Kinds
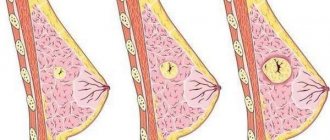
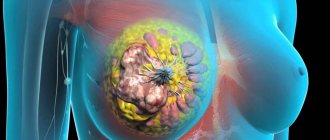
Most often, nodular formations of the mammary glands are observed on one side - in the right or left breast. There are three known pathological processes that contribute to the formation of focal lumps - lipoma, fibroadenoma and cystic mastopathy. Each of these diseases has distinctive features. They are diagnosed and treated differently.
You may be interested in: How to delay menopause: methods, medicinal herbs and drugs
Fibroadenoma
Many people are interested in the size of breast fibroadenoma for surgery. Let's look at this issue in more detail.
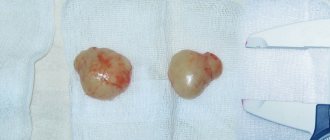
Fibroadenoma is a nodular formation of the mammary gland with unclear contours. This is a type of nodular mastopathy that usually affects one of the mammary glands. Often the development of this disease is a consequence of a hormonal imbalance in a woman’s body. Fibroadenoma reaches up to 7 cm in diameter. In this case, the formation is not associated with subcutaneous tissue and skin and is benign. If a lump is detected in the mammary glands, women should undergo a high-quality diagnosis, consult a mammologist and undergo tests. A diagnostic method such as histology helps to find out whether a given tumor is malignant. A piece of pathological tissue is taken for examination and a biopsy is performed.
Hamartoma
A breast hamartoma is a lump in the breast. The nodular area is formed by adipose, connective and glandular tissue. Hamartoma is formed as a result of embryogenesis. Usually the compaction is small, so it remains undiagnosed for a long time. This tumor is not dangerous; removal is performed if it is large or if the tumor interferes with the patient’s life.
Treatment of any breast disease depends on the stage at which the disease is detected. Prevention methods: regular examinations and maintaining a healthy lifestyle.
Dimensions of the tumor
You may be interested in: Failure of the menstrual cycle after 40 years: reasons for the changes
Let's talk about the size of breast fibroadenoma for surgery. If the tumor is no more than 8 mm, then treatment begins with traditional methods: taking hormonal medications, using folk remedies. Conservative methods of therapy are used for 6 months with constant monitoring of the condition of the formation using ultrasound.
If the doctor notices that the nodular formation of the mammary glands has increased in size, an operation may be prescribed, which involves removing the pathological focus. The absolute indication for intervention is the rapid growth of the tumor, the likelihood of transformation into an oncological tumor and pregnancy planning. Large fibroadenomas are considered to be nodes exceeding 2 cm in diameter. Most often they lead to a change in the shape of the gland.
You may be interested in: Removal of an ovarian cyst - laparoscopy: reviews of the operation and the postoperative period
Fibroadenoma is classified into several types:
- leaf-shaped;
- pericanalicular;
- intracanalicular;
- involutive.
Lipoma
This is a benign neoplasm in the mammary gland, formed due to excessive growth of adipose tissue. This compaction looks like a capsule. It is not painful, but is soft and mobile. The lipoma reaches 2 cm in size, but in some cases it can increase to 10 cm in diameter. Such a large formation in the mammary gland begins to compress the surrounding tissues and cause pain.
Neoplasms in the brain
Brain tumors cause the greatest concern for patients. A cystic-solid formation (even a benign one) always compresses neighboring areas of the brain, which causes unbearable headaches in the patient. The reason for such difficult sensations lies in the fact that the brain is enclosed in a hard shell (skull), so any tumor simply has nowhere to go.
A neoplasm in soft tissues has the ability to protrude outward or occupy body cavities. Compression forces the brain tumor to put pressure on neighboring cells, preventing blood from reaching them. In addition to pain, this is fraught with disruption of the functioning of all body systems (digestive, motor, reproductive, and so on).
Causes of lipoma
The causes of lipoma formation are:
- violation of metabolic processes;
- hereditary predisposition;
- blockage of the sebaceous gland duct;
- accumulation of toxins in the body.
Cases of such a node degenerating into a malignant tumor are quite rare, but it probably still exists. Surgical intervention in this case is necessary if the formation has greatly increased in size and deformed the breast, as well as if pain develops. The operation is also performed in cases where the lipoma affects other tissues and organs. Typically, small lipomas are removed under local anesthesia. For large nodular formations of the mammary glands, general anesthesia is used.
Intraductal papilloma
These breast nodules are also called papillary cystadenomas or cystadenopapillomas. They are papillary benign outgrowths developing from the epithelium of the gland ducts. Pathology can occur at any age. Macroscopically, such neoplasms resemble cystic balls with papillary growths. The papilloma is easily injured, and the bloody fluid released from it penetrates the excretory ducts and begins to flow out. Necrosis and hemorrhage are possible in the area of this tumor. Multiple breast formations of this type most often undergo malignancy.
The factor leading to the appearance of intraductal papillomas is hormonal imbalance. The development of papilloma can be provoked by any changes in hormone levels: oophoritis, ovarian dysfunction, adnexitis, obesity, abortion, stress, etc. Smoking and nulliparous women are at risk. Patients who were breastfeeding, having children, and using hormonal contraception are less susceptible to the development of such neoplasms.
You may be interested in: Postoperative period after conization of the cervix: features of rehabilitation
Papillary cystadenomas occur against the background of fibrocystic (diffuse or nodular) mastopathy. As a result of the development of this disease, local expansion of the gland ducts occurs, in which papillary growths develop. The first clinical symptoms of intraductal papilloma include the appearance of discharge from the nipple. They can be white, transparent, greenish, brown and contain blood impurities.
You can palpate the papilloma only when it is located in the main duct. In this case, upon palpation in the area of the areola, a round node of soft consistency is felt, painful when pressed.
Surgery for intraductal papilloma of the mammary gland is considered the most effective method of therapy.
Classification
In clinical practice, the histological classification of benign breast tumors, which was developed by specialists from the World Health Organization in 1984, is usually used. It takes into account the characteristics of the cellular structure and the growth of neoplasia. In accordance with this classification, there are six main groups of breast tumors:
- Epithelial neoplasms. This group is represented by adenomas (nipple, tubular, lactating) and intraductal (intraductal) papilloma.
- Mixed tumors. Such neoplasias are formed by both epithelial and connective tissue. The group includes fibroadenoma and leaf-shaped (phylloid) tumor.
- Neoplasia of other types. In addition to the epithelium and stroma, the tumor process can affect soft tissue, epidermis and dermis of the mammary glands. In this case, lipomas and skin tumors are formed.
- Unclassified tumors. This diagnosis is made in cases where the histological structure of neoplasia is not determined, but the bulky process is benign.
- Tumor-like formations. Volumetric neoplasms of this category are non-proliferative in nature and arise as a result of ectasia, inflammation, developmental abnormalities (hamartoma), etc.
- Breast dysplasia. The disease is also known as mastopathy (fibrocystic disease). The dysplastic process can be diffuse or nodular.
Cystic mastopathy
This neoplasm is a capsule filled with liquid. Cysts can be single or multiple. This neoplasm provokes frequent stress and hormonal imbalances, which are characterized by an increase in estrogen levels in the body. Pain most often worries a woman before the onset of menstruation, due to an increase in progesterone levels and the resulting fluid retention. In this case, a fluid similar to colostrum, mixed with pus or blood, may be released from the nipples. The disease in most cases develops after menopause, but nulliparous and smokers, patients with a genetic predisposition and a history of numerous abortions are also at risk. The disease can also occur due to improper treatment with hormonal drugs, pathologies of the endocrine glands and liver.
If the breast cyst is small in size, it is usually treated without surgery. The patient is prescribed vitamin and iodine-containing medications, diet, and some hormonal therapy.
Treatment is carried out for a long time, under the supervision of a doctor. If after its completion no positive result is observed, the specialist may recommend surgical removal of the tumor.
Breast mastitis in non-lactating women
Non-lactation mastitis is an inflammatory pathology of the mammary gland that occurs in women outside the lactation process. The causes of this disease are injuries, infections, chronic diseases of other systems and organs. This disease is not classified as a nodular disease, however, during its course, focal changes resembling nodules may be observed in the mammary gland.
Mastitis in non-breastfeeding women occurs for several reasons:
- menopause, during which hormonal imbalance occurs;
- chest injuries;
- complications after operations;
- decreased immunity;
- avitaminosis;
- metabolic disorders;
- infectious lesion.
Most often, non-lactational mastitis occurs in women after 35 years of age. At risk are patients with endocrine disorders, as well as those who abuse alcohol and smoking.
An advanced form of mastitis leads to serious consequences: the transition of the pathology to the chronic stage, the formation of an abscess, sepsis.
Possible complications
Complications of a breast tumor:
- bleeding from large tumors;
- severe inflammation of the tumor and tissues around it occurs;
development of metastases, due to which appear:
- pathological bone fracture (fractures resulting from exposure to minor traumatic force or physiological load on the bone);
- liver failure;
- severe shortness of breath while moving.
Complications after surgery:
- Inflammatory process in the postoperative wound area;
- Suppuration of a postoperative wound;
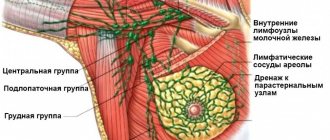
- Lymphorrhea is a long-term leakage of the light part of the blood (lymph). Occurs mainly after removal of lymph nodes;
- Swelling of the arm - occurs due to the removal of a large number of nodes and the slow flow of lymphatic fluid.
If a woman is diagnosed with breast cancer and they do not take any action, then within a year or two she will die. Conclusion: it is necessary to fight a small tumor rather than a large one, which can provoke the development of metastases.
Dear women, if you have breast cancer, do not turn to traditional medicine for help! By applying lotions or compresses to your breasts, you will not only aggravate the situation, but also accelerate the development of malignant cells. If you truly value your life, then you will not self-medicate, but immediately seek help from a doctor.
Symptoms of mastitis
With this disease, women notice the following symptoms:
- breast pain;
- inflammation of the cervical and axillary lymph nodes;
- aching joints, muscle pain;
- fever, febrile syndrome.
What to do if you suspect a breast nodule?
Cystic-solid formation in the kidneys and pelvis
Kidney tumors occur with approximately equal frequency in men and women. But in women much more often than in men, cystic-solid formations appear in the pelvis. What can this bring to patients? Since this pathology is mainly observed in women of childbearing age, without timely treatment it can lead to infertility. The main cause of the disease is hormonal disorders caused by:
- Pregnancy.
- Climax.
- Abortion.
- Taking birth control pills.
Tumors manifest themselves as pain in the lumbar region and/or lower abdomen, headaches, and menstrual irregularities.
Cystic-solid formations appear on the kidneys for the following reasons:
- Organ injuries.
- Tuberculosis (developing in the kidneys).
- Infections.
- Operations.
- Stones, sand in the kidneys.
- Hypertension.
- Congenital anomalies of the organ.
Patients complain of pain in the lumbar region, difficulty urinating, and unstable blood pressure.
Diagnostics
To confirm the development of nodular lumps in the mammary gland and make a diagnosis, the specialist first collects information regarding the patient’s medical history and her complaints, after which he examines the breast. If there is a suspicion of the presence of neoplasms, an additional diagnostic examination is prescribed, including laboratory and instrumental research methods. These include:
- Mammography for breast nodules is the most informative method. The accuracy of the procedure is 100%. The image is obtained in lateral and direct projections, which makes it possible to assess the picture of the pathological process with maximum accuracy. This procedure is recommended for all women over 40 years of age.
- Contrast X-ray. This method is used if the patient has discharge with bloody or serous impurities. To perform this procedure, a contrast agent is injected into the ducts of the affected breast, which provides the opportunity for a detailed examination of the tumor structures.
- Ultrasound. It is recommended to be carried out in the first phase of the menstrual cycle. The technique is very informative when examining the breasts of young patients, since the connective tissues in this case have a denser structure.
- Pneumicystography. This technique is used in cases where there is a suspicion of the presence of a cystic formation in the gland. During this diagnostic procedure, the doctor punctures the tumor, the cavity of which is filled with a special gas. Next, a snapshot of the node is taken for later study.
- Cytology. This procedure is carried out if a woman has pathological discharge from the nipples. To conduct a laboratory study, it is necessary to obtain a fragment of biomaterial from the nodal seal.
Causes and possible diseases
Benign nodes in the breast
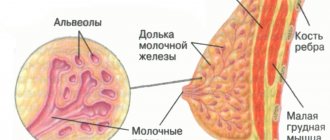
Cysts are fluid-filled cavities in the glandular lobes of the breast that are benign and also cannot develop into cancer. This way you do not increase your risk of breast cancer. Cysts develop when the glandular duct through which fluid normally drains is closed. Cysts can also develop outside of pregnancy (milk in the lobes usually forms during pregnancy). Cysts often occur in women aged 30 to 50 years and at the beginning of menopause. Why exactly cysts occur is not known for certain.
After a certain size, cysts put pressure on the surrounding tissue and displace it, which can cause pain. They often occur in connection with hormonal fluctuations in the menstrual cycle and mastopathy.
Benign fatty cysts contain tissue fluid with a high fat content. They are formed when adipose tissue is damaged, for example, after surgery.
Fibroadenomas are benign nodules of connective tissue and glandular cells that also do not increase the risk of breast cancer. They feel rough and elastic, and the knot in the chest moves easily. Fibroadenoma is a common benign tumor that occurs primarily in young women between the ages of 20 and 40. Fibroadenomas grow under the influence of female sex hormones.
Lipomas are formed from adipose tissue. They are not associated with an increased risk of breast cancer. Lipomas tend to feel soft. Also, this knot in the chest is easily displaced because it is not fused with the skin.
Breast disease is a benign change that usually occurs in women between 30 and 55 years of age and almost always affects both breasts. Breast changes are affected by hormones depending on the menstrual cycle and menstrual bleeding in a variety of ways - typical signs include breast lumps, cysts, swelling, increased sensitivity to touch, breast pain (mastodynia) and breast enlargement. When palpating the breast, you can identify clear moving nodes the size of a cherry. Sometimes fluid may leak from the nipple.
Mastopathy is often associated with cysts. As glandular cells grow, they produce more fluid. This is how many small cysts form in the glandular lobe. Doctors talk about “cystic mastopathy”. They are grown primarily by connective tissue cells called “fibrous mastopathy.” The most common is a combination of both forms (“fibrocystic mastopathy”).
Symptoms increase and decrease as the cycle progresses. No later than after menopause, they completely disappear. This suggests that hormones play an important role in mastopathy. Doctors speculate that hormonal dysregulation—that is, too much estrogen and not enough progesterone—is responsible for the changes. Too much estrogen can cause a kind of inflammatory reaction in the tissues.
Mastopathy can also be caused by thyroid hormone disorders or the use of certain medications that affect the production of hormones. These include, for example, antidepressants or heart medications with digitalis.
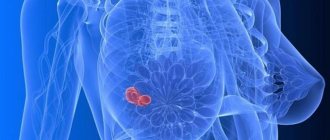
Malignant nodes in the chest
A noticeable, palpable, and non-displaceable lump in the breast may indicate breast cancer. Here, further studies are needed to classify the nodule as benign or malignant. One of the changes associated with breast cancer is microcalcemia. It is not noticeable and is only visible with mammography. Micro-lyme is a sign that remodeling is happening in the breasts. Important here are the distribution, size and location of microcalcifications.
Knot in a man's chest
Men, like women, have mammary glands, but they are much smaller. Even in men, a knot can form in the chest, although it is very rare. As in women, the cause of a breast tumor can be benign or malignant. Among other things, benign swelling of the mammary glands (gynecomastia), cysts, lipomas, fibroadenomas or mastopathy are possible. But even breast cancer can affect men. It is estimated that there are currently about 600 men living with breast cancer in Russia. Often men come to the doctor only very late, because they consider breast cancer a typical woman's disease. By then, breast cancer has often already spread widely. Breast cancer is diagnosed and treated in men in the same way as in women.
Treatment of breast nodules
A gynecologist or mammologist is involved in prescribing a range of therapeutic measures for nodular neoplasms. The choice of treatment method is based on the data obtained from the diagnostic examination. Traditionally, therapy is carried out in two ways:
When should you see a doctor?
In general, women should not wait too long, and all changes and every lump in the breast should be checked by a doctor! In most cases, a breast lump turns out to be harmless, which is a great relief for all women. A lump in the breast may also indicate breast cancer. One in eight women will develop breast cancer during her lifetime. It is estimated that around 74,000 women are affected every year. And most women feel a malignant tumor in the breast itself
It is also important that breast cancer is detected in a timely manner before it spreads to other organs and tissues - then it is highly treatable and even curable
Surgery
Surgery to remove nodular tumors can be performed in three ways:
Source
What do macrophages fight?
For any pathological neoplasms of the thyroid gland, be it nodes, cysts or tumors, a fine-needle biopsy is performed.
Under local anesthesia, a puncture is made into each tumor and a small amount of cellular material is sucked out using a very thin aspiration needle.
Competent endocrinologists make not one, but 3 to 5 punctures of each node in order to get the most complete picture of the nature of the contents, the parietal elements and the capsule.
Each sample is applied to a separate slide and sent to the laboratory, which examines the cellular composition in detail and draws up a cytological report.
In what cases will the analysis show a lot of macrophages:
- During the inflammatory process in the thyroid tissues.
This type of phagocyte does not spread with the bloodstream, but is always present in tissues.
This arrangement makes it possible to instantly solve any problem that arises.
The immune system works like an army with a well-structured hierarchy.
A special subgroup of leukocytes called T-helpers is responsible for the activation and maturation of macrophages.
As soon as the immune system notices the invasion of foreign microorganisms, T-helper cells begin to produce gamma interferon and other specific protein compounds.
As a result, the number of macrophages increases, and an active fight against infection begins.
In case of thyroiditis or poisoning, cytology will show an increased level of macrophages relative to the norm.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=VlFxLMQufnY
Regardless of what caused the inflammation, macrophages eliminate all dead cellular material and cleanse the intercellular substance.
In an autoimmune process, the volume of lymphocytes is usually greater than the volume of macrophages, but if the puncture is done repeatedly and in detail, the needle can capture the entire cellular composition of the selected area of the gland.
- For hemorrhages in the thyroid gland.
The pigment that contains iron oxide is called hemosiderin.
It is formed when hemoglobin, which is found in red blood cells, is broken down.
If for some reason the death of red blood cells begins in the vessels of the thyroid gland, then macrophages capture the destroyed cells and absorb hemosiderin.
Injuries to blood vessels are caused by squeezing the neck, blows to the throat, suffocation and similar mechanical impacts.
In addition, hemosiderin is released as a result of rupture of a blood vessel and splashing of blood into the intercellular substance.
- For thyroid cancer.
One of the main purposes of phagocytes is to devour cells that are defective and dangerous to the body.
The danger of cancer cells is that when the main focus of malignancy is destroyed, the cells can enter the bloodstream and lymph flow, migrate and metastasize to regional lymph nodes or distant organs.
Macrophages actively interfere with tumor growth in the thyroid gland, synthesize gamma interferon, hydrolytic enzymes and cationic proteins, nitric oxide and reactive oxygen species.
And this is good news, because malignant tumors usually disintegrate under the influence of chemotherapy or other treatment.
The average lifespan of each macrophage is about 5 days, so the analysis reflects the situation with a slight delay.