From hydroturbation to laparoscopy
The adhesive process occurs as a result of chronic inflammation of the female genital area. It is often the cause of female infertility. In this case, there is complete or partial obstruction of both or one pipe. This prevents the sperm from fertilizing the egg, resulting in the impossibility of pregnancy.
Today, medicine offers four methods of cleaning the fallopian tubes: hydroturbation, laparoscopy, fertiloscopy, recanalization. The attending physician will select a method based on the individual characteristics of the body and the degree of the disease. For many years, in domestic gynecology, hydroturbation has been used - this is a method of cleaning the fallopian tubes, in which a woman is washed with a solution through the vagina with a syringe. However, in recent years, the effectiveness of this method of cleaning pipes has been questioned, which is why laparoscopy has now become more popular.
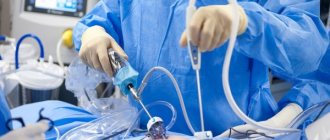
Laparoscopy is a modern and less traumatic way to clean the fallopian tubes. Its essence is that the doctor makes three small punctures in the peritoneum. Through them, small instruments are used to excise formations leading to the formation of adhesions, and the fallopian tubes are cleaned. The fallopian tubes are then sutured. The patient is under general anesthesia during the procedure. The positive aspect of this method is that after the operation the patient quickly recovers and returns to active life. This is the most common method of cleaning the fallopian tubes today.
Fertiloscopy is similar to laparoscopy. The main difference between these operations is that during fertiloscopy, instruments are inserted through the vagina. In this way, the doctor cleans the woman’s fallopian tubes.
Hysterosalpingography (metrosalpingography)
This is an examination using x-rays.
Preparation:
- vaginal smear;
- blood tests for HIV, hepatitis B and C, syphilis;
- fluorography;
- negative pregnancy test;
- a few hours before the procedure you can take no-shpa and baralgin.
Just as with USGSS, a liquid - a radiopaque substance - is injected into the uterus. The contrast gets into the fallopian tubes and in the pictures you can track how it passes through them, whether there are areas of narrowing or complete obstruction.
The contrast agent is chosen by the doctor; it can be water- or fat-soluble. Water-soluble penetrates better into the folds of the mucous membrane, so you can get more detailed pictures of the pipe relief. In addition, it is quickly eliminated and does not cause pain when absorbed.
The oily contrast is thick and does not coat the mucous membranes well, but has an undeniable advantage - after it pregnancy occurs much easier. It lingers in the tube for up to a day and can cause abdominal pain as it dissolves.
After the contrast is administered, several x-rays are taken. Hysterosalpingography lasts no more than half an hour, after which the woman goes home.
The radiation dose during hysterosalpingography is minimal, so you can conceive a child already in the current cycle.
Chromosalpingography
This is a surgical (laparoscopic) examination of the patency of the fallopian tubes.
Preparation for the procedure:
- general and biochemical blood test;
- blood clotting test (coagulogram);
- analysis for HIV, hepatitis B and C, syphilis;
- fluorography;
- vaginal smear;
- exclusion of pregnancy in the current cycle;
- the day before - only liquid food, in the evening - a cleansing enema;
- On the day of laparoscopy, you should not consume food, liquids, or tablets.
The procedure is performed at any time during the cycle, except menstruation, in the operating room under general anesthesia. The gynecologist-surgeon makes a puncture with a thin tube - a trocar in the navel area. Through it, a laparoscope is inserted into the abdominal cavity - a device with a video camera, the image from which is displayed on the monitor. At the same time, a solution of indigo carmine (“blue”), a harmless dye, is supplied through the uterus into the tubes. Normally, it should pour into the abdominal cavity, which will be visible on the monitor.
Video: Normal patency of the fallopian tubes during chromosalpingography
The trocar can also be inserted through the vagina; such a study is called fertiloscopy. In any case, the surgeon has the opportunity to immediately begin surgical treatment. To do this, he cuts the anterior abdominal wall in several more places and inserts manipulators through the holes. So, you can immediately perform the operation and restore the patency of the fallopian tubes.
After the operation, the woman requires hospitalization for up to one week. During this period, she is given antibiotics, painkillers and other drugs if necessary. Immediately after the operation, there may be slight mucous-blood discharge from the genital tract; menstruation usually begins on time. It is better to postpone conceiving a child at least until the next cycle.
All types of examinations are prescribed only by the attending physician, taking into account the clinical picture of infertility.
A procedure such as blowing out the fallopian tubes is used during diagnostics to determine the causes of infertility. But it is carried out when all possible causes have already been excluded.
With partial damage to the fallopian tubes
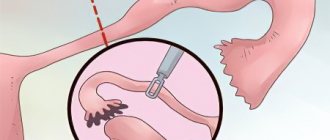
Recanalization is used for women in whose tubes the inflammatory process has not started. A special feature of recanalization is that a catheter moves through the fallopian tubes, separating the welded sections of the tubes. On average, the procedure takes about half an hour. The woman does not require observation in a hospital and can go home immediately.
It is worth saying that often a woman undergoes cleaning of the fallopian tubes not once, but several times. This is due to the resumption of the inflammatory process in the pipes. To reduce the risk of secondary formation of adhesions after cleaning the fallopian tubes, physical therapy is prescribed.
Source
How does tubal obstruction occur?
The fallopian tubes, also called fallopian tubes, are long, thin tubes that connect the ovaries to the uterus. The main function of the oviduct is the connection between the egg and the sperm, and it is natural that if obstruction is diagnosed, conception is not possible. Then the gynecologist prescribes blowing of the uterine tract.
As you know, after the follicle ruptures in the middle of the menstrual cycle, the egg is sent to the uterus. It makes its way through connecting pathways towards the sperm. However, if one of the oviducts is blocked or damaged, fertilization of the corresponding egg will not occur. It should be noted that blocking the channel does not pose a threat to a woman’s life. Pipe obstruction occurs in the following cases:
- adhesive process on the outside of the oviducts;
- operations in the abdominal cavity, including those not related to the reproductive system;
- complication of abortion;
- tumors, abnormalities;
- ectopic pregnancy;
- endometriosis;
- blockage of the channel inside the connecting path.
Particular attention should be paid to the appearance of obstruction inside the oviducts. Quite often, inflammatory processes occur unnoticed and are often treated untimely. During the proliferation of pathogenic bacteria, their metabolic products in the form of pus and mucus are deposited on the walls of the fallopian tubes, which gradually clogs them.
Frequent causative agents of asymptomatic diseases are the bacteria mycoplasmosis, chlamydia, ureaplasmosis and others. The most dangerous disease associated with obstruction is tuberculosis of the oviduct, which becomes more active with a sharp decrease in the immunity of the infected person.
The more often inflammatory diseases occur, the higher the chance of lack of adequate connection between the uterus and ovary.
Pipe cleaning procedures
Doctors often send patients to have their oviducts blown out, but this is not the only way to combat canal dysfunction. Modern medicine assumes hydroturbation, laparoscopy, hysterosalpingography, fertiloscopy and recanalization as the main, most accurate procedures for diagnosing and cleaning pipes. The main thing in this matter is to undergo all the necessary examinations to detect contraindications to the prescribed operations.
Hydrotubation is the introduction of mucus-removing fluid using a syringe into the oviduct. A special procedure for washing the fallopian tubes, if they are completely blocked, can be accompanied by severe local pain.
The procedure begins a few days after the end of menstruation and ends when the water pressure result of 60 mm Hg is recorded on the recorder tape. Art.
Laparoscopy is less traumatic than hydroturbation, since internal pressure is not applied to the walls of the uterine canal. Cleaning takes place under general anesthesia; several deep holes are made in the abdominal cavity and the uterine canals in women are cleaned using special miniature surgical equipment.
Cleaning takes place using a camera—a cavity enlarged 40 times is displayed on the screen.
Hysterosalpingography or HSG is one of the methods of salpingography - a type of diagnosis of the condition of the oviducts, which involves an x-ray. It is carried out by introducing a balloon into the cervical canal using local anesthesia. The study is aimed at a more detailed study of the intricacies of the anatomical structure of the body and the causes of infertility.
Fertiloscopy involves a procedure similar to laparoscopy, but without incisions in the abdominal cavity, but through the genitals (cervix).
Recanalization involves cleaning by inserting a catheter with a contrast fluid, which creates pressure and breaks the adhesions.
Diagnosis is carried out by a gynecologist in accordance with the prescribed preparatory list on a certain day. After determining the degree of obstruction, a physical cleaning procedure is prescribed.
Types of purging
In modern medicine, there are two types of blowing and each of these types differs in a number of features in its implementation.
Perturbation is the process of purging with carbon dioxide. The latter is best suited because it has a high dissolution rate in the bloodstream.
In addition, it includes a number of features:
- Before starting the procedure, it is important to empty the bladder and cleanse the intestines through the use of an enema;
- Carried out by a specialist. In this case, special equipment is used, connected to a container filled with gas. Using a rubber tube with a tip inserted into the cervical canal, gas is supplied;
- Before the procedure, the external genital organs are treated with a disinfectant solution. Then the tip of the device is installed and fixed and gas supply begins. This must be done with extreme caution; feeding too quickly can lead to damage to the integrity of the internal organs;
- If the patency is normal, air will enter the abdominal cavity without any problems. This can be noted by the drop in pressure level on the pressure gauge installed on the device that supplies air. In addition to changes in the pressure gauge readings, there will be a clearly audible noise in the peritoneal area. This is the result of air movement.
There is no need to worry that this type of intervention may cause injury to the inside of the uterus or fallopian tubes. When performing it, low pressure is used, which has a gentle effect on the internal genital organs.
Hydroturbation is the process of purging through the use of isotonic saline sodium chloride solution.
Mostly similar to perturbation. However, an important difference is the fact that the diagnosis of patency is carried out by blowing with liquid. The latter, like air, is supplied under slight pressure.
How to blow out the fallopian tubes
One of the factors influencing conception is the patency of the tubes, and in the case of diagnosing various disappointing patency of the oviducts, women are interested in the question: “how is the uterine canal blown out?” Treatment of adhesions in the fallopian tubes is possible without surgery; as mentioned above, recanalization promotes the rupture of adhesions. The condition for recanalization is the absence of inflammatory diseases in the reproductive system.
The uterine canals are cleaned using conservative and surgical methods. The conservative method involves injections, antibiotics and physical therapy. This technique is relevant in non-advanced cases - the formation of adhesions is just beginning. But the surgical method involves any surgical intervention.
Before carrying out the classic procedure of blowing out the uterine tract, the bladder is emptied, the cervix and cervical canal are disinfected with ethyl alcohol and iodine. Using a special mirror, the uterus is pulled out, after which a rubber tip is inserted into the cervical canal to supply air flow.
Other home treatment options
Treatment of disorders of the reproductive system can be supplemented by taking burdock juice and douching with celandine tincture; beaver uterus, bergenia root and flax seeds are also popular.
Women who have been diagnosed with obstruction can try honey and propolis tampons as a treatment. It is necessary to take into account the fact that honey is one of the most common allergens when choosing this method. Balls made from honey and medicinal herbs, which must be consumed within twenty days, help to get pregnant.
Is it possible to clean pipes using folk remedies?
According to many women, cleaning the oviductal canals is possible using folk remedies. Based on numerous experiences, the International Association of Gynecologists made a negative conclusion about common methods of self-medication.
Cleaning the oviduct at home using douching is fraught with dysbacteriosis in the vagina. It is usually followed by inflammatory processes, which indicates the opposite results of the method. And the hog uterus for conception (plant) in some cases provokes an ectopic pregnancy. You can read more about this in our article about the hog queen.
The use of medications and herbs can cause the opposite effect due to possible intolerance to the elements. If you suspect blockage of the oviductal canals, even to prevent the disease, you should seek help from specialists.
Diagnosis and cleaning of the connecting tubes between the uterus and ovary should be carried out by an experienced specialist using the least traumatic manipulations. Before conducting a diagnosis, the specialist must collect the necessary gynecological tests and schedule a day for the examination. After diagnosis, a suitable cleaning method is selected. The main thing is not to self-medicate!
Source
Contraindications
Despite the obvious effectiveness of the method of treating the disease, blowing is not recommended for:
- Mud treatment or less than two months from the date of its completion;
- Malignant neoplasms of the uterus and its appendages;
- Individual immunity to medications recommended for use during the procedure;
- Bloody discharge from the cervical canal;
- Less than four months from the development of acute inflammatory processes of the reproductive system;
- Presence of bacteria, fungi or viruses. The most common include: staphylococci, streptococci, E. coli bacteria, the presence or absence of which also determines the level of vaginal cleanliness;
- The beginning of the menstrual cycle;
- Suspicion of pregnancy;
- Development of general or local inflammatory processes;
- A sharp jump in ESR levels in the blood, leukocytosis;
- A sharp increase in body temperature;
- Severe pathologies of the cardiovascular system;
- Alkaline environment of the vaginal smear;
- Cervical erosions.
Obstruction of the fallopian tubes - treatment, symptoms, causes, alternative treatment, diagnosis
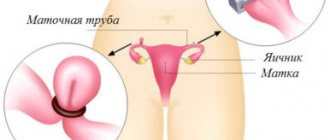
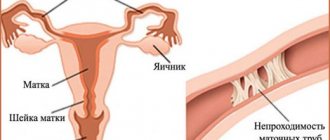
The fallopian tubes, also known as the oviducts, are two thin long processes that extend from the uterus on both sides and reach the left and right ovaries. Together with the ovaries, the tubes make up the uterine appendages, and when they become inflamed, the diseases are called salpingitis (tubes), oophoritis (ovaries), inflammation of the appendages (salpingoophoritis, adnexitis), hydrosalpinx.
In recent decades, the problem of infertility has become very urgent. Moreover, primary infertility is often registered in young girls, women under 30 years of age, who have not previously had an abortion, have not undergone any operations, and who seem to have had no serious illnesses. One of the most common causes of infertility is obstruction of the fallopian tubes, the treatment of which is most often difficult and only with the help of laparoscopy of the fallopian tubes, surgery to restore them, or IVF can a woman achieve the desired pregnancy (read about pregnancy after laparoscopy).
The role of the fallopian tubes in conception
In one of the ovaries, every month in a healthy woman, a dominant follicle matures; during ovulation, approximately in the middle of the cycle, when the follicle ruptures, an egg is released, giving rise to a future pregnancy. From the ovary, the egg must enter the fallopian tubes and move along them towards the uterus. At this time, sperm from the vagina rush through the cervix, the uterus itself to the fallopian tubes towards the egg, where they must fertilize it.
After this, the egg becomes an embryo and continues its journey through the tubes to the uterus, this period is usually 7-10 days. If fertilization fails, the egg dies and is resorbed within 24 hours. Therefore, the fallopian tubes play the most important role as transporters that deliver the egg to the uterus.
The length of the fallopian tubes is almost 10 cm, and the diameter is only 1 cm, and the internal canal of each tube is only from 0.1 cm to 1 cm (narrow at the entrance to the uterus, wider at the ends of the tube). However, this is quite enough for microscopic eggs and sperm to move freely in them.
What is the danger of fallopian tube obstruction?
In cases where both or one tube is blocked, inactive, rigid, or the mobility and function of the cilia (villi, fimbriae) that direct the egg into the fallopian tube is impaired, pregnancy cannot occur. Tubal obstruction does not pose a threat to a woman’s health, but is one of the most serious problems with conception and the cause of tubal infertility.
Today, clinical data states that 15% of married couples face the problem of infertility due to the woman’s fault, and 20-25% of this number is due to problems with the patency of the fallopian tubes. Moreover, with various abnormalities, dysfunctions of the uterine appendages, with partial blockage of the tubes or an inflammatory process in the appendages, a very serious complication is an ectopic pregnancy, which can deprive a woman of one of the fallopian tubes.
Symptoms and causes of the disease
Many gynecological diseases are diagnosed based on complaints from patients who note pain, heavy discharge or lumps on the chest and other symptoms. But a girl may not be aware of the problem of obstruction until she is planning a pregnancy. With partial obstruction, pregnancy can develop in the tubes, and if the tubes are completely obstructed, attempts to become pregnant end in failure. Complete obstruction may be a reason to prescribe IVF.
There are several reasons for the development of this serious disease:
- common infections of the urinary tract and reproductive system;
- inflammatory processes in the pelvic organs;
- sexually transmitted diseases;
- endometriosis;
- complications after abortion;
- fallopian tube tumors;
- consequences of surgical operations;
- intestinal diseases.
The main causes of obstruction of the fallopian tubes
It should be noted right away that the concept of obstruction includes several pathological conditions:
- Complete obstruction of the pipes
- One impassable pipe
- Adhesions around the uterine appendages
- Partial obstruction - since the movement of the egg occurs due to contraction of the tube, in various pathological conditions its contraction is disrupted and the transportation of the fertilized egg becomes difficult, sometimes leading to ectopic pregnancy
- Violation of the activity of villi, fimbriae, which are not able to capture the egg and direct it into the fallopian tubes
Obstruction can occur either when a narrow channel inside the pipe is blocked, or during an adhesive process due to squeezing the pipe from the outside. The main causes of fallopian tube obstruction are as follows:
Inflammatory diseases of the uterine appendages
Any inflammation of the uterine appendages can occur both acutely and latently, with few symptoms, especially with such hidden sexually transmitted infections as chlamydia in women, ureaplasmosis, mycoplasmosis, cytomegalovirus infection, etc. In acute processes, treatment is carried out in the hospital with antimicrobial, anti-inflammatory drugs, then long course of recovery, resorption therapy. But with hidden infections, the process is not noticeable. During the proliferation of bacteria, their waste products, mucus, and pus fill the narrow passages in the fallopian tubes. If timely treatment and resorption therapy are not carried out, adhesions and scars remain on the thin sensitive walls, which leads to partial or complete obstruction.
Tuberculosis of female genital organs
Many sources of medical literature indicate that tuberculosis very rarely affects the genitals and is considered an uncommon cause of infertility. However, today the decline in the level of health of the nation, the decline in immunity among the population, as well as the resistance of Mycobacterium tuberculosis to drugs leads to the fact that many chronic patients who cannot be treated, as well as unexamined citizens, live in cities. Infection and morbidity among children is becoming very high. And almost the entire population becomes infected with Koch's bacillus before the age of 15-20, and the disease can manifest itself years or decades after infection.
It should be borne in mind that the insidiousness of this disease is that it affects not only the lungs, but also any organs of the human body and is asymptomatic; moreover, extrapulmonary forms are extremely difficult to diagnose. When a girl is infected during the period of growth and formation of the genital organs, tuberculosis can lead to abnormalities in the development of the uterus and appendages, hormonal imbalance, underdevelopment of the mammary glands (hypomastia), complete obstruction of the fallopian tubes, and impaired ovarian function.
Reviews from patients who have undergone the procedure
I was also blown out, it doesn’t hurt, it’s unpleasant when they stick the tube in, then you need to relax, and you should hear a gurgling sound, this means that your pipes are passable, and in the evening your collarbone will hurt, well, if the pipes are passable...
Alena https://www.babyblog.ru/community/post/conception/1741899
I was blown out twice. The procedure is not pleasant, but it is not very painful either. Some kind of instrument shows how easily air passes through your pipes, then your shoulders hurt a little - if the pipes are passable. The main thing is to relax well, otherwise the result may be bad. They gave me a purge, it showed that everything was bad, the doctor said that I was very tense. They prescribed 3 procedures, the meaning of which is that saline solution is poured into the uterine cavity and into the tubes and you lie there for about 20 minutes. Then they did another blowing, which showed that the tubes were 69% passable. The doctor said that this was enough. There was just no point. Pregnancy still did not occur. My pregnancy came later, after 3 years, somewhere from another partner, in the first month.
Margarita https://deti.mail.ru/forum/v_ozhidanii_chuda/planirovanie_beremennosti/pro_produvanie_matochnyh_trub/
Blowing out the fallopian tubes is a relatively simple and quite effective procedure that can help not only diagnose the pathology, but also successfully eliminate it, giving the woman the joy of motherhood. However, its implementation should only be entrusted to a specialist whose qualifications you are sure of.
Source
Symptoms, signs of tubal obstruction
If the fallopian tubes are obstructed, there may be no symptoms or signs; this pathology may not affect the general state of health and well-being in any way. There are cases when a young woman is protected in order not to become pregnant during periods of life when they are not planning to have children, and when the desire to have a child comes, the absence of pregnancy and the diagnosis indicated serious problems with the fallopian tubes.
This happens, unfortunately, not rarely. The woman did not even know about such a pathology, because there were no symptoms of obstruction of the fallopian tubes and no serious health problems either. However, with chronic recurrent inflammatory diseases, as well as with hydrosalpinx, many women experience the following signs of tubal obstruction, which can occur with other pathological processes of the female genital organs:
Recipes
Traditional treatment for fallopian tube obstruction will help you feel the joy of motherhood. Herbs for infertility can solve not only such a problem as tubal obstruction, but also improve the health of the female body and prepare it for pregnancy. The specialists of the herbal center have the necessary knowledge and experience; they can recommend herbs that need to be drunk if the fallopian tubes are blocked. They will offer recipes taking into account the woman’s health condition and the complexity of the disease, talk about methods of preparing tinctures and the peculiarities of their use.
Let's look at some of the most basic methods and recipes for treating fallopian tube obstruction using folk remedies:
- One of the leading methods is the use of plantain seeds. Pour 1 teaspoon of plantain seeds into 1 cup of boiling water, cook over low heat for 5 minutes, stirring constantly. Take 13 cups of decoction 3 times a day 30 minutes before meals
- An equally effective remedy for the treatment of obstruction of the fallopian tubes is an extract from the herb uterine cloves. Uterine clove not only fights obstruction of the tubes, but also straightens the villi in the tubes and strengthens the muscles of the uterus, preparing it for the period of gestation, which is not unimportant.
- Collection of herbs for ovarian cysts, cystomas of the ovaries and fallopian tubes, and obstruction of the fallopian tubes. Ingredients: chicory root, nettle, rose hips, peppermint, celandine, sea buckthorn, calendula, chamomile, bird cherry. Directions for use: 1 tbsp. Pour 1 cup of boiling water over a spoonful of the mixture, leave for 4-6 hours, strain. Take warm, 1/3 cup 3 times a day, 1 hour before meals. The course of treatment is 1 month, a break of 2 weeks, then the 2nd course, etc. of necessity. In addition to the collection, you must take burdock juice according to the following scheme: 1st and 2nd days, 1 tsp. 2 times a day, 3rd and 4th days – 1 tsp. 3 times a day, then 1 tbsp. l. 3 times a day for a month.
In addition, you can douche with celandine infusion (0.5 liters).
How to determine, how to check for obstruction of the fallopian tubes - diagnostics, examinations
- To begin with, it is determined whether a woman has regular ovulation - a regular ultrasound or transvaginal (with a vaginal sensor); a woman can also measure basal temperature over several cycles on her own
- Then the sexual partner should undergo a semen analysis
If a man’s spermogram is normal, and a woman has regular ovulation, a normal structure of the genital organs, and no signs of inflammation, the most likely cause of infertility is obstruction of the fallopian tubes. In this case, additional instrumental diagnostic methods are indicated.
Hydrosonography (echohysterosalpingoscopy) or ultrasound determination of fallopian tube patency
It is clear that conventional transvaginal ultrasound cannot determine the patency of the tubes. But a special UZGSS can give a general conclusion about whether the pipes are passable or not. The disadvantage of this diagnosis is that it is not an accurate method, unlike diagnostic laparoscopy or HSG. However, this is a very fast and low-traumatic method that does not require anesthesia, surgery (as with laparoscopy), or radiation exposure (HSG), so the study is safe and can be performed several times.
Hydrosonography occurs in this way - before the procedure, the doctor injects a sterile physiological or other solution into the uterine cavity in order to straighten the walls of the uterus and make them more visible on ultrasound. After this, the doctor determines where the injected fluid flows. With tubal patency, fluid flows from the uterine cavity into the tubes, and then into the abdominal cavity, and a specialist can see this using an ultrasound. If the fallopian tubes are obstructed, the uterus will stretch and its cavity will expand. However, in case of partial obstruction, adhesions, or other pathologies, it is impossible to clearly see the picture of the condition of the pipe using this method.
HSG – hysterosalpingography, x-ray of the uterus and tubes
This method of checking the patency of pipes is more informative than hydrosonography, but in recent years it has been used much less frequently than before. For diagnosing tuberculosis of the female genital organs, this method is the most informative. The essence of the procedure is as follows: after local anesthesia, the doctor injects a contrast agent into the uterine cavity and takes several x-rays after a certain time.
The images will show clear outlines of the uterus, then as the fluid moves through the tubes, the fallopian tubes will be visible, as well as the flow of fluid into the abdominal cavity when the tubes are patency. If the fluid stops in any part of the pipe, the doctor can record its obstruction. This procedure should be carried out in phase 1 of the menstrual cycle to avoid irradiation of the egg.
Many doctors find this method to be somewhat therapeutic, since the injected solution has a flushing effect. However, today this diagnostic method has begun to be used less frequently also for the reason that this procedure should only be performed by an experienced doctor, and it also does not always bring reliable results (in 15-20% of cases there may be false results) when, due to a spasm of the tube, the contrast the substance does not enter the pipes.
In addition, HSG harms women's health due to radiation, can cause exacerbation of salpingitis and causes pain after the procedure. Then the doctor has to repeat the test or use other diagnostic methods. HSG also cannot diagnose ovarian adhesions and endometriosis.
Reasons for the formation of adhesions in the fallopian tubes
Before considering the causes of adhesions in the fallopian tubes, you should familiarize yourself with the mechanism of development of the adhesions process. The fallopian tubes are externally covered with visceral peritoneum, and the abdominal cavity itself is lined internally with parietal tissue. These layers have a smooth surface and secrete a certain amount of fluid, which allows the organs to move freely relative to each other.
If reasons arise that lead to the formation of adhesions, then the fallopian tubes and other organs involved in the pathological process become swollen. A sticky fibrin coating appears on their surface. It is he who contributes to the fact that organs located next to each other are connected to each other. When the inflammatory process has a long course or becomes chronic, adhesive cords form in place of the glued surfaces. In this way, the body responds to inflammation and prevents its further spread. However, the formation of adhesions cannot be considered a normal physiological phenomenon, since it is both pathological and protective in nature.
When the infection penetrates the fallopian tubes, exudate begins to accumulate in them. With adequate therapy, it resolves and does not lead to the formation of adhesions. However, situations are not uncommon when this exudate becomes purulent and spreads throughout the pipe. It is capable of pouring into the peritoneal cavity with fibrin loss. This provokes blockage of the abdominal opening of the fallopian tube by adhesions.
Further progression of the pathological process leads to the fusion of the opposite surfaces of the pipe with each other through partitions. Often, adhesions glue the fallopian tubes to the uterus, oviduct, ovary, intestines, and omentum.
So, doctors consider the inflammatory process to be the main reason for the formation of adhesions in the fallopian tubes, although other factors also influence the growth of strands, including:
Endometriosis.
This pathological process is characterized by the growth of the endometrium in atypical places, including in the fallopian tubes. (Read more: What is endometriosis? Causes and symptoms of endometriosis).
Mechanical effects on the fallopian tubes, namely surgical interventions.
In this regard, surgical abortion, ovarian resection, myomectomy, hysteroscopy, intrauterine contraception, IVF attempts, etc. are dangerous. Statistics show that 50% of women who have undergone gynecological operations develop adhesions. Factors such as heavy blood loss, the addition of a purulent infection, and a prolonged course of the operation increase the risk of their formation.
Undergoing laparoscopy of the genital organs.
No matter how carefully the procedure is performed, it is almost impossible to avoid trauma to the serous membrane of the peritoneum. Therefore, even this operation can trigger the formation of adhesions, which can ultimately block the lumen of the fallopian tubes.
Difficult childbirth can result in the formation of adhesions
. In this case, the connecting cords grow in the uterine cavity, reach the fallopian tubes and block the entrance to them. A cesarean section, as well as multiple ruptures during the delivery process, are the main factors that lead to the proliferation of connective tissue cords.
Injuries to the pelvic area accompanied by rupture of an ovarian cyst are dangerous.
In this case, external adhesions are able to attach to the wall of the fallopian tube and block its lumen.
Infections play a role in the pathogenesis of adhesions formation
sexually transmitted diseases: syphilis, gonorrhea, mycoplasmosis, chlamydia, etc. No less dangerous is genital tuberculosis, which leads to deformation of the tissue structure and the formation of obstruction of the fallopian tubes due to adhesions and scars.
Inflammatory diseases of the reproductive system
non-infectious nature, for example, salpingitis is another cause of tubal obstruction.
Reasons that less often lead to the formation of adhesions
– these are hormonal imbalances and irradiation of the genital organs for the treatment of cancer.
The number of inflammatory processes experienced directly affects the risk of developing adhesions in the fallopian tubes.
Single inflammation of the fallopian tubes – the risk of formation of adhesions is 12%.
Having had inflammation twice – the risk increases to 35%.
Three episodes of inflammation of the appendages - the risk of formation of adhesions in the fallopian tubes is 75%.
How to treat tubal obstruction
All of the listed methods for diagnosing tubal patency can be erroneous, not 100%, so do not despair, a woman always has a chance of becoming pregnant if she has a uterus and at least one tube and an ovary. You can use modern methods of anti-inflammatory, absorbable therapy, as well as laparoscopy and IVF.
Tubal obstruction causes only 25% of all cases of infertility; in all other situations, the inability to conceive is caused by endometriosis, ovarian dysfunction, ovarian cysts, polyps in the uterus, uterine fibroids, immunological incompatibility of partners (that is, a woman’s allergy to her husband’s sperm), as well as pathological disorders in the man’s body, or simultaneous problems in both partners.
When tubal obstruction is determined, before starting any treatment, the attending physician must make sure that this is the only main cause of problems with conception, and not a complex of other disorders in the woman and her man. A standard comprehensive examination of a married couple is as follows:
- Does a woman ovulate regularly?
- Determining a woman's hormonal balance
- Condition of the uterine mucosa
- Analysis of husband's sperm quality - spermogram (how to take, results)
If it is determined that the woman produces follicles regularly, the menstrual cycle is not disrupted, the hormonal levels are also normal, the uterus is able to support the development of the fetus, the man has normal sperm quality, and instrumental methods diagnose obstruction, then experts can recommend conservative and surgical treatment.
- Conservative is a course of anti-inflammatory therapy when an inflammatory process of the uterine appendages is detected. It consists of: a course of antibiotic injections, a course of Longidase injections, physiotherapy (electrophoresis with absorbable drugs that improve local blood circulation). This will be effective if treatment is carried out no later than 6 months after adnexitis and when a pronounced adhesive process has not yet developed.
- Surgical treatment to restore tubal patency is indicated for women under 35 years of age with regular ovulation in cases of partial obstruction.
And even such serious measures cannot guarantee success, since there is a high probability of developing an ectopic pregnancy, and restoration of tubal patency may not be enough if the activity of the fimbriae is impaired, or if the contraction of the fallopian tubes is impaired.
A woman after tubal surgery in the future, if the pregnancy test is positive, should immediately consult a doctor to find out the location of the fertilized egg. Because after inflammatory processes and surgery, the risk of ectopic pregnancy increases 5-10 times.
In cases where several types of different diagnostics confirm complete obstruction, a woman who wants to have children should not waste time on various types of treatment for obstruction of the fallopian tubes, but prepare for IVF. Today, this procedure is becoming more and more accessible both in terms of price (no more than 150 thousand rubles with all tests and diagnostics), and in terms of a large number of accessible centers with experienced specialists and equipment for performing the operation. In doubtful cases or when the patency is impaired in one of the pipes, laparoscopy may be used to eliminate, if possible, existing disorders, obstructions and adhesions.
In themselves, such operations do not guarantee either conception or the normal course of pregnancy, since the presence of a lumen does not mean at all that the egg will be able to move through them. Therefore, it is important to carry out further physiotherapeutic, absorbable treatment, as well as eliminate possible menstrual cycle and hormonal disorders.
In case of infertility due to obstruction of the fallopian tubes, the choice of treatment also depends on the age of the spouses, the degree of damage to the tubes, additional factors of infertility of the man and woman, as well as the financial capabilities of the couple. Nevertheless, IVF is recognized today as the most effective, not very expensive and more successful, reliable method:
| ECO | Surgery | |
| Efficiency of the method | for women under 35 years old 60% | for women under 35 years old in unadvanced cases 40-70% in advanced cases 15-20% |
| Risk of ectopic pregnancy | 1-3% | 25-30% |
| Success or failure becomes known | In 2 weeks | during a year |
Customer Reviews
To conclude this article, I would like to provide a few reviews from our grateful patients.
Lyudmila, 26 years old, Moscow: “Thank you very much. I drank plantain seeds. checked. pipes are passable. Well, I’m so emotional)))) thank you and your work many, many times. »
Valeria, 29 years old, Moscow region: “We have been trying to become parents for 3 years! Everything is unsuccessful and inconsolable! It seemed to us that we would never hear the baby’s cheerful laughter. OUR baby! In phyto, I learned about an extract from the herb uterine cloves. I did everything according to the recipe, diligently, and did not forget anything. Bottom line: I am a wonderful mother of a 4-month-old toddler, Mishutka! THANK YOU. This is happiness. »
Marina, 30 years old, Moscow: “ Last September, I was diagnosed with a cyst with an internal septum. The doctor insisted on surgery, saying that it was an endometrioid cyst. I refused the operation and asked for treatment. Phyto specialists advised us to use a variety of herbs for ovarian cysts and told us an effective recipe, as I remember now: 1 tbsp. pour a spoonful of herbal mixture into 1 tbsp. boiled water, leave for about 5 hours, be sure to strain. Drink 1/3 cup warm 3 times a day 1 hour before meals. I recently had an ultrasound and they said there was nothing. Many thanks to the staff! I will always be grateful to specialists like you!
- Consulting doctors
- Gastroenterology and FGDS
- Hematology
- Dermatology
- Day hospital
- Immunoprophylaxis
- Cardiology
- Nursing care manipulations
- Manual therapy
- Massage
- Neurology
- Otorhinolaryngology
- Ophthalmology
- Psychological adaptation
- Therapy
- Traumatology and orthopedics
- Urology
- Physiotherapy
- Surgery
- Dietetics
- Endocrinology
- Rheumatology
- Oncology, mammology
- Non-surgical treatment for trigger finger
- Vascular surgery
- Stroke Prevention Center