mandatory biopsy of questionable areas of the organ.
A preliminary diagnosis of mixed mastopathy can be made by a doctor based on mammography and ultrasound examination data. The type of process and histological changes in the gland tissue can only be reliably confirmed by biopsy. But to obtain reliable data, it is necessary to collect biological material in places of the greatest changes in the breast.
Diagnostic measures
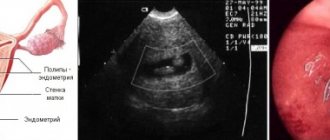
The most common diagnostic method is ultrasound of the mammary glands. The method is safe for health and allows you to differentiate volumetric compactions in glandular tissue.
Using ultrasound, the diagnostician identifies:
- Fabric volume
- Dimensions of the tumor
- Condition of the ducts
- Homogeneity of glandular tissue
- Fabric structure
- Echogenic level
Normally, glandular tissue is homogeneous during ultrasound examination. The ducts are not visible in it, the connecting stroma is hypoechoic. Hyperechoic layers are diagnosed between the fatty layers.
Diagnosis and treatment
When diagnosing this disease, the doctor examines and feels the breast, prescribes a blood test (general and biochemical), and hardware tests (CT, MRI, radiography, ultrasound). If necessary, take biomaterial from the site of proliferation.
Sometimes, as a result of an ultrasound, you can get a description of the changes, where, along with the detection of foci of proliferation, the diagnostician determines an enlarged lymph node (hyperplasia of the axillary lymph nodes). If the growth of the proliferation focus is not observed and the size of the lymph node is within normal limits, there is nothing to worry about. It is visualized in cases of cancer, including benign ones. Lymphoid tissue responds to changes in the mammary gland.
Treatment of the disease can be conservative and surgical. Depending on the form of hyperplasia and the danger of its degeneration into cancer.
With this we say goodbye to you. And we hope you will share the article with your friends via social networks.