Modern technologies make it possible to perform this procedure not by touch, but by visualizing it on the screen of an ultrasound scanner. Puncture under ultrasound control of the mammary glands ensures high precision of the procedure, eliminates unnecessary tissue trauma and allows you to take exactly the material that is needed for diagnosis.
Indications and contraindications
In essence, the technique comes down to a biopsy - taking a piece of tissue from the mammary glands during puncture under ultrasound guidance.
Indications for its implementation are:
- lump in the chest, determined by touch;
- a tumor detected on mammography to clarify its nature;
- breast cyst;
- nodular mastopathy;
- fibroadenoma;
- changes in shape, breast enlargement not associated with pregnancy and lactation;
- inverted nipples;
- nipple discharge;
- the presence of an “orange peel” type area (compaction and infiltration);
- the presence of areas of ulceration;
- the presence of an inflammatory infiltrate.
Usually, a puncture is sent after a preliminary examination - mammography or ultrasound, which reveals an area of compaction, a cavity or a neoplasm.
Contraindications to the study are:
- severe diseases of internal organs with dysfunction;
- infectious diseases;
- increased body temperature;
- During pregnancy and breastfeeding;
- menstrual days;
- decreased blood clotting;
- condition after recent operations;
- when a woman has already had a breast tumor removed, there is a relapse and at the time of the examination metastases were detected.
What diseases can be detected by breast biopsy?
This study is invasive and has a considerable cost, so patients are usually interested in its information content.
Here are just some of the diseases that can be detected using a puncture:
- fibroadenoma of the mammary gland (FAM);
- cyst;
- calcifications of glandular tissue;
- fat necrosis of the mammary gland;
- malignant neoplasms;
- adenocarcinoma of the breast.
Considering that the biopsy method is relatively safe and gives a quick and reliable result, we can say that the cost of the study is completely justified.
Types of research
According to its purpose, puncture of one or both mammary glands can be of 2 types:
- diagnostic – puncture biopsy;
- therapeutic – removal of fluid from the cyst cavity, introduction of sclerosing drugs into its cavity.
According to the technology of implementation, there are 4 types:
- fine-needle simple - puncture the area with a thin needle;
- thick needle simple - puncture with a thick hollow needle;
- fine-needle stereotactic - puncture with a thin needle in several places;
- thick-needle stereotactic – several punctures of the formation with a thick needle.
The choice of procedure method is determined individually for each patient.
Survey methodology
Usually, a conversation is held with the woman in advance about how and during what period a breast puncture is taken, how to prepare for it, and how to behave after the procedure.
Preparation for the procedure
A puncture biopsy of the breast does not require any special preparation. It is important to choose a period when the mammary glands are least susceptible to the influence of estrogens, and their tissue is less dense. The optimal period is from the 7th to the 14th days of the menstrual cycle, provided that it is 28 days. If an urgent examination is necessary, it is carried out on any day of the cycle.
3 days before the procedure, you should stop drinking alcohol and drugs that affect blood clotting, including aspirin and non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. Reduced blood clotting can cause bleeding and hematoma formation. On the eve of the procedure, you need to take a hygienic shower and stop using cosmetics and perfumes.
Puncture technique
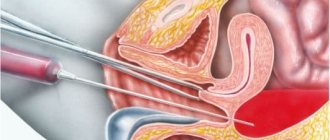
Breast puncture is taken both on an outpatient basis and in a hospital if the woman is under treatment. The woman is in a supine position. First, local anesthesia is performed with a solution of novocaine or lidocaine.
A fine-needle puncture is performed using a syringe; after puncturing the desired area, the tissue material is sucked out with a syringe. It is then blown onto a glass slide with a syringe and sent to the laboratory. This technology allows contrast material to be injected into the breast for further X-ray examination, for example if a cavity is detected.
When performing a thick-needle puncture, biopsy needles with a wide lumen are used; they allow you to take more material in the form of a “column” of tissue. A special aspiration “gun” is connected to the needle; it creates negative pressure, and the desired material is sucked into the needle, then placed in a test tube and sent for examination.
After the puncture, the wound is closed with an aseptic bandage, and to prevent hematoma, a small ice pack is temporarily applied, which is pressed tightly with a bra.
Research of punctate in the laboratory
Laboratory testing of punctate includes the following main methods:
- cytological;
- immunohistochemical;
- flow cytometry;
- molecular genetic.
Cytological method
The slides with the material are sent to the cytology laboratory, where a smear is made from it, as in a general blood test, stained with special dyes and examined under a microscope. Smears are also made from the biopsy sample in a test tube for cytological examination.
Under a microscope, the structure of cells is studied, their typing is carried out, that is, what they look like, what tissue they belong to, and whether they are atypical. Cancer cells differ in structure from normal tissue cells, which is called atypia.
Immunohistochemical method
In the material, through microscopy and chemical reactions, the presence of a special protein, HER2, is detected, which is located on cell membranes and is a growth factor for tumor cells. Determines the dependence of cancer on estrogen, progesterone and sensitivity to chemotherapy drugs.
Flow cytometry method
This method is based on the production of monoclonal antibodies to a cancer tumor - a special type of “specialized” B-lymphocytes. A suspension of the resulting biopsy is administered to the patient, the body produces antibodies, and then they are determined. The study allows us to identify tumor metastases.
Molecular genetic method
The most innovative and accurate research method in which the cells of the taken material are studied at the level of gene structure. Includes several tests: MammaPrint, TargetPrint, BluePrint. The study allows you to accurately determine the stage, degree of malignancy of the tumor, and even predict its “behavior” for the next 2, 5, 10 years with a high degree of probability.
Preparation
The procedure does not require special preparation. However, there are some recommendations to minimize possible risks and unpleasant consequences.
Of these, we can highlight the need to avoid taking alcohol and drugs that thin the blood, such as aspirin, several days before the procedure. You should carefully monitor your health and report them if you experience any adverse symptoms.
The best period for performing a puncture of the mammary gland is from the 7th to the 14th day of a woman’s menstrual cycle.
Interpretation of puncture results
Analysis of the punctate is usually done within 3-4 days, but if necessary, an urgent study can be carried out - within a few minutes.
Conclusion options may be as follows:
- results are within normal limits;
- a benign tumor was detected (adenoma, lipoma, fibroma, cystoadenopapilloma);
- a breast cyst was discovered;
- an inflammatory process is detected;
- a cancerous tumor has been identified - its detailed characteristics are given in accordance with the methods used;
- The diagnosis has not been clarified; additional research is required.
The results obtained are the basis for developing treatment tactics - conservative, surgical treatment, or combined treatment in an oncology clinic.
What is the research?
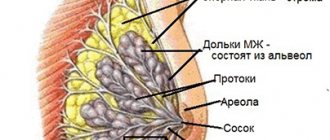
A puncture or biopsy consists of taking a piece of tissue (in this procedure, the mammary gland) for further sending to the laboratory for histological examination. In most cases, the biopsy is monitored using ultrasound technology. This helps to take tissue from exactly the area that is pathologically changed, and not damage the milk duct or blood vessels.
Photo 1. Puncture
What to do after the puncture procedure?
Pain is quite normal after a puncture. Usually they are mild, but if a woman has increased sensitivity to pain, analgesics can be taken for several days.
For the first 2 days you should not wet your breasts, and for 2 weeks you should refrain from heavy physical activity, sports, visiting the solarium and sauna, and thermal procedures. You should not walk without a bra, especially if your breasts are large, so that they have support and do not sag, and there is no stagnation of blood and swelling at the site of needle damage.
Progress of the puncture
Photo 2. TAB
After questioning and studying the medical history, the patient is placed on her back or side. Anesthesia is usually performed locally with a solution of novocaine. For incisional biopsy and in some other cases, the procedure can be performed under general anesthesia. The skin at the site of the intended puncture is thoroughly disinfected. After this, the study resembles taking venous blood for analysis with a syringe. For precise localization of the pathological process, the needle is inserted under the control of an ultrasonic sensor, as shown in the photo. Once it is removed, a cold compress can be applied to the puncture area; a surgical dressing is usually not required. After a correctly performed biopsy, there are usually no visible marks left on the skin, swelling and pain quickly disappear.
Complications after breast puncture
The consequences of a puncture biopsy are rare, but still sometimes occur:
- hematoma – hemorrhage into the gland tissue due to damage to a large vessel;
- persistent swelling – due to damage to the lymphatic vessels;
- infection of the gland – area of redness, infiltration;
- allergic reaction to an anesthetic drug.
No one can guarantee that complications will not appear; the anatomy of blood vessels is always individual. Allergic complications can be avoided if you notify your doctor in time about the presence of intolerance to drugs or other substances. If you experience any problems after the procedure, you should immediately consult a doctor.
Is breast puncture dangerous?
Some women are afraid of the puncture and delay the procedure. This should not be done.
The puncture is not associated with internal organs, and in no way can pose a health hazard. It is much more dangerous when a tumor is found in the breast, and a delay in examination can cost the woman’s health and sometimes even her life. After all, modern medicine is able to completely cure breast cancer if it is detected at an early stage.
How are tumors different?
Unlike fibroadenomatosis, fibroadenoma is treated only surgically. This neoplasm is a benign tumor that cannot be treated with either folk remedies or medications. This tumor does not degenerate into breast cancer.
However, ultrasound often makes an erroneous diagnosis and treatment of fibroadenoma is prescribed through surgery. After the incision, the doctor discovers a cancerous tumor, and the patient incorrectly believes that cell degeneration has occurred. But this fact does not exclude the formation of oncology from this tumor.
Where to do a breast puncture, what is its price?
A diagnostic puncture of the mammary gland can be done both in a public medical institution and in a private clinic, as well as in an oncology hospital or dispensary.
This procedure is performed only with the direction of a doctor. Who should I contact to be referred for this study? This depends on the area of residence and the structure of medical institutions there. If problems with the breast are detected, you can contact a surgeon, an oncologist; in large multidisciplinary hospitals there is a specialist mammologist who deals with breast pathology. There are specialized mammology centers at regional hospitals and oncology clinics.
The cost of the procedure in Moscow ranges from 2-3.5 thousand rubles , depending on the technology and the list of subsequent studies. For women who have an insurance policy, upon referral from a doctor, the puncture is performed free of charge, because it is included in the compulsory medical insurance program.
Reviews about breast puncture
There are many women who are hostile when the doctor talks about the need for a puncture. Some people think that if they refer to it, then it is almost certainly cancer. However, after the procedure, the opinion changes. Fortunately, in the vast majority of cases, its result does not portend danger.
Accordingly, reviews from patients after puncture are mostly positive. Most people do not experience any particular pain or complications. But fear goes away and understanding of the need for research comes, and trust in the doctor grows.
Folk remedy for mastopathy
A useful remedy is a decoction of sweet clover. The plant is brewed like this:
- 1 tbsp. l. sweet clover
- 250 ml boiling water.
You should infuse the herb for half an hour and drink it throughout the day. The course is at least 3 months, but signs of fibroadenomatosis disappear after 1 month of use. If the cysts recur after this, you should again undergo treatment for fibroadenomatosis.
This effect on fibroadenomatosis cysts can be repeated many times as necessary. In a situation where the disease cannot be treated with any medical or folk remedies, surgical intervention to remove the cyst is possible.
What is better to do: ultrasound or mammography
Comparing mammography and ultrasound is not very correct. An X-ray can only reveal a shadow in the chest, determine its location and approximate parameters, and therefore is a preliminary study.
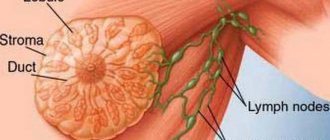
Ultrasound provides a more detailed “portrait” of the identified pathology, its structure and exact dimensions, down to the smallest intraductal formations. In addition, ultrasound allows you to examine the lymph nodes of the axillary region and identify metastases there. And modern color Doppler ultrasound scanning provides the most reliable data.
Mammography is a radiation method; it is contraindicated during pregnancy and lactation; moreover, compression of the gland is necessary during the image. Ultrasound has no contraindications and is an absolutely painless and harmless method. The photo shows examples of images of a breast tumor on mammography and ultrasound.
How does the procedure work?
First of all, puncturing requires little preparation. The woman is recommended to completely stop taking medications that are aimed at thinning the blood. You should also stop taking all medications except those prescribed by your doctor. Before the puncture, mammography and ultrasound diagnostics are recommended, which allows you to get the most useful information from the study.
Since the results of the puncture strongly depend on the professionalism of the doctors involved in the procedure and the technique of the procedure itself, women are advised to carefully select specialists. The more correct the procedure, the more reliable the results will be.
There are several main methods used to conduct research:
The needle is inserted directly into the tumor node under ultrasound guidance. Using a needle, a small amount of cellular material is taken, which is then stained using special techniques and examined under microscopes. Ultrasound is done in order to most reliably bring the needle to the tumor. Women are usually not in pain, so this method does not require anesthesia.
- If it is impossible to reach the tumor with a simple needle, doctors use an alternative method of collecting material. The procedure is performed under local anesthesia, as it is painful, and doctors use an elongated and thicker needle or a special device that resembles a pistol in appearance.
Any technique used to perform a puncture leaves no scars or scars. A woman may have a hematoma at the site where the needle was inserted, but it does not last long, dissolving in a few days.
There are several other techniques that are used much less frequently:
- Puncture using a thin needle. Used if the tumor is close to the skin.
- Stereotactic puncture. Requires mandatory monitoring of an ultrasound machine or mammograph. Necessary in order to obtain material from different parts of the neoplasm.
- Puncture using a thick needle. This is done if the doctor needs a large amount of research material to clarify the diagnosis.
- Incisional puncture. This is rather a small-scale operation aimed at removing damaged tissues from the body. During the puncture, the doctor removes the tumor and immediately sends it for examination. An incisional form of puncture is resorted to if there is reason to believe that the tumor is malignant.
- Trephine biopsy. This technique is used when the tumor is located too deep in the tissues of the gland. The study uses a biopsy gun under ultrasound guidance.