- Types of research
- Advantages over excisional biopsy
- Indications
- Contraindications
- How to prepare?
- Equipment for puncture and its types
- How is a breast puncture performed?
- Possible complications
- Diagnostic value of the study
- Decoding the results
A breast biopsy, which is performed using a puncture (puncture) with special needles, makes it possible to accurately diagnose most diseases of this organ.
This study is practically safe and does not cause serious complications. After manipulation, there is no deformation of the organ, so it is used in most patients with breast diseases, especially if a malignant tumor is suspected. What is the difference between a puncture and a biopsy?
A puncture is a type of biopsy, along with an excisional one, which is performed by cutting the gland tissue. This concept also refers to the procedure for taking material (puncture), and biopsy refers to a diagnostic method, that is, biopsy is a broader concept.
Types of research
To obtain material, different types of puncture biopsy of the breast are used:
- fine-needle aspiration - used to obtain a suspension of cells with their subsequent cytological examination;
- core biopsy with a larger diameter needle using a biopsy gun or a vacuum biopsy system (such methods allow you to obtain a “column” of tissue and examine their histological structure).
Advantages over excisional biopsy
An excisional biopsy involves a surgeon using a scalpel to remove a suspicious area of breast tissue. Compared to this method, diagnostic puncture has a number of advantages:
- there is no need to visit the surgeon before the intervention and for a follow-up examination, thus, the time required for diagnosis is reduced;
- since up to 80% of biopsies are performed for benign breast processes, removing a larger volume of tissue is impractical and can lead to its deformation;
- scars formed after a surgical (excisional) biopsy may later be mistaken for pathological formations on a mammogram and will lead to the need for repeated examination;
- examination of surgically obtained material takes longer, which causes additional stress for the patient;
- the cost of the study is approximately 2 times lower;
- puncture of breast fibroadenoma or other benign formation often makes it possible to avoid surgical intervention.
Analysis results
Puncture of a breast cyst is a minimally invasive diagnostic and therapeutic intervention, which consists of puncturing the cyst with a special needle in order to obtain its contents.
Cyst puncture (biopsy) is usually performed under local anesthesia, but if the patient wishes, general anesthesia can also be used. For women of reproductive age, it is advisable to puncture breast cysts during the period from 6 to 14 days of the menstrual cycle - then the breasts are softer and more pliable. For women during menopause, puncture is performed on any day of the cycle.
Puncture of the cyst is carried out in the following stages:
- Determining the puncture point by palpation or under ultrasound control.
- Conducting local anesthesia.
- Insertion of a special hollow needle at the moment of sensation of failure inside.
- Aspiration of the fluid contained in the cyst, with its further histological examination.
- Treat the puncture site with an alcohol solution and apply a bandage.
A breast cyst biopsy does not require any special preparation. As with any other disease, with a pathology such as a breast cyst, it is recommended to undergo a preliminary examination, take the necessary tests, and study blood coagulation parameters in detail.
When performing a puncture (biopsy) of a breast cyst, you should also refrain from drinking alcohol 2 days before the procedure, and avoid all medications (especially those that affect blood clotting), except for those recommended by your doctor.
On what day is it better to do a breast puncture? Doctors allow a breast biopsy to be performed on any day of the cycle, but it is better to take the test between 7 and 14 days. The procedure does not require any special preparation: the woman just needs to refrain from taking blood thinning medications and alcohol 2-3 days before the puncture. After the procedure, you should place an ice pack in the bra cup to avoid swelling or bruising at the puncture site.
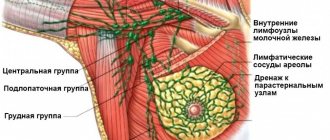
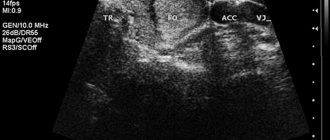
A breast biopsy is performed with the patient in the supine position. Under the control of an ultrasound device, a puncture needle is inserted into the chest. When it gets inside the nodule, the doctor collects tissue cells by pulling out the syringe rod. The samples taken are placed on glass, dried and pigmented for further microscopic examination.
Read about methods to cure mastopathy, diagnosis and prevention of the disease.
The study is prescribed by an oncologist, mammologist or surgeon when a tumor-like formation is detected in the patient. Breast puncture is indicated in the following cases:
- detection of areas of tissue compaction;
- nodular neoplasms, breast cysts;
- pathological discharge from the nipples, the presence of signs of inflammation or ulceration;
- nipple retraction;
- change in breast shape and size;
- breast deformation;
- changes in the skin of the organ - peeling, redness, dryness.
In such conditions, ultrasound-guided puncture of the mammary gland is often used. The doctor determines when to do the test. The procedure is used if other diagnostic procedures have been ineffective and it has not been possible to reliably establish the nature of the neoplasm.
Before a puncture is taken from the breast, the woman is prescribed a mammogram and an ultrasound examination. The technique allows for differential diagnosis and accurate identification of present pathological changes.
- Despite the minimal invasiveness, there are some limitations to the manipulation. If breast puncture is used, contraindications may be as follows:
- acute inflammatory process of any localization;
- pregnancy, breastfeeding period;
- recovery period after surgery;
- increased body temperature;
- blood clotting disorder.
In such conditions, ultrasound-guided puncture of the mammary gland is not performed. Are there any contraindications to the study from other internal organs? The procedure is not performed during exacerbation of any chronic pathologies.
If a puncture of the mammary gland is prescribed, contraindications should be completely excluded. This is the only way to obtain reliable data on the woman’s health status, reduce the risk of complications and make the procedure safe.
No special preparation is required to perform the study. 2-3 days before the planned procedure, it is necessary to avoid taking blood thinning medications and also give up alcohol. If on the eve of the study a woman was concerned about any disturbances in her general health, she should be sure to inform the doctor about this before the procedure begins.
How is a breast puncture performed? The manipulation is minimally invasive and is performed on an outpatient basis. To collect biomaterial, the woman takes a supine position.
- How is a puncture taken from the mammary gland? The sequence of the procedure will be as follows:
- performing local anesthesia (if necessary);
- determining the exact location of the pathological focus - when using ultrasound control, determining it is quite simple;
- antiseptic treatment of the chest puncture area;
- insertion of a puncture needle and obtaining biomaterial for research;
- removal of the needle, antiseptic treatment of the puncture, application of a sterile bandage.
- How a puncture is taken from the mammary gland depends on the type of needles used to collect tissue. Taking this factor into account, several types of research are distinguished:
- Fine needle puncture - used to collect fluid.
- Thick-needle - performed to obtain a column of cells from a pathological focus.
- Stereotactic - biomaterial is collected from several anatomical sites. Used for voluminous neoplasms.
- Initiation - the most invasive, but at the same time highly accurate. Involves excision of a tumor fragment (seal) for subsequent examination.
The specialist determines how a breast puncture is performed individually in each clinical case, taking into account the present symptoms and the expected diagnosis.
To obtain reliable data about the patient’s health status, the menstrual cycle should be taken into account and the study should be performed at the “right” time. On what day of the cycle is breast puncture performed? The optimal period is considered to be from 7 to 14 days.
It is highly undesirable to collect biomaterial during menstruation (on days 1-4) and immediately before it begins. If you are scheduled for a breast puncture, the doctor determines which day of the cycle to do the examination individually for each woman.
When it comes to research, many women ask: does breast puncture hurt? This depends primarily on the type of tissue sampling. If a puncture of the mammary gland is performed using a fine-needle or stereotactic method, pain can only occur at the moment the skin is punctured.
However, the discomfort is moderate and such procedures are often performed even without local anesthesia. However, if you have a high sensitivity threshold, local anesthesia may be used before tissue collection.
If we are talking about more complex techniques - thick needle or initial puncture, anesthesia is a mandatory step during the study. Thanks to this, the procedure is not accompanied by discomfort and is well tolerated by patients.
Whether breast puncture is painful depends on the individual level of sensitivity, as well as the type of tissue sampling. When performed correctly, the procedure does not cause significant discomfort.
Deformation of the nipple shape is an indication for breast puncture
Breast puncture is prescribed by a mammologist to identify various diseases of the mammary gland, which are accompanied by changes in the tissue structure. The development is accompanied by the appearance of tumor formations that begin to grow. These include fibrocystic mastopathy, malignant neoplasm, fibroadenoma, intraductal papilloma, apocrine adenomatosis, and cyst.
- The presence of nodes and compactions in the breast tissue, which were identified after palpation during a clinical examination.
- An inflammatory reaction of the skin of the nipples, which is accompanied by the formation of long-term non-healing erosions and ulcers.
- The appearance of pathological discharge from the nipple, which includes mucus, streaks of pus, and blood. Research may be necessary when milk is released outside the lactation period, when there is no need to feed the baby.
- Specific changes in the skin of the breast, which include redness, peeling, dryness.
- Deformation (change in shape) of the mammary gland, nipple retraction.
Indications for puncture are determined by a mammologist during a clinical examination, which includes taking an anamnesis, examination, palpation, percussion and auscultation of organs. He explains to the patient why a puncture is necessary. If necessary, other non-invasive diagnostic techniques are pre-prescribed, which include breast ultrasound and mammography (X-ray examination).
Mastitis is a contraindication to the procedure
Before the procedure, the doctor makes sure that the woman does not have the following contraindications:
- exacerbation of chronic somatic pathology of various localizations in the body;
- acute infectious pathology of various origins;
- intoxication, including of unknown origin, which is accompanied by an increase in body temperature;
- recent surgery;
- pregnancy at any stage of the course – it is not advisable for pregnant women to undergo invasive manipulations;
- acute inflammation of breast tissue – mastitis;
- lactation period - the physiological formation of milk for breastfeeding after the birth of a child, which can only occur normally;
- blood clotting disorder.
Before performing a puncture of the mammary gland, the patient is sent for an ECG
Indications
At what size of tumor is a breast puncture performed?
As soon as the formation becomes noticeable on a mammogram or ultrasound, the issue of manipulation can already be decided. The cyst is usually punctured when its size is from 1 to 1.5 cm.
Can a puncture cause cancer?
No, it cannot, mechanical removal of part of the tissue does not lead to malignant degeneration of surrounding cells. If the needle gets into a malignant tumor, then there is a minimal probability that cancer cells will “reach out” after it. This has no clinical significance.
What does this analysis show?
It is prescribed for suspected cysts, benign tumors or malignant neoplasms and is necessary to determine treatment tactics and the extent of required surgical intervention.
Taking a puncture of the breast
Indications:
- the presence of a formation in the gland tissue detected by mammography or ultrasound;
- multiple lesions;
- violation of the internal structure of the organ;
- detection of microcalcifications;
- discharge from the nipple outside the lactation period;
- deformation of the nipple area or the surface of the skin of the organ.
Volumetric formation of the gland
Any large lesion in women over 25 years of age requires a biopsy. If a calcified fibroadenoma, lipoma, fat necrosis, or a scar after surgery is detected, no further diagnosis is prescribed.
The study is performed:
- in younger women, if ultrasound reveals a lesion without obvious signs confirming its benignity;
- in cases where a suspicious formation is visible on a mammogram, but it is not detected on an ultrasound.
Violation of the organ structure
Distortions of the normal structure of ducts and glandular tissue may be the first signs of cancer. They are associated with a malignant process in 10-40% of cases. Many of these disorders are poorly visible on ultrasound and therefore require puncture under X-ray control. If the result is cells with atypia, further surgical biopsy is necessary. In case of structural abnormalities, at least 10 tissue samples are required to assess the condition of the gland.
Microcalcifications
These are small areas of calcified tissue that have a very high density on the mammogram and stand out clearly against the background of surrounding structures. All of them require an X-ray-guided study, but a fine-needle biopsy is not indicated in this case. Vacuum aspiration can be used to suction the suspicious area.
Cyst aspiration
To remove simple cysts that cause discomfort in the patient, a fine-needle puncture under ultrasound guidance is indicated. Asymptomatic cysts do not require removal unless they are accompanied by abnormal ultrasound findings.
These signs include:
- thickened wall or internal partitions;
- wall deposits;
- heterogeneous internal structure;
- no amplification of acoustic shadow.
Vacuum biopsy system for breast core biopsy
Preparation and methods of puncturing
Before performing a puncture of the mammary gland, the patient is sent for an ECG.
To reduce the likelihood of errors and complications, before performing the procedure, the woman adheres to several preparatory recommendations:
- Inform the doctor about taking medications, including drugs to reduce blood clotting - if necessary, medications are discontinued several days before the procedure.
- Submission of mandatory tests - clinical blood test, urine test, biochemistry, tests for viral hepatitis, HIV infection, syphilis, fluorography, ECG.
- Compliance with dietary recommendations - limiting fatty fried foods the day before, avoiding alcohol.
- Limiting physical and emotional stress on the day of the puncture, excluding the application of cosmetics.
Fine-needle puncture of the mammary gland
Technologies for taking tissue for biopsy:
- Fine-needle puncture - puncture and collection of punctate is carried out using a special syringe with a thin needle. To do this, the doctor pulls back the syringe plunger, which allows the punctate to be sucked out. The fine-needle option is preferable for small tumors or the presence of a follicle filled with fluid and lined with epithelium. Using a similar technique, red bone marrow is taken, for which the sternum is pierced.
- Stereotactic targeted puncture - using a syringe with a needle, the doctor can take tissue from several areas of the breast. The punctate can be taken under visual control using ultrasound.
- Thick-needle puncture or trephine biopsy is the removal of tissue using a special thick needle that contains a cutting element. This allows you to capture a large area.
- Incisional puncture is a low-traumatic procedure, which involves taking a small area of tissue and is performed using a puncture.
- Excision puncture - the procedure is necessary to capture a large area of tissue, for which a thick needle is used or a technique of cutting the skin and subcutaneous tissue is used.
If the formation is deep, the tissue of which must be taken for histological examination, a puncture of the mammary gland is performed under ultrasound guidance. This makes it possible to insert the needle without damaging nearby structures. The choice of technique is carried out by a mammologist individually based on a preliminary examination. Decoding is carried out after receiving the results of histological examination. A special table is used for quick assessment. The price of research in private clinics is no higher than surgical intervention.
Contraindications
A puncture biopsy is not informative in all patients. It is not prescribed in the following cases:
- obvious benignity of the formation, which requires only regular mammography;
- lesions located deep in the gland, close to the chest wall or in the armpit area;
- the size of the lesion is less than 5 mm, while the lesion can be completely removed during the study, and if it turns out to be cancer, further determination of the location of the tumor will be difficult; such a study is possible only with modern stereotactic equipment, and the site of removal of the nodule is marked with a metal bracket.
Other diseases and conditions:
- inability to remain still for 30-60 minutes;
- severe pain in the neck, shoulders or back caused by any reason;
- Parkinson's disease;
- blood clotting disorders;
- carried out during menstruation;
- acute infectious diseases.
How to prepare?
If the patient is taking anticoagulants or antiplatelet drugs, such as Aspirin or Warfarin, it may be necessary to gradually reduce the dose of the drug in advance and then stop it for a while. Before this, you must consult with the specialist who prescribed the medicine and take a blood test for coagulation (coagulogram).
It is undesirable to carry out manipulation in the first 5 days of the cycle (during menstruation). It is necessary to wash and dry the mammary glands and remove jewelry. There is no need to follow a special diet; you can have breakfast in the morning.
Consequences of puncturing a mammary cyst
There are very few consequences of the puncture, and it is easy to deal with them. Most often, the consequences of the procedure go away on their own, but in some cases it is impossible to do without medications.
Possible consequences include:
- swelling of the mammary glands;
- the appearance of bruises;
- allergy to anesthesia;
- fading pain and discomfort;
- bruising at the puncture site.
As a rule, these effects go away within a few days. In the case when the symptoms do not disappear, but rather intensify, you should consult a specialist.
To avoid infection, the procedure should be performed by an experienced doctor under antiseptic conditions.
Equipment for puncture and its types
The choice of research method largely depends on the equipment available in the medical institution.
Stereotactic puncture (core biopsy)
The device operates on the principle of triangulation. The location of the lesion is determined using a series of x-rays taken from different angles. Next, the exact position of the formation is calculated by computer processing, and the biopsy device is placed at the desired point on the skin under X-ray control.
During the procedure, the patient can be in two positions:
- lying on your stomach, with your chest lowered into a special hole on the X-ray table;
- sitting, as during a mammogram.
The position is chosen depending on the location of the tumor and the physical capabilities of the patient.
Fine needle puncture
The procedure is performed with a thin, small-diameter needle, which is less painful and safer, especially for women with bleeding disorders. The main disadvantages are lower diagnostic accuracy. Erroneous conclusions about the absence of cancer occur in 1-30% of cases. On the other hand, with a fine-needle biopsy of a fibroadenoma or lipoma, the result may be false positive. Puncture of a breast cyst is used when a cavity filled with liquid content is detected on a mammogram or ultrasound.
The patient is lying on her back with her arms raised or on her side, with her hands behind her head.
In any case, if the data from the study and mammography do not correspond, a core biopsy or surgical intervention is required.
Preparation for the procedure
After ultrasound and mammography, puncture of the cyst may be permitted.
The fact is that it is precisely such preparatory examinations that make it possible to determine the type, size and shape of the pathology. For example, a puncture can be performed only for those formations that are larger than 2 cm. First, about 7 days before the operation is performed, it is necessary to stop taking aspirin. This is due to the fact that the actions of these types of drugs are aimed at thinning the blood. This in turn can increase bleeding during the manipulation process.
However, the procedure has certain contraindications:
- Breast-feeding;
- Pregnancy;
- Availability of painkillers.
It is prohibited to perform a puncture in such situations when:
- There is evidence of the presence of metastases in the breast (obtained by other studies);
- There is no way to carry out the procedure safely;
- The puncture may negatively affect further treatment.
How is a breast puncture performed?
The procedure is performed without anesthesia; less often, it requires the injection of a small amount of anesthetic into the tissue or superficial anesthesia with an anesthetic cream. The puncture is carried out either by one doctor or by an assistant, for example, for ultrasound control.
The puncture site is limited with sterile napkins, the skin is disinfected and a needle attached to a 10-20 ml syringe is inserted, or a biopsy machine is used. With a stereotactic biopsy, this entire process takes place while simultaneously scanning with X-rays, and if a puncture of the mammary gland is performed under ultrasound guidance, the doctor applies a sensor that shows the passage of the needle. The number of punctures depends on the goal, the number and size of the lesions. Doctors try to do as few punctures as possible to reduce the likelihood of complications.
After the procedure, the puncture site is treated with alcohol, and a sterile gauze pad is applied. After 2-3 days, the hole after the puncture heals completely. Until this point, it is advisable to constantly wear a support bra, and you can apply cooling compresses.
How is a biopsy performed?
At its core, the whole procedure consists of puncturing the breast tissue and collecting material for further research.
It is performed mainly in cases where symptoms characteristic of cancer appear.
To ensure that the procedure is carried out correctly, accurate diagnostic methods are performed the day before, such as ultrasound and computed tomography.
The woman must arrive at the clinic at the time prescribed by the doctor. A puncture of the mammary gland is performed, as a rule, without the use of anesthesia.
In some situations, when the patient has particular sensitivity or it is painful to perform a puncture of the mammary gland, doctors use local anesthesia. The most common position is lying down, but in some cases you can sit or stand.
During the procedure itself, the woman must bare her breasts. For convenience, it is better to wear a special medical gown or nightgown.
The specialist inserts a needle into the seal and collects fluid or tissue. The material that can be obtained in this way is painted with a special substance and sent to the laboratory for detailed study under a microscope.
The puncture site is treated with a special bactericidal agent. For several days after the material is taken, a hematoma remains on the woman’s body.
Its specific treatment is not required, it goes away on its own within a few days and does not pose a health hazard. Scars and noticeable marks after the procedure are completely eliminated.
If the lumps are too far from the surface of the breast, the doctor may use particularly long needles or alternative diagnostic methods.
A woman can take a loved one (husband, mother, friend) with her to the biopsy itself. This will reduce psychological discomfort.
The results of breast puncture can be obtained within a few days after the procedure.
Painfulness of the procedure and evaluation of the results obtained
Stereotactic and fine-needle biopsies are virtually completely painless and require no painkillers or anesthesia.
A completely different situation is observed with aspiration and incisional types of biopsy. Depending on the depth of the pathology and the exact location of the tumor, they can be performed under local or general anesthesia. In this case, planning for the puncture occurs several days before it is carried out.
All biomaterials obtained as a result of the study, taken from neoplasms, are sent to the laboratory.
Thanks to special technology, the cells are carefully stained and then examined under a microscope.
Compared to healthy cells, parts of tissues already affected by the oncological process may appear in a modified version.
There are situations when a biopsy does not confirm the diagnosis of an oncological tumor, but after some time it may still appear.
This situation occurs when the puncture is carried out without the control of an ultrasound machine, or when too little material is taken.
The specialist accidentally takes part of the healthy cells, but misses those affected by cancer.
What should the patient do in this case? Confirm that the diagnosis is incorrect using several other types of examinations, including blood tumor markers.
With a high probability, the doctor can establish an accurate diagnosis when the most complete examination is carried out.
Possible complications
Is breast puncture dangerous?
Serious complications after core biopsy are observed in only 2 women out of 1000. These include hematomas (bleeding into tissue) and inflammation. In extremely rare cases, bleeding from the puncture site may occur. Approximately 5% of patients experience dizziness and fainting, which are quickly eliminated.
Milder consequences of breast puncture develop in 30-50% of patients:
- pain that lasts up to 2 weeks after the procedure;
- noticeable bruising on the skin;
- emotional stress.
If there is pain in the mammary gland after a puncture, the use of conventional painkillers is acceptable. If such sensations persist for more than 2 weeks, you should consult a doctor.
There is a single observation of a complication in which, during a core biopsy, a milk fistula formed in a nursing woman, which healed within 2 weeks. A case of the development of a large hematoma in a patient with a blood clotting disorder is also described. This hemorrhage “camouflaged” the biopsy area in which the cancerous tumor was diagnosed. After 3 months, the hematoma resolved, and it became possible to perform surgery. Cases of puncture of the chest wall with the formation of pneumothorax are also described - in 1 out of 10 thousand cases.
Is it painful to have a breast puncture?
A biopsy using a fine needle causes virtually no discomfort or any complications. Local anesthesia may be used for core biopsy.
Vacuum aspiration biopsy of the breast
Vacuum aspiration biopsy today is an advanced method for the early detection of benign and oncological breast diseases. The procedure is minimally invasive. It can be used to remove a breast cyst.
Vacuum biopsy has the following advantages over sectoral breast resection:
- The procedure is performed quickly, within 30 minutes;
- No anesthesia is required, local anesthesia is sufficient;
- Patients do not need rehabilitation after the procedure;
- 100% diagnostic accuracy;
- The procedure is aesthetic, there are no scars left after it, and the shape of the breast is preserved.
Vacuum biopsy of the breast is performed on an outpatient basis under ultrasound guidance. A special needle is inserted into the cavity of the cyst through a small puncture. The contents of the cyst are removed using a vacuum. After the procedure, the nurse applies a tight bandage. The patient remains under the supervision of a mammologist for an hour. After an hour, the dressing is changed and the patient can leave the hospital. Histological examination of the removed tissues is carried out within 8-10 days. After the procedure, a tiny red spot 2-3mm in size remains on the skin, which disappears after a few weeks.
In order to avoid adverse consequences, the procedure is carried out after preliminary preparation:
- 3 days before the puncture, the patient is prescribed to take the hemostatic drug tranexam 250 mg 3 times a day;
- On the day of the procedure, a light breakfast is offered (porridge, cheese sandwich, yogurt, sweet tea or coffee);
- The day before the procedure, it is recommended to refrain from drinking alcoholic beverages.
The patient undergoes an examination, which includes:
- General (detailed) blood test;
- General urine analysis;
- Determination of blood glucose levels
- Coagulogram
- Tests for hepatitis B and C, HIV, rw, blood group, Rh factor (validity of tests - 10 days);
- Registration of an electrocardiogram with interpretation (no later than 1 month);
- Fluorography (no later than 8 months)
- Conclusion from a gynecologist (no later than 1 year).
If you have signs of a breast cyst, call. After a clinical and instrumental examination, the mammologist will perform a diagnostic puncture of the breast cyst. After studying the research results, the doctor will individually determine the most suitable treatment method for the patient. At the Yusupov Hospital, breast cysts are removed by puncture. Reviews about the procedure are good.
Author
Natalya Aleksandrovna Vyaznikova
Oncologist
Diagnostic value of the study
The accuracy of the results depends on the accuracy of the manipulation, careful histological analysis and their coincidence with the results of mammography or ultrasound.
Probability of accurate diagnosis with core biopsy:
Why is a repeat puncture prescribed?
The problem is cases of discrepancy between the results of biopsy and mammography. If radiography shows every reason to suspect a malignant tumor, and the puncture gives a “benign” result, it is necessary to either repeat the core biopsy or perform surgery. If the results do not match, in 47% of cases, patients end up with a malignant tumor.
In addition, there are cases when the lesion is accompanied by cancer cells and benign lesions. Sometimes the analysis reveals only a benign component. Therefore, there are risk groups that require either regular puncture or surgical biopsy:
- atypical ductal hyperplasia or ductal atypia, which is often adjacent to a malignant tumor or degenerates into it;
- radial scars in the gland tissue;
- fibroepithelial neoplasms, when differential diagnosis between fibroadenoma and leaf-shaped tumor is difficult;
- lobular carcinoma in situ;
- cases where, after puncture of the mammary gland, the size of the tumor increased.
Patient's actions after puncture
After the procedure, it is necessary to avoid visiting the bathhouse or sauna for at least 3 days.
Breast puncture is performed on an outpatient basis and does not require the woman to be hospitalized. Sometimes a doctor's observation may be required for several hours. To prevent the development of complications after manipulation, you should follow several simple recommendations:
- The skin in the puncture area should not be wetted with water for 2 days.
- Avoid visiting bathhouses, saunas, and the beach - high temperatures and sunlight have a harmful effect on tissues. You need to wait several days - at least 3 days.
- Loads on the muscles of the chest and upper limbs are limited, as they are painful.
- If severe pain is a concern, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs are prescribed - which drugs and how much to take should be determined by the attending physician.
After performing a thick-needle excision puncture, care for the puncture area is required for several days. Treatment is carried out with an antiseptic ointment, after which a bandage is applied.
It is advisable to carry out the procedure in the manipulation room of a clinic at the place of residence. The attending physician informs the patient about the measures after puncture of the mammary gland before the manipulation.
Possible allergic reactions to injected anesthetics
Breast puncture is a minimally invasive procedure. In rare cases, the following complications and dangerous consequences may develop:
- Pain syndrome – in the first days there may be pain in the area of puncture and tissue collection for biopsy, especially after a thick-needle puncture.
- Formation of a hematoma due to bleeding, while brown discharge may appear from the nipple.
- Bleeding from the site of tissue puncture, caused by damage to a large vessel.
- Tissue swelling of varying degrees of severity, which may increase against the background of an inflammatory reaction.
- The development of allergic reactions provoked by the introduction of anesthetics (Novocaine, Lidocaine) - depending on the severity, a rash may appear on the skin, itching, urticaria, angioneurotic swelling of soft tissues with a predominant localization in the facial area may develop. Repeated allergies are often accompanied by a progressive decrease in systemic blood pressure, multiple organ failure and pose an immediate danger to human life.
Responsible preparation makes it possible to minimize the development of complications and unpleasant consequences. Treatment of negative reactions is carried out by the attending physician.
Reviews about breast puncture are mostly positive. The woman is not afraid: there is no significant tissue damage during the manipulation, anesthetics eliminate pain. The study makes it possible to accurately detect a large number of diseases, including oncology. The procedure minimizes misdiagnosis.
The result of breast biopsy analysis makes it possible to identify:
- Presence of cancer.
- Stage of development of the pathology.
- The structure of the neoplasm.
- The nature of the tumor (benign or malignant).
Inflammatory or hormonal processes in the early stages of development can also be determined by puncture. Such results help determine further patient management tactics and treatment regimens. The procedure is carried out using special equipment and needles of various sizes. There are indications and contraindications for such manipulation.