- My side hurts. After complete healing of the wound, pain may be observed in the area of the operation. This is due to the formation of adhesions, which are present during any type of operation. In this case, the nature of the pain will be as follows:
- aching pain in the lower abdomen;
nagging pain of a tolerable nature;
Anomalies are profuse, strong bloody discharge with an increase in temperature.
White cheesy discharge can be observed during antibacterial therapy; additional therapy with vaginal suppositories will be required to normalize the microflora.
Surgical intervention as a way to eliminate ectopic pregnancy
There is a drug cure for the problem, however, it is used in rare cases. This depends on the location of the ovum and the duration of pregnancy. If the pathology is detected early and there are no unpleasant symptoms, then there is a chance for drug treatment.
However, the types of such pregnancies are different - it all depends on where the fertilized egg is attached. If it is located in the cervix, and this happens very rarely, then there is every chance of not having surgery. But if the fertilized egg is in the fallopian tube or in the abdominal cavity, surgical intervention cannot be avoided. The sooner you start the removal procedure, the fewer consequences and complications there will be.
To identify pathology in time, you should pay attention to the following symptoms:
- prolonged periods;
- menstruation comes at the wrong time and is heavy;
- bleeding after conception;
- dizziness;
- drop in blood pressure;
- pale skin;
- loss of consciousness.
If nothing is done, after a while the fallopian tube bursts, due to large blood loss, hemorrhagic shock occurs, which leads to death. Therefore, it is absolutely impossible to refuse surgical intervention in the hope of self-healing. Since even minor bleeding in the abdominal cavity leads to an inflammatory process. And this is a double threat to life. So immediate surgery is simply necessary.
How to remove adhesions in the fallopian tubes without surgery
While surgery is a common treatment for fallopian tube adhesions, there are natural options that can show excellent results without causing recurrent fallopian tube adhesions. Natural treatments include the following options:
USEFUL INFORMATION: Piroxicam tablets
Systemic enzyme therapy
Systemic enzyme therapy is a method that helps the body cleanse itself of excess tissue, scar tissue, purify the blood, increase blood circulation to the reproductive organs and reduce the immunological response. Enzyme therapy consists of using systemic enzymes (naturally found in the body) to help the body reduce inflammation, pain, scarring and more.
This therapy may help reduce scar tissue that forms adhesions in the tubes
Systemic enzyme therapy can help reduce the scar tissue that forms adhesions in the tubes. This type of therapy holds tremendous promise for helping the body reduce excessive scarring and inflammation.
Abdominal massage and Mercier therapy
Massage is another natural therapy that can help maintain health and relieve tubal adhesions. Massage helps increase blood circulation and break up adhesions. It is an excellent non-surgical treatment option.
Created by Dr. Jennifer Mercier, Mercier Therapy is a manual pelvic manipulation technique that mobilizes the reproductive organs and restores blood flow. Obstructions in the genitals are released and movement between the organs and surrounding structures is improved to improve their natural function.
Abdominal massage
For women with past infections or adhesions in the tubes, deep manipulation can make positive changes to the fallopian tubes, Dr. Mercier says.
Castor oil
Castor oil treatments have been used for centuries to help with problems in the body, particularly the reproductive system. A cloth soaked in castor oil is placed on the skin to improve blood circulation and promote healing of tissues and organs under the skin. Castor oil helps the fallopian tubes by softening the tissue and increasing circulation in the area.
Castor oil promotes healing of the reproductive system by stimulating blood circulation and the lymphatic system, which is responsible for removing metabolic waste and old diseased cells and tissues. It helps treat adhesions in the fallopian tubes, especially if they are caused by an ectopic pregnancy, STD, infection from past surgeries, endometriosis, uterine fibroids, ovarian cysts, or PVD.
Herbal therapy
There are many herbs that are traditionally used to support fallopian tube health:
- Goldenseal has antibiotic properties and acts as an antimicrobial and anti-inflammatory agent. It helps cure any infection in the reproductive system while reducing pain and inflammation from external tissue growth. Reducing inflammation can help eliminate adhesions.
- Ginger root is used to improve blood circulation and promote blood flow to the reproductive organs. Good blood circulation helps reduce inflammation in the pelvic organs.
- Angelica chinensis is one of the best herbs for stimulating blood circulation to the reproductive organs. It acts on the circulatory system and lymphatic system, reducing tissue blockages. The herb has both pain-reducing and anti-inflammatory properties.
- Hawthorn reduces stagnation in the pelvis. It improves the integrity of blood vessel walls, helps the body in proper utilization of oxygen and improves blood circulation, helping to treat fallopian tube adhesions.
Contraindications
There are a number of contraindications for surgical intervention:
- comatose state of the patient;
- cardiovascular diseases;
- respiratory diseases;
- hernia of the anterior abdominal wall.
In rare cases, laparoscopy is performed for symptoms such as:
- large blood loss into the abdominal cavity - more than 1 liter of blood;
- adhesions on internal organs;
- scars and cicatrices from previous operations;
- obesity.
In this case, laparoscopy can be replaced by laparotomy. In the presence of peritonitis or various infectious diseases, laparoscopy is also contraindicated due to the high risk of possible consequences. Laparoscopy cannot be performed if the fetus is large or if there are malignant neoplasms. Then a laparotomy is performed.
If a woman has a cervical ectopic pregnancy, a circular suture is placed around the cervix, then curettage is performed to preserve the uterus. Curettage can be used for diagnostic purposes if symptoms of pregnancy are present and the fertilized egg is not detected during an ultrasound examination.
Consequences of adhesive disease
If treatment of intestinal adhesions is not carried out in a timely manner, then there is a possibility of developing dangerous complications. The following negative consequences are possible:
- disruption of the digestive process;
- acute or chronic intestinal obstruction;
- secondary dysmenorrhea;
- difficulties in conceiving a baby;
- intestinal obstruction;
- dysfunction of the pelvic organs.
Connective tissue cords can change the location of individual parts of the intestine. Possible stretching or bending. This is fraught with a decrease in the intestinal lumen. Food cannot move properly. The greatest danger is posed by a condition such as complete intestinal obstruction. It causes severe pain and can result in tissue necrosis. This is fraught with penetration of intestinal contents into the abdominal cavity and peritonitis. Sepsis may develop. In women, the formation of adhesions leads to dysfunction of the uterus.
Preparation for surgery - tests and examinations
Before prescribing treatment, diagnostics are carried out using different methods. During a gynecological examination, you may notice a discrepancy in the size of the uterus. The location of the formed compaction is felt on the side where the fertilized egg is located.
A clinical blood test will show how low the hemoglobin and hematocrit are. Detects low red blood cell count. Determines elevated levels of ESR and leukocytes. And also a blood test in the presence of ectopic pathology indicates a low level of human chorionic gonadotropin (written as hCG).
To identify the condition of the internal reproductive organs and the place of attachment of the embryo, a vaginal ultrasound is performed.
If after all the tests performed the picture is not clear due to weak clinical indicators, the patient is admitted to the hospital and the hCG level is constantly monitored. If hCG decreases or the general condition worsens, women are recommended to undergo laparoscopy for a more accurate diagnosis.
Diagnostic laparoscopy for suspected ectopic pregnancy allows you to much more accurately determine the presence of pathology. It is carried out in cases where other diagnostic methods have not given a definite result regarding the presence of an embryo outside the uterus. The procedure is performed under general anesthesia.
What types of operations are there?
In gynecology, there are several methods of surgical treatment of ectopic embryo attachment, which differ significantly in duration and nature of the procedure. The choice depends on the patient’s condition, the development of pathology and technical capabilities.
Today, abdominal surgery and laparoscopy are considered the most popular. However, the latter, despite a number of advantages, is not always used due to possible pathological complications.
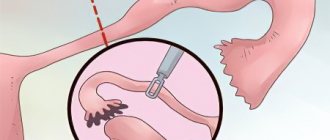
Open tubectomy
This method involves making a transverse incision in the abdomen through which the “pregnant” fallopian tube is removed. However, in case of an emergency procedure or insufficient skill of the surgeon, a median laparotomy is used - a vertical abdominal incision from the navel to the pubic bone. This occurs due to an insufficiently good view of the pelvic organs.
How does the process of cavity pipe removal occur:
- An abdominal incision is made.
- The uterus and appendages are brought out into the visible area by hand.
- The bleeding is stopped by pinching.
- A clamp is applied to the pipe.
- The organ is cut with a special device and removed.
- Blood clots are removed and the peritoneum is sutured.
Tubectomy is performed when other methods of eliminating the pathology are impossible.
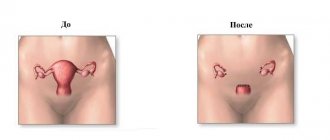
Organ-preserving operations
Surgical manipulations with preservation of the tube and ovary are possible only in the short term, when the fertilized egg does not exceed 4 cm and there is no rupture of the organ. This will allow you to remove only a fragment of the tube with the embryo, leaving everything else in place.
The course of the surgical intervention is as follows:
- After the incision is made, clamps are applied to the tube on both sides of the embryo.
- Then the tube is cut at the site of attachment of the embryo or part of it is cut out.
- For bleeding, electro- or laser coagulation is used.
- Both ends are sewn together so that one end is joined to the other end-to-end.
- The abdominal cavity is sutured.
To ensure that reproductive function is not affected, the procedure is carried out as carefully as possible, avoiding tissue damage, as this can lead to adhesions and clogging of the organ.
Diagnosis and treatment of adhesions in the fallopian tubes
The primary indicator of the presence of adhesions is the inability to become pregnant. Fortunately, there are medical tests that detect any abnormalities or adhesions in the female genital organs:
A hysterosalpingogram is an x-ray test that uses contrast dye to view any obstructions in the fallopian tubes. The dye is inserted through a thin tube that is placed through the vagina into the uterus. This dye is then released into the fallopian tubes. X-rays are then used to determine if there is injury or abnormal shape of the uterus and fallopian tubes, including adhesions in the tubes.
This test is similar to a hysterosalpingogram because chromotubation involves a dye going into the uterus and fallopian tubes. It is performed during laparoscopy so doctors can see the dye leaking from the fallopian tube. The dye used for this procedure cannot be seen on an x-ray and is blue in color. This test is considered the most reliable way to determine fallopian tube adhesions, but requires surgery.
This is a non-invasive procedure that uses ultrasound to determine if there are any abnormalities in the reproductive organs. This type of test is not always a reliable way to detect fallopian tube adhesions because they are so small.
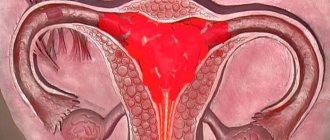
Ectopic pregnancy: discharge and other signs
Ectopic pregnancy is an unpleasant and dangerous pathological condition that seriously affects a woman’s body. If it is not diagnosed on time, it can cause complications and chronic diseases, as well as lead to infertility and even death of the patient.
A quick reaction and immediate medical intervention are very important in case of an ectopic pregnancy - which is why every woman should recognize the symptoms that indicate a problem.
So, what are the signs of an ectopic pregnancy?
Why is an ectopic pregnancy so dangerous?
An ectopic pregnancy is a pathology during the development of pregnancy, during which the fertilized egg does not enter the uterus and is located outside of it. If this condition is left unattended, the egg growing outside the uterus can cause the following conditions:
- rupture of the fallopian tube;
- peritonitis, abdominal infections;
- abdominal bleeding.
Each of these options can be fatal, so if you have symptoms of an ectopic pregnancy, you should contact the clinic as soon as possible.
Currently, a laparoscopic method is used to remove a fertilized egg: it does not require removal of the fallopian tube, so it does not cause serious harm to the body. After laparoscopy, a woman is not at risk of infertility, but such intervention is used only in the early stages of detecting pathology.
In the event that an ectopic pregnancy was noticed too late, and a rupture of the fallopian tube has already occurred, the surgeon will have to remove not only the embryo, but also the tube itself or its fragment. In this case, the woman’s reproductive function will be lost after the operation.
This is another important reason why it is important to determine the signs of an ectopic pregnancy on your own: if a woman can understand in time what is happening to her, this will save her not only life, but also health.
Mechanism of development of the condition
The main difference between an ectopic and a normal pregnancy is the incorrect location of the embryo. It determines all other non-compliances with the norm. But at first everything happens as always:
Embryo in the fallopian tube during ectopic pregnancy
A delay in menstruation during an ectopic pregnancy can be up to 14 days. If we consider that all other manifestations are similar to the signs of the usual development of this position, a woman can independently determine it. The only thing that is not available at the moment is identifying the location of the fertilized egg.
The only thing that can be seen clearly and differs from the normally proceeding process is a delay in menstruation, the test is negative, an ectopic pregnancy at this stage can “deceive” him. HCG, on the basis of which the pharmaceutical product works, will appear in the blood a week later than if the condition develops correctly. And its level can be reduced compared to normal.
But you cannot rely on these signs, since they exist even in the absence of an “interesting situation.” And yet, a barely visible second line on the test should convince a woman to listen more carefully to what is happening in her body.
The first symptoms of an ectopic pregnancy
The appearance of an ectopic pregnancy is characterized by several important signs that appear both individually and in combination with each other. Each of these symptoms can have varying degrees and individual manifestations: for the most part it depends on the body of the individual woman, as well as on the timing and type of pathology.
Important symptoms of an ectopic pregnancy include the following:
Bloody issues
Bloody discharge is the most important symptom of ectopic pregnancy. In itself, it may indicate other pathological conditions, such as cervical erosion, endometriosis or other symptoms. Discharge during an ectopic pregnancy can be of different shades, consistency and released in different volumes.
Painful sensations
Most often, the pain is localized in the lower abdomen, in the lumbar region, and also at the site of attachment of the fertilized egg. The pain is spasmodic in nature, and when bleeding intensifies, it also becomes stronger.
This symptom does not occur in everyone, but in combination with bloody discharge and severe pain in the lower abdomen, it clearly indicates the occurrence of pathology. Toxicosis can be severe or practically unexpressed, it depends only on the characteristics of the woman’s body - the very fact of its presence is important.
Lethargy, general deterioration in health, loss of consciousness and dizziness are symptoms that indicate significant blood loss in the body. In addition, a woman may also appear pale, have low blood pressure and a weakened pulse.
If any of these symptoms are present, a gynecological examination is necessary. Even if the problem is not an ectopic pregnancy, all these signs are dangerous in themselves and indicate serious illnesses that need to be treated as soon as possible.
Types of discharge during ectopic pregnancy
Discharge mixed with blood is the most important sign of ectopic pregnancy, which manifests itself in any type of such pathology. The consistency, volume and color of the discharge depend on the specific subtype of ectopic pregnancy, as well as on the stage of its progression.
The following types of discharge are typical for ectopic pregnancy:
- scanty and spotting;
- long, unrelenting;
- brown, red or pink;
- breakthrough uterine bleeding;
- bloody discharge mixed with pus;
- discharge mixed with epilelia of the mucous membrane.
What discharge is typical for each specific type of ectopic pregnancy? Let's look at all the subtypes and their symptoms in more detail.
Progressive ectopic pregnancy
Progressive VD, also known as “unimpaired”, is a subtype in which the embryo implants into the muscle wall and continues to develop without affecting the general condition of the body. Most often, with this type of ectopic pregnancy, the discharge is absent or weakly expressed, which makes diagnosis difficult.
Signs of pregnancy with such a pathology usually persist, and its presence is established after a routine gynecological examination of the pregnant woman: an ultrasound reveals that the uterus is not growing according to the period, and only then is medical intervention performed.
Tubal abortion
This type of disrupted (or interrupted) VB is characterized by complete or partial exfoliation of the embryo, as well as its further exit into the abdominal cavity. Brown discharge during an ectopic pregnancy is typical specifically for a tubal abortion: it can be either light or almost black in color, and also vary in consistency and volume.
The abundance and duration of discharge in this case depends on the general clinical picture. In case of an interrupted ectopic pregnancy, brown discharge is supplemented by blood clots; tubal abortion is also characterized by severe pain in the lower abdomen and soreness in the posterior vaginal vault.
Fallopian tube rupture
This is the most dangerous subtype of interrupted VB. The embryo located in the fallopian tube continues to grow and gradually stretches its wall, which leads to its rupture. The fertilized egg enters the abdominal area, and there may also be blood there, causing dangerous internal bleeding.
Bloody discharge at first seems scanty and insignificant, but after a few hours such a large amount of blood and rejected epithelium is released that going to the clinic becomes necessary. The woman feels acute unbearable pain in the abdomen, weakness and malaise, and may lose consciousness.
Symptoms of fallopian tube adhesions
If the adhesive process is combined with an inflammatory process, the leading symptoms become acute or chronic salpingitis.
The patient complains of pain of varying intensity - from episodic discomfort, heaviness and nagging pain in the lower abdomen and groin area to severe one- or two-sided cramping pain. The pain syndrome usually intensifies during sexual intercourse, with physical activity or sudden movements. Vaginal discharge is moderate or quite abundant, mucous or mucopurulent. During the period of remission or after complete cure of the inflammatory disease, the only sign of adhesive lesions of the fallopian tubes is infertility. Due to a violation of the physiological mechanism of fertilization, the patient, despite regular sexual activity, does not become pregnant for 6-12 months. In this case, menstrual function is usually not impaired. In some cases, patients with adhesions experience not a normal pregnancy, but an ectopic pregnancy.
Discharge after pathology
After laparoscopy, if it passed without complications or consequences, the reproductive system is restored within a month or a month and a half. A new menstruation after surgery begins no earlier than 25 days later! The onset of menstruation ahead of schedule should alert you: this is dangerous uterine bleeding that requires urgent examination by a gynecologist.
A delay in menstruation after surgery is also a rather dangerous condition. If after 40 days your period has not started, this may indicate either a serious hormonal imbalance or another conception. In any of these cases, consultation with a specialist is necessary.
Discharge after an ectopic pregnancy can vary: bloody, brown, and pink discharge is normal, as well as the presence of clots and film that may be present after tubal removal surgery. It is only important that these bleedings do not become too profuse, long and pus is not mixed with them.
Now you know how an ectopic pregnancy is diagnosed and what discharge is typical for it. This disease cannot be left unattended, and at the slightest symptoms of pathology you should see a doctor: this will save your health and life.
Possible complications
Adhesions are a rather complex complication after surgery, which can not only disrupt the functioning of internal organs, but also provoke complications, including:
- acute intestinal obstruction;
- necrosis of a section of the intestine;
- peritonitis;
- infertility;
- menstrual irregularities;
- bend of the uterus;
- obstruction of the fallopian tubes;
- ectopic pregnancy.
Complications of adhesive disease often require immediate surgical attention.
Periods after ectopic pregnancy
An ectopic pregnancy is a pregnancy in which a fertilized egg develops outside the uterus - in the fallopian tube, ovary, cervix and even the abdominal cavity. This condition is often accompanied by internal bleeding, and therefore poses a huge danger to a woman’s life.
When undergoing surgical (laparoscopy) or drug treatment, the first menstruation should begin 28-40 days after the termination of the ectopic pregnancy. A prerequisite for this is the absence of problems and serious complications. A simple method will help you calculate more accurate dates:
- Add to the day of the operation the number of days that corresponds to your usual cycle length.
- Subtract 5 days from the received date.
- Add another 10 days to the result.
It is this period of time that should become the period of the expected onset of menstruation.
Laparoscopy (complete or partial removal of the fallopian tube) puts a greater burden on the body than taking medications. The nature of bleeding after surgery can be different (scanty/heavy, short/long), but the sensations in both cases will be very noticeable:
- Abdominal pain is caused by contractions of the uterus or insufficiently restored tissue. Their intensity depends on the woman’s ability to tolerate cramps and the level of surgical intervention;
- General weakness, lethargy, drowsiness are caused by the influence of anesthesia, a natural decrease in immunity during critical days and hormonal imbalance.
Probability of subsequent pregnancies
Subsequent pregnancies are possible if you follow the recommendations during the recovery period. It is important to follow hygiene rules and take into account general recommendations:
- do not swim in open sources (staves, sea) for the first 3 months;
- Bathing is prohibited (shower only for the first month);
- physical activity is unacceptable;
- taking intravaginal medications without a doctor’s prescription;
- use tampons for the first 3–4 cycles.
If you follow all the recommendations, then if you have a second healthy tube, pregnancy will occur. The main thing is not to plan it before 9 months, ideally after 1.5 years.
The general prognosis for women who have undergone organ removal but have a second part is positive: this will not affect the likelihood of motherhood and quality of life. However, in most cases, the question is about preserving the life of a woman who could die at any moment from rupture and sepsis. Therefore, there is no choice.
Often, removal of the fallopian tube is the only chance to save life. In order to also preserve the ability to bear a child, it is necessary to contact an antenatal clinic at the first signs of pregnancy. In the early stages, ectopic pregnancy is a pathology that can be easily eliminated without removing the fallopian tube.
- hormonal levels have improved;
- the previous cyclicity of menstruation resumed;
- an ovary with a healthy tube was again able to release healthy eggs for fertilization.
Other secretions
Some women begin bleeding earlier than 25 days after surgery. You should not mistake this situation for the beginning of your period - we are most likely talking about uterine bleeding.
In this case, you need to urgently contact the gynecologist who observed you.
It is especially important that such discharge is not accompanied by fever, severe abdominal pain that even painkillers cannot eliminate, and an unpleasant odor. All this indicates the development of an infection that could enter the female body during surgery or due to non-compliance with hygiene rules by the patient herself.
When will the menstrual cycle resume?
The exact timing of the restoration of menstruation after an ectopic pregnancy is quite difficult to calculate. It all depends on the woman’s hormonal background and the individual characteristics of her body. This process is also affected by changes in the reproductive system that arise as a result of the treatment. In most cases, the recovery process lasts 28-40 days, but if there are serious problems (both physiological and psychological), the time frame can extend to 2-2.5 months.
To help your body recover faster, follow these recommendations:
- Stop smoking, using drugs and alcohol;
- Lead a moderately active lifestyle - engage in light exercise, sleep up to 8 hours, do not lift heavy objects;
- Take vitamin and mineral complexes;
- Follow the advice of your doctor;
- In case of severe psychological condition, consult a psychologist.
Even with complete restoration of the menstrual cycle and the absence of any complications, we can talk about the next pregnancy no earlier than after 6 months. During this time, the body is not ready for new fertilization, so do not forget about birth control methods. It is also necessary to find out what exactly caused the development of the pathology and completely eliminate this factor. Only in this case will the risk of recurrent health problems be minimized.
What to do if you miss your period?
If the cycle has not been restored within 40 days after removal of the ectopic pregnancy, we can talk about a delay in menstruation. This condition requires a routine examination by a gynecologist and additional examinations. Possible reasons for the absence of menstruation are:
- Hormonal disorders - in most cases they existed even before pregnancy, and worsened after treatment;
- Stress - nervous shock does not contribute to the restoration of the menstrual cycle;
- The complexity of the treatment is what determines the degree of trauma to the reproductive organs and the time it takes to restore their function. The more complex the intervention, the longer the delay will be.
Menstruation after treatment
An ectopic pregnancy does not resolve on its own. Depending on the degree of its development, it is possible to remove the fertilized egg laparoscopically or using a special drug; in the worst case, the woman loses one of the fallopian tubes.
Naturally, she is worried about what and when her periods will be after an ectopic pregnancy. After all, doctors try to preserve the chance of becoming a mother whenever possible.
Cycle recovery
Laparoscopy for ectopic pregnancy
The most burning question: when will your period start after an ectopic pregnancy? Many are in a hurry to try again, because they are sure that time is working against them in this regard. This is a big mistake, the body needs rest and time to recover.
It is also necessary to find out the reasons for improper attachment of the fertilized egg, so that in the future they do not interfere and do not cause a similar situation again. The second tubal localization of the embryo will reduce the chances of having a child.
For some, the first period after an ectopic pregnancy occurs immediately after surgery, within a day or two. This can be regarded in two ways, as it is caused by different reasons:
- Rapid restoration of the reproductive system;
- Hormonal imbalance that provoked uterine bleeding.
The last option is the most likely. Doctors do not consider it something dangerous; rather, they perceive it as cleansing the uterus from an overgrown layer of mucous cells. But the process is always monitored, and if necessary, hemostatic drugs are prescribed.
For the majority of those operated on, menstruation occurs 25-30 days after the intervention. This is the standard cycle size, indicating the good ability of the reproductive organs to recover.
At the rehabilitation stage, the woman’s behavior is important; she needs to monitor her own regimen, minimize physical activity, avoid taking a bath, limiting herself to a shower. Sex should also be moderate and accompanied by protection.
Lack of menstruation
A delay in menstruation after a problem is also a likely occurrence. It can be caused by several circumstances:
- Hormonal disorders. They can be observed even before pregnancy and cause its incorrect development. After treatment, the problem can worsen, as other factors come into play (nervous tension, anesthesia, medications);
- Stress. The very fact of the ectopic location of the ovum can be a serious shock for a woman who wants to become a mother. There is also increased anxiety associated with surgical intervention and fear of the inability to have a child in the future;
- The complexity of the treatment. The level of trauma to the reproductive organs, and therefore the speed of restoration of their functions, depends on it. The more severe the intervention, the more likely and longer the delay will be.
Absence of menstruation for the above reasons is considered acceptable for up to 2 months. Further delay requires targeted elimination, that is, drug therapy.
We advise you to read the article about signs of pregnancy before your missed period. You will learn about the first symptoms, such as breast sensitivity, pain in the sacral area, problems with the digestive system, toxicosis and others.
Character of menstruation
Menstruation after surgery may change compared to what was recorded before. Since the “memory” of the reproductive system is long, it can be expressed in the nature of menstrual flow. However, difficulties with the cycle and the characteristics of menstruation are not always to blame for the operation.
The causes of problems of all kinds can be the same factors that led to the localization of the embryo in the fallopian tube or other inappropriate place in the abdominal cavity. These are chronic inflammation, hormonal deficiency, constant stress and gynecological diseases.
The first period after an ectopic pregnancy can provoke very noticeable sensations. This:
- Pain in the abdominal area. Its intensity depends on the level of intervention and the woman's ability to tolerate cramps. The pain is caused by the normal contractions of the uterus during menstruation, which radiate to the area of the fallopian tube. If it persists, adhesions may form in the tissues, adding to the discomfort. If the tube is removed, painful periods occur due to insufficiently restored tissues, to which vibrations are transmitted from the contraction of the smooth muscles of the organ;
- General weakness. The intervention takes place under anesthesia, which is necessary, but does not add strength to the woman. During menstruation, immunity decreases, due to hormonal imbalance, lethargy and drowsiness appear. After surgery and great emotional upheaval, they may intensify.
Even medical removal of the fertilized egg, which is possible in the early stages, requires “quarantine” for at least six months. For this purpose, oral contraceptives are prescribed, which are selected by a specialist.
Features of pregnancy planning after an ectopic pregnancy with tube removal
Pregnancy after an ectopic pregnancy (if surgery was performed and one fallopian tube was removed) most often does not occur on the first or even on the second attempt. Still, the chances of becoming a mother after such an operation are halved, but the statistics do not apply to some women. Much depends on the woman’s health, preparation for subsequent pregnancy, and the patency of the remaining tube. But first things first.
Features of preparation for pregnancy after VB
The first thing doctors recommend to all women who have survived surgery is to protect themselves from pregnancy for about six months. Moreover, it is recommended to use birth control pills - oral contraceptives - as protection. Firstly, this guarantees almost a 100th result (pregnancy will not occur; today oral contraceptives are the most reliable means of contraception, except for the Mirena coil, but you should not use the coil). Secondly, there is evidence that after “rest” the ovaries begin to work with redoubled force - pregnancy after an ectopic pregnancy and the removal of one tube can occur sooner. And you can take modern low-dose oral contraceptives without interruptions for as long as you need, of course, if there are no contraindications to taking them.
Different birth control pills may be prescribed to different women. There is a myth that the choice depends on the individual hormonal background of the woman. However, it is not. The first choice drugs are combined oral contraceptives with a dosage of ethinyl estradiol - 20-30 mcg. These include Logest, Novinet, Janine, Lindenet 20 (and 30), Yarina, etc. You can choose depending on your financial capabilities. The price of tablets can vary quite a lot. Let's say, a pack of Lindenet 20 (30) costs about 300 rubles, and its analogue Logest (the composition is the same, but the manufacturers are different) is 2-2.5 times more expensive. It is recommended to start taking the pills at the beginning of the next menstrual cycle after the operation (you cannot make love for 1 month after the operation).
Those planning a pregnancy after an ectopic pregnancy should undergo a full examination. There is only one fallopian tube left, which means everything needs to be done to prevent the situation from happening again. This means that before active planning, it is necessary for both partners to undergo all tests in order to detect possible sexually transmitted infections. Everyone needs to do this. Even those who have previously undergone similar tests or are confident that they are healthy. There are many so-called hidden infections that are not always detected the first time by tests. Meanwhile, pathogenic bacteria provoke inflammatory processes in the pipes, which leads to the formation of adhesions. And adhesions in the tubes in many cases prevent the fertilized egg from moving into the uterus for implantation, and it is forced to implant right there, in the tube, ovary or in the abdominal cavity. Thus, an ectopic pregnancy may occur again after an ectopic pregnancy and removal of one tube.
In addition, it is necessary to undergo another important examination - to check the patency of the fallopian tubes, or rather the one remaining one. This procedure is familiar to many women and is called hysterosalpingography (HSG). The procedure is not very pleasant, but it is not painful either, but some sensitive or simply restless women may require pain relief. A thin flexible cannula is inserted into the cervix, through which a special aqueous solution is injected. It fills the uterus and fallopian tubes, after which the doctor takes several x-rays. This way you can clearly see whether there are adhesions in the pipe or not, whether it is passable or not. If yes, then intrauterine pregnancy after an ectopic pregnancy is quite possible. If not, your doctor may recommend laparoscopy, a simple operation without incisions to cut through adhesions. But let's return to the HSG procedure. Many women notice after this procedure the appearance of such unpleasant things as thrush, and inflammatory processes in the area of the internal genital organs may occur, so HSG is not done without special indications. Most often, the surgeon who performed the operation for VD can tell you about the condition of the second fallopian tube. If he said that her condition is not important, you can immediately go for laparoscopy.
How to speed up conception with one fallopian tube
Many doctors claim that ovulation in healthy women occurs alternately in one ovary and then in the other. In reality, it turns out differently, one ovary “leads”. And the woman will be very lucky if this ovary is on the side where she still has the fallopian tube. Then pregnancy after an ectopic pregnancy can occur without problems and very quickly, especially if the woman is still young - under 30 years old. If not, then you need to try to find out the day of ovulation in order to be sure to hit it, and thereby increase the chances of conception. There are several ways to track ovulation. We'll look at them briefly.
1. Ovulation tests.
This method is suitable for those who are not too burdened with material resources, since one cycle of tests will require at least 5 pieces and it is not at all a fact that everything will work out right away. Ovulation test strips are very similar to pregnancy tests. As a rule, ovulation (the only day when conception can occur) occurs in the middle of the cycle. The most optimal days for the test can be determined as follows: you need to subtract 17 from the number of days in the cycle. For example, the cycle is 28 days. We subtract 17 and get 11. This means that tests need to be performed from 11 to 15 days of the MC, on average. But if, for example, the test turns out to be positive on the 12th day, then, as you understand, there is no point in continuing to be tested. The second stripe appears due to an increase in the content of luteinizing hormone. The test remains positive for up to 36 hours, and during this period, sexual intercourse in terms of possible conception will be most successful. It is advisable to perform the test at the same time, and it is even more reliable if it is done 2 times a day.
2.
A more budget-friendly option to speed up pregnancy after an ectopic and removal of one tube is
measuring basal temperature
. Mountains of literature have already been written about this. And although many modern doctors consider this method to be outdated, that is, uninformative, it is still worth a try. This method can be used not only as an independent method, but also as a supplement to existing ones. For example, you can very accurately determine the onset of ovulation using an ultrasound examination. But you will have to do it for several days in a row, which is not financially feasible for everyone. Therefore, you can use basal temperature to identify the desired day, and use an ultrasound to confirm or refute your doubts. But you can do without an ultrasound if the diagnosis of infertility has not yet been made, and there is a chance that pregnancy after an ectopic pregnancy will occur quickly and easily.
3. Observation of your own feelings.
During ovulation, a woman may experience mild, aching pain in the area of the ovary where the egg has matured. Sometimes pain is felt in the lower abdomen. Clear, “stretchy”, odorless vaginal discharge appears. Many women note an increase in sexual desire.
There are many folk ways to help the egg mature. For example, after sexual intercourse, stand in the “birch tree” position so that the sperm reaches the uterus faster. You shouldn’t get up immediately after an act of love; it’s better to lie down with your pelvis raised, and you definitely shouldn’t take a bath. Some women claim that some herbal infusions also help to become a mother faster, for example, sage infusion. But all this has not been scientifically proven.
Many people fail to conceive a child due to a serious psychological barrier. This is understandable, because there is at least a 5% chance that a pregnancy after an ectopic pregnancy will again be pathological, and if the tube has to be removed again, then there will be no chance of becoming a mother in a “natural” way, without medical intervention. An experienced psychologist with a medical education can help get rid of fears. Hope should also be given by the fact that if the fallopian tube is preserved, the likelihood of VD occurring is higher. And for those who have one fallopian tube, but it is definitely passable, the chances of a repetition of the situation are negligible. You can read the stories of women who have already experienced a similar situation and after that successfully became mothers. It wouldn't hurt to go on a relaxing vacation. The main thing is to set yourself up for the good and not even think about the fact that you may fail again.
If you can't get pregnant on your own
No matter how good everything is, a certain proportion of women who have undergone this operation cannot get pregnant on their own. You need to start looking for other solutions after a year of unprotected sexual activity, if conception has not occurred. In this case, a diagnosis of infertility is already made.
But the female gender is not always “to blame” for the absence of children. And this must be taken into account. The spouse must also be examined. And if conception does not occur due to some “male” pathology, such as too few live sperm capable of fertilization, the ICSI procedure can be performed. What it is? In short, the procedure is similar to IVF, but with ICSI, active sperm can be isolated from a man’s sperm, even if they are present in minimal quantities. Both IVF and ICSI are practically the only ways (not counting surrogacy) to continue the birth for infertile couples. The presence or absence of fallopian tubes no longer plays any role here. The eggs are taken directly from the woman's ovary and fertilized in vitro.
As you can see, it's not all bad. And pregnancy after an ectopic and removal of one tube is possible. You just need to be thoroughly examined, follow all the doctor’s instructions, monitor your health and well-being, and just that. believe that everything will definitely work out.
Adhesive neoplasms in the ovaries
The formation of adhesions in the ovaries is dangerous due to the fact that they are connected to the nearest internal organs, the uterus and fallopian tubes. The danger is that normal blood flow is disrupted and female-type infertility or the inability to bear a child develops.
Causes of formation in the ovaries
If we talk specifically about the root causes that provoke the appearance of adhesions in the ovaries, doctors call:
- Diagnosing negative processes in women caused by infections and STDs.
- Previous abortions and curettages. Trauma, as well as previous caesarean section, operations on the uterine cavity.
- Diagnosing a woman's ectopic pregnancy. Adhesions can also be caused by an incorrectly installed intrauterine device and its prolonged wearing.
- Injuries to the peritoneum and hemorrhages into its cavity.