Breast tumor (nodule) does not automatically mean that it must be associated directly with breast cancer! However, most women react with alarm when they feel something unusual in their breasts or their doctor finds something abnormal. Most congestion, swelling and bumps are not malignant tumors, but have harmless causes. However, you should always discuss any breast changes with your doctor. Read what may be hidden behind a pectoral node, how to diagnose and treat it.
General concept of breast disease
The emergence and progression of nodular formations in the structure of the breast tissue occurs against the background of pathological or physiological changes occurring in the endocrine glands. They have an effect on the reproductive organs and reproductive system. An important factor is the disruption of the nervous regulation of the functioning of such systems.
The appearance of formations in the mammary gland most often occurs due to hormonal changes that occur in the female body during certain periods, dyshormonal imbalances. For example, menopause, pregnancy followed by feeding, puberty. Such situations are the norm, and nodular neoplasms disappear spontaneously upon completion of functional restructuring and stabilization of hormonal imbalance.
Some types of breast tumors indicate the rapid development of diseases that require urgent diagnosis and qualified treatment, in particular:
- mastitis, abscesses
- neoplasms of benign and malignant types
- cysts
- infectious diseases
- intraductal papillomas
- lactostasis
- consequences of surgical operations, injuries
If nodes are found in the chest, a visit to the doctor with subsequent examination and comprehensive treatment is strictly indicated.
Types of knots
There are several most common types of seals:
- Fibrous. Most often, fibrous nodes appear against the background of gynecological disorders. The presence of mastitis, abortions, and injuries also increases the risk of fibrous nodes. This type of lump occurs in 15% of women aged 30 to 50 years.
- Fibromatous. Diagnosed in 20% of women. Dependence on age is not observed. Nodes of this type occur in the cavities of the mammary glands and muscle tissue of the uterus. The fibromatous type is accompanied by heavy bleeding and painful sensations during menstruation.
- Diffuse. This type of formation can significantly affect the risk of breast cancer. When a woman is of reproductive age, her breasts undergo various types of changes. The consequence of errors in these processes is diffuse restructuring.
- Hypoechoic. Characterized by multiple seals. It occurs in parallel with oncology or cystic formations. It can be asymptomatic, so this type is the most dangerous.
Experts also distinguish between bilateral and unilateral formations. Oddly enough, unilateral lumps are more dangerous and are localized only in the right or only in the left breast.
The main causes of mammary gland pathologies
In the female body there is a close relationship between the reproductive system and the mammary glands. The condition of the latter is negatively affected by various diseases that progress in the internal organs. Based on this, it is customary to identify a number of reasons that result in the formation of nodules in the structure of the breast tissue.
Education within normal limits
The relationship between the reproductive organs and the mammary glands leads to the fact that during adolescence, during the premenstrual period, nodular formations develop in the right and left breasts. They cause swelling of the soft tissues, unpleasant pain with burning and itching. This condition is considered normal; at the end of the acute period, with increased production of prolactin and female sex hormones, it resolves itself.
As for menopause, the appearance of any type of breast inclusions is associated with involutive changes in the reproductive system, disturbances in neuroendocrine regulation, and strong dishormonal changes.
Pathological changes
Seals form in the mammary glands, which indicate permanent functional changes and act as a kind of symptomatology of serious diseases:
- Mastopathy is a benign formation with blurred contours. A characteristic sign is the appearance of a distinct vascular pattern on the skin, cyanosis of the skin, and enlarged lymph nodes. Usually causes increased discomfort with the onset of menstruation. The cycle goes astray, the condition of the hair and skin deteriorates, and increased emotionality progresses.
- Fibroadenoma is a type of mastopathy. The diameter of a mobile, fairly dense body is 2–7 mm; if it is exceeded, surgical intervention is indicated. There is no pain on palpation. But, despite this, it is recommended to eliminate the nodular tumor before pregnancy; during gestation it will begin to grow rapidly.
- Leaf-shaped fibroadenoma is extremely rare and poses a health hazard. It has a rounded shape, is of epithelial origin, and appears painful during examination, especially in the premenstrual period.
- Abscess or mastitis are inflammatory pathologies resulting from infection. Symptoms include high fever, general weakness, and pain.
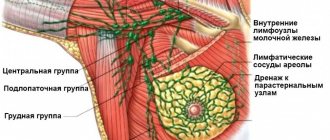
- Malignant formations and metastasis from internal organs have compacted, tuberous nodes with vague sizes and shapes. A clear sign is a retraction of the nipple, a change in skin tone, and wrinkling. On the affected side, the axillary lymph node associated with the mammary gland is usually enlarged.
- Lipoma consists of a fatty structure. Wen rarely exceed 2 cm in diameter, they are soft and elastic, mobile under the skin, and are represented by a capsule with clear boundaries. The operation is performed in case of cosmetic discomfort, and local anesthesia is used.
- The papilloma that has developed inside the duct is of epithelial origin and resembles a growth in shape. It is distinguished by mobility, elasticity during palpation, bloody type nipple discharge appears.
- A cyst affecting the mammary gland is a dense capsule filled with fluid. It is represented by single nodular formations, which, when growing, are combined into groups. The cyst does not cause pain and is often discovered during a routine examination.
- A hamartoma in the mammary gland develops from fatty, fibrous or glandular tissue. It often forms and develops during the prenatal period. Differs in small size. Excised when it reaches large sizes.
- Lymphadenopathy is the formation of lumps in the chest, caused by a pathological change in the size of the lymph nodes. Lymphadenopathy progresses and grows sharply under favorable conditions, transforming into a malignant form.
Symptoms
Lumps and nodes in the mammary gland appear and disappear mainly under the influence of hormones - their increased production or a decrease in their activity and concentration in the blood.
If nodes or small lumps appear in both mammary glands before the onset of menstruation and are combined with engorgement, discomfort, swelling of the breasts, and disappear spontaneously in the first phase of the menstrual cycle, this is considered one of the symptoms of a premenstrual symptom and does not require treatment.
Also, a two-way process of formation of multiple nodes and compactions is observed in mastopathy and multiple cysts. These pathological changes develop with persistent dyshormonal imbalances caused by:
- stress;
- chronic fatigue syndrome;
- physical and mental stress;
- disturbance of neuroendocrine regulation;
- gynecological diseases and other diseases of the genitourinary system;
- menopause;
- protracted somatic and infectious processes.
Nodules of one breast are considered more dangerous and have a poor prognosis. They can be of various shapes, sizes, localization and require clarification of the type and cellular composition.
Fibroadenoma
The most common type of nodes. They are dense, round in shape, painless on palpation, not fused to the skin and do not disappear in the first phase of the menstrual cycle. This is a benign tumor that in most cases must be removed.
Breast cyst
Cystic formations appear due to persistent dishormonal changes caused by:
- inflammatory diseases of the reproductive system;
- neoplasms of the genitourinary system (ovarian cysts, uterine polyps) or endocrine organs (pituitary gland, hypothalamus, thyroid gland or adrenal glands);
- neurohormonal disorders due to prolonged stress, psychological or physical fatigue, depression.
Lactostasis or lactocele
Seals or small nodes during lactation occur when milk stagnates or accumulates in a certain part of the mammary gland (cyst filled with breast milk). In this case, it is necessary to eliminate the causes of lactostasis and express. When diagnosing a lactocele, it is punctured and this section of the gland is removed.
Mastitis or breast abscess
These pathologies are caused by an inflammatory process in the mammary gland caused by pyogenic microflora. The appearance of compaction and nodular formation is accompanied by pain, swelling of the chest area, weakness, and fever. If left untreated, the inflammation site turns into an abscess with softening in the center. Treatment is only surgical.
Other benign nodular neoplasms (atheromas, lipomas)
In most cases, these are painless nodes located in the subcutaneous fat or between the lobules. They are not fused to the skin and are diagnosed during a preventive examination or rapid growth, deformations of the breast and nipple, as well as during instrumental examinations (ultrasound or radiography).
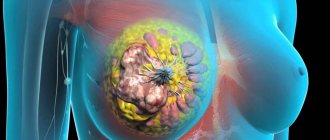
Malignant neoplasms or metastases from other organs
This is the most dangerous type of nodular neoplasm that must be diagnosed in the early stages. The nodes are dense with unclear outlines and a bumpy surface. In most cases, there is deformation of the nipple and changes in the skin over the tumor.
How to examine breast pathology
To diagnose a nodular formation as accurately as possible, three main studies are carried out. This includes ultrasound (for indications up to 35 years), mammography, biopsy for histology in case of suspected oncology. The doctor must palpate the mammary glands with regional lymph nodes during the initial examination. An important procedure also involves laboratory testing of blood and establishing hormonal status.
If the development of papillomas inside the ducts is suspected, ductography is prescribed, with the help of which the patency of the ducts is checked with the injected contrast fluid.
The ultrasound procedure is necessary to establish the stage of echogenicity of tissues that have undergone pathology with nodular formations.
If there is a cyst, there is a need to detect an area of anechoicity. In particular, fibroadenomas and fibrocystic densities appear to be hypoechoic formations. As for hyperechogenicity, it occurs with fibrous nodes, lipoma with dense and fairly voluminous breast tumors.
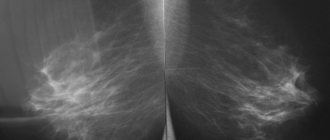
Based on the obtained echo signs and the birads scale, the existing pathology is accurately determined. Suspected oncology on mammography is represented by compactions with unclearly visible boundaries and dusty calcifications. If the image contains darkened areas with high intensity and uniformity, mastopathy is suspected. When we are talking about a nodular formation with unclear contours, blurry, an MRI is performed.
Detailed verification of mammary gland formations and study of vascular growths is carried out using Dopplerography.
Modern diagnostics of nodal seals
The appearance of a node is often discovered accidentally or during self-examination. If you notice alarming symptoms that may indicate the presence of a disease, you should immediately contact a medical facility, where you will be examined using the following diagnostic methods:
- X-ray of the mammary glands (mammography). This diagnostic method is effective for any type of formation. Its accuracy is 95%. X-rays are taken in two projections: frontal and lateral. This allows you to fully analyze the picture of the pathology. A similar procedure is recommended for adult and elderly women to undergo annually.
- Contrast X-ray (ductography). If there is discharge with bloody or serous inclusions, experts recommend this diagnostic method. During the procedure, contrast is introduced into the cavity of the milk ducts, allowing a more detailed examination of the structure of the formation.
- Breast ultrasound. Ultrasound examination is carried out in the first phase of the menstrual cycle. The method is most accurate when used on young patients due to the presence of denser connective tissue.
- Pneumicystography. Recommended for suspected cysts. During the procedure, a seal is punctured, which is subsequently filled with gas. In this condition, the nodular formation of the mammary gland is photographed and the images are examined. The gas dissolves on its own after a week or ten days. Sometimes this method helps eliminate the cyst.
- Cytology examination. It is carried out in the presence of pathological discharge from the nipples. For analysis, fluid is collected and a fine-needle aspiration puncture biopsy is performed.
- Sectoral excision. If the development of oncology is suspected, doctors perform resection of pathological lumps, which are then examined for the presence of malignant cells.
Diagnosis of nodular formations involves methods such as thermography, CT and MRI.
Which doctor should I contact if a node is detected?
A mammologist or gynecologist specializes in pathologies of the mammary glands.
Treatment of lumps in the mammary gland
The therapeutic process for breast nodules involves stabilizing the endocrine balance. Treatment can be surgical or conservative, it all depends on the type of lump in the mammary gland. Surgery is performed in the following cases:
- there is a possibility of transformation of the nodular tumor into cancer
- the diameter of the formation exceeds 1 cm
- rapid growth of the nodular body
- the presence of two or more formations in one mammary gland
It is necessary to preliminarily verify and also treat pathology accompanied by the development of nodular formations based on the stage of its progression. Maintenance therapy is recommended, including vitamins, hormones, and symptomatic medication prescribed by a doctor. Based on the results of the study of the nodular formation, oncological drugs are prescribed.
Traditional medicine in the treatment of mammary glands
There are many positive reviews regarding traditional medicine tips that help with breast nodules. Thus, herbal medicine is based on tinctures, decoctions, and all kinds of lotions. For these purposes, it is customary to use medicinal herbs, presented:
- mountain lavender
- common horehound
- medicinal angelica
- oregano
- blue clay
- tarragon, wormwood, etc.
Natural adaptogens provide benefits. For treatment, it is customary to use dietary supplements that improve overall well-being, normalize blood flow, and other functions in the mammary gland. However, the indicated drugs are used under the strict supervision of the attending physician and are only auxiliary or maintenance therapy.
It is easier to cope with formations that appear in the mammary glands at the beginning of the disease. Their forms in an advanced stage require long-term and complex therapy. Things are worse if the compaction develops into oncology. The quadrant of the nodular formation in the mammary gland that requires verification accurately determines the location of pathological progression. As a result, there is no need to expand the area to be treated.
Removal of a node in the chest
Modern methods of surgical intervention involve a gentle, painless approach. The glands are little damaged. Only a mastectomy is noticeable. Typically, the tumor is removed when the pathology and pain of the tumor are severe. If the doctor insists on the need to have surgery, you should not delay.
Elimination or cauterization of the tumor stops the development of the pathology. After this, the woman can give birth and even breastfeed. After surgery, maintenance therapy is performed. Nodes stop appearing. The patient's rehabilitation after removal of the nodule does not last long.
Prevention
There are no basic rules to prevent structural changes in breast tissue. Prevention involves a systematic and thorough self-examination of the mammary glands. In the case of a hereditary predisposition, an annual visit to a mammologist with preventive mammography is indicated.
Timely treatment of diseases of the reproductive system, pancreas, and thyroid glands will help minimize the appearance of hormone-dependent breast formations.
Breast nodules appear at any age. The acute period is considered to be puberty, menopause, when serious hormonal changes occur in the female body. It is not difficult to cope with such pathologies if they are detected in a timely manner. The specialist prescribes a number of diagnostic measures, accurately determines the type of nodule, and conducts effective comprehensive treatment.
What to do if a node has been detected
A benign tumor usually has no obvious signs and is not characterized by pain. Such a node is easy to palpate; it is located shallowly in the thickness of the chest.
In order for the doctor to prescribe the correct treatment, it is necessary to exclude a cancerous tumor. This will require a thorough breast examination.
In some situations, radiation diagnostics is prescribed. Tomography and x-rays are performed every 3-4 months. An axillography is required to reveal the condition of the lymph nodes in the armpits. Using contrast-enhanced ductography, the milk ducts are examined.