The female breast is considered one of the most vulnerable areas on the body. It is in its structure that nodular compactions appear and progress. Focal formation of the mammary gland is represented by multiple or single tumors, which are characterized by blurred or clear contours and different sizes.
Forms of pathologies
Focal-type formations that affect the female breast are classified into several types:
- Fibroadenoma is a compaction, the formation of which occurs from excess fibrous or glandular tissue. A characteristic feature is lobular division with clear boundaries. An alarming signal is a leaf-shaped focal fibrolipoma of the breast, which is likely to transform into oncology.
- Mastopathy (fibrocystic mastopathy, FCM) is a pathological focal lesion of the mammary gland, accompanied by the appearance of nodular inclusions that differ in shape and size.
- A breast growth called a lipoma is created in the body from fatty tissue cells. Location: subcutaneous tissue. But in the absence of proper treatment, the focal formation penetrates deeper into the chest. This process is practically asymptomatic; if the nodules are not detected in a timely manner, sarcoma may develop.
- A cyst in the thoracic part of the body appears from glandular tissue and is shaped like a capsule. Inside it is filled with liquid of varying consistency. In most cases, focal cysts occur near the milk ducts.
- Avascular tumors are devoid of capillaries and there is no blood supply inside.
Focal formations of a malignant type of breast are diagnosed very rarely. This is explained by the fact that cancerous lumps are aggressive, they appear and grow quickly, and are prone to metastasis. Among these are:
- Sarcoma - a formation formed from supporting, connective tissue, the danger is represented by a high probability of mortality.
- Lymphoma is not a separate focal formation. In the process, cancer cells rapidly multiply in the lymph.
Types of lipoma
Lipoma in the breast can be different. So, in accordance with the number of neoplasms, it is customary to distinguish:
- Single lipoma - diagnosed if the “ball” is located in only one breast and is not diagnosed in other places.
- Multiple lipomatosis - formations were identified in large numbers.
A separate classification suggests dividing the disease according to the form of the pathological formation. Highlight:
- Diffuse lipomatosis - it is difficult to palpate a clear boundary of the formation; adipose tissue grows and becomes heterogeneous.
- Nodular - compaction with clear boundaries, looks like a dense but mobile capsule.
Based on what exactly the node contains, it is called:
- Fibrolymphoma - contains mainly connective tissue, with a small admixture of fat.
- Lipofibroma - a tumor consisting mainly of fat and some connective tissue.
- An angiolipoma is a lump on the chest that contains a large number of small vessels, so surgery to remove it is often accompanied by severe bleeding.
- Myolipoma - in addition to the usual adipose tissue, muscle fibers are added.
- Myxolipoma - characterized by the presence of mucus.
ICD-10 code
In most cases, focal compactions that form in the structure of the mammary glands are benign. Their international code according to ICD 10 is D24.
As the focal tumor grows and enlarges, compression of the healthy tissue adjacent to it occurs, which can lead to a deterioration in the blood supply. In the absence of diagnostic measures and timely treatment, a focal formation formed in the soft tissues of the breast can develop into oncology.
The slightest change in the mammary gland cannot be ignored.
Fibroadenoma of the breast
FIBROADENOMA IS A BENIGN HORMONE-DEPENDENT TUMOR OF THE BREAST, CHARACTERIZED BY FOCAL EXCESSIVE PROGRESS OF FIBROUS AND Glandular TISSUE.
In the International Classification of Diseases (ICD-10), fibroadenoma is classified as a benign tumor of the mammary gland (D24). However, some scientists believe that fibroadenoma is a consequence of hyperplasia of individual lobules and should not be classified as true tumors. To establish a diagnosis of breast fibroadenoma , a clinical examination, technical imaging (ultrasound or mammography) and fine-needle biopsy are sufficient. Such a triple test gives 99% confidence in the quality of the process.
Breast fibroadenomas are detected in every fifth woman throughout her life, but the peak incidence occurs at 20-30 years of age. In young women, a multiple form of the disease is more common; large fibroadenomas (up to 20 cm) are typical for adolescents. During menopause, tumor growth stops or decreases markedly. During pregnancy, the process can progress quickly.
Causes of fibroadenomas
In most cases, the appearance of breast fibroadenomas is associated with hormonal imbalances, in particular, with an increase in estrogen levels during the formation of the menstrual cycle. Hormonal imbalance can also be a consequence of pathology of the thyroid gland or ovaries.
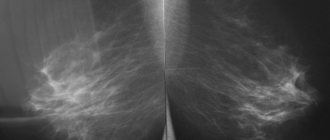
Fibroadenoma on mammography
Despite numerous studies on this problem, clear reasons for the development of the tumor have not been identified to this day. Risk factors include family history (breast tumors in maternal relatives), various menstrual irregularities, prolonged stress and poor environmental conditions.
Causes of pathological processes
The opinion of experts is that the manifestation of various focal neoplasms in the breast tissue is due to hormonal changes. The reason for this may be:
- production of estrogen in excess, which disrupts the functioning of other hormones
- uncontrolled use of hormonal contraceptives - such medications are prescribed by the attending physician, based on tests and examination of the woman
- ovarian dysfunction, lack of conception
- hormonal replacement therapy, which women undergo during menopause - with prolonged use of such drugs in the body, a process based on the appearance of new cells and tissues progresses
- uterine inflammation, in particular endometritis
- regular stressful situations
- metabolic disorders as a result of poor nutrition - overweight ladies are at risk, because estrogen is present in fat cells
- frequent abortions, which are hormonal stress for the body
- diseases of the thyroid gland, inflammatory processes affecting the fallopian tube and leading to pathology of the appendages and uterus
- in exceptional cases, the appearance of lumps in the mammary glands is facilitated by dysfunction of the gallbladder and its ducts
- osteochondrosis affecting the thoracic spine
It is worth carefully monitoring your health and periodically examining your breasts yourself if a woman has tumors in other internal organs.
Fibroadenoma of the breast
FIBROADENOMA IS A BENIGN HORMONE-DEPENDENT TUMOR OF THE BREAST, CHARACTERIZED BY FOCAL EXCESSIVE PROGRESS OF FIBROUS AND Glandular TISSUE.
In the International Classification of Diseases (ICD-10), fibroadenoma is classified as a benign tumor of the mammary gland (D24). However, some scientists believe that fibroadenoma is a consequence of hyperplasia of individual lobules and should not be classified as true tumors. To establish a diagnosis of breast fibroadenoma , a clinical examination, technical imaging (ultrasound or mammography) and fine-needle biopsy are sufficient. Such a triple test gives 99% confidence in the quality of the process.
Breast fibroadenomas are detected in every fifth woman throughout her life, but the peak incidence occurs at 20-30 years of age. In young women, a multiple form of the disease is more common; large fibroadenomas (up to 20 cm) are typical for adolescents. During menopause, tumor growth stops or decreases markedly. During pregnancy, the process can progress quickly.
Causes of fibroadenomas
In most cases, the appearance of breast fibroadenomas is associated with hormonal imbalances, in particular, with an increase in estrogen levels during the formation of the menstrual cycle. Hormonal imbalance can also be a consequence of pathology of the thyroid gland or ovaries.
Fibroadenoma on mammography
Despite numerous studies on this problem, clear reasons for the development of the tumor have not been identified to this day. Risk factors include family history (breast tumors in maternal relatives), various menstrual irregularities, prolonged stress and poor environmental conditions.
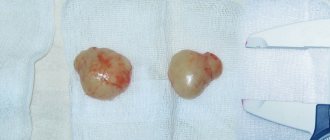
The tumor is represented by a clearly limited node of dense elastic consistency. On section, it is most often whitish with noticeable lobulation. The size of most fibroadenomas does not exceed 3 cm, but giant nodes are also found. Histologically, the tumor is represented by the proliferation of two components - fibrous and glandular in different proportions. Long-existing fibroadenomas can become denser due to hyalinosis and calcification. In this case, as a rule, the size of the formation decreases, and calcifications appear in the structure. In large nodes, infarctions may occur as a result of circulatory problems. Leaf-shaped fibroadenomas are histologically characterized by increased cellularity; the malignant variant is characterized by invasive growth and an abundance of mitotic figures, which are signs of aggressive growth.
Main symptoms
Small focal formations are almost invisible; they are detected only with careful palpation of the chest. With their active development, general health deteriorates, which is the first sign of a possible disease. Periodically, pain occurs in the breast tissue; when the upper limb is raised, the mammary gland takes on an unusual lumpy shape. On palpation, a tumor is detected; with slight pressure, pain appears.
Some patients indicate an unpleasant feeling of fullness, accompanied by a burning sensation in the chest. In this case, redness may be observed at the site of focal formation. A feature of the progressive degree of the pathological process is the spread of compaction to the milk ducts. In this case, fluid mixed with blood is released from the nipples. A change in breast shape in a calm state is observed due to a significant increase in tumor size.
For many women, some symptoms make themselves felt only during menstruation, after which the state of health stabilizes. If an infection is associated with the described condition, then the nipple discharge is likely to contain pus, the skin of the breast becomes very red and hard, and bluish swelling is also possible.
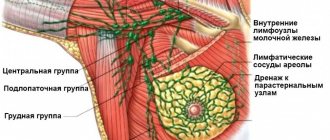
With such a course of development of focal breast formation, it is necessary to monitor the body temperature, which will rapidly increase, and check the condition of the axillary and inguinal lymph nodes.
Carrying out diagnostics
During an examination by a mammologist, a woman is offered the following procedures:
- Initial examination with palpation of the breast.
- Blood sampling for general analysis.
- Blood test for laboratory testing of hormones.
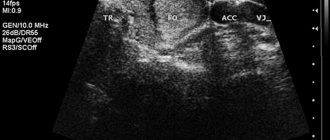
- Ultrasound of the focal (focal) node - usually a similar procedure for violation of the structure of the mammary glands is prescribed for patients under the age of 35 years. It makes it possible to identify small hypoechoic formations in the photo and their shadows.
- Carrying out mammography - the procedure involves examining the affected focal area with weak, low-concentrated X-rays, and is prescribed to patients over 35 years of age to accurately determine the pathology.
- In some cases, a computed tomography scan is performed at the discretion of the attending physician; such a diagnostic examination is considered very informative.
- If a voluminous focal compaction begins to change in size and causes pain, there is a risk of developing into a malignant tumor. In this case, a biopsy aimed at detecting mutating cells in the tumor is indicated for an accurate diagnosis.
- If necessary, the lymph nodes passing near the chest are additionally examined.
- Chromoductography, which uses a special contrast agent, is effective.
- An echographic study of FCM helps determine the degree of progression of the pathology. The echo signs obtained during diagnosis describe in detail the picture of the formation and development of focal compaction. To obtain an accurate final diagnosis, a special bi-rads scale is used.
Classification of tumors
In modern medicine, breast cancer is classified on various grounds. Thus, according to the degree of prevalence, three types are distinguished: primary tumor, cancer with damage to regional lymph nodes, and malignant tumor with distant metastases.
Experts have developed an extensive classification by stages, which is used when making a diagnosis all over the world. There are 4 stages of development of a malignant breast tumor, on which treatment tactics and prognosis depend.
The main indicators of the effectiveness of an oncologist are his experience and cooperation with the medical community. Modern oncologists not only classify breast cancer with ICD, but also develop treatment regimens taking into account concomitant diseases and the characteristics of the course of the disease.
Highly qualified specialists at the Yusupov Hospital not only improve their knowledge and skills, but also interact with leading research centers in Moscow, making it possible to use rare drugs and conduct complex studies.
Standard Treatments
Any treatment is carried out only after examination and determining the exact diagnosis of the patient. It is impossible to treat large benign focal formations or any types of oncology (cancer). For medical reasons, surgical intervention is indicated in such cases.
Specialists, if the case allows, strive to perform organ-preserving operations, when a focal compaction with closely adjacent tissues is excised. If the contours of the focal formation are unclear, if it cannot be localized, a total mastectomy is performed followed by chemotherapy.
Focal lumps in the mammary glands appear due to hormonal imbalance. To stabilize it, conservative therapy is used. In this case, the patient is prescribed:
- Dydrogesterone, Duphaston - medications that are analogues of progesterone and replenish its deficiency
- Zemid, Tamoxifen - a group of antiestrogens that block the production of estrogen in excess
- Bromocriptine, Parlodel are prolactin agents.
- sedatives (Novopassit, Valerian) that normalize the functioning of the central nervous system
- if focal lesions of the mammary glands occur due to diseases of the thyroid gland, hormonal agents are prescribed to stabilize its activity; in case of iodine deficiency, taking Iodomarin is indicated, etc.
- when the development of focal formations is accompanied by inflammation, enzyme medications and NSAIDs are prescribed
- complex vitamins are indicated for general strengthening of the body
Prevention measures
There are no special procedures that would prevent focal breast formations. But simple rules will help to minimize the pathological changes described:
- regular breast examination by a mammologist or gynecologist
- taking hormonal medications only on the recommendation of a doctor
- first pregnancy and childbirth after 30 years
- proper diet and avoidance of bad habits
- long lactation
- prevention of physical and emotional fatigue
- timely treatment of inflammatory and infectious diseases in the body, which will mean minimizing the appearance of mastopathy, tumors, etc.
The provocateurs for the development of many diseases, including breast formations, are the living environment and lifestyle features. Timely ultrasound and other diagnostic measures to detect focal shadows in the mammary gland. Comprehensive treatment will help the woman fully recover. You can’t neglect your health; you should respond to any changes in your general well-being.