A woman’s reproductive health is very vulnerable – it is exposed to many negative factors every day. Stress, poor nutrition and other companions of modern life lead to hormonal imbalance, which provokes various abnormalities in the functioning of the reproductive system.
One of the frequently diagnosed diseases is endometrial polyp. How dangerous it is, how it affects pregnancy and whether it prevents conception - the answers to these questions are ambiguous and depend on the individual clinical picture. Doctors identify a number of factors that determine the compatibility of pregnancy and endometrial polyp.
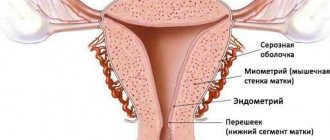
What is an endometrial polyp
A polyp is a benign formation that is formed from the endometrium, more precisely, from the basal layer. To put it more clearly, polyps are finger-shaped soft growths that form on the mucous membrane. That is, polyps are a pathological growth of the endometrium that needs to be treated. This is a hyperplastic process, so taking drugs that increase cell regeneration for this disease is dangerous and only worsens the situation. Women over 40-45 years of age are most susceptible to this disease; the disease is less commonly diagnosed in girls 20 years of age and older.
Polyps come in different forms, according to the modern classification there are 4 types: glandular, fibrous, glandular-fibrous, adenomatous. It is important to understand that not all endometrial polyps lead to the development of cancer. Only adenomatous polyps are precancerous. They are most often observed in women during or after menopause. Glandular neoplasms most often occur in young women.
Do I need to remove it to get pregnant?
It is not always necessary to remove such growths surgically so that it does not affect conception in any way. This is due to the fact that women experience endometrial shedding every month.
If the polyp is small and there is no chronic pathology that provokes its appearance, then it can go away on its own. Or, with a “successful” location and small size, it may not in any way affect the process of fertilization and subsequent attachment of the fertilized egg.
It is impossible to say unequivocally whether the polyp needs to be removed or not. Many doctors prefer more aggressive management and offer hysteroscopy or RDV right away. But there is another tactic. In this case, time is given to independently resolve the problem (2 - 3 months), and hormonal medications can also be prescribed for the same period.
If the polyp remains after this, the likelihood that it will go away on its own is minimal. And if a woman is trying unsuccessfully to conceive a baby, it is better to remove the tumor.
What are the symptoms of endometrial polyp?
As a rule, the disease is practically asymptomatic. Thus, the combination of “endometrial polyp and pregnancy” is detected during an ultrasound examination of the expectant mother. In this case, pregnancy has risks of complications, but often women carry a healthy baby without problems.
Suspicion of an endometrial polyp is caused by:
- Painful periods;
- Unpleasant odor or yellowish tint to leucorrhoea;
- Bleeding or slight discharge of blood;
- Irregular menstruation;
- Infertility;
- Unpleasant sensations or pain during sexual intercourse;
- Nagging pain in the lower abdomen;
- Chronic miscarriage;
- Bloody discharge after sexual intercourse or douching;
- Iron-deficiency anemia;
- Weakness, irritability, fatigue;
- Noise in ears.
As you can see, the symptoms of endometrial polyps are quite vague, so a diagnosis requires an examination by a gynecologist and examination.
Diagnosis of this disease is relatively simple. If the polyps are large, then an experienced doctor will detect them during examination. However, the doctor needs to conduct additional research to exclude the presence of an oncological process. For this purpose, a Pap test is performed.
It is also necessary to:
- Ultrasound examination;
- Endometrial biopsy using aspiration method;
- X-ray examination (hysterosalpingogram);
- Metrography;
- Examination of the mucous membrane using a hysteroscope.
All types of examination are relatively painless. However, minor bleeding may occur after the biopsy is taken.
What to do if the formation is discovered after conception?
If the polyp does not manifest itself in any way, the pregnant woman should undergo regular gynecological examinations and monitor the condition of the pathology.
If the growth begins to bleed , then the following is prescribed :
- vaginal sanitation;
- after 12 weeks, therapy directed against urogenital infection;
- in the second half of pregnancy, interferon therapy;
- in particularly difficult situations - removal of the formation.
If there is a threat of miscarriage:
- hormone therapy;
- drugs that relieve spasms and sedatives - strictly according to indications.
A cervical polyp during pregnancy must be removed if:
- its size exceeds 1 cm;
- education bleeds;
- there are pronounced signs of inflammation and necrotization of the polyp;
- presence of dyskaryosis;
- rapid growth of education.
In all other cases, if the polyp is not complicated, the formation can simply be observed without taking any action.
IMPORTANT!
In general, pregnancy in the presence of an uncomplicated polyp proceeds normally, and the woman has every chance of giving birth to a healthy baby.
How does the disease affect fertility?
Endometrial polyps often cause infertility. Thus, multiple large growths can cause obstruction of the fallopian tubes. In this case, sperm may not reach the egg. According to some reports, neoplasms cause irritation of the uterine mucosa, which prevents the embryo from settling. In addition, the body often tries to destroy polyps, which provokes chronic inflammation of the uterine tissue. There are other reasons why polyps directly or indirectly cause infertility.
Therefore, if a woman with endometrial polyps is planning a pregnancy, she must first undergo treatment for the disease. Research confirms that conservative and surgical treatment increases the chances of successful conception and pregnancy. However, it is necessary to understand that endometrial polyps do not guarantee the impossibility of conception. Therefore, women who do not want to have children should not neglect contraception. Endometrial polyps make the abortion procedure dangerous to the life and health of a woman.
Pregnancy after surgery
Of course, you won’t be able to get pregnant removing the tumor .
After the operation, the woman takes a course of hormonal therapy, and conception in this case is simply impossible.
After the doctor is convinced that the mucous membrane has recovered, there is no inflammation, and all tests are normal, he stops taking hormonal medications . Just a couple of months after stopping the drugs, a woman can become pregnant.
Currently, there are many ways to remove a polyp from the uterus without harming a woman’s reproductive ability.
The following are considered the safest removal methods for women planning a future pregnancy::
- burning out a polyp with a laser;
- excision of the formation using radiosurgical method;
- cryodestruction – freezing with liquid nitrogen;
- hysteroscopy - twisting the stalk of the formation using special equipment.
Endometrial polyp and pregnancy
Successful conception and pregnancy can occur even in the presence of endometrial polyps. In most cases, pregnancy proceeds without complications. If there are any complaints, a pregnant woman should consult a doctor. Usually, if there is a danger to the mother or fetus, the woman is sent to hospital treatment necessary to maintain the pregnancy.
Why is the combination of endometrial polyp and pregnancy dangerous?
- Intense increase in polyps due to increased estrogen levels;
- Chronic miscarriage;
- Miscarriage;
- Bleeding during pregnancy;
- Increased risk of infectious diseases;
- Iron deficiency anemia;
- Premature birth;
- Postpartum hemorrhage.
These complications are quite rare, but they can complicate or terminate the pregnancy or cause harm to the mother or baby. But usually pregnancy occurs against a background of mild pain in the lower abdomen and mild bleeding. But even if the endometrial polyp did not affect the pregnancy and the birth was successful, the woman still needs to be re-examined and undergo a course of treatment. In rare cases, endometrial polyps may disappear during pregnancy.
Causes of polyp formation
The reasons for the formation of polyps are varied and not fully understood. Age over 35 years is an additional risk factor, but the disease is diagnosed in women at different periods of life. Most often, pathology occurs against the background of:
- Chronic infectious diseases of the reproductive sphere. The development of inflammatory processes contributes to the formation of polyps.
- Disturbances in the secretion of sex hormones. Glandular hyperplasia of the endometrium and other pathologies are often observed.
- Endometriosis, fibroids, adenomyosis.
- Endometrial hyperplasia. During menstrual bleeding, the shed endometrium is sometimes not completely removed, and the remaining areas in the uterus can turn into polyps.
- Prolonged mental overload and stress.
- Frequent abortions, curettages.
- Long-term hormonal therapy, contraception (IUD).
- Diseases of the digestive system - intestines, gall bladder, liver.
- Genetic predisposition.
- Partial removal of the placenta during abortion or childbirth. Fragments remaining in the uterus can lead to the development of a placental polyp.
- Hormonal changes during menopause.
Despite the fact that pregnancy can occur in the presence of such formations, they have a negative impact on the development of the embryo and can lead to spontaneous abortion.
In rare cases, a polyp in the uterus forms during pregnancy - as a reaction of the endometrium to this physiological process.
Removal of endometrial polyps and pregnancy
It has been proven that after resection of polyps, the chances of successful conception and pregnancy without complications increase dramatically. Hysteroscopy and laparoscopy are relatively simple and minimally invasive treatments. That is, during surgery, healthy tissue is not harmed, and polyps are removed using a special instrument - a hysteroscope or laparoscope.
Another method of treatment, curettage, is already outdated. It is quite dangerous, since during the procedure the uterine mucosa is scraped. It is better not to agree to this method of treatment. Firstly, healthy tissue suffers during the procedure. Secondly, the method does not guarantee removal of the polyp. Moreover, this method can lead to the formation of scar tissue, which reduces the chances of conceiving and carrying a child.
After treatment, there is a chance of successful natural conception. In some cases, hormonal therapy, physical therapy and other auxiliary procedures may be prescribed. The therapy is aimed at improving the health of the expectant mother and increasing fertility, however, in the presence of scar tissue and other complications, it may not give the desired result.
For couples who are unable to conceive naturally, other options remain. Thus, the IVF procedure after treatment of endometrial polyps gives good results. Intrauterine insemination can also be performed. Thus, endometrial polyps are not at all a sentence to childlessness.
Polyp during pregnancy
We have already said that polyp and pregnancy are sometimes quite compatible concepts. As a rule, we are talking about small growths that the expectant mother does not even know about until she undergoes the first ultrasound.
If the appearance of a growth is not associated with hormonal disorders, they are only monitored throughout the entire period of gestation to exclude the possibility of growth. After all, pregnancy can stimulate the growth of formations.
Surgical treatment is postponed until the postpartum period. However, sometimes it is not required: the polyp disappears on its own after childbirth. In extreme cases, surgery is performed during pregnancy.
To get rid of worries about possible formations in the uterine cavity, gynecologists recommend planning conception in advance in order to identify the pathology in time and quickly begin treatment, preserving the woman’s reproductive function.
What causes endometrial polyps
Scientists have not yet found out for certain what exactly provokes the growth of the endometrium. However, factors have been identified that increase the risk of developing this disease:
- Hormonal imbalances, including elevated estrogen levels;
- Thyroid diseases;
- Diabetes;
- Chronic inflammation of the cervix and diseases that cause them (oophoritis, endometritis);
- Abortion;
- Obesity;
- Injuries to the uterus (after accidents, childbirth, etc.);
- Genetic predisposition;
- Neuropsychiatric disorders;
- Immune abnormalities;
- Long-term wearing of an intrauterine device.
Taking care of your health can significantly reduce the risk of endometrial polyps, even in the presence of a genetic predisposition.