Intramammary lymph nodes: methods of diagnosis and therapy
Lymph nodes are an integral part of the human immune system. Thanks to it, the body is protected from the harmful effects of various factors. Any change in the lymph nodes indicates that the body is fighting something bad. Often during examinations, women are given a conclusion about the presence of an intramammary node. So, intramammary lymph node - what is it? This is a lymph node from the axillary group, located in the glandular tissue. Its increase indicates the presence of inflammation or breast cancer. Therefore, it is important to detect this node at the very beginning of its formation.
Anatomy and functions of intramammary lymph nodes
Lymph nodes, ducts and vessels are part of the immune system. The lymph nodes in women's breasts are the first to respond to the inflammatory process and the penetration of foreign particles into the body. The lymph nodes of the breast belong to the axillary regional lymph nodes. They follow the course of the lymphatic vessels and are located in the fatty and glandular tissue of the breast. This is a group of lymph nodes on the chest. Normal intramammary lymph nodes:
- located in the glandular tissue of the breast;
- not palpable;
- they are not visible to the naked eye;
- painless;
- normal body temperature;
- the skin of the breast is not changed.
The function of the lymph nodes is to protect the body from infections. Its role is as follows:
- removal of certain metabolic products from the body;
- are responsible for the correctness of the body’s immune response;
- responsible for the maturity of lymphocytes;
- biological filter;
- trap and neutralize cancer cells.
The lymph nodes of the mammary gland primarily collect lymph from the thoracic ducts and glandular tissues.
Important! You need to know what intramammary lymph nodes of the mammary glands are. Normally, they do not manifest themselves in any way and do not cause any complaints.
So, intramammary lymph nodes of the mammary gland, what are they? This is a lump in the upper outer quadrant of the chest. They can be either unilateral or bilateral. There are various reasons for the increase in this education, which we will consider below.
Causes of enlarged breast lymph nodes
Lymph nodes in the mammary gland can enlarge with or without the participation of an inflammatory process. If we are talking about the usual enlargement of lymph nodes in women in the chest, that is, lymphadenitis, its causes are:
- cancer metastases;
- imbalance of the hormonal system;
- irregular sexual activity;
- mammary gland injuries;
- with fibroadenoma;
- concomitant gynecological diseases;
- induced or medical abortions;
- disturbances in the functioning of the immune system.
Lymphadenitis is a condition known as inflammation of the thoracic lymph nodes. They can become inflamed due to:
- diseases caused by infection - staphylococcus, streptococcus, protozoa;
- the presence of foci of chronic infection in the body - chronic tonsillitis, tonsillitis, carious teeth;
- presence of silicone implants in the breast;
- diffuse purulent diseases of the anterior chest wall - phlegmon.
Bacteria play a fundamental role in the development of the purulent process in the lymph nodes. If you do not seek help in a timely manner, the inflammation progresses to the stage of abscess formation (accumulation of pus).
Diseases that cause inflammation of the chest lymph nodes
First of all, it is worth clarifying that the very fact of the appearance of this lymph node is not a disease. Indeed, often the causes of intramammary lymph node of the mammary gland are other diseases, such as:
- mastitis – inflammation of tissue in the mammary glands;
- mastopathy is a breast disease associated with hormonal imbalance;
- metastases of cancerous tumors from other parts of the body.
Mastitis is a fairly common disease among women. The intramammary lymph node of the mammary gland most often enlarges precisely for this reason. More women suffer from this disease after pregnancy. During lactation, milk stagnates in the thoracic ducts. This creates ideal conditions for the proliferation of pathogenic microorganisms, and the nodes begin to become inflamed. If you do not follow the gynecologist's recommendations regarding breastfeeding, there is a high probability of suffering from mastitis.
Breast mastopathy, or fibroadenomatosis, is a benign growth of breast tissue associated with hormonal imbalance. Enlarged lymph nodes with mastopathy occur in women of childbearing age, from 18 to 45 years. This condition may be accompanied by inflammation of the lymph nodes of the chest. The main symptoms of mastopathy are:
- periodic or constant breast tenderness, which intensifies at the beginning of the cycle;
- white discharge from nipples;
- the appearance of nodular compactions in the gland tissue.
Important! What to do to avoid mastopathy? It is necessary to express the milk remaining in the breast and treat concomitant diseases in a timely manner
Regional metastases most often enter the mammary gland through blood or lymph. They can also dissipate:
- into the skin above the chest;
- kidneys;
- brain;
- liver;
- lungs.
Metastases are difficult to treat and can lead to death. Therefore, it is important to diagnose the process in a timely manner and begin treatment as early as possible.
Which doctor can help?
First of all, you need to contact your family doctor. He will conduct an examination and try to find out the cause of the enlarged lymph nodes in the mammary gland. The doctor will decide whether consultation with other specialists is necessary. Such consultants may be:
The function of a gynecologist is to identify infections of the female reproductive system in the early stages. Also, during the examination, he may notice inflammation of the breast lymph node. This doctor treats various inflammations and hormonal disorders in the body.
An oncologist treats breast cancer, depending on the stage of the disease. In the first stages, minimal excision of the tumor is possible. Subsequently, a total mastectomy may be required. Very often, the hands swell after breast removal. Also includes treatment. After such an intervention, it is necessary to carry out a set of rehabilitation measures. Rehabilitation includes gymnastics and exercises. Recovery lasts from 3 to 5 months.
The surgeon treats mastitis, namely the purulent form. The operation is performed under general anesthesia. It includes the following steps:
- Skin incision.
- Opening and sanitation of the abscess.
- Suturing and draining the wound.
Having cured the primary pathology, the enlarged lymph node gradually returns to its previous shape.
Necessary diagnostic methods
As a rule, diagnosing intramammary lymphadenitis is not difficult. Diagnostic methods include the following:
- self-examination;
- mammography;
- ultrasonography;
- chest x-ray;
- CT scan;
- thermography;
- node biopsy.
Self-examination is carried out on the 10th day of the cycle in two positions - standing and lying down. It needs to be done every month. It is necessary to carefully examine the skin of both mammary glands and the nipple area. This manipulation must be carried out both with lowered and raised arms. Next, using circular movements, you need to slowly feel each quadrant of the chest on both sides. If there is compaction, pain or other sensations, consult a doctor immediately.
Important! It must be remembered that intramammary lymph nodes of the mammary gland are dangerous
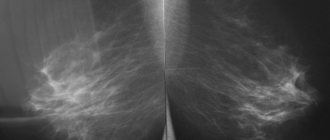
Mammography and ultrasound are among the most informative diagnostic methods that can be used to see:
- localization;
- dimensions;
- quantity;
- adhesion to surrounding tissues;
- the structure of the node that is inflamed.
Prevention and diagnosis
To maintain your health, you need to pay enough attention to prevention and diagnosis.
Enlarged lymph nodes can be detected before they reach critical sizes and begin to hurt.
This can be done during periodic self-palpation of the mammary glands and axillary areas.
If the intramammary lymph node is noticeable upon palpation, then there is an infectious component.
The source of infection can be either internal pathologies of the body: tuberculosis, measles, HIV and others; as well as external causes: infection from cat scratches, if the animal is unwell, manipulation of the skin (tattooing) using an unsterile instrument.
Identification of alarming symptoms should alert you and serve as a reason to make an appointment with a doctor.
The specialist will conduct an examination and make an accurate diagnosis, based on:
- results of clinical laboratory tests of blood and urine;
- x-ray mammography;
- ultrasound examination of the mammary glands and axillary areas;
- biopsy (taking a tissue sample from the affected organ).
Preventive actions:
- Give up bad habits so as not to saturate your body with dangerous toxins. Clean, unburdened lymph flow is the key to long and good health.
- Exercise. In addition to the general strengthening effect on the body as a whole, they are useful in that they prevent stagnation of lymph, accelerating its outflow from the periphery.
- Maintain daily hygienic body care.
- Wear underwear that fits properly so as not to expose your body to unnecessary compression and tugging.
- Treatment of all pathologies, especially infectious ones, must be completed, preventing them from becoming chronic. Many people are afraid of long-term use of antibiotics and stop taking medications long before the end of the course. One of the consequences of such a decision may be the development of a chronic form of pathology. Taking modern antibacterial drugs causes much less harm to health than a sluggish process that destroys the body for years.
- Do not neglect periodic medical examinations, and visit specialists (including a mammologist) at least once every two years.
Normally, if a woman is not pregnant, nothing should be released from the mammary gland. Discharge from the mammary gland when pressed may indicate the presence of pathologies.
Why suppuration occurs in the breast tissue and how to treat a breast abscess, read in this publication.
Inflammation of the axillary and mammary lymph nodes may be caused by silicone breast implants.
It is easier and simpler to prevent any pathology than to treat it. Inflammation of intramammary lymph nodes is no exception. Following simple rules and prevention are effective for maintaining health.
Definition of the concept
To understand the characteristics of the pathology in question, it is necessary to consider the anatomy of the mammary glands. Lymph nodes, along with the ducts and vessels that run through the chest, form part of the body's immune defense system. They are the first to respond to pathogenic agents. The lymph nodes of the mammary glands are located between the layers of fatty and glandular tissue in the chest area. Upon palpation, these formations are not detected and do not cause pain.
Lymph nodes perform the following functions:
- take part in the processes responsible for removing metabolic products from the body;
- provide the correct immune response;
- support the maturity of lymphocytes;
- prevent infection;
- neutralize cancer cells, preventing their spread.
Diagnostic methods
A mammologist will visually examine the breasts and refer you for additional examinations to make the correct conclusion. The results of a general analysis of urine and blood may indicate an increased level of ESR and leukocytes, which indicates an inflammatory process in the body. If the nature of the disease does not lie in infection, then modern research methods will help establish the diagnosis:
- MRI. Detects the slightest changes in the lymphatic system and breast, which will distinguish mastopathy from tumor formations (both benign and malignant).
- Mammography. It detects pathologies in the breast in the early stages, therefore it is considered one of the most reliable methods. Among the contraindications to the procedure, experts note the period of lactation and pregnancy in any trimester.
- Axillography. The method is used to determine metastases in diagnosed breast cancer.
- Ultrasound. Detects the slightest changes in the structure and tissue of the mammary glands. The study is informative even in the presence of implants. Palpation and visual inspection are not able to detect silicone rupture. Experts recommend undergoing an MRI if there is a suspicion of a violation of the integrity of the implant.
The drugs are effective against swelling and hyperemia of the skin. The therapeutic regimen is drawn up only by a doctor, since the use of folk remedies or self-medication “on the advice of a friend” will lead to disastrous results.
The therapeutic course for mastopathy depends on its form:
- fibrous-diffuse;
- fibrocystic;
- nodular - only surgical intervention is indicated.
All forms of the disease require an integrated approach:
- Compliance with diet and a healthy lifestyle, a course of vitamin therapy.
- Using a comfortable bra that does not squeeze or restrict the breasts.
- Non-hormonal therapy using venotonics, drugs containing iodine, antiseptics and diuretics.
- Hormonal medications prescribed by a doctor after additional examination.
Dietary supplements (Mastodinon, Mulimen) have proven themselves well, and should be taken only as prescribed by a mammologist.
If inflammation of the node is caused by infection, then therapy includes antibacterial drugs. To normalize body temperature, Ibuprofen and Nise are allowed, and the chronic form of the disease is treated with antibiotics and physiotherapy. Surgical intervention is indicated in cases of purulent lesions of the mammary glands, when scrupulous cleaning of the problem areas is indispensable.
Antitumor therapy usually includes:
- use of targeted medications;
- radio, chemotherapy or radiation therapy;
- operation.
After surgery, restorative treatment and regular examinations by a mammologist and oncologist are prescribed. The destruction and removal of cancer cells and areas is aimed at preventing the development of metastases, therefore, along with the tumor, the surgeon can also remove nearby lymph nodes.
Causes
Intramammary lymph nodes become inflamed under the influence of various factors, each of which often leads to severe complications. Similar violations are observed when:
The probable causes of the development of lymphadenitis (inflammation of intramammary lymph nodes) include the following:
- infection of breast tissue with staphylococcus and other pathogenic agents (mastitis develops);
- the course of chronic pathologies of infectious etiology in different parts of the body;
- mastopathy (benign growth of glandular tissue in the breast);
- suppuration of breast tissue;
- Silicone leakage from breast implants.
Basically, intramammary lymph nodes become inflamed due to bacterial infection of the mammary glands.
Causes
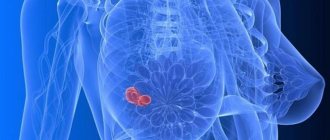
The axillary lymph nodes are the main ones for lymph drainage. When inflammatory processes develop in the mammary glands, the intramammary node is the first to respond to them. It is visualized in the upper quadrant of the mammary gland. Such a lymph node looks like a shadow in the picture, in the center of which there are small light areas. These are accumulated fat cells.
The immediate causes of an intramammary breast lymph node may be:
- mastitis,
- mastopathy,
- tumor.
Mastitis occurs more often in women after childbirth and during lactation. The causative agents of the disease can be various pathogenic microorganisms (streptococci, staphylococci). Their entry into the mammary glands causes an inflammatory process.
Mastopathy is a benign lump in the glandular tissues of the breast, which is usually a consequence of hormonal disorders. Intramammary lymph nodes can be a dangerous symptom of cancer. They may indicate an advanced malignant process that requires emergency treatment.
Find out about the first signs of trophic leg ulcers in diabetes mellitus, as well as about the treatment of the pathology.
Read about the causes of the formation of a nodule with calcifications in the thyroid gland and methods of its treatment at this address.
Symptoms
Also, with inflammation of the intramammary lymph node, the following symptoms are noted:
- increased sweating (usually observed during sleep);
- general weakness;
- pain in the upper chest.
In some cases, asymptomatic development of the pathological process is possible. This option is the most dangerous, as it often indicates a malignant degeneration of glandular tissue.
Symptoms of infectious infection
Mastitis has characteristic symptoms that distinguish this disease from other lesions. The course of the pathology is accompanied by:
- high body temperature (up to 39-40 degrees);
- feeling of fullness in the chest;
- redness of the skin in the affected area;
- increase in breast size;
- discharge of purulent exudate from the nipples;
- headaches;
- growth of local lymph nodes.
Symptoms of mastopathy
The main reason for the development of mastopathy is hormonal imbalance, which determines the symptoms of the disease. With this pathology, frequent pain in the mammary gland is noted, the intensity of which increases towards the end of the menstrual cycle. During palpation of the affected breast, one or more large lymph nodes are identified. Pressure on the areola causes the appearance of purulent exudate flowing from the nipple.
Symptoms of a malignant tumor
The tumor process in the mammary gland develops asymptomatically for a long time. The only sign indicating malignant degeneration of local tissues may be an enlarged intramammary lymph node. Over time, the following clinical phenomena are added to this symptom:
- cloudy discharge from the nipple, often including bloody clots;
- change in breast shape (deformation, appearance of depressions, irregularities);
- apathy;
- active sweating at night;
- a sharp decrease in body weight;
- change in areola pigmentation.
Symptoms of damaged breast implants
In approximately 10% of clinical cases, the cause of intramammary lymph node growth lies in improper implantation of breast implants. Such errors lead to silicone penetrating into the mammary tissue, which provokes inflammation.
With such violations, the woman’s general condition does not change. The presence of a problem is indicated by changes in the shape of the breast, pain in the mammary glands and redness of the skin in the affected area.
Features of the disease
The appearance of an intramammary node on an x-ray does not indicate its pathology. Only a significant increase in size can be regarded as an alarming sign.
A feature of the painful conditions of intramammary nodes is that they are secondary, that is, they arise against the background of existing health problems.
After a mastectomy, women consider themselves unattractive. To restore self-confidence without surgery, breast exoprostheses were invented. They make a woman's figure the same as before the operation.
Read about the causes of lumps in the mammary glands in men here.
To prevent discomfort during chemotherapy for breast cancer, you need to eat a balanced diet. Read about the features of the diet in this topic.
Diagnostic methods
Due to the fact that in most cases the intramammary lymph node becomes inflamed due to mastitis, if lumps are detected in the upper part of the chest, a general blood test is performed to assess the level of leukocytes and ESR. In addition to this research, the following are prescribed:
- Mammography. Allows you to diagnose various pathologies of the mammary glands, including malignant growth of local tissues.
- Ultrasound. Used for all diseases of the mammary glands. Ultrasound is allowed to be performed during pregnancy and breastfeeding. Using this method, it is possible to identify disorders that cannot be diagnosed by mammography (in particular, fibroadenomas).
- MRI. Helps identify minor growths of breast tissue. Also, using MRI, it is possible to differentiate nodular neoplasms and cancerous tumors.
- Axillography. The method is used if metastases in the axillary lymph nodes are suspected.
If these studies do not exclude a malignant neoplasm, a breast biopsy is prescribed.
Diagnostic measures
It's no secret that doctors recommend that women perform breast self-examination every month. A correctly performed procedure often contributes to the early diagnosis of various diseases. On the other hand, this is the least accurate diagnostic method.
In most cases, an intramammary nodule is diagnosed by mammography or chest x-ray. In the image, the doctor can see a shadow with light inclusions (these are fatty tissues). In the future, of course, additional procedures are carried out.
Diagnosis includes standard blood tests that help determine the presence of an inflammatory process. An ultrasound examination of the breast will also be informative. The most accurate method to determine whether a lymph node is affected by cancer cells is a biopsy.
Using a special needle, the doctor pierces the pathological structure and takes samples, which are then sent to the laboratory. Unfortunately, sometimes damage to the lymph node, on the contrary, can trigger the process of malignant tissue degeneration. That is why it is important to find a really good specialist who can create the safest possible diagnostic and treatment regimen.
Treatment methods
For intramammary lymph nodes, it is highly not recommended to use traditional medicine methods. Often this approach causes the development of severe complications.
Treatment for mastitis
In case of an infectious form of the disease, broad-spectrum antibacterial drugs are prescribed. Along with these medications, it is recommended to use non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (Nise, Ibuprofen), which relieve pain.
If the course of mastitis is accompanied by suppuration of local tissues, an open operation is performed, during which abscesses are removed and the affected cavity is drained. Treatment of pathology in lactating women is carried out with the help of hormonal drugs that suppress lactation.
In the chronic form of the disease, in addition to antibacterial drugs, physiotherapeutic techniques are used.
Treatment for mastopathy
Treatment tactics for mastopathy are developed based on the form of the disease.
For cystic and diffuse forms of mastopathy, lifestyle and daily diet adjustments are required. At the same time, the following are used:
- non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs;
- diuretics and iodine-containing agents;
- venotonics;
- hepatoprotectors;
- vitamin complexes.
For cystic mastopathy, hormonal medications are indicated, which are selected by the doctor.
Treatment for malignant tissue growth
Treatment of cancerous tumors growing in the mammary glands is usually carried out by excision of the affected tissue. Also, this approach is often complemented by:
- chemotherapy;
- radiotherapy;
- radiation therapy (only the mammary glands or the entire body are irradiated).
An approach that uses targeted drugs . The latter have an effect exclusively on malignant cells, without affecting healthy tissue.
Features of treatment
Treatment of lymphadenopathy is carried out under medical supervision; self-medication and the use of alternative medicine recipes are prohibited. Such actions are life-threatening for the patient.
To eliminate intramammary lymph nodes in the mammary gland, various therapeutic techniques are recommended. When prescribing them, the doctor takes into account:
- The reason for the enlargement of the node.
- General health of the patient.
- Presence of concomitant diseases.
- The nature of the provoking factor (malignant, benign).
For the inflammatory nature of lymphadenopathy, the following is used:
- Conservative treatment.
- Surgical intervention.
However, regardless of the root cause of the pathological phenomenon, ointments, creams, that is, topical preparations are always prescribed to relieve pain in the breast and improve the patient’s quality of life:
- Doctor.
- Traumeel.
- Mastofit.
Using ointments:
- Breast swelling is eliminated.
- The intensity of inflammation is reduced.
- The size of the compaction decreases with further resorption.
Other therapeutic nuances are developed based on the diagnostic results.
Mastopathy
How is inflammation of the lymph nodes due to mastopathy treated? The nature of treatment measures depends on the form of the pathology, which has several variations in manifestation:
- Nodal.
- Fibrous-diffuse.
- Cystic fibrous.
Nodular mastopathy can be eliminated exclusively by a radical method - surgery, since this form of the disease does not respond to conservative treatment, and on the other hand, there is a serious threat to the woman’s life.
The remaining two types of mastopathy require complex therapy, which includes:
- Use of non-hormonal drugs.
- Taking medications containing synthetic hormones.
- Drastic lifestyle correction.
- Reviewing your diet towards healthy foods.
- Choosing a comfortable and high-quality bra that does not disrupt the normal blood flow in the mammary glands.
A non-medicinal approach is advisable only in the initial stages of the disease, but if the disease is accompanied by inflammation of the regional lymph node, then it is impossible to do without medications.
A wide range of medications are prescribed:
- Preparations with iodine.
- Diuretics.
- Venotonics.
- Hepatoprotectors.
- Complex vitamins.
- Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs.
As a supplement, biologically active supplements (BAA) are recommended to support women’s health:
- Kelp.
- Mouliman.
- Mastodinon.
- Indinol.
- Mastofit.
- Mamoclave.
Therapy for cystic-diffuse mastopathy is carried out with hormonal medications. The specific remedy is determined only by a specialist based on test results.
Mastitis
The manifestation of an intramammary node as a consequence of infectious mastitis requires an integrated approach using the following drugs:
- Antiviral.
- Antibacterial.
- Anti-inflammatory.
- Antifungal.
In addition, the following remedies have a healing effect:
- Antipyretic.
- Antihistamines.
- Painkillers.
Main features of mastitis treatment:
- Relief of chest pain and reduction of elevated temperature is carried out using anti-inflammatory non-steroidal drugs, for example, Nise or Ibuprofen.
- For purulent mastitis, an operation is performed during which the surgeon opens the abscess and removes its contents.
- If inflammation of the breast occurs in women who are breastfeeding, it is necessary to stop lactation. For this purpose, drugs are prescribed that suppress the production of breast milk.
- Chronic mastitis is treated with antibacterial agents in combination with physiotherapy such as ultrasound or electrophoresis using Troxevasin or Dimexide.
Malignant tumors
When inflammation of a lymph node is a sign of a cancerous tumor, which is clinically confirmed by extensive diagnostic methods, a therapeutic regimen is selected by an oncologist.
In this situation, the following treatments may be recommended:
- Operation.
- Chemotherapy.
- Radiotherapy.
- Target group drugs.
- Remote irradiation.
- Intraoperative radiation therapy.
The main goal of all these therapeutic manipulations is the inhibition and destruction of atypical cells in the mammary gland.
During surgery, the malignant body is removed along with nearby lymph nodes, including the intramammary node. This approach avoids the possible metastasis of malignant cells throughout the body.
Intramammary lymph node of the mammary gland: causes of inflammation, symptoms and treatment methods
The intramammary lymph node of the mammary gland is often subject to inflammation, which can occur either without symptoms or with pronounced signs. This disease occurs in women and children. Diagnosis and treatment are carried out by mammologists. Sometimes they resort to surgical removal of the inflamed node. The prognosis of the disease is favorable. When the first signs appear, you should immediately contact your physician for advice and referral to a specialist.
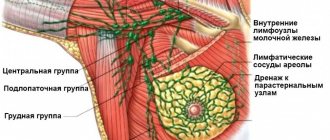
The female breast is located above the pectoralis major muscle. In cross section, it consists of muscles, and at the edge there are lymph nodes. Their main group is the paramammary system. It is located on the pectoralis major muscle and connects the asyllar lymph nodes of the chest and their ducts. Nodes in the body are presented in several types:
Location of intramammary lymph nodes
The main load falls on the central ones, thanks to them the outflow of lymph from the muscles of the mammary glands into the common lymphatic duct occurs. The lymph nodes of the mammary glands are an element of the immune system. Intramammary lymph nodes belong to the group of axillary regional ones and are the very first to respond to inflammation and the penetration of foreign bodies into the body.
Normally, they are localized in the glandular tissue of the breast, are painless, and cannot be seen with the naked eye. Intramammary lymph nodes are a biological filter; they retain cancer cells and also remove metabolic products from the body. Lymph is also collected from the thoracic ducts and glandular tissues.
This disease occurs in women. According to research by doctors, children under 12 years of age are often exposed to it. This is due to the fact that during this period the body's lymphatic system is not fully developed.
Inflammation of intramammary lymph nodes (lymphadenitis) occurs against the background of diseases caused by staphylococcus or streptococcus. Tonsillitis or sore throat, purulent infections of the chest walls can also affect the appearance of the disease. If the patient has silicone implants, then inflammation of the nodes may develop due to silicone leakage.
The development of this pathological process of axillary nodes is influenced by the presence of cancerous tumors and benign seals. The appearance of lymphadenitis provokes mastitis in the patient - inflammation of the mammary glands, which occurs due to the ingestion of pathogenic microorganisms during lactation or after injury. Hypothermia, taking medications and infectious diseases (measles, tuberculosis, HIV) are not the cause of lymphadenitis.
The main sign of node damage is the formation of infiltrates (seals) near the armpit measuring 1-1.5 cm, which can be felt by palpation (palpation). The most common symptoms are pain when pressure is applied, increased sweating at night, and a feeling of weakness. Sometimes this disease is asymptomatic, and the node is detected during a routine examination.
Patients complain of skin rashes, breast swelling and increased body temperature. Sometimes there is weight loss and the appearance of “bumps,” i.e., the lymph nodes increase in size. There is redness around the inflamed area. During examination, the doctor may detect an enlargement of the liver and spleen.
There are several forms of lymphadenitis, each of which has its own manifestations:
| Form | Characteristic |
| Localized | There is inflammation of one node. It is the most common form (70% of cases of lymphadenitis) |
| Regional | Enlargement of several nodes in one or closely spaced two zones |
| Generalized | Involvement of three or more nodes in several areas. The most malignant type of disease |
| Acute | Pain, tissue swelling and fever are observed |
| Chronic | There is a latent course, i.e. without obvious symptoms |
Some women experience a rapid heartbeat (tachycardia) and decreased blood pressure. With this disease, the lymph nodes become mobile and soft. Their symmetry in arrangement is broken.
Clinical picture
In almost half of cases, breast disease is accompanied by damage or enlargement of intramammary lymph nodes. This is accompanied by the following clinical symptoms:
- the appearance of cloudy or bloody discharge from the nipple;
- aching pain in the gland, which intensifies in the area of the projection of the lymph node;
- change in skin color over the breast;
- increase in body temperature to subfebrile or febrile levels;
- the appearance of small painful compactions of lymphoid tissue in the thickness of the gland;
- the appearance of local swelling of the mammary gland;
- increased local chest temperature;
- unilateral deformation of the mammary gland;
- increased sweating;
- manifestations of general intoxication: loss of appetite, nausea, weakness, low performance, weight loss, tachycardia, fluctuations in blood pressure;
- an increase in the size of the liver and spleen (hepatosplenomegaly).
An important point is the characteristics of the lymph nodes themselves upon palpation. When inflamed, they will become hard and increase significantly in size. During oncological processes, the nodes “fuse” with the surrounding tissues.
Features of intramammary lymph nodes of the mammary gland
The main sign of lymphadenopathy of the intramammary node is the presence of a compaction near the armpit measuring 1 - 1.5 cm, felt during palpation or visualized during hardware examination of breast tissue
Lymph nodes are spindle-shaped or bean-shaped structures with a diameter of 2-20 mm. They are usually stored in fat or connective tissue. Lymph nodes occur individually, in groups, or in a chain along the lymphatic vessels. Lymphatic fluid is “filtered” in the lymph node and leaves it through one or more lymphatic vessels.
Anatomy and physiology
What is an intramammary lymph node in the breast area? It is located near the armpit, in the upper outer quadrant of the breast. It is one of the axillary (axillary) lymph nodes.
Lymph nodes are part of the human immune system and play an important role in protecting against infections. When the body fights an infection, different types of lymphocytes are stimulated to divide. As a result, the lymph nodes may increase in size.
Normal sizes
In diseases, foreign cells and particles enter the lymph nodes. Substances that carry signs of genetically foreign information accelerate the production of B and T lymphocytes. As a result, the lymph node becomes enlarged, becomes hard, and sometimes painful. If the intramammary lymph node enlarges by more than 2 cm, this may indicate various diseases.
Forecast and prevention of diseases
For any diagnosis, to eliminate pain and improve the condition of the mammary glands, it is recommended to use local agents - Traumeel ointment
The prognosis of enlarged intramammary lymph nodes is conditionally favorable. This mainly occurs in response to an infectious disease. Usually the swelling lasts no more than 2-3 weeks. Sometimes the lymph nodes can also be enlarged for much longer, especially if the patient has had a large number of infections in 1 year. For malignant tumors, the prognosis depends on the therapeutic success of the underlying disease.
There is no targeted prevention to help prevent swollen lymph nodes. General measures that protect against infectious diseases also reduce the incidence of swollen lymph nodes. A balanced diet, exercise, fluid intake, and a regular daily schedule with rest periods can reduce the incidence of infectious diseases.
Especially during the colder months, you should pay attention to hand hygiene and limit close contact with sick people as much as possible. Since infection cannot always be avoided, enlarged nodes may also appear from time to time.
Even with malignant tumors of the lymph nodes, there are no methods of absolute prevention. Patients are recommended to undergo regular preventive examinations in order to detect the disease early and stop its progression.
Reason to visit the doctor
If you experience fever (temperature above 38.5 degrees Celsius), sudden weight loss or night sweats (between 4 and 6 am), you should contact your GP. The family doctor, depending on the underlying cause of the symptoms, will refer the patient to an otolaryngologist, oncologist, endocrinologist or other specialized specialists. They will help identify the exact cause of enlargement or pain in the lymph nodes. Self-treatment is strictly not recommended.
The cost of an initial consultation with an otolaryngologist varies from 1,400 to 3,400 Russian rubles. A secondary consultation is almost always cheaper and ranges from 800 to 2900 Russian rubles. Prices for medical services vary significantly. It is recommended to check the final cost in each specific clinic.
Enlarged lymph nodes
If an intramammary lymph node is detected during examination, it means that it has become inflamed and enlarged, and this indicates that pathological processes are occurring in the mammary gland
What does the treatment regimen look like?
What therapy does an enlarged (or changed) intramammary mammary lymph node require? Treatment in this case depends on many factors, including the reason for its appearance on x-rays.
For example, if there is mastitis or inflammation of the lymph node itself, then the use of anti-inflammatory drugs is necessary. Depending on the cause of the inflammatory process, antiviral, antifungal or antibacterial therapy may be needed.
If malignant cells are detected during the diagnostic process, the treatment regimen is selected by the oncologist. Naturally, the affected tissue, including the lymph node, must be removed. This is followed by radiation or chemotherapy to help destroy any remaining cancer cells, followed by a period of recovery and observation.
Diagnostics: basic methods for detecting pathology
Magnetic resonance imaging makes it possible to detect the slightest changes that have occurred in the mammary glands and lymph nodes, characteristic of cancerous formations and differentiate them from the nodular form of mastopathy
An enlarged intramammary lymph node is clearly noticeable upon palpation. A doctor may notice enlarged lymph nodes during a physical examination. An ultrasound mammogram can be done to make sure it is a lymph node. Using it, the doctor can determine the size of the node.
Benignly enlarged lymph nodes appear oval on ultrasound. They also have a homogeneous structure and are weakly attached to surrounding tissues. Malignant lymph nodes often have an irregular shape, a hard consistency, and are tightly connected to surrounding structures.
To identify signs of malignant lymphadenopathy, it is recommended to remove the lymph node and conduct a histological examination. The pathologist can make a clear distinction between benign and malignant neoplasms.
If the presence of a malignant tumor is confirmed, further diagnostics are carried out to determine the extent of the spread and malignancy of the disease: X-ray and MRI mammography.
Diagnosis of the pathological condition
If an enlarged regional lymph node in the armpit is detected, you must contact a mammologist to establish a diagnosis. The doctor will prescribe an instrumental examination of the mammary glands.
First of all, a woman needs to undergo laboratory tests:
- General blood test.
- General urine examination.
The presence of inflammatory processes in the chest is indicated by:
- High white blood cell count.
- Increased ESR.
If laboratory tests do not confirm inflammation, instrumental diagnostics are prescribed to determine the provoking factor of lymphadenopathy.
| Hardware examination methods | Peculiarities |
| Ultrasound | It is the main method for diagnosing abnormal manifestations in the structure of the breast, which are difficult to establish through radiology, for example, the presence of fibroadenomas in the plural. Prescribed to women of the following categories: - Young age. - Pregnant. — Those who have undergone mammoplasty for breast augmentation. |
| Mammography | Detects a variety of breast diseases in the early stages of development: - Benign neoplasms. - Tumors of malignant origin. Not carried out during pregnancy and lactation. |
| Axillography | The essence of this instrumental method is to take an x-ray of the axillary area. Can determine the presence of malignancy (metastasis) in breast cancer. |
| MRI | Allows you to identify even the slightest disturbances in breast tissue and lymph nodes, including atypical inclusions and distinguish them from nodular mastopathy. |
| Biopsy | Tissue is collected from the pathological area. Confirms or denies breast cancer. |
When undergoing instrumental diagnostics, you need to pay attention to the following nuances:
- Research is carried out from the 5th to the 12th day of the monthly cycle or on any day if a woman has menopause.
- The rupture of a mammological prosthesis is difficult to determine visually or by palpation of the breast.
- If an intramammary lymph node appears after mammoplasty, it is recommended to undergo an MRI. This hardware technique is capable of detecting leakage of the silicone component of the implant.
Is inflammation of the mammary gland dangerous?
If an intramammary lymph node in the breast area enlarges, is it dangerous? The danger of inflammation of the lymph nodes largely depends on the underlying cause that caused the condition. It's basically just the immune system's reaction to a harmless infection. Even after vaccination, swollen lymph nodes are a harmless phenomenon. Pressure-sensitive lymph nodes that are characterized by redness and severe local overheating indicate a harmless cause.
In rare cases, a malignant disease or serious infection may be behind this symptom. If the lymph nodes do not hurt and have a hard consistency, this also indicates a malignant cause.
The duration of inflammation of both intramammary and other lymph nodes greatly depends on the underlying cause. If the inflammation is due to a bacterial or viral cause, symptoms will disappear within 1-2 weeks. If inflammation occurs after an injury, enlarged lymph nodes may also persist for several days.
Reasons why you need to consult a doctor promptly to rule out serious illnesses:
- Swelling of the lymph nodes, which persists for a longer period (from 4 weeks).
- Hard and difficult to move lymph nodes.
- Painless enlarged lymph nodes.
Symptoms
Painful sensations, as well as visual enlargement of the lymph nodes, are far from the only symptoms that characterize the presence of hyperplasia. A woman may also feel:
- Increased body temperature.
- Profuse sweating, especially at night.
- Rapid weight loss due to a malfunction of the digestive system.
- Hypotension.
- Cardiopalmus.
- General weakness.
You can notice inflammation of the lymph nodes not only if they are enlarged. As a rule, characteristic signs of the inflammatory process of the lymph nodes are their softness. Observing them, you can note that they are extremely mobile, and upon palpation, unpleasant and even painful sensations arise.