Sex hormones are the main regulator of vital processes in the human body. These substances have a huge impact on metabolism and are responsible for the formation of character and personality.
For women, one of the main hormones is estrogen. The health of the fair sex, the formation of secondary sexual characteristics and the ability to bear children depend on it. An estrogen test is of great importance for assessing the possibility of conception and identifying various pathologies.
Amazing Hormones
All organs of our body work on a clock, and each of them has its own period of activity and recovery. All systems are interconnected and one cannot work without the other. This is the so-called “internal clock”. And hormones are the regulators of the clock, the conductors of our entire body, the driving force.
Little molecular pranksters are like cogs, without which not a single mechanism will work.
Hormones control many processes and affect almost the entire body!
They help us quickly adapt to various life incidents:
- determine our rhythm of life;
- give us a feeling of euphoria when we are in love;
- help overcome depression and stress;
- prepare us for motherhood;
- are responsible for the external attractiveness of a woman, preserving her natural beauty and determine the degree of sexuality.
During menopause, the production of hormones decreases and the body has to get used to new conditions, which means that everything works differently.
Estrogen
Our “messengers” work without a single day of rest, and what a day, there isn’t even a single free minute. They plow for many days and nights to maintain the necessary biorhythm of the body. These are the heroes the world needs to know about! Today we will tell you about the secrets of one of the guardians of health.
There are several types of hormones in the female body - testosterone, estrogen and progesterone, etc. Progesterone is considered our main hormone responsible for procreation, but also one of the important female “helpers” is the hormone estrogen.
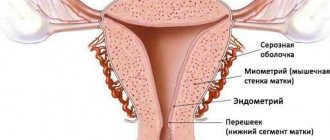
Estrogen is mainly synthesized by the ovaries (uterine appendages), responsible for the regularity of the menstrual cycle. In the first phase of the cycle it is produced by the ovarian follicles, and in the second half of the menstrual cycle - by the corpus luteum.
In addition, estrogens help in the formation of secondary reproductive organs in girls, increase the tone of the uterus, and maintain the health of the mother and child during pregnancy; strengthen bone tissue, affect metabolism, support libido; participate in the regeneration of the body, are responsible for good memory, and maintain proper cholesterol levels in the body.
Indications for the study
There are certain signs that clearly indicate problems in a woman’s body. Increased estrogen is characterized by heavy and painful periods, excess body weight, unstable emotional background, and frequent migraines. Excess of female hormones often leads to endometrial growth and cancerous tumors.
A reduced concentration of estradiol manifests itself as scanty and irregular menstruation, frigidity, vaginal dryness and painful sexual intercourse, brittle bones, and infertility.
If a woman cannot become pregnant for a long time, it is estrogens and progesterone (the pregnancy hormone) that should become the objects of close study.
Only the balance of these hormones guarantees quick conception and a successful pregnancy. If your monthly cycle is not regular, there is excessive male-pattern hair growth on your body, and acne constantly appears on your face, you need to urgently take an estrogen test.
Types of estrogens
Estrogens affect almost the entire body!
Estrogens are a group of steroid hormones that are divided into several types:
- Estrone.
- Estradiol.
- Estriol.
The most important in its role is estradiol, it is responsible for the woman’s reproductive system. Other types of estrogens affect the body to a much lesser extent, so all hormonal preparations are based on estradiol.
Estrogens may be synthesized by the uterine appendages, but their receptors also spread to other organs: mammary glands, liver, bone tissue, genitourinary system and even the brain (estrogen synthesis is controlled by hormones of the hypothalamic-pituitary system: FSH and LH).
In girls, estrogens are synthesized at 7-8 years of age and grow rapidly over the years.
Definitions
Estrogens are a group of steroid-type sex hormones. They contain approximately 30 different compounds. The key ones were estriol and estrone, as well as estradiol. The most significant is estradiol. It is the most active element. The external attractiveness of a representative of the fair half of humanity mainly depends on it.
Estrogen production occurs in the ovaries. A relatively small amount is formed in the placenta during pregnancy, as well as in the pituitary gland. There are special estrogen receptors in the woman's body. They are located in the myocardium, in the liver and mammary glands, as well as in the uterus with the ovaries. There are receptors in the fallopian tubes, directly in the vagina.
It is important to understand that with the development of inflammatory processes in the body, receptors may begin to be blocked. It is imperative to undergo examinations and undergo appropriate tests to determine whether hormonal balance is maintained. It is especially important to do this during pregnancy.
It is known that after menopause ends, the formation of peculiar estrogens in adipose tissue continues. However, these elements are atypical and do not have the necessary properties and do not bring the necessary benefits to the woman’s body.
Laboratory to help
Having learned what dangerous consequences can be, you probably have many questions.
Among the frequently asked questions you can find these:
- How to get tested for estrogen?
- When to take an estrogen test?
- On what day of the cycle should I take it?
Calm down, dear ladies! Below you will find answers to all your questions.
Before taking tests, let’s first clarify one point: all types of estrogens have their own specific amount, and it is by referring to these numbers that you can understand whether your estrogens are reduced or increased.
Estradiol standards:
- In the first phase of the menstrual cycle (before ovulation) –14 – 150 ng/l.
- During the period of ovulation (approximately 14 days of the menstrual cycle) – 35 – 420 ng/l.
- In the second half (after ovulation) – 26 – 250 ng/l.
- In menopausal women – 5 – 30 ng/l.
Estriol, which is produced during pregnancy:
- In the early stages of pregnancy – 0.6 – 8.5 nmol/l.
- In mid-pregnancy – 11 – 50 nmol/l.
- By the end of the period – 25 – 100 nmol/l.
Estrone:
- During the first sexual period of the menstrual cycle – 5 – 8 ng%.
- In the second half of the menstrual cycle – 5 – 25 ng%.
Attention! Data may vary depending on the day of the menstrual cycle.
Should pregnant women be tested?
The main role is played by the indicators of estradiol and progesterone. With one blood draw, as a rule, tests are performed for level 2 of these hormones.
Tests for estradiol and progesterone during pregnancy are carried out:
- mandatory, at 12-15 weeks to assess the development of the fertilized egg and the condition of the placenta;
- with severe uterine bleeding and pain;
- if the fetus, during ultrasound or MRI, reveals physiological abnormalities in the development of the adrenal glands, thyroid gland, small size of the fetus at this stage of pregnancy, lack of calcium in the placenta;
- post-term pregnancy for more than 10 days;
- the fetus has Down syndrome (determined by DNA testing). Intrauterine infection, inflammatory processes of unknown etiology;
- impaired blood supply to the placenta, decreased amount of amniotic fluid;
- at the request of the mother after drinking alcohol, in particular beer, narcotic and other psychotropic substances, including antidepressants;
- if you need to prescribe medications or folk remedies that affect the level of estradiol - reducing - no less than 1000 in the first, 2500 in the second, 6000 in the third trimester; increasing - no higher than 500, 1000, 4000, respectively;
- Ultrasound and MRI record the low mobility of the embryo or the absence of its movement.
Interesting! Post-term pregnancy is a great danger - a sharp increase in the concentration of salts in the placenta.
There is a high probability of both physiological and anatomical pathologies in the newborn. Premature pregnancy poses a greater danger at 8 than at 7 months - at 8 months there is a high probability of damage to the central nervous system during childbirth.
We take tests
How to take a blood test for estrogen? Hormone testing is a laboratory test. Hormone levels are determined by blood tests.
Therefore, to determine the amount of estrogen, you need to donate blood for estrogen. Based on the results of blood hormone tests, your doctor will tell you whether you have a hormonal imbalance and whether treatment is required.
Expert opinion
Roman Andreevich
Candidate of Medical Sciences, gynecologist-obstetrician, 14 years of work experience.
To get a consultation
Venous blood is given for analysis. You can donate blood in any laboratory, but not at any time; the test must be taken not during the day or in the evening, but STRICTLY in the morning on an empty stomach. The day before the test, you should not eat fatty or spicy foods and avoid alcohol; cancel physical activity, sexual intercourse and stressful situations.
How can women understand when to get tested?! Of course, in the best case, the analysis should be taken without any reason, so as not to miss even the slightest violations. But, unfortunately, our women only grab themselves when they have problems.
Study indicators vary depending on age and cycle period.
Reasons to get tested for estrogen:
- Menstrual irregularities (irregular menstruation, absence of menstruation).
- Lack of ovulation.
- Infertility.
- Polycystic ovary syndrome.
- Cysts in the ovaries.
- Hormone-dependent formations (tumors).
- Endometrial hyperplasia.
- Problems with body weight.
- Estrogen control during the premenopausal period.
On what day of the cycle should you take a blood test for estrogen?
Since the level of estrogen depends on the day of the menstrual cycle, the test, in the best case, should be taken in both phases of the cycle on days 5-7 of the menstrual cycle and days 21-24 of the menstrual cycle; if it is impossible to take the test in both phases, you can take it once on 21 days of the menstrual cycle. The days of the cycle are counted from the beginning of menstruation.
Violation of estrogen concentration in the body
There is a physiological increase and decrease in estrogens: estrogens begin to increase from 7-8 years of age, and decrease after 45-50 years during menopause (cessation of the menstrual cycle).
As practical research shows, if a hormonal imbalance is observed during a woman’s reproductive age, this indicates a pathology that urgently needs to be prevented.
Consequences of fluctuations in the amount of estrogen:
- The main disorder is delayed puberty.
- Irregular menstrual cycle, lack of ovulation, lack of menstruation.
- Early aging, hair loss.
- Depression.
- Decreased libido.
- Sudden mood swings.
- Gallstones.
Varicose veins (damage to veins and blood vessels).
- Edema.
- Hypothyroidism (syndrome associated with thyroid hormone deficiency).
- Osteoporosis (chronic skeletal disease, decreased bone density).
- Cardiovascular diseases.
- Pathology of the mammary glands.
- Memory impairment.
- Ovarian cysts.
- Endometrial hyperplasia (proliferation of the uterine lining, leading to its thickening).
- Oncological process in the endometrium of the uterus, and tumors in the mammary gland.
- Obesity.
- Acne (inflammation of the skin, accompanied by acne).
- Hypertrichosis (excessive hair growth).
- Increased pain before and during the menstrual cycle.
- Late menarche (first menstruation in girls).
- Infections of the genitourinary system.
- Reduction of mammary glands in adolescents after their formation.
- Blood clot formation.
- Increase or decrease in blood pressure.
- The appearance of multiple papillomas (benign formations) on the skin.
Such small “cogs” and such big problems, often even life-threatening. This may not be surprising, because they monitor the work of our body, without them everything could collapse. Therefore, we should monitor their condition so that our little friends do not get tired and do not stop working.
The role of progesterone
After the release of a mature egg from the dominant follicle, the corpus luteum is formed - a temporary endocrine gland engaged in the production of progesterone. If fertilization of the egg has occurred, progesterone will continue to be produced in an increasing manner to create all the conditions for maintaining the development of the fetus. That's why it is called the pregnancy hormone. Also, during gestation, it prepares lactation, helping the growth of the mammary glands. If there was no conception, the corpus luteum dissolves and progesterone drops. These changes are cyclical and monthly. In the complete absence of ovulation, progesterone is not produced - there is no corpus luteum.