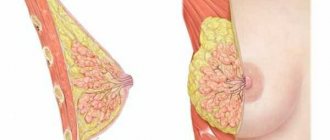
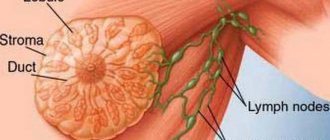
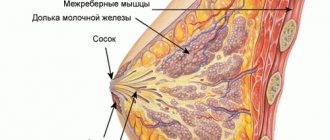
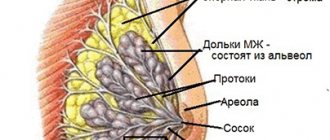
Swelling of the mammary glands in infants is a typical case, which, in most situations, does not threaten anything. This is the normal development of the mammary glands, associated with hormonal changes in the body. Let's figure out whether you should worry, how to recognize the pathology and not miss the disease.
Breast engorgement in newborns can be very frightening for parents. It would seem that the mammary glands are not even fully formed yet - why should they swell? This looks especially strange if the boy’s nipples are swollen. Along with breast changes, other symptoms may also occur - small pimples on the face, changes in skin color.
This is all a normal process. The newborn develops the correct hormone ratio for its gender. If the baby was not diagnosed with any pathologies in the maternity hospital, then there is no need to worry ahead of time.
Hormonal crisis in newborns
Hormonal crisis in newborns is the medical name for a phenomenon associated with hormonal changes in the first days of life. The baby adapts to the world around him, adjusts his body to interact with the environment. Why is this necessary? The fact is that during intrauterine development, the child receives hormones from the mother. They are needed to maintain pregnancy and to protect against early birth.
At the moment of birth, the child stops receiving maternal hormones, their concentration drops sharply, and the body begins to produce its own. Severe swelling occurs mainly in girls. Some parents believe that it is the breasts growing, but in fact the breasts only grow temporarily. This phenomenon is called age-related mastopathy and also occurs in boys. True, in boys, hormonal changes occur differently, so the breasts return to normal faster.
Age-related mastopathy in newborns is manifested by the following symptoms:
- Around the beginning of the second week of life, the skin around the nipples turns red.
- The mammary glands enlarge and can reach a diameter of 5 cm. This largely depends on the weight of the newborn and gender.
- There may be some slight discharge from the nipples. They are considered normal if they resemble colostrum in color, white-gray.
Interestingly, severe age-related mastopathy is observed only in three quarters of newborns. In 25% of children, symptoms are so mild that they may not be noticed. Mastopathy may be mild in children born with underweight. All doctors agree that breast engorgement in newborns in the first weeks of life is a physiological norm. You need to be wary only if you experience any atypical symptoms other than those described above.
The following symptoms are also normal:
- Discharge from the genitals may be mixed with blood. This is normal, since the genitals are open to the external environment, they produce their own mucous membrane and get rid of excess cells.
- Swelling in the genital area. A hormonal rash on the face is called milia. It looks like a scattering of small light pimples with white dots in the center.
It is important to practice good hygiene to help your child’s body adapt to the world around it.
Diagnostics
The nature of the pathology that causes engorgement of the mammary glands is determined by a mammologist. The specialist interviews the patient, finds out when and under what circumstances the symptom arose, and how the disease developed. During the examination, the doctor examines the condition of the mammary glands, palpates regional lymph nodes, and identifies general changes. The further examination program includes:
- Gynecological examination.
It is carried out to establish pregnancy and detect diseases of the female genital organs. Supplemented with a pregnancy test. - Ultrasound of the pelvic organs.
It is carried out to confirm physiological gestation, exclude the ectopic location of the ovum and timely detect pathological pregnancy. - Ultrasound of the mammary glands.
An accessible basic study that allows you to visualize space-occupying formations, inflammatory changes, and disorders of the structure of the mammary glands. Recommended for young women. - Mammography.
It detects the same pathologies as ultrasound; due to age-related changes in the mammary glands, it is more informative in patients of the older age group. According to indications, it is supplemented with ductography, pneumocystography, and digital tomosynthesis. - Breast biopsy.
Indicated in the presence of inflammatory, fibrous, cystic, tumor changes. The tissue or fluid samples are then examined through morphological or microbiological examination. - Lab tests
. The nature and scope of laboratory tests depend on the identified symptoms. Most often, general and biochemical blood tests, a general urine test, and hormone tests are prescribed. A microbiological examination of nipple discharge and determination of the level of tumor markers may be required.
How to behave as parents
You need to carefully monitor the signs of a hormonal crisis. If atypical symptoms appear, you should not put off going to the pediatrician. Pimples should not be squeezed; they will go away on their own. The task of parents is to prevent infection. In the first days of life, the body is especially vulnerable to viruses and bacteria.
Adherents of traditional methods of treatment often talk about the need to apply various compresses and use anti-inflammatory ointments. In fact, this is strictly prohibited. Neonatal mastopathy is a physiological, natural condition. There is no need to interfere with the body’s formation of hormonal levels.
Pediatricians also advise refraining from tightly swaddling the baby in the chest area. It is important to avoid any injury. Otherwise, microcracks will appear on the chest, through which it is easy to get infected.
On average, the crisis passes in 3 weeks. All this time, natural symptoms can be observed. You need to worry if, a month after birth, the signs of mastopathy do not become less noticeable.
Interesting fact: age-related mastopathy also occurs in adolescents, regardless of gender. Breasts increase in both young men and girls. Of course, girls' breasts are more enlarged and they begin to actively grow. And in boys, signs of puberty mastopathy usually disappear by the end of puberty. If the mammary glands remain enlarged, this is a reason to suspect gynecomastia.
Therapeutic measures
Treatment is carried out according to the clinical protocol, depending on the etiology, form of the disease and the age of the child. If you suspect a disease, there are several options for where to go. In the maternity hospital, you can immediately complain to the supervising doctor. After discharge, go to the local pediatrician. But the best option is a pediatric mammologist.
They try to cure mastitis in infants using non-drug methods of physiotherapy. In the early stages of the disease, UHF or ultraviolet irradiation is used for the smallest children. The action of a high-frequency electromagnetic field has an anti-inflammatory effect. UV therapy strengthens the body's defenses.
Both procedures have no contraindications for infants. They inhibit the development of pathogenic bacteria, improve blood microcirculation, and if additional medications are used, enhance their effects.
Medicines are resorted to in case of transition to those forms of mastitis that are classified as purulent - when an abscess appears with the leakage of exudate and subsequent tissue necrosis. The doctor selects the most gentle antibiotic pharmaceuticals for a child under one year of age. Additionally, immunostimulants and antipyretic suspensions are used, suitable for small children.
Treatment of mastitis with physiotherapeutic methods in teenage girls involves not only ultraviolet irradiation and UHF. Can be used:
- magnetic therapy;
- ultrasonic massage;
- light therapy;
- electrical neurostimulation;
- laser therapy.
Surgery is used for purulent, phlegmonous and gangrenous forms of the disease. But it’s better not to let it get to this point.
With the help of surgery, you can quickly and easily get rid of the abscess, dead tissue and cure the disease. But such intervention carries certain consequences. Due to the incision with the installation of a drainage outlet, the breast tissue is deformed, a dent remains, and sometimes a scar. In addition, damaged structures will interfere with lactation processes when the girl grows up and becomes a mother.
How to determine the disease
Mastopathy can be not only physiological, but also pathological. How to determine the disease? The disease occurs due to the penetration of infection into microcracks in the chest. A newborn’s body does not yet know how to fight bacteria and viruses, so any infection is extremely dangerous.
If infection occurs against the background of age-related mastopathy, purulent mastitis develops. Inflammations occur, enlarging the already swollen mammary glands, and the temperature rises. Since the child is not able to overcome the infection, a mandatory consultation with a doctor and taking all prescribed medications is required.
Symptoms of mastitis:
- Develops only on one breast.
- A lump appears in the mammary gland and it becomes harder.
- It hurts when touched.
- Literally every hour the swelling and inflammation increase.
- Increased body temperature, convulsions and vomiting may occur.
- The skin on the affected breast is red and hot.
- The child refuses to eat and sleeps poorly.
- Purulent discharge appears from the nipples.
If you have the symptoms described above, you should consult a doctor immediately. In the early stages, mastitis is treated with medications. If the disease is advanced, surgery may be required.
Norm or pathology
Studying the nature of the enlargements helps determine that infants have swollen mammary glands due to a sexual crisis and exclude the occurrence of diseases.
Normally, the size of the changes in a baby reaches 3 cm in diameter. Both mammary glands enlarge equally or with a slight difference. The areola area may be slightly red, but this does not cause discomfort.
In this case, the baby does not need treatment. Manipulation (application of bandages, compresses or squeezing out secretions from the mammary glands) is prohibited.
When there are no other symptoms, the condition is not dangerous. Parents must follow the rules for caring for a newborn and prevent hypothermia. If cloudy fluid is discharged from the vagina, parents should practice proper toileting of the genitals and consult a doctor.
If, when touching a child’s chest, he shows that he is experiencing discomfort, painful sensations, and externally there is a change in skin color, excessive growth of the mammary glands, uneven swelling - this indicates the presence of pathology. Mastitis requires immediate medical attention, because a complication in the form of an abscess will develop into acute purulent inflammation of phlegmon.
Treatment
Treatment tactics are chosen based on many factors: the health of the child, the severity of symptoms, the presence or absence of underweight. If only inflammation is observed, and purulent foci have not yet appeared, then antibacterial drugs, physiotherapeutic procedures and semi-alcohol compresses are prescribed. Treatment of newborns is carried out in a hospital setting.
If mastitis becomes purulent, surgery will be required. The incision is made under general anesthesia, pus is removed through the incision, and then drainage is installed to further clean the wound. After the operation, a course of antibiotic therapy will be required.
If you do not call a doctor for a while, phlegmon can form - these are purulent-inflammatory foci that are located under the skin, at the level of fatty tissue. Through these foci, the infection can enter the bloodstream and sepsis will develop. In the first weeks of life, a child's health is very fragile.
For girls, mastitis is even more dangerous - surgery, purulent foci can damage the milk ducts, which will not make it possible to breastfeed in the future. In addition, any trauma to the mammary glands increases the risk of developing mastopathy at a young age and breast cancer in adulthood.
Why does newborn mastitis develop?
If, during the development of physiological mastopathy, an infection enters the child’s body (usually staphylococcal or streptococcal), there is a risk of newborn mastitis: moreover, it can occur in both newborn girls and newborn boys. Staphylococcal or streptococcal bacteria can live in the mother's body (for example, on the surface of her skin or on the mucous membrane of the nasopharynx), and can also be found on surfaces in toilets and bathrooms.
Most often, mastitis in a newborn develops after discharge from the hospital - approximately on the 10th day of the baby’s life. By this time, the baby’s mammary glands should return to normal. And if the mother sees that this did not happen, it is necessary to urgently consult a pediatrician.
Microorganisms enter the body under certain conditions, usually when parents do not properly care for the child, not taking into account the special properties of his skin:
- it has a lot of microvessels;
- it has high permeability, so any substances from its surface immediately enter the body and the bloodstream;
- the fatty tissue under the skin is very thick and loose;
- sweat and sebaceous glands cannot yet function normally and create antibacterial protection; and if maternal immunity was unable to protect the child from bacteria (after all, the baby’s skin does not immediately accept all its microorganisms from the mother - the process of this colonization occurs gradually), they immediately cause an infectious pathology in the body;
- the thermoregulation process has not yet been adjusted;
- the skin is very saturated with liquid.
- How and why can an infection occur?
- if the child is dressed without taking into account the air temperature, and diaper rash occurs on his skin;
- if the baby’s clothes have rough seams or edges that injure delicate skin;
- if, while treating the child’s skin, the mother accidentally scratches or damages the skin (for example, with a manicure).
Symptoms of breast engorgement in children
Swelling of the mammary glands in newborn boys is less common than in girls. Regardless of the sex of the child, it is manifested by the following signs and characteristics:
- Enlargement of the mammary glands up to 2-3 cm, while the nipple of the breast is hard, which indicates engorgement.
- Changes are recorded mainly in the first week of a child’s life.
- When pressing on the mammary glands, the child reacts calmly, which indicates the absence of pain.
- The color of the skin over the enlarged mammary glands does not change, hyperemia is not detected.
- The subcutaneous tissue may not swell due to the absence of edema.
- White discharge appears from the milk ducts - an opaque liquid that resembles milk or colostrum may flow out.
The inflammatory reaction in the mammary gland has distinctive signs and features in comparison with physiological enlargement:
- Often there is an enlargement of one mammary gland.
- Breast enlargement can exceed 2-3 cm.
- The appearance of a local compaction in the form of a ball, the diameter of which varies, usually reaches 1-2 cm.
- The skin over the inflamed area becomes red, which is a consequence of blood stagnation. Not only the breasts, but also nearby areas of skin may turn red.
- Swelling of the subcutaneous tissue is noted due to increased permeability of the microvasculature and the release of the liquid part of the blood into the intercellular substance.
- When trying to palpate the mammary gland, the child begins to worry and cry, which indicates the occurrence of pain.
- General intoxication develops - the temperature rises to 38 ° C and higher, appetite and sleep worsen, the baby becomes restless and often cries.
- Mastitis can develop in a one-year-old child and later, while physiological enlargement of the mammary glands occurs only before the age of one year.
Reasons for changes
Physiological mastopathy, as a rule, appears in the first month of a baby’s life and goes away on its own.
Sexual crisis always has a physiological origin and develops in 80% of cases. Mostly occurs in the first month of life. The condition is characterized by the accumulation of sex hormones in the child’s blood, which enter the mother’s body through the placenta in late pregnancy and after birth affect the receptors of breast cells. Within a month, a gradual decrease in hormone levels begins and by the year it returns to the physiological norm.
Mastitis is an inflammatory process in the tissues of the child’s mammary gland. The main cause of development is infection with pathogenic or conditionally pathogenic microflora: staphylococci, streptococci, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Escherichia coli. The risk of infection may increase due to the presence of certain provoking factors:
- Decreased activity of the immune system, which is often associated with immaturity of defense mechanisms.
- Development of a hormonal crisis. First, physiological swelling of the mammary glands occurs, which can expand the excretory ducts through which infectious agents penetrate.
- Features of the anatomical structure of the mammary gland, which are of hereditary origin and are realized at the genetic level.
- The mother’s lack of proper skills in caring for the mammary gland of a newborn baby and insufficient hygiene provokes the accumulation of microorganisms with their subsequent penetration into the ducts.
Most often, parents panic when they suddenly discover that the mammary glands of newborn boys have enlarged. Especially cases when a cloudy liquid is released from the ducts. This is also called physiological mastopathy. What can you find in a baby:
- The enlargement may be parallel, or one breast may be larger than the other. Changes in diameter do not exceed 2 - 3 cm.
- Several droplets of light or cloudy odorless liquid may be released from the center of the nipple.
- Slight redness of the areola area is acceptable.
- Breast swelling appears in most cases on the 2nd - 3rd day of life and disappears during the first month of life.
- Girls are more susceptible to this than boys.
In these cases, the swelling does not require any treatment. Moreover, it is forbidden to try to squeeze out secretions from enlarged breasts. Various dressings, lotions, compresses, and pressure on the mammary glands can cause damage to the skin and infection - a life-threatening complication for the baby.
Physiological signs, treatment and care
Baby clothes should be made of soft natural fabrics
Physiological engorgement of the mammary glands in newborns does not require special therapeutic measures. It usually goes away on its own until the age of one, after which the mammary glands stop swelling. Experts, including Dr. Komarovsky, give recommendations for care that are aimed at preventing the development of the inflammatory process in tissues and other pathological conditions:
- Use soft, baby-friendly clothing made from natural fabrics. The use of synthetics is excluded.
- Before use, bedding and baby clothes are ironed and then allowed to cool to a comfortable temperature.
- Before carrying out procedures for caring for the baby, be sure to thoroughly wash your hands with soap, which is washed off with clean running water.
- If the breast is enlarged by more than 2 cm, it is recommended to apply a clean, dry bandage to prevent mechanical irritation from clothing.
If swollen mammary glands are detected in newborn girls or boys, you should not panic and immediately begin to treat the condition. With physiological enlargement, in which there is no swelling and inflammation, the use of Vishnevsky ointment, Levomekol, cold or hot lotions, or expressing the contents of the mammary gland ducts, which significantly increases the risk of infection, is excluded.
Mastitis in young children is treated by a doctor. Etiotropic therapy is prescribed, aimed at destroying the causative agents of the infectious process, for which antibiotics are used. They must be safe for the baby’s body and effective in destroying the bacterial pathogen. In clinical practice, protected semi-synthetic penicillins and cephalosporins are used. Local antiseptics in the form of a solution are also additionally used.
Mastopathy in children appears during childbirth or in the first days after birth (3–5 days). In the normal course, this condition lasts about a week, but can last up to a month, which is also considered normal.
The symptoms of mastopathy in newborns are the same, regardless of whether it is a girl or a boy. These include:
- Swelling of the mammary glands. They become enlarged, dense, and swollen.
- Discharge of fluid from the nipples, similar to colostrum.
With physiological mastopathy, touching the mammary gland area does not cause concern in the child - The glands are painless.
- Strict symmetry of enlarged glands.
Newborn boys may have more pronounced pigmentation of the areola around the nipple.
Physiological mastopathy in newborns does not require medical intervention or specific treatment. It goes away on its own without consequences for the baby’s health. Often this condition goes unnoticed by parents and pediatricians.
Compresses with vodka and other warming procedures for physiological mastopathy are prohibited
Previously, to eliminate mastopathy, the child was prescribed semi-alcohol compresses, ointments, and heat to the chest area. Now such physiotherapeutic methods have been abandoned, as they can provoke the development of mastitis.
Caring for a child with this condition requires compliance with certain rules:
- careful swaddling, changing clothes;
- clothes or diapers should not squeeze the baby’s chest;
- daily hygienic bath;
Neonatal mastopathy is not a contraindication to water procedures
- When bathing, do not rub your breasts;
- careful and timely care of the nipples when fluid is released from them, especially if it is summer or just hot weather.
It is not recommended to lubricate nipples with Fukortsin or a solution of potassium permanganate. Washing with clean warm water is sufficient.