— Advertising —
Mammography is the visualization of the structure of breast tissue using X-rays. Essentially, this is a photo of your breasts in several projections, which the doctor examines to identify abnormalities.
What does breast mammography show?
An annual mammogram can detect cancer at an early stage. Therefore, doctors advise regularly undergoing this medical examination. This procedure is especially relevant for women over 40 years old. At this age, hormonal changes begin that can lead to abnormalities in the breast tissue. You should definitely undergo the procedure if:
- there is discharge from the nipples;
- lumps and chest pain appeared;
- deformation of the shape of the breast or nipples has occurred.
Mammography is a diagnostic procedure that is necessary to assess the patient’s condition. After 35 years, it is mandatory for all women. It is enough to undergo the procedure once every 2 years to identify tumors. After age 50, mammograms are performed annually.
If there is a genetic predisposition (there have been cases of breast disease in the family), you should undergo mammography from the age of 30.
If malignant tumors are detected, the procedure must be done once a month. It will allow you to trace the dynamics of the development of formations.
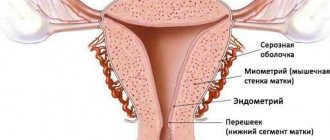
Mammographic imaging of the mammary glands may show cysts, mass formations (tumors), and calcifications. The general type of structure of the organ is also assessed (glandular, fibro-fatty, mixed with a predominance of one of the components). Attention is paid to the milk ducts, their structure and diameter.
Some mammographs are equipped with equipment for a needle biopsy, which is performed immediately to confirm or exclude the malignant nature of the process.
Visualization of the mammary organs can show cysts, space-occupying formations (tumors), and calcifications.
Video
Watching a video on how to properly undergo a breast examination is useful for preparing for the examination. Video provided by the Jit Zdorovo channel.
In this short video you will see what a mammography room looks like, where the doctor is during the procedure and how the examination itself takes place. You will also see how mammologists study the images after receiving them. All of this information will help you feel more confident about your mammogram exam.
Practicing mammologist Dr. Levchenko talks about mammography. From this video you will learn what mammography is, what indications and contraindications the procedure has, how to prepare for the examination, and what prejudices patients have about this examination. You will learn the pros and cons of analog and digital mammography. Find out why it is recommended to do an ultrasound and not a mammogram before the age of 40. What should you tell your doctor before the procedure? In the video you will see what a fibroadenoma, cyst and breast cancer look like on a mammogram.
If you are still afraid of getting a mammogram, be sure to watch this video. You will learn that modern digital mammographs make the mammogram procedure virtually painless. If during film mammography the female breast experienced a load of 20 kg, then with modern mammographs the load on the breast is 2 times less. In the video, the doctor shows how the load is applied gradually, making the procedure painless.
Mammography has reduced breast cancer mortality. Mammography is a revolution in women's medicine. Once a year after 40 years you need to do a mammogram! Find out why it's important to get regular mammograms (breast x-rays) every year. This video is for those who are hearing about mammography for the first time and want to know the essence and principle of the study. You will see a live video of how a mammogram is done. See what a breast tumor looks like on a mammogram. From this video you will learn how to properly prepare for the study. Find out why you need to do a mammogram from the 5th to the 12th day of menstruation and cannot conduct the study in the second half of the cycle. Why is it not recommended to drink coffee a week before the procedure? And how can regular deodorants and talc ruin mammogram results? What should you not do during the procedure itself? Why the main thing is not to move, so as not to get a false positive diagnosis of cancer while moving.
Breast diseases are the most common pathology faced by middle-aged and older women. Almost 15% of them are cancer. This means that effective preventive screening of the population is necessary to detect the disease at an early stage of development. The main one is mammography.
Indications
Doctors recommend that all women who have reached puberty undergo this examination once a year. But this is especially true for those over 40 years old. According to statistics, between the ages of 40 and 49 the risk of breast cancer is 1 in 69. This risk increases to 1 in 27 for women 70 and older.
Symptoms that require urgent mammography:
- nipple discharge;
- the appearance of compactions;
- chest pain;
- deformation of the breasts or nipples.
It is important to remember that the first stage of breast cancer is not accompanied by pronounced symptoms, so mammography can be preventive. If breast cancer is detected at the first stage, the patient's survival rate is 90%. The survival rate at the fourth stage is no more than 10%.
Factors that increase the risk of developing breast cancer for which regular mammography is recommended:
- hormonal deficiency;
- elderly age;
- taking hormonal medications;
- early onset of first menstruation;
- late menopause;
- obesity;
- one of the relatives had cancer.
Since during the examination the patient receives, albeit a small amount of radiation, this procedure has contraindications.
Contraindications for examination:
- pregnancy;
- lactation.
Mammography is performed on all older women at regular intervals.
A palpable formation in one of the glands is an indication for screening.
Also, an extraordinary study is prescribed if there are certain indications, such as:
- palpable hard or soft formation in one of the glands;
- visual deformation of the nipple or any other area;
- the appearance of blood when pressing on the nipple;
- local pain, signs of swelling, change in skin color, violation of symmetry on both sides.
Women of the young age category are referred for mammography under the following conditions:
- risk group for breast cancer (close relatives have been diagnosed with a malignant neoplasm);
- cancer of the uterus or ovaries;
- inability to get pregnant;
- diseases of the endocrine system;
- surgical interventions on mammary organs in the past.
Breast mammography is an X-ray with a small dose of radiation. Therefore, doctors do not recommend it:
- pregnant women;
- nursing mothers.
What does the procedure reveal?
Mammography can detect benign and malignant neoplasms. The procedure allows you to analyze changes in the mammary gland, their size and distribution.
- Cyst. This fluid cavity is a common occurrence in the mammary glands. It is not a cancerous disease. But mammography, unfortunately, does not allow distinguishing a cyst from a malignant tumor - further examinations are needed.
- Fibroadenoma. Tumor-like formations that are subject to growth. More common in young women. They are not malignant.
- Calcifications. Small, numerous accumulations of calcium salts in tissues can be the first sign of the initial stage of cancer. Large lesions are most often not associated with cancer. However, the presence of calcifications in the mammary gland may be due to the presence of an oncological process.
Even if there is a lump on only one side, both mammary glands are examined. This is done for comparison pictures and to identify changes in the other breast. If you have pictures of past procedures, you need to show them to the radiologist.
Indications for diagnostics
The indication for referring a woman to this type of examination is the need to clarify the diagnosis. There is no strict criterion at what age diagnostic mammography is performed if this research method can provide the required information.
Diagnostic mammography can be primary, when the doctor refers the patient for examination based only on her complaints or a medical examination. Or secondary, when the doctor has the results of previous studies.
For example, ultrasound of the mammary gland with detected changes in the structure of the tissue. Or data from a previously taken image of a routine preventive mammography. If a radiologist, when studying a routine mammogram, detects accumulations of calcium salts (calcifications) in the gland tissue, then this serves as a basis for the doctor to refer the woman for a repeat examination. Detection of signs of benign tumor growths is another reason for referral to repeat mammography, where the radiologist, on the instructions of the attending physician, conducts a targeted examination aimed at a specific task.
How is a breast mammogram done?
Mammography is carried out as a preventative measure for all women over 40 years of age once every 2 years. At the discretion of local institutions for the female population over 50 years of age - once a year.
In addition, there are unscheduled indications for this type of examination.
Carrying out a mammogram while breastfeeding is completely acceptable.
During pregnancy at any stage, it is preferable to use the ultrasound method due to the absence of side effects, primarily radiation exposure to the body of the mother and fetus. Carrying out a mammogram during breastfeeding is quite acceptable, but it is not very informative for a doctor. It is recommended to use other auxiliary studies.
It is considered most correct to undergo a mammological examination on days 5-13 of the menstrual cycle, i.e. in the first phase. In the second phase, the breast tissue undergoes some hormonal changes: the ducts expand, the structure of the glandular component changes, and swelling of the soft tissues may appear. In this case, the result may be unreliable, and the examination will be endured with a feeling of discomfort and pain.
According to basic recommendations, mammography should be performed no more than once a year. But in urgent cases, up to 2-3 times are allowed. If more frequent examinations are necessary, it is reasonable to use auxiliary methods - ultrasound (ultrasound), magnetic resonance imaging (MRI).
Mammography is carried out in the X-ray room, where the mammography machine is located. The woman is shown how to position herself next to him. The position depends on the type of equipment (standing or sitting). Next, a protective apron made of lead material is placed on the waist area, covering the lower abdomen.
The mammary glands are placed on a plate intended for this purpose, and the chest is pressed on top with a similar plate.
If a pathology is detected, the woman may additionally undergo radiography in a different projection - lateral and/or oblique. At the discretion of the doctor, a targeted mammography is possible, when the affected area of the gland is directly imaged on an enlarged scale.
A photo with a description can be received on the same day. Some clinics are equipped with digital equipment that provides more detail in the resulting image. All information can be saved on electronic media and used at any time.
On the first day, a woman may complain that her breasts hurt after a mammogram. This is due to the mechanical pressure of the plates, does not last long and eventually goes away on its own.
Other X-ray examinations should be rescheduled on this day so as not to exceed the permissible radiation dose.
Types of mammography
Based on the method of recording the resulting image, there are two types of examinations: film and digital mammography. In the first case, the image is recorded on X-ray film; in the second, it is displayed on the monitor and can, if necessary, be recorded on a disk or flash drive. Digital mammography is considered a more accurate method, since it has high resolution and allows you to work with the resulting image, for example, to enlarge the area that causes suspicion. In addition, the digital method is more informative in women under 50 years of age, as they have high breast density.
The primary examination is usually carried out in two projections (direct and oblique) and a survey mammography is performed. In some cases, the study is done in three projections: direct , oblique and lateral . This allows the doctor to see the largest possible volume of the gland and regional lymph nodes from different angles.
a targeted mammography is additionally performed - an image that clarifies the nature of the tumor. This study complements the plain mammogram and avoids image errors caused by overlapping tissue shadows.
How to prepare for a mammogram
No special measures are required before the manipulation. The results of mammography are not affected by food or liquid intake. The only recommendation is to avoid using cosmetics for the skin of the axillary area on the day of the study.
The radiologist or laboratory assistant warns the woman about all possible side effects, asks the day of the menstrual cycle, and asks about pregnancy at the time of the mammary gland examination.
To correctly interpret changes in the mammary organs, you need to have with you the protocols of previous studies (mammography, ultrasound, MRI).
Before the procedure, anxious women often ask: “Does mammography hurt or not? How will I feel? Mammography is an absolutely painless procedure. It lasts about 10–30 minutes. Before the procedure, the doctor will tell patients on what day the mammogram is done. However, for urgent diagnosis, the day of the cycle is not important.
Some women may experience discomfort during the examination if they experience chest pain. Therefore, on the recommendation of a doctor, they may be prescribed painkillers.
Jewelry should be removed during the procedure. The individual characteristics of patients will be fundamental to calculating on what day a mammogram is done. Usually this is 6-12 days from the start of the cycle.
If you have breast implants, you should tell your doctor. On the day of the procedure, you cannot use deodorant or cream. The armpit and chest area must be clean so that darkening does not appear on the film.
How to pass correctly
- Before entering the office, undress to the waist and gather up your loose hair. Wear a lead apron to protect other organs from radiation.
- Warn the radiologist about previous operations.
- The doctor will fix the breast in the desired position to equalize the thickness of all tissues. If the procedure is very painful, please report this to reduce pressure.
- Don't move while taking pictures. Hold your breath when asked by a healthcare professional.
- When performing a computed tomography scan, there are attacks of claustrophobia (fear of closed spaces). In some private clinics, the procedure is performed under anesthesia.
- Wait for a description of the result.
How long
Preventive mammography of the mammary glands takes 10–20 minutes. If the images are of poor quality, the procedure is repeated. Computed tomography to confirm the diagnosis and search for metastases lasts up to 2 hours.
How does the procedure work?
Before the procedure, patients ask: “Is mammography an ultrasound? How is the examination going?” Both methods do not require special training from women. X-ray examination differs from ultrasound examination.
Ultrasound allows you to monitor the condition of soft tissues. And visualization of dense ones is better diagnosed on mammography. Therefore, if the patient’s condition is of concern, then both examinations are prescribed.
X-rays pass through the human body, capturing the image on a special film. Mammography is a procedure that is performed on an outpatient basis. The radiologist places the patient's breast on the platform and fixes it. Several pictures are taken (top to bottom and side), during which the patient changes position.
For a clear image, the woman should freeze and hold her breath. The principle of the procedure is reminiscent of fluorography. But, unlike her, the radiologist takes pictures of each breast separately. During the procedure, the breast is slightly compressed by the device. Why is this being done?
- To even out the thickness and unevenness of the breast.
- To get a clearer image.
- To distribute the soft tissue, visualizing compactions and possible formations.
- To reduce the radiation dose - the smaller the tissue layer, the less dose it requires for a full image.
After receiving the images, the radiologist analyzes them and provides documentation to the attending physician. In some cases, mammography descriptions are received in person. Based on the results of the procedure, the attending physician may prescribe additional examinations to clarify the details of the diagnosis.
What is mammography and what types are there?
Any examination of the breast performed using x-rays is a mammogram.
The process of X-ray examination of the mammary gland itself has its own characteristics, which led to the creation of specialized devices.
In order to take an X-ray, the mammary gland is fixed between special plates of the device and compressed. This is done so that radiologists can correctly interpret the resulting images. Fixing the gland allows you to obtain the same location of its tissues in space, and compression makes it possible to reduce the thickness of the examined layer of gland tissue and obtain the optimal density of the object.
Today, there are two types of mammography machines that exist and are used in practice: conventional and digital X-ray machines. Their difference is based on the way information is processed.
In a conventional X-ray machine, information is obtained as a result of X-rays hitting a special film and stored after appropriate processing in the form of an X-ray image.
A digital device uses the capabilities of a computer to obtain information. Information on a digital X-ray machine arrives in the form of X-rays, but not on film, but on a special receiving sensor. From this sensor, in the form of a regular digital signal, the information enters the computer, is processed by special programs and converted into a picture. This image can be enlarged, reduced, and its contrast can be changed. Using a special printer, the photograph can be printed on paper. In any case, the obtained result is stored in the computer’s memory and can always be retrieved again for work.
Digital mammography has advantages over conventional mammography:
- The ability to change the scale and contrast of an already captured image. This allows the radiologist to do additional work with the image being studied. Sometimes, by changing the contrast or scale of the image, the doctor receives information that allows him to finally make a diagnosis. In the case of a conventional mammograph, if there is any doubt, the radiologist will refer the patient for a repeat mammogram or additional examination.
- Lower radiation levels.
- Possibility of obtaining any number of copies of the resulting image. But in a regular mammograph, the image exists in a single copy and cannot be restored if damaged.
- Lower cost of the examination (due to the lack of expensive film, reagents, and equipment for image processing).
The main disadvantage of digital mammography is the significantly higher cost of the hardware systems themselves for performing it.
Video: “How mammography of the mammary glands is performed”
Can be used for breast examination and computed tomography. This is a method when multiple layer-by-layer X-ray images of an organ are taken. The results obtained are combined using a computer into one overview image.
The advantage of tomography is only the ability to obtain information about the volumetric configuration of the desired object. That is, if only a rounded shadow is visible on a simple image, then a series of tomograms can already determine the shape of the tumor. In terms of its resolution, that is, the ability to detect small objects, tomography does not differ from conventional radiography.
A simplified technique has been developed specifically for the study of mammary glands using computed tomography and a computer tomomammography apparatus has been created. Instead of a huge number of layer-by-layer images, this device takes only 11. In different projections, moving around the fixed (but not compressed, as in a mammograph!) mammary gland.
After computer processing, a computer-synthesized three-dimensional image of the object under study is obtained. The time spent on the study, compared to computed tomography, is significantly less. And the result is almost equivalent. This method is called “tomosynthesis”.
Carrying out regular mass preventive X-ray examinations of the breast using X-ray machines specially designed for this is the popular meaning of the concept - mammography.
Mammography can be divided into preventive and diagnostic. Prophylactic treatment is carried out for healthy women over 39 years of age on the basis of the woman’s voluntary consent.
Diagnostic mammography is performed on the direction of a doctor. The purpose of its implementation is to exclude or confirm the doctor’s diagnosis when he detects symptoms (external manifestations) of any disease.
Is the procedure harmful?
Some patients, due to their incompetence, claim that mammography is harmful. Allegedly, the radiation dose is high, so it is better to do an ultrasound. Doctors assure that if the standards for conducting x-ray examinations are followed, the damage to health will be minimal.
Firstly, there are standards for undergoing x-ray procedures throughout the year.
Secondly, the dose for radioactive exposure is too small (less, by the way, than with fluorography).
Ultrasound and x-ray examination complement each other. Therefore, doctors often prescribe both diagnostic methods.
Mammography or ultrasound of the mammary glands - which is better?
Both methods, mammography and ultrasound, are highly accurate and specific for the presence of breast tumors. Ultrasound is preferable if visualization of areas located near the chest from different angles is necessary. These areas are difficult to reach for x-rays.
In addition, the ultrasound method more accurately differentiates the cystic and solid components of the tumor, identifies small pathology, and shows the presence of blood flow. It is also more informative in young females due to the increased density of organ tissue at this age. Ultrasound can be used at any stage of pregnancy.
Ultrasound is preferable if visualization of areas located near the chest from different angles is necessary.
Ultrasound allows you to analyze the size and shape of lymph nodes - an important marker for differential diagnosis between benign and malignant formations.
However, mammography makes it possible to detect single or multiple small calcifications, extensive tissue restructuring, and precise identification of the type of cyst, which is impossible with ultrasound.
What to do if you have high breast density
Approximately 50% of women have high density breasts. This means that the parenchyma of the mammary glands has a minimal amount of fat and is represented mainly by glandular and connective tissue. The sensitivity of mammography in this case is only 27–30%. As a rule, if the doctor sees on a mammogram that your breast density is high, he should recommend alternative diagnostic methods: ultrasound, magnetic resonance imaging or tomosynthesis.
Decoding the results
The results of mammography are assessed by a radiologist. The conclusion is issued on the same day. The research protocol describes the types of tissues that make up the mammary gland (fibrous, glandular, fatty), their relationship with each other, homogeneity or heterogeneity of the structure.
The shape of the organ is analyzed: round, oval, lobed or irregular. The size of the ducts is indicated (normally up to 0.4 cm in women of childbearing age, up to 0.2 in menopause), whether they are straight or convoluted, contain homogeneous or inhomogeneous contents, in which area they are better developed.
The age of the patient must be taken into account. In women over 40 years of age, involution processes begin (the glandular component is gradually replaced by fibro-fatty component). Mammography for fibrocystic mastopathy shows that during this period the glandular component predominates.
Dilated ducts and cysts are also clearly visible on x-rays. The doctor describes in detail their location (using a watch dial for convenience), diameter, contours, and internal contents. Types of cysts are presented as simple and complicated (festering).
The space-occupying lesion stands out quite well on the mammogram, as it is accompanied by a darkening symptom on the X-ray film. Its presence is confirmed in two projections. If visualization occurs in only one projection, then they speak of a focus of compaction in the mammary gland.
Tumors are described qualitatively by analogy with cysts, only the contours (even, uneven, presence of a capsule), density (low, mixed, high, asymmetrical), the presence and main characteristics of calcifications are analyzed in more detail.
It is now customary to assess the condition of the mammary organs according to the international system for describing and processing data BI-RADS (Breast Imaging Reporting and Data System), which is used in most countries.
The resulting changes are expressed as points. This algorithm accurately indicates to the attending physician further tactics for managing the patient and the necessary therapeutic measures. BI-RADS creates continuity between all treatment and diagnostic links that a woman goes through.
The scale includes 7 categories: 0 and 3 – cases subject to auxiliary research, re-monitoring after six months, 1 and 2 – sent to the treating gynecologist, 4 and higher – consultation with an oncologist, fine-needle biopsy is recommended.
The quality of the examination also depends on the experience and training of the specialist. In addition, there is a small percentage of false-positive diagnoses, which once again confirms the need for an integrated approach to the examination.
The age of the patient must be taken into account. In women over 40 years of age, involution processes begin (the glandular component is gradually replaced by fibro-fatty component). Mammography for fibrocystic mastopathy shows that during this period the glandular component predominates.
If during this period the glandular component predominates according to mammography, then fibrocystic mastopathy is diagnosed.
Dilated ducts and cysts are also clearly visible on x-rays.
Survey results
The most expected mammogram result is negative. This means that no abnormalities were found in the mammary glands. A positive result indicates that pathological formations have been identified in the breast. In this case, you will need to undergo an additional examination: perform a targeted mammography, which allows you to obtain a more detailed image of the area of interest to the doctor.
If the presence of a tumor is confirmed, you will be prescribed a puncture biopsy of the breast. Under ultrasound or X-ray guidance, the doctor will use a thin needle to remove a small area of tumor tissue for histological analysis. It is the pathologist who will make a conclusion about the nature of the tumor process, since it is impossible to accurately determine the nature of the tumor from a mammogram.
Unfortunately, with mammography, as with any other method, diagnostic errors are possible. False positive result – something that is not there is detected. A more in-depth examination does not confirm the presence of a tumor.
False negative result – the existing tumor is not detected. In what cases is this possible? The accuracy of mammography in detecting tumor processes reaches 70-80%. However, the likelihood of error increases with high breast tissue density, as well as with breast implants.
Signs of a benign tumor on a mammogram
Mammography can differentiate or suspect the nature of the formation. The main disadvantage is the difficulties encountered in women under 35 years of age due to the increased density of the organ parenchyma.
Among benign focal changes in the mammary gland there are lipoma, fibrolipoma, leaf-shaped fibroadenoma, fibroadenolipoma, etc. They are characterized by the following signs:
- clearly defined, smooth boundaries;
- shape in the form of a circle, oval or lobes;
- homogeneous structure;
- absence of small calcifications;
- low density.
Breast cancer appears on mammography with certain properties:
- irregular or lobed shape;
- fuzzy (blurry), uneven contours;
- asymmetrical density;
- germination into healthy tissues;
- violation of architectonics;
- the presence of a local accumulation of small (up to 1-2 mm) calcifications in the structure or duct;
- enlargement and pathological changes in lymph nodes;
- thickening, swelling of the skin and subcutaneous fat layer above the tumor.
Other distinctive signs of malignant pathology in the mammary glands are the lack of compressibility and mobility of the formation, the vertical orientation of germination into the organ.
Thus, mammography of the mammary glands is a diagnostic technique that can establish the correct diagnosis as early, effectively, non-invasively, accurately, and easily as possible. In complex or doubtful cases, examination of the mammary organs should be carried out in combination with other methods.
Among benign focal changes in the mammary gland there are lipoma, fibrolipoma, and leaf-shaped fibroadenoma.
Candidate of Medical Sciences, mammologist-oncologist, surgeon
More articles
Preparing for a breast examination
Mammography does not require complex preparation.
Before having a mammogram:
- tell your doctor about the presence of breast implants;
- do not use deodorant before the procedure;
- Make sure your chest and armpits are dry;
- remove all metal jewelry;
- if the presence of lumps is already known, the doctor can give you an anesthetic to make the procedure comfortable.
Experts recommend undergoing this type of examination in the first half of the cycle. This is due to the hormone progesterone. After ovulation, in the second half of the cycle, the amount of this hormone increases and it affects the mammary glands. This can make the mammogram procedure a little unpleasant for the patient and make it difficult for the doctor to make a diagnosis.
If there are any symptoms in the mammary glands, you should immediately consult a doctor and have a mammogram, regardless of the day of your cycle.
There are several types of menstrual cycle, for each you can determine the period when it is best to have a mammogram.
| Type of menstrual cycle | Favorable days for mammography |
| Short (21–28 days) | From 3 to 7 days of the cycle |
| Medium (28–35 days) | From 5 to 12 days of the cycle |
| Long-term (more than 35 days) | From 9 to 18 days of the cycle |
If the cycle is irregular, the examination takes place immediately after the end of menstruation. During menopause, screening can be done at any time.
The first day of the cycle is considered the first day of menstruation.
Mammography with tomosynthesis is a three-dimensional image of the breast in the form of thin (1 mm) sections. This is a new method that has not undergone enough clinical trials.
MRI is a more gentle method that does not use harmful radiation. But it is not able to display some anomalies.
Optical mammography is a method using projection and tomography devices. Not applicable for diagnostic type of research. Optical fluorescence mammography involves introducing phosphors into the tissue. This helps to see the growth of the tumor.
Ultrasound is an ultrasound examination that allows you to get a clear picture from different angles. It is used during pregnancy and lactation, as it is less harmful than the x-ray method.
A biopsy is the removal of tissue samples for further examination. It is this method that allows you to verify the presence or absence of breast cancer.
How is the procedure performed?
The procedure is carried out for 10–15 minutes. The patient stands in front of the machine, the mammologist fixes the breast and sometimes asks her to hold her breath for a while.
Breast fixation is done for several reasons:
- to level out unevenness;
- to get a clearer image;
- to increase the clarity of the image of seals;
- The smaller the layer of tissue, the less radiation is needed to scan it.
Each breast is checked separately so that their anatomical structure can be compared. Pictures are taken in two projections; sometimes it is necessary to take pictures in additional projections to clarify the diagnosis.
The video shows how mammography is done using various techniques. Video courtesy of Health{amp}amp; Life.
Film
Film mammography is the first method of breast X-ray, which appeared in the 60s of the last century. The resulting image is recorded on film and cannot be converted into digital form. In addition, this method is 20% less accurate than digital mammography. Such devices are preserved only in government institutions, since the transition to digital equipment costs a lot of money.
Digital
To record the image, not film is used, but detectors. They convert X-rays into an electrical impulse and transmit the image to a computer.
This type of mammography is optimal for:
- patients with dense breasts;
- patients under 40 years of age;
- patients before menopause.
Microwave
Microwave mammography uses the intensity of the patient's own tissue radiation. In this case, X-ray radiation is not used. The essence of the technique is that compactions and foci of disease differ in temperature from healthy tissue. This allows them to be identified with high accuracy in the early stages.
Advantages of this method:
- safety;
- non-invasive;
- diagnosis in the early stages of the disease;
- determination of tumor growth rate;
- identifying patients at high risk of developing breast cancer.