Types of Tubal Ligation Methods
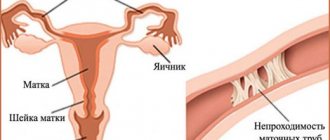
The fallopian tubes are located in the pelvic cavity, they extend from the sides of the uterine body and bend slightly at the back. In order for a woman to have her tubal ligation performed, she must have access to the pelvic cavity. This can be done in the following ways:
- through the anterior wall of the abdomen, making an incision during laparotomy, a puncture during laparoscopy or during a cesarean section;
- through the vagina using hysteroscopy or by incising the retrouterine pouch.
The technology for accessing the uterus and tubes is selected individually. It depends on the number of abdominal surgeries and childbirth history, the position of the uterus and gynecological diseases. During the operation, various techniques can be used to cut the tubes in women, which can even involve removing the median fragment of the oviduct.
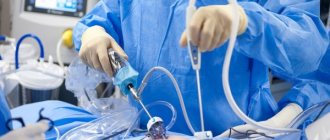
Laparoscopic technique
Tubal ligation by laparoscopy is performed under general anesthesia. Three small incisions are made in the skin on the abdomen, through which metal tubes are inserted. These are conductors for video endoscopic equipment and surgical instruments.
During the operation, the doctor examines the uterus, grabs the tubes one by one, and places clamps on them. The dressing technique is chosen by the doctor individually. This may involve crossing between two clamps or removing a piece of pipe to avoid spontaneous recanalization.
After surgery, 1-2 small stitches remain on each skin incision to improve wound healing. The recovery period is short.
Minilaparotomy access
With a minilaparotomy approach, an incision is made on the anterior wall of the abdomen with a scalpel, but its dimensions are significantly smaller than with a full laparotomy. When ligating the fallopian tubes, they are brought out into the surgical wound. This type of operation is an additional convenience for the doctor, but full intervention in the abdominal cavity carries a greater risk of side effects and complications.
Laparotomy
Laparotomy for tubal ligation is rarely used. During the operation, a wide incision is made in the abdomen, so a long recovery period is required after the operation. The risk of bleeding and infection of the surgical wound also increases .
After the procedure, the woman experiences severe pain, so narcotic analgesics are needed to alleviate the condition. Laparotomy access is used only if a cesarean section was performed before tubal ligation and the mother’s condition allows adding another stage of the operation.
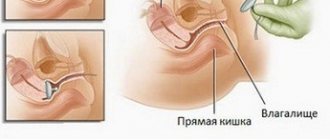
Hysteroscopic and colpotomy approaches
With the hysteroscopic method of sterilization, video equipment is introduced into the uterine cavity. The doctor looks for the openings of the fallopian tubes, after which he coagulates them with a laser or injects a drug that causes sclerosis. Connective tissue grows in them and obstruction develops.
Colpothymic sterilization is also carried out under anesthesia. A woman has an incision made behind her cervix, through which the fallopian tubes are brought into the vagina. They are clamped one by one, two non-absorbable threads are applied, and an incision is made between them. After this, the tubes are placed back and the wound is sutured.
Attention! When using methods of coagulation of the fallopian tubes, the risk of restoring patency in the first year is higher than after ligation with cutting.
Female sterilization methods
Sterilization methods
Sterilization of a woman itself involves creating an artificial obstruction of the fallopian tubes. Currently, occlusion of the fallopian tubes can be carried out by:
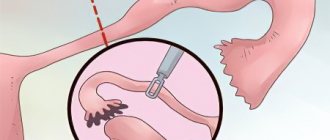
- dressings and separations. The fallopian tubes are first tied (ligated) using a special suture material, and then a section of the tube is cut (divided) or excised. In this case, occlusion can be performed by two methods: 1) according to Pomeroy, when the fallopian tube is folded to form a loop, then tightened using absorbable suture material and excised near the ligation site; 2) according to Parkland, when the tube is tied in two places and a small internal section is removed;
- blocking using various devices. For such mechanical occlusion of pipes, silicone rings or clamps (Filshi, Halka-Wulf) are used. They are applied to the isthmus of the tube at a distance of 1–2 cm from the uterus. The clamps cause less trauma to the tissue of the tube, which, if necessary, makes it easier in the future to restore a woman’s fertility (ability to conceive);
- coagulation (collapse). Using thermal energy effects (for example, a laser), the fallopian tubes are blocked at a distance of 3 cm from the uterus;
- blocking by other methods. To do this, a removable plug or liquid chemicals can be introduced into the pipes, which lead to the formation of a scar structure.
After any of these actions (technologies), fertilization is impossible, because the egg and sperm are isolated from each other.
It is important to understand that having your tubes tied does not mean protecting yourself from sexually transmitted infections, including HIV. This is simply protection against unplanned pregnancy. In this regard, if you are at risk of contracting an STI, you should at least use a condom.
Advantages and disadvantages of tubal ligation
Tubal ligation does not affect the woman’s body. Sterilization has its advantages over other methods of contraception:
- there is no need to constantly monitor the use of contraception;
- no effect on metabolism, hormonal levels;
- efficiency approaches 100%;
- can be used for excess weight, smokers and diabetics;
- the number of women suffering from inflammation of the appendages is decreasing.
The disadvantage of this method is the lack of protection against sexually transmitted infections, so women who often change sexual partners must use a condom. Ligation of the oviducts is irreversible, but does not affect the condition of the endometrium. Therefore, there is always the opportunity to carry out IVF with your own eggs.
Where to do it and how much does it cost?
If you have a policy, female sterilization is carried out free of charge in municipal medical institutions; all major expenses are covered by the state.
If you have a policy, female sterilization will be performed free of charge
The operation is performed for a fee in private clinics, or in public ones, choosing more convenient conditions for being in a hospital. The cost of sterilization is influenced by many factors - the level of the medical institution, the qualifications of the doctor, the method of intervention, the type of anesthesia. The average price is 10–50 thousand rubles.
Consequences of ligation and reversibility of the operation
There are no serious consequences for a woman's health from tubal ligation. The operation does not affect hormonal levels, because The fallopian tubes do not produce hormones, but act as conductors for the fertilized egg. There is no decrease in the level of estrogen, they constantly enter the blood from the ovaries, therefore premature menopause and aging are not associated with sterilization.
For women who need a reversible method of contraception, sterilization is not suitable . After ligation, spontaneous conception can occur in the first year in approximately 5 women out of 1000 operated on. But in subsequent years this becomes impossible due to obstruction of the pipes. There are recanalization methods, but they are ineffective. Restoration of the lumen of the tube can occur, but peristalsis, the state of the lining epithelium, is disrupted, which makes natural fertilization impossible.
Advantages, disadvantages
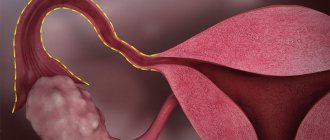
The fallopian tubes perform a transport function for sperm and eggs. The female reproductive cell matures and is sent through the fallopian tube into the uterine cavity, where it is fertilized by sperm, after which it is implanted through the same tube into the cavity of the uterine body, where it is implanted into the wall of the organ. The main purpose of ligation of the fallopian tubes is to exclude the possibility of the egg meeting the male reproductive cells, as a result of which pregnancy becomes impossible.
Although surgical sterilization belongs to the category of irreversible operations, in isolated cases self-healing of the patency of the fallopian tubes occurred. Most often, such processes occurred due to non-compliance with the DHS technique or incorrect selection of surgical approach techniques. But in general, restoration of the tube after ligation is possible only with the help of plastic surgical interventions, which are not always successful, expensive and technically complex.
Therefore, if the patient urgently wants to give birth after surgical sterilization, doctors can offer her in vitro fertilization. But this method is also very expensive financially and does not always provide the desired result. That is why you need to think a thousand and one times, weigh all the factors, and only then decide to take such a crucial step. After all, having a child after DHS is almost impossible. The dressing procedure is not without its disadvantages and advantages.
- Firstly, after such an intervention there is a 100% guarantee of contraception, and there is no chance of conception.
- Secondly, such sterilization can be carried out after cesarean section, which is very convenient and does not require additional preparation of the patient for the operation.
- Thirdly, such an intervention does not in any way affect a woman’s sexual desire, does not affect her general health, and does not disrupt the patient’s hormonal levels.
The disadvantages of DHS include the irreversible lack of fertility, the need for anesthesia during ligation, and the existing likelihood of an ectopic ectopic event due to insufficient qualifications of the doctor who performed the sterilization. In addition, this procedure is a surgical intervention, and therefore may have characteristic complications and consequences such as inflammatory processes, bleeding, etc.
Who is dressing indicated for?
By law, in most CIS countries, sterilization by tubal ligation in women is carried out at the request of any patient after 35 years of age, even if she does not have children at that time. For all women younger than this age, dressing will be performed only if there are 2 children born, as well as for medical reasons. These include serious illnesses that make bearing a child and the birth process dangerous or fatal for the mother. Most often these are pathologies of the following systems:
- heart and blood vessels;
- respiratory system;
- liver and kidneys;
- hematopoiesis;
- hereditary genetic syndromes.
Tubal ligation in women with mental disabilities is not forced, but in some cases it can be done by court decision.
The age at which tubal ligation can be done varies in Western countries. In Sweden, the operation will be performed on a woman over 25 years old, even if she does not have children.
IVF is the solution to the problem
If a woman wants to get pregnant after the sterilization procedure, then she has such a chance, and this is the IVF method. There is no need for the functionality of the pipes here, that is, they are actually not needed for this. The success of the procedure is determined by the condition of the uterus. A separate role, of course, is played by the specialists who will be involved in this procedure, as well as the availability of funds for it, and a certain amount of luck.
In theory, the procedure in question looks extremely simple. It requires an egg from a woman's ovary. She is fertilized in a test tube, then she is implanted into the uterus.
Despite its apparent simplicity, this process is actually quite complex; it consists of several stages:
- stimulation of the ovaries to achieve “superovulation”, for which hormonal drugs are used, the effect of which increases the number of maturing eggs (normally, only one matures every month, the more there are for the procedure, the better);
- extraction of the egg, it occurs under anesthesia, under ultrasound observation, then the egg is placed in the environment required for its storage;
- collection of sperm from the patient’s partner (spouse);
- fertilization in a laboratory (more often the process is close to natural, because sperm are simply added to the environment in which the eggs are contained);
- monitoring embryos during their fertilization;
- the embryo is implanted into the uterine cavity.
As you can see, some of the events from the fertilization process are absent during IVF, and the condition of the pipes in this regard does not matter. Two weeks later, the woman takes a test that will determine whether the procedure was successful. If there are more fertilized embryos during the procedure, they are frozen, and if pregnancy does not occur, they are used for the next attempt at conception.
Contraindications for surgery
Ligation of the fallopian tubes in women is possible in the absence of an absolute contraindication, which is acute inflammation. It is impossible to properly secure a ligature on a swollen and enlarged tube, and there is also a risk of infection of the abdominal cavity and the development of peritonitis. Relative contraindications are:
- infectious diseases of any localization;
- cardiovascular pathologies;
- tumor processes in the pelvis;
- diabetes;
- tendency to bleed;
- obesity;
- adhesive disease.
But after eliminating contraindications or stabilizing the condition, tubal ligation can be performed.
Feedback from those who made
Zvezdochka
Before the operation, I talked with different doctors, all unanimously asserted that sterilization would not affect my weight or well-being. But after the bandage, I gained 15 kg in 2 months; diets and daily workouts don’t help.
Lissa_Alissa
She gave birth to two children, when she became pregnant again, she decided to have a caesarean section and tubal ligation. It’s been 5 years now, I’ve never regretted it – I don’t need to think about contraception, I look young, I feel great, my weight is normal.
Kira_69
The dressing was done after the second birth, sensitivity and sexual desire almost immediately became zero, no drugs or traditional methods help restore libido. Menopause came early, I experienced all the delights of this period, constant vaginal dryness, sex does not bring any pleasure.
Rules for preparing for tubal ligation surgery
The time for tubal ligation is selected individually. It is recommended to do this after the end of menstruation, but delayed sterilization in the second phase of the cycle is not contraindicated. The procedure is also carried out 6 weeks after an uncomplicated birth, during an induced abortion using colpotomy access.
Preparation for the operation is carried out according to the standard scheme. The woman undergoes an examination during which the following diagnostic methods are used:
- clinical blood and urine tests;
- vaginal smear;
- biochemical blood test;
- ECG;
- Ultrasound of the pelvis;
- blood test for HIV, syphilis, hepatitis.
The operation is carried out strictly on an empty stomach as planned. The evening before the intervention, it is not recommended to have a large dinner, drink alcohol or fatty foods.
Is it possible to get pregnant with tubal ligation naturally?
Trying to return everything to normal, patients wonder whether it is possible to get pregnant with ligated tubes. Natural pregnancy, despite any of the procedures affecting the tubes, is still possible in the following cases:
- the operation or installation of implants was performed poorly or incorrectly;
- development of defects after surgery;
- the welded fallopian tubes spontaneously grow together, thereby ensuring patency for sperm;
- the woman is already pregnant at the time of the operation.
Let us repeat, if the tubes are tied, you can get pregnant “incorrectly”; moreover, here the risk of ectopic pregnancy, as already noted, increases. How do you know if the fallopian tubes are ligated, if there are any defects, and if the tubes were affected correctly when using one method or another? To do this, it is enough to undergo ultrasound diagnostics.
Recovery period and possible complications
Complications from tubal resection are rare. They may occur during surgery. Sometimes intestinal perforation, intra-abdominal bleeding, and complications associated with anesthesia are possible.
In the postoperative period, delayed internal bleeding, infection of the uterus or pelvic cavity, disturbances of intestinal motility, or dysuric disorders are likely. But in most cases they are rarely observed.
Recovery after cauterization or ligation of the oviducts lasts about 2 weeks. During this period, you should not take a hot bath, lift weights or sunbathe. Sexual relations are also excluded. After examination by a doctor, you can return to your normal lifestyle.
We recommend reading
- Natural methods of birth control
- Non-hormonal contraceptive suppositories for women
- Review of contraceptive suppositories Patentex Oval N
Symptoms of ectopic pregnancy
An ectopic pregnancy occurs when a fertilized egg implants in the fallopian tube rather than in the uterus.
An ectopic pregnancy may initially cause the same symptoms as a normal pregnancy. However, some additional symptoms may occur:
- vaginal bleeding;
- abdominal pain;
- acute pain in the pelvic area;
- feeling of pressure on the pelvis.
An ectopic pregnancy can cause the fallopian tube to rupture, causing internal bleeding. A woman should seek emergency medical help if she experiences the following symptoms:
- heavy vaginal bleeding;
- severe pain in the abdomen or pelvis;
- loss of consciousness;
- left shoulder pain;
- dizziness.
Your doctor will usually prescribe medication to stop an ectopic pregnancy if it is detected early. The doctor will monitor the woman's hormone levels to make sure they are falling. If medications fail to stop the pregnancy, your doctor may recommend surgery.